Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Precision Die Cut Parts

Engineering Insight: Precision Die Cut Parts – The Critical Role of Material Selection
In the production of precision die cut parts, material selection is not merely a preliminary design consideration—it is a decisive engineering parameter that governs performance, durability, and functional reliability. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize that off-the-shelf rubber components frequently fail in demanding industrial applications due to mismatched material properties. Standardized parts are often manufactured from generic elastomers optimized for cost and availability, not for specific operational environments such as extreme temperatures, dynamic compression, or exposure to aggressive media.
Precision die cutting demands materials with consistent durometer, tensile strength, and elongation characteristics. Variability in these properties leads to dimensional inaccuracies, edge deformation, and premature failure. For example, a gasket cut from an inappropriate rubber compound may exhibit compression set under sustained load, resulting in seal leakage. Similarly, exposure to oils or solvents can cause swelling or embrittlement if the elastomer lacks chemical resistance.
The performance gap between generic and engineered materials becomes evident in mission-critical sectors such as automotive sealing systems, medical device housings, and industrial automation components. These applications require elastomers tailored to precise thermal, mechanical, and chemical conditions. Nitrile rubber (NBR) may suffice for fuel-resistant seals in moderate temperature ranges, but fluorocarbon (FKM) is essential for high-temperature aerospace applications where stability above 200°C is required.
Material selection also influences the die cutting process itself. Softer compounds (below 40 Shore A) tend to deform during cutting, leading to burring or inconsistent thickness. Conversely, overly rigid materials may resist clean shearing, resulting in jagged edges or tool wear. The ideal elastomer balances processability with end-use performance, ensuring clean cuts and long service life.
To illustrate the importance of matching material properties to application demands, consider the following comparative analysis of common rubber compounds used in precision die cut components.
| Material | Hardness (Shore A) | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Resistance Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrile (NBR) | 50–90 | -40 to +105 | Oil, fuel, water | Automotive gaskets, hydraulic seals |
| Silicone (VMQ) | 30–80 | -60 to +230 | Heat, ozone, UV | Medical devices, food-grade seals |
| EPDM | 50–80 | -50 to +150 | Steam, weathering, water | HVAC seals, outdoor enclosures |
| Fluorocarbon (FKM) | 60–90 | -20 to +230 | Chemicals, oils, high heat | Aerospace, semiconductor manufacturing |
| Neoprene (CR) | 40–70 | -40 to +120 | Flame, ozone, moderate oils | Electrical insulation, industrial belts |
Selecting the correct elastomer involves a systematic evaluation of environmental stressors, mechanical loads, and regulatory requirements. At Suzhou Baoshida, we support OEMs with material testing, prototyping, and specification validation to ensure that every precision die cut part performs reliably under real-world conditions. Custom formulation and die cutting alignment eliminate the compromises inherent in off-the-shelf solutions, delivering engineered reliability.
Material Specifications
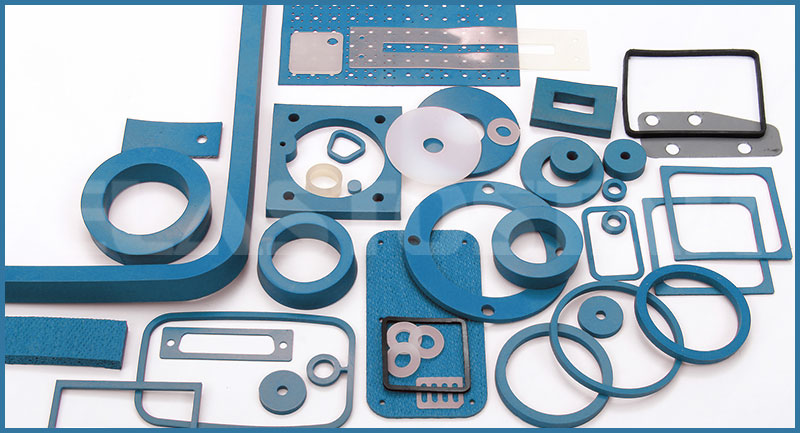
Material Specifications for Precision Die Cut Rubber Parts
Material selection fundamentally dictates the performance and longevity of precision die cut rubber components in demanding industrial applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we prioritize elastomer properties that align with operational stressors including temperature extremes, chemical exposure, compression set, and mechanical resilience. Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ) represent three critical material families for custom molded rubber parts, each exhibiting distinct advantages and limitations. Understanding these specifications ensures optimal part functionality in sealing, gasketing, and vibration damping scenarios.
Viton fluorocarbon rubber delivers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and fuels. Its operational range spans -40°C to 230°C, with intermittent peaks up to 300°C. Viton maintains integrity in aerospace hydraulic systems, semiconductor manufacturing, and automotive fuel handling where exposure to oils, acids, and chlorinated solvents is routine. However, its high cost and reduced flexibility at low temperatures necessitate careful application vetting. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) offers a cost-effective solution for petroleum-based fluid resistance, functioning reliably between -40°C and 120°C. Widely specified in automotive O-rings, fuel injectors, and hydraulic seals, NBR provides excellent abrasion resistance and tensile strength but degrades in ozone, ketones, and brake fluids. Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature stability from -60°C to 200°C, with electrical insulation properties critical for medical devices and food processing equipment. Its biocompatibility and low toxicity meet FDA/USP Class VI standards, though poor tear strength and susceptibility to compression set limit use in dynamic mechanical seals.
Critical material properties are summarized below for rapid technical evaluation:
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Resistance Properties | Typical Hardness (Shore A) | Common Industrial Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | -40 to 230 (300 intermittent) | Fuels, oils, acids, solvents, ozone | 50–90 | Aerospace seals, chemical pumps, semiconductor tooling |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -40 to 120 | Petroleum oils, aliphatic hydrocarbons, water | 40–90 | Automotive fuel systems, hydraulic O-rings, industrial gaskets |
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 to 200 | Extreme heat/cold, ozone, UV, steam | 30–80 | Medical tubing, food-grade seals, electrical insulation |
Precision die cutting demands rigorous material validation against ASTM D2000 standards for physical properties. Viton’s low gas permeability suits vacuum environments, while NBR’s cost efficiency drives adoption in high-volume automotive production. Silicone’s inertness is non-negotiable for biopharmaceutical diaphragms but requires design compensation for mechanical weakness. All materials must undergo compression set testing per ASTM D395 to predict long-term sealing force retention. Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering team collaborates with OEMs to analyze fluid compatibility charts, dynamic stress requirements, and regulatory certifications—ensuring material selection mitigates field failure risks. Final part performance hinges on harmonizing elastomer chemistry with die cut geometry, tooling precision, and post-cure processes. Consult our technical staff for application-specific material validation data sheets and accelerated aging protocols.
Manufacturing Capabilities
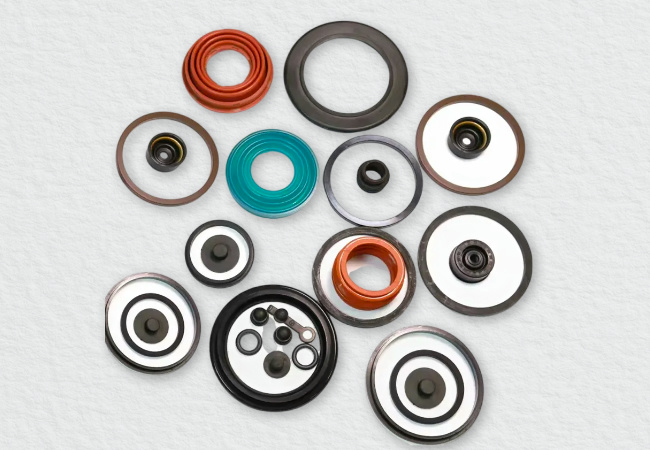

Engineering Capability: Precision Die Cut Parts for Demanding Industrial Applications
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering capability forms the backbone of our custom molded rubber parts manufacturing, particularly in the production of precision die cut components. With a dedicated team of five experienced mold engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, we integrate material science with precision tooling to deliver high-performance rubber solutions tailored to exact OEM specifications. Our multidisciplinary approach ensures that every die cut part meets stringent requirements for dimensional accuracy, material resilience, and functional reliability across diverse operating environments.
Our mold engineering team specializes in designing and fabricating precision cutting dies for both flat and complex-profile rubber components. Utilizing advanced CAD/CAM software and CNC machining technologies, we develop progressive, rotary, and steel rule dies optimized for high-volume production and tight tolerance applications. Each die design undergoes rigorous simulation and fit-testing to ensure long service life, minimal flash, and consistent part geometry. This precision-driven methodology supports industries such as automotive sealing systems, medical device manufacturing, and industrial machinery, where repeatability and performance under stress are critical.
Complementing our tooling expertise, our two in-house rubber formulation engineers bring deep knowledge of elastomer chemistry and compound customization. We formulate proprietary rubber blends using materials including NBR, EPDM, silicone, FKM, and CR, adjusting hardness, compression set resistance, thermal stability, and fluid compatibility to meet exact application demands. This vertical integration of material development and die cutting enables us to solve complex sealing and damping challenges that standard off-the-shelf components cannot address.
Our OEM capabilities are built on a foundation of collaborative engineering support. From initial concept and prototype development to full-scale production, we work closely with clients to refine designs for manufacturability, conduct DFM analysis, and validate performance through environmental and mechanical testing. This end-to-end control ensures rapid time-to-market and long-term supply chain stability.
We maintain strict quality control protocols in accordance with ISO 9001 standards, with in-process inspections and final testing for dimensional conformity, durometer, and material properties. Our facility supports small-batch prototyping as well as high-volume automated die cutting, providing scalability without compromising precision.
The following table outlines key technical specifications and capabilities for our precision die cut rubber parts:
| Parameter | Specification Range |
|---|---|
| Material Types | NBR, EPDM, Silicone, FKM, CR, Neoprene, SBR |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 30 to 90 |
| Tolerance (Standard) | ±0.1 mm (tighter on request) |
| Maximum Die Cut Size | 600 mm × 1000 mm |
| Minimum Feature Size | 1.0 mm (depending on material and thickness) |
| Thickness Range | 0.5 mm to 10.0 mm |
| Production Capacity | Up to 500,000 pcs per week (varies by part) |
| Tooling Lead Time | 7–15 days (prototype), 15–25 days (production) |
Our engineering-led approach ensures that every precision die cut part we manufacture is not only dimensionally accurate but also optimized for performance, longevity, and integration into the final assembly.
Customization Process
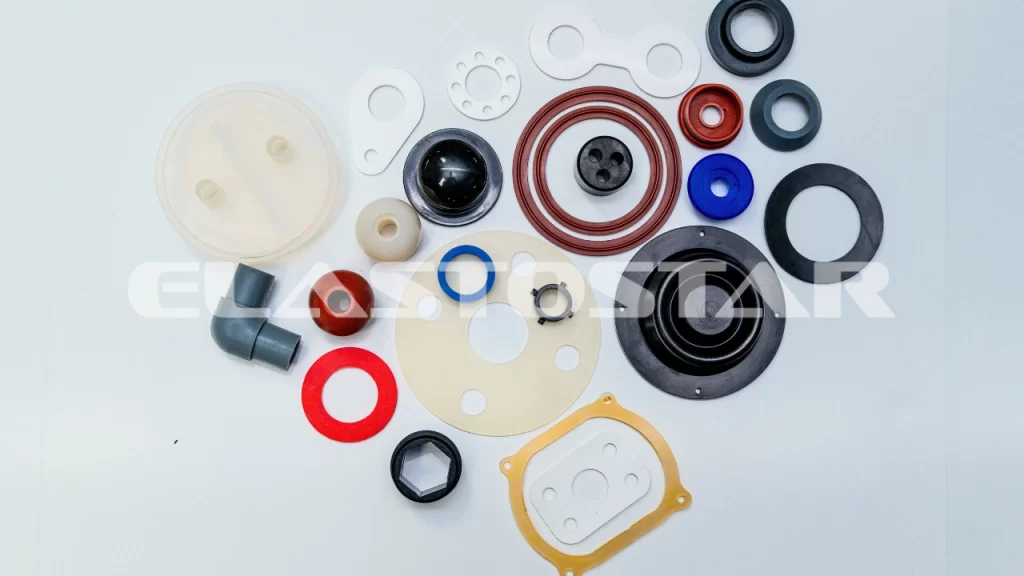

Precision Die Cut Parts Customization Process: Engineering Excellence from Concept to Volume
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our customization process for precision die cut rubber components integrates rigorous engineering protocols to ensure OEM-grade performance. This structured workflow transforms client specifications into validated production-ready parts, minimizing risk and accelerating time-to-market for mission-critical applications in automotive, medical, and industrial sectors.
Drawing Analysis initiates the process with meticulous technical validation. Our engineers scrutinize CAD files and 2D prints against ISO 10110 optical tolerancing standards, verifying critical dimensions, geometric tolerances (GD&T), and material callouts. We cross-reference client requirements with ISO 3302-1 elastomer tolerance classes, identifying potential manufacturability conflicts such as undercuts, draft angles below 1°, or wall thickness deviations exceeding ±0.05mm. This phase includes material compatibility assessment against fluid exposure, temperature ranges, and regulatory frameworks like FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 for medical use, ensuring zero downstream rework.
Formulation Development leverages our proprietary rubber chemistry expertise. Based on the application’s mechanical and environmental demands, we select base polymers (NBR, EPDM, FKM, or silicone) and engineer custom compounds. Key parameters include optimizing Shore A hardness (30–90A), tensile strength (10–30 MPa), compression set (<25% per ASTM D395), and fluid resistance. Each formulation undergoes computational simulation for flow behavior in mold cavities, followed by lab-scale mixing and vulcanization trials to validate cure kinetics and physical properties. This stage directly influences part longevity under dynamic stress or chemical exposure.
Prototyping employs rapid tooling with CNC-machined aluminum molds for 50–200 pre-production units. Parts undergo dimensional validation via CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) against original drawings, with critical features measured to ±0.02mm accuracy. Simultaneously, we conduct accelerated life testing: 72-hour fluid immersion per ASTM D471, ozone resistance at 50 pphm (ASTM D1149), and dynamic compression set analysis. Client feedback on prototype performance triggers iterative refinements until all functional and dimensional criteria are met.
Mass Production transitions validated designs into high-volume manufacturing with full statistical process control (SPC). We implement automated vision inspection systems for 100% critical dimension verification and real-time monitoring of cure pressure/temperature profiles. Every batch includes certified material test reports (MTRs) traceable to raw material lot numbers, with hardness, tensile, and elongation tested per ASTM D2000. Our ISO 9001-certified facility maintains ±0.5°C mold temperature control and 24-hour humidity stabilization, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency at volumes exceeding 500,000 units monthly.
Key material and process specifications are summarized below for reference:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Testing Method | Tolerance Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 30–90 A | ASTM D2240 | ±2 points |
| Tensile Strength | 10–30 MPa | ASTM D412 | ±1.5 MPa |
| Compression Set (70°C) | <15% (FKM) to <25% (EPDM) | ASTM D395 Method B | ±3% |
| Dimensional Tolerance | ±0.05mm (critical features) | ISO 3302-1 Class M2 | ±0.02mm |
| Fluid Resistance (IRM 903) | Volume swell <15% | ASTM D471 | ±2% |
This end-to-end engineering discipline ensures Suzhou Baoshida delivers precision die cut rubber parts that exceed functional requirements while maintaining absolute repeatability in global supply chains. Our process reduces client validation cycles by 30% and scrap rates by 18% versus industry averages through proactive material science and precision manufacturing integration.
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Die Cut Rubber Components
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. stands at the forefront of industrial rubber component manufacturing, specializing in custom molded and precision die cut parts for demanding OEM applications. With over 15 years of experience serving automotive, medical, electronics, and industrial equipment sectors, we deliver engineered rubber solutions that meet exact dimensional, material, and performance specifications. Our advanced die cutting technologies—ranging from flatbed to rotary die cutting—ensure repeatability, edge quality, and micron-level tolerance control across high-volume and prototype production runs.
When sourcing precision die cut rubber parts, consistency, material integrity, and supply chain reliability are non-negotiable. At Baoshida, we combine ISO 9001-certified quality management with in-house tooling design, material testing, and rapid prototyping to support your development cycle from concept to mass production. Our engineering team works directly with clients to select optimal elastomers—including NBR, EPDM, silicone, FKM, and neoprene—based on environmental exposure, compression set resistance, hardness requirements, and regulatory compliance.
To ensure seamless integration into your assembly process, all die cut components undergo rigorous inspection protocols, including dimensional verification via optical comparators, hardness testing, and visual defect screening. We support custom packaging, kitting, and barcoding to align with just-in-time manufacturing workflows.
Partnering with Suzhou Baoshida means gaining more than a supplier—you gain a technical collaborator committed to solving complex sealing, damping, or insulation challenges with precision-engineered rubber solutions.
For immediate assistance with your next precision die cut project, contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Account Manager and Rubber Formula Engineer, directly at [email protected]. Mr. Boyce brings deep expertise in elastomer formulation, compression and transfer molding, and high-tolerance die cutting processes. He will guide you through material selection, tolerance optimization, tooling design, and production planning to ensure your components perform reliably in real-world conditions.
We respond to all technical inquiries within 4 business hours and offer sample turnaround in as few as 7–10 days, depending on complexity. Whether you require 100 prototypes or 500,000 annual production units, our facility in Suzhou is equipped to scale efficiently while maintaining full traceability and quality control.
Reach out today to begin your project with a partner who values precision, performance, and partnership.
Material and Tolerance Specifications
| Parameter | Standard Capability | High-Precision Option | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Types | NBR, EPDM, Silicone, FKM, CR, Neoprene, SBR | Custom compounds available | FDA, ROHS, UL, and NSF options |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 30–90 | 40–80 (±5 tolerance) | Measured per ASTM D2240 |
| Thickness Tolerance | ±0.1 mm | ±0.05 mm | For sheets 0.5–5 mm thick |
| Die Cut Tolerance | ±0.2 mm | ±0.1 mm | Depends on material and geometry |
| Minimum Feature Size | 1.0 mm | 0.5 mm | Applicable for rotary die cutting |
| Production Volume | 100 – 1,000,000+ units | Scalable batches | Automated lines for high volume |
| Lead Time (Prototype) | 7–10 days | 5–7 days (rush available) | Based on approved drawings and tooling |
| Certifications | ISO 9001:2015, RoHS, REACH | FDA, UL, NSF upon request | Full material traceability provided |
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
