Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Vacuum Lamination

Engineering Insight: The Critical Role of Material Selection in Vacuum Lamination
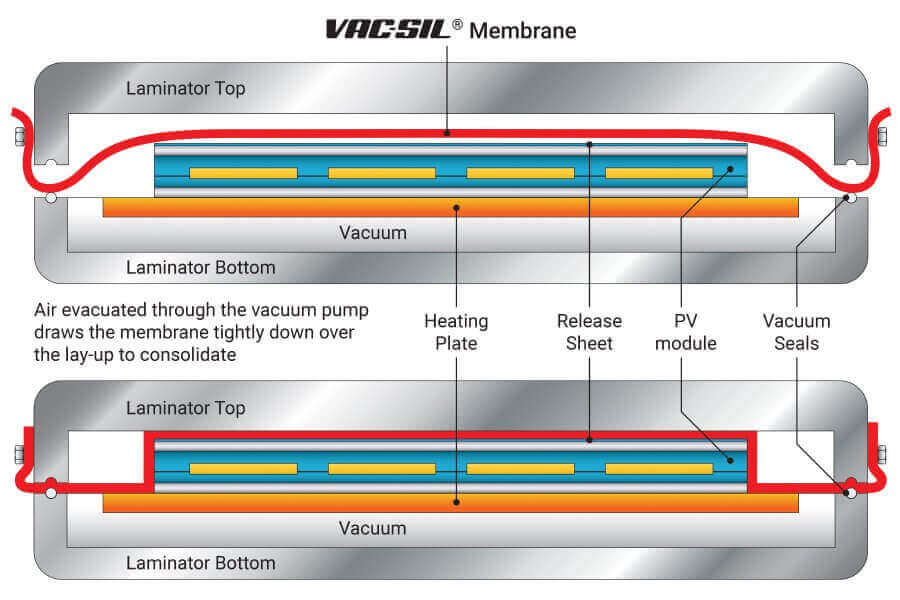
Vacuum lamination is a precision-driven manufacturing process widely employed in industries ranging from electronics and photovoltaics to aerospace and medical device assembly. At its core, the process relies on the application of uniform pressure and controlled heat under a vacuum environment to bond multiple layers of materials without entrapped air or micro-voids. While equipment calibration and process parameters are often scrutinized, one of the most overlooked yet decisive factors in successful vacuum lamination is the selection of elastomeric materials used in the vacuum membrane or sealing components.
Standard off-the-shelf rubber membranes or gaskets may appear cost-effective at first glance, but they frequently fail under the rigorous demands of industrial vacuum lamination. These failures stem from inadequate resistance to thermal cycling, poor elasticity retention, or insufficient mechanical strength under repeated compression. For instance, a generic silicone rubber may degrade rapidly when exposed to continuous cycles above 180°C, leading to outgassing, surface cracking, and compromised vacuum integrity. Similarly, low-grade EPDM or neoprene seals may exhibit compression set after only a few hundred cycles, resulting in vacuum leaks and inconsistent lamination quality.
The root cause lies in the absence of tailored material formulation. High-performance vacuum lamination requires elastomers engineered for specific thermal stability, tensile strength, elongation at break, and outgassing characteristics. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize custom-compounded rubber solutions designed to match the operational profile of each lamination system. Our formulations undergo rigorous testing for resilience under dynamic vacuum conditions, ensuring long-term reliability and dimensional stability.
Below is a comparative overview of critical material properties for vacuum lamination applications:
| Material Type | Continuous Use Temperature (°C) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Compression Set (22h at 150°C) | Outgassing (TML %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Silicone | 180 | 6.5 | 350 | 28 | 1.8 |
| High-Performance Silicone | 250 | 9.0 | 450 | 15 | 0.7 |
| Fluorosilicone | 200 | 8.0 | 400 | 20 | 1.0 |
| FKM (Viton®) | 230 | 12.0 | 250 | 18 | 0.5 |
| Custom Baoshida HT-250 | 250+ | 10.5 | 480 | 12 | 0.6 |
As demonstrated, off-the-shelf materials often fall short in one or more critical parameters. In contrast, engineered solutions such as our HT-250 compound offer superior performance across the board, ensuring consistent vacuum integrity, extended service life, and reduced downtime.
Material selection is not a commodity decision—it is a precision engineering requirement. Choosing the right elastomer is fundamental to achieving repeatable, high-yield lamination outcomes in demanding industrial environments.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Vacuum Lamination Applications
Precision material selection is paramount in vacuum lamination processes, where seal integrity directly impacts yield and product reliability. Industrial rubber compounds must maintain dimensional stability, resist outgassing, and sustain elastic recovery under deep vacuum conditions. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineered solutions prioritize molecular integrity and performance consistency across critical operational parameters. Viton, Nitrile, and Silicone represent the core material families for these demanding applications, each offering distinct advantages based on chemical exposure, temperature profiles, and mechanical requirements.
Viton fluorocarbon rubber delivers unparalleled resistance to aggressive chemicals, fuels, and high temperatures, making it indispensable for aerospace and semiconductor lamination. Its low permeability and minimal outgassing ensure vacuum integrity in environments exceeding 200°C, though higher cost necessitates strategic application targeting. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) provides an optimal balance for cost-sensitive applications involving oils, greases, and moderate heat. Its robust abrasion resistance and sealing force retention suit automotive and general industrial lamination where temperatures remain below 120°C. Silicone rubber excels in extreme temperature cycling from -60°C to 200°C, offering exceptional flexibility and low compression set. While less resistant to hydrocarbons, its biocompatibility and electrical insulation properties are critical for medical device and electronics lamination processes.
All materials undergo rigorous per ASTM D2000 classification and ISO 3601 flange testing to validate vacuum compatibility. Compression set resistance is non-negotiable; values exceeding 30% risk permanent seal deformation under prolonged vacuum hold. Shore A hardness must align with groove geometry—typically 60–80 durometer—to balance sealing force and extrusion resistance. Tensile strength and elongation directly influence handling durability during lamination setup, where material must withstand assembly stresses without micro-tearing.
The following comparative analysis details critical specifications for informed material selection:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Temp Range | -20°C to +230°C | -40°C to +120°C | -60°C to +200°C |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 12–20 (ASTM D412) | 15–25 (ASTM D412) | 5–10 (ASTM D412) |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–300 | 200–500 | 200–700 |
| Typical Hardness (Shore A) | 65–85 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Compression Set (22h/150°C) | ≤15% (ASTM D395) | ≤25% (ASTM D395) | ≤20% (ASTM D395) |
| Key Vacuum Applications | Semiconductor chambers, fuel cell lamination | Hydraulic seal lamination, automotive gasketing | Medical device encapsulation, LED panel lamination |
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. validates all formulations through in-house vacuum decay testing at 10⁻³ mbar levels. Material recommendations derive from OEM-specific process mapping—considering cycle duration, cleaning protocols, and substrate interactions. Partner with our engineering team to specify compounds meeting ISO 10993 biocompatibility or UL 746C chemical resistance standards where applicable. Precision lamination demands materials engineered beyond baseline specifications; our technical data sheets provide full traceability to ASTM/ISO test methodologies for audit compliance.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. maintains a robust engineering framework specifically tailored for advanced industrial rubber applications, particularly within the domain of vacuum lamination processes. Central to our capability is a dedicated team of five mould engineers and two specialized rubber formulation engineers, all operating under strict ISO-compliant protocols to ensure precision, repeatability, and material integrity across production cycles. This integrated engineering structure enables us to deliver fully optimized rubber components that meet the stringent thermal, mechanical, and dimensional demands of vacuum lamination systems used in electronics, photovoltaics, and high-performance composites.
Our mould engineering team specializes in designing and refining precision rubber moulds that support consistent part geometry, minimal flash, and optimal flow dynamics under vacuum and elevated temperature conditions. Each design undergoes rigorous simulation for thermal distribution, compression behavior, and demoulding efficiency, ensuring compatibility with automated lamination lines. Utilizing advanced CAD/CAM software and CNC machining techniques, our engineers achieve tolerances within ±0.05 mm, critical for sealing surfaces and uniform pressure distribution during lamination cycles.
Complementing this is our in-house rubber formulation expertise. The two senior formula engineers on staff possess extensive experience in elastomer chemistry, with a focus on silicone, EPDM, and fluororubber (FKM) systems engineered for high-temperature stability, low outgassing, and long-term compression set resistance. These formulations are developed to withstand repeated exposure to vacuum environments up to 10⁻³ mbar and temperatures exceeding 250°C without degradation. Custom compounds are validated through accelerated aging tests, dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), and vacuum thermo-gravimetric analysis (TGA) to ensure performance fidelity.
Our OEM capabilities are built upon this dual foundation of precision tooling and advanced material science. We support full turnkey development—from concept and material selection to prototype, validation, and serial production—ensuring seamless integration into client-specific lamination equipment. All rubber components are traceable through batch coding and material certification, meeting RoHS, REACH, and FDA (where applicable) standards.
The following table outlines key engineering specifications and performance benchmarks achieved through our integrated development process:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Mould Tolerance | ±0.05 mm |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +280°C (material-dependent) |
| Compression Set (24h @ 200°C) | ≤25% (silicone), ≤30% (FKM) |
| Outgassing (TML <1%, CVCM <0.1%) | ASTM E595 compliant |
| Vacuum Compatibility | Up to 10⁻³ mbar continuous |
| Material Systems | Silicone, FKM, EPDM, NBR |
| Lead Time (Prototype) | 15–25 days |
| Tooling Life | 50,000+ cycles (standard steel), 100,000+ (hardened) |
This technical depth positions Suzhou Baoshida as a strategic partner for OEMs requiring mission-critical rubber components in vacuum lamination systems, where reliability, repeatability, and material performance are non-negotiable.
Customization Process

Customization Process for Vacuum Lamination in Industrial Rubber Solutions
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our vacuum lamination customization process integrates rigorous engineering protocols to ensure precision and performance consistency for OEM partners. This four-phase methodology transforms client specifications into mission-critical rubber components, adhering to stringent industrial standards.
Drawing Analysis
Initial technical assessment begins with comprehensive CAD drawing evaluation. Our engineering team scrutinizes dimensional tolerances, material thickness variations, and interface geometries to identify potential lamination stress points. Critical parameters such as edge sealing requirements and substrate compatibility are validated against ISO 2768-mK tolerancing standards. This phase includes finite element analysis (FEA) simulations to predict vacuum-induced deformation under operational loads, ensuring design feasibility before material commitment.
Formulation
Based on drawing insights, our rubber chemists develop bespoke elastomer compounds targeting optimal adhesion and thermal stability. Key considerations include:
Cure kinetics tailored to vacuum chamber cycle times
Viscoelastic properties for gap-filling under low-pressure conditions
Chemical resistance profiles matching end-use environments
Formulations undergo accelerated aging tests per ASTM D573 and peel strength validation (ASTM D903) to guarantee interfacial integrity. All compounds are traceable to ISO 9001-certified batch records.
Prototyping
Pre-production samples are manufactured using client-specified vacuum lamination parameters. Each prototype undergoes:
Dimensional verification via CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) at 23°C ±2°C
Vacuum decay testing at 0.1 mbar for 60 minutes
Cross-section microscopy to detect delamination or voids
Client feedback drives iterative refinements, with typical lead times of 15–20 days for three prototype iterations.
Mass Production
Upon prototype approval, OEM-managed production lines activate with real-time SPC (Statistical Process Control) monitoring. Every lamination cycle is documented for full traceability, including vacuum pressure curves, temperature profiles, and cure state data. Final inspection employs 100% visual checks per AQL 1.0 and random destructive testing of peel strength. All components ship with certified material test reports (MTRs) and RoHS/REACH compliance documentation.
Critical Vacuum Lamination Parameters
| Parameter | Standard Range | Tolerance | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Pressure | 0.05–0.5 mbar | ±0.02 mbar | ISO 21348 |
| Lamination Temperature | 120–180°C | ±3°C | ASTM D5229 |
| Cycle Time | 15–45 minutes | ±90 seconds | Internal SOP-VM07 |
| Peel Strength | ≥6.0 kN/m | ±0.3 kN/m | ASTM D903 |
This structured approach eliminates guesswork in vacuum lamination, delivering rubber components that meet exacting industrial demands. Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM partnership model ensures seamless scalability from prototype to high-volume production while maintaining uncompromised quality control. All processes are audited against IATF 16949 requirements, providing clients with end-to-end technical accountability.
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Vacuum Lamination Solutions
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in delivering high-performance industrial rubber solutions tailored to the exacting demands of modern manufacturing. Our expertise in vacuum lamination processes positions us as a trusted partner for OEMs and industrial engineers seeking reliable, repeatable, and contamination-free bonding results. Whether you are working in electronics, photovoltaics, aerospace composites, or advanced material assembly, our engineered rubber components and technical support services ensure optimal process efficiency and product integrity.
Vacuum lamination requires precise control of pressure, temperature, and material compatibility. Our fluoroelastomer (FKM), silicone (VMQ), and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) membranes are formulated to withstand repeated exposure to high vacuum environments, thermal cycling, and chemical sterilization—critical for maintaining seal integrity and dimensional stability. Each product is manufactured under ISO 9001-certified conditions, with full traceability and rigorous QC testing to meet international industrial standards.
We understand that every production line presents unique challenges. That’s why we offer custom formulation and molding services to match your specific vacuum chamber geometry, service life requirements, and regulatory needs. From prototype development to full-scale production runs, our engineering team collaborates closely with clients to optimize material selection, compression set resistance, and outgassing performance.
To support seamless integration into your vacuum lamination workflow, we provide detailed technical data sheets, aging test reports, and on-site consultation when required. Our commitment extends beyond supply—we are your long-term technical partner in process innovation and yield improvement.
For immediate assistance or technical consultation, contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Manager and Rubber Formula Engineer at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. He leads our industrial rubber solutions division with over 12 years of experience in elastomer formulation and vacuum process optimization. Mr. Boyce is available to review your application requirements, recommend suitable materials, and coordinate sample delivery or testing protocols.
Reach out via email at [email protected] for confidential, expert support in advancing your vacuum lamination performance.
| Material Property | FKM (Fluoroelastomer) | VMQ (Silicone) | EPDM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +250 | -60 to +230 | -50 to +150 |
| Vacuum Compatibility | Excellent | Very Good | Good |
| Compression Set (22 hrs, 150°C) | 18% | 22% | 25% |
| Outgassing (TML <1%, 24h) | Pass | Pass | Pass |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding | Moderate | Good |
| Typical Applications | High-temp vacuum seals | Cleanroom lamination | General industrial bonding |
Partner with Suzhou Baoshida to elevate your vacuum lamination outcomes with scientifically engineered rubber solutions. Contact Mr. Boyce today to initiate a technical discussion tailored to your production needs.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
