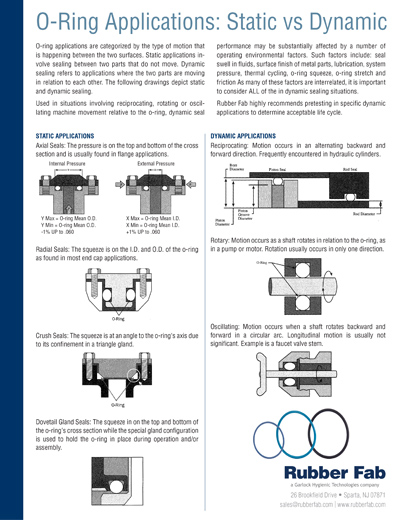
Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: O Ring Types

Material Selection Fundamentals in O-Ring Engineering
The performance longevity of an O-ring is intrinsically tied to precise material selection, not dimensional conformity alone. Off-the-shelf solutions frequently fail because they prioritize generic compatibility over the thermodynamic equilibrium required for specific fluid, temperature, and mechanical stress conditions. Polymer degradation kinetics accelerate under mismatched chemical exposure or thermal cycling, leading to compression set, extrusion, or catastrophic seal failure. For instance, an NBR O-ring in a ketone-rich aerospace hydraulic system will swell and lose resiliency within hours, while an FKM seal in low-temperature refrigeration may harden below its glass transition point, causing leakage. Material selection must account for dynamic variables: fluid composition pH levels, intermittent vs. continuous exposure, pressure differentials, and surface finish of mating hardware. Ignoring these factors transforms a simple elastomer component into a critical failure point, risking system downtime, contamination, or safety hazards.
Why Standardized O-Rings Underperform
Pre-manufactured O-rings assume uniform operating environments—a dangerous oversimplification. Industrial applications exhibit nuanced chemical cocktails; a “fuel-resistant” NBR compound may degrade when trace esters from biofuels interact with conventional antioxidants. Similarly, EPDM’s excellent water resistance becomes irrelevant in oil-lubricated transmissions where hydrocarbon swelling occurs. Off-the-shelf inventories rarely address compound modifications like peroxide curing for improved heat aging or custom filler systems to resist amine-induced cracking in CO₂ capture systems. The cost of a $0.50 generic O-ring pales against the $50,000+ downtime from a failed pump seal in continuous-process manufacturing. Material substitution without rigorous application validation violates ISO 1629 and ASTM D2000 standards, exposing OEMs to liability.
Critical Material Properties for Precision Sealing
The table below outlines key elastomer families and their engineering constraints. Selection requires matching all operational parameters, not isolated traits.
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Strengths | Key Limitations | Typical Failure Modes in Mismatched Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | -30 to +120 | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, aliphatic hydrocarbons | Poor ozone/weathering resistance; degrades in ketones, esters, brake fluids | Swelling in oxygenated biofuels; hardening in low-temp hydraulics |
| FKM | -20 to +250 | Superior chemical resistance (acids, bases, aromatics); low gas permeability | Limited low-temperature flexibility; expensive; incompatible with ketones, amines | Brittleness below -20°C; swelling in phosphate ester hydraulic fluids |
| EPDM | -50 to +150 | Exceptional steam/hot water resistance; ozone/weathering stability | Poor oil/fuel resistance; moderate abrasion resistance | Swelling in petroleum-based lubricants; compression set in dynamic oil seals |
| SIL | -60 to +230 | Wide temperature flexibility; biocompatible; low toxicity | Low tensile strength; poor acid resistance; high gas permeability | Extrusion in high-pressure systems; degradation in strong acids |
Baoshida’s Precision Engineering Approach
At Suzhou Baoshida, we reject one-size-fits-all solutions. Our OEM process begins with fluid analysis and stress modeling to identify polymer backbone chemistry, cure system, and additive package requirements. For a semiconductor tool manufacturer, we developed a peroxide-cured FFKM compound resistant to plasma-etched fluorocarbon gases at 200°C—impossible with standard FKM. Material selection isn’t procurement; it’s predictive engineering. Partner with us to convert failure risks into reliability metrics. Your application’s chemical-thermal profile demands a bespoke elastomer solution, not a catalog number.
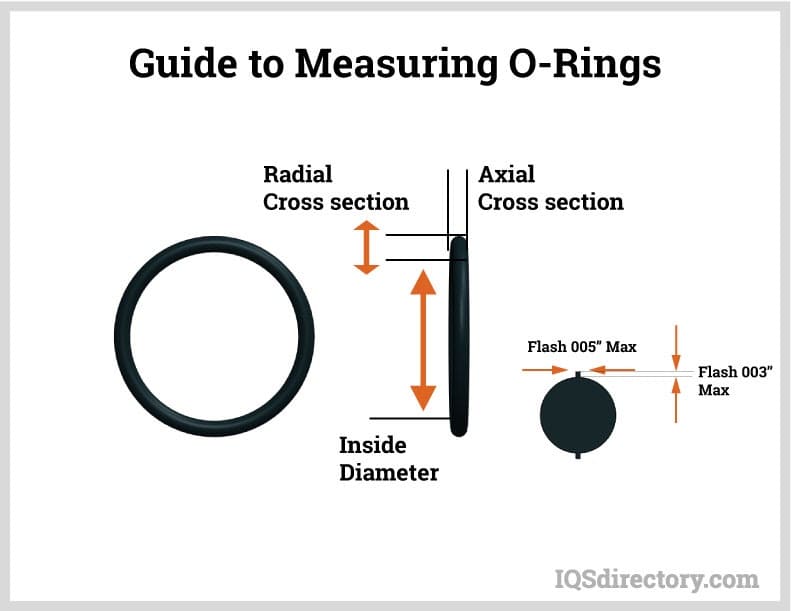
Material Specifications
Material selection is a critical factor in the performance and longevity of O rings used in precision sealing applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-integrity rubber seals engineered to meet the demanding requirements of industrial, automotive, aerospace, and chemical processing environments. Among the most widely used elastomers in our product line are Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone. Each material exhibits distinct chemical, thermal, and mechanical characteristics that determine its suitability for specific operating conditions.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber (FKM), is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and hydrocarbon fuels. It performs reliably in continuous service temperatures up to 200°C and can withstand short-term exposure to even higher temperatures. Viton O rings are ideal for applications involving oils, acids, and halogenated hydrocarbons, making them a preferred choice in engine systems, fuel handling, and chemical processing equipment. However, Viton has limited flexibility at low temperatures and is generally not recommended for dynamic applications involving significant flexing at sub-zero conditions.
Nitrile rubber (NBR) remains one of the most cost-effective and widely used materials for general-purpose sealing. It offers excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids, with operational temperature ranges typically spanning from -30°C to 100°C. Its high abrasion resistance and good tensile strength make NBR suitable for dynamic sealing in pneumatic and hydraulic systems. While NBR performs poorly when exposed to ozone, weathering, and polar solvents, its balance of performance and affordability ensures its continued use across a broad spectrum of industrial applications.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature environments, with continuous serviceability from -60°C to 200°C depending on formulation. It exhibits excellent resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and ozone, and maintains flexibility at cryogenic temperatures. Silicone is commonly used in food, pharmaceutical, and medical applications due to its inertness and compliance with regulatory standards. However, it has relatively low tensile strength and poor resistance to petroleum-based fluids, limiting its use in high-pressure or oil-exposed environments.
The following table summarizes key performance characteristics of these materials to guide optimal selection based on application demands.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 200 | -30 to 100 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–25 | 10–20 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–500 | 200–600 |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Resistance to Acids | Good to Excellent | Poor to Fair | Fair |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Common Applications | Aerospace, chemical seals, fuel systems | Hydraulic systems, automotive seals | Medical devices, food processing, extreme temp seals |
Selecting the appropriate O ring material requires a thorough understanding of the operational environment. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides technical support to ensure material compatibility and sealing performance across diverse industrial challenges.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision Sealing Through Material Science and Mold Innovation
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering framework for O-ring manufacturing merges molecular-level material design with advanced mold technology to deliver failure-resistant sealing solutions. Our dedicated team comprises five specialized mold engineers and two certified rubber formula engineers, ensuring every component transitions from theoretical specification to industrial reality with micron-level accuracy. This dual-expertise model allows us to solve complex sealing challenges where material behavior and geometric precision intersect—critical for aerospace, semiconductor, and high-pressure hydraulic applications.
Our formula engineers leverage proprietary polymer compounding methodologies to tailor elastomer properties for extreme operational environments. By manipulating filler dispersion, crosslink density, and additive synergies, we achieve custom balances of compression set resistance, thermal stability, and chemical inertness unattainable with off-the-shelf compounds. Concurrently, our mold engineering division utilizes 3D flow simulation and cavity pressure monitoring to eliminate knit lines, flash, and dimensional drift during vulcanization. This integrated approach reduces prototyping cycles by 40% while ensuring ±0.05mm dimensional repeatability across production runs.
As a certified OEM partner, we implement closed-loop process validation from material lot tracing to final inspection. Clients receive full technical ownership of designs through our secure IP management system, with options for co-engineering support during R&D phases. Our ISO 9001-certified facility accommodates low-volume specialty batches (as small as 500 units) to high-volume automated production, maintaining consistent quality via real-time SPC data tracking.
Material selection is foundational to O-ring performance. Below is a comparative specification guide for our most engineered elastomers:
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Pressure Rating (MPa) | Key Applications | Chemical Resistance Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogenated NBR | -50 to +150 | 35 | Automotive fuel systems | Excellent for oils, fuels; poor for ketones |
| Perfluoroelastomer (FFKM) | -15 to +327 | 70 | Semiconductor CVD chambers | Exceptional against acids, plasmas, solvents |
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 to +230 | 20 | Medical devices, food processing | Good for water, oxygen; poor for strong acids |
| EPDM | -55 to +150 | 30 | HVAC, pharmaceutical | Superior for steam, alkalis; poor for oils |
| Aflas® (TFE/P) | -20 to +250 | 45 | Geothermal energy systems | Unmatched for hot acids, amines, steam |
We prioritize failure mode analysis in every project, utilizing ASTM D2000 standards to define critical tolerances and material thresholds. For instance, in subsea hydraulic connectors requiring 20,000-hour service life, our team developed a custom FKM variant with 50% lower compression set at 200°C versus industry benchmarks—validated through 720-hour accelerated aging tests. This precision engineering capability ensures clients receive not just a component, but a documented performance guarantee aligned with their operational lifecycle requirements.
Suzhou Baoshida’s value lies in transforming material science into engineered reliability. By controlling both the molecular architecture of elastomers and the precision of their formation, we eliminate the guesswork in critical sealing applications—where every micron and every durometer point directly impacts system integrity.
Customization Process
Drawing Analysis
The customization process for precision O-ring seals begins with a comprehensive drawing analysis to ensure dimensional accuracy, material compatibility, and functional performance under specified operating conditions. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team meticulously reviews technical drawings provided by clients, focusing on critical parameters such as inner diameter, cross-sectional diameter, tolerance grades per ISO 3601 or AS568 standards, and any special surface or chamfer requirements. We validate geometric feasibility, assess moldability, and identify potential sealing challenges related to groove design or installation stress. This stage often involves close collaboration with the client’s R&D or design team to clarify ambiguities and recommend design optimizations that enhance manufacturability without compromising performance.
Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, our rubber formula engineers initiate material formulation tailored to the application environment. The selection of polymer base—whether Nitrile (NBR), Fluorocarbon (FKM), Silicone (VMQ), Ethylene Propylene (EPDM), or specialty compounds like FFKM or ACM—is determined by exposure to temperature extremes, chemical media, pressure cycles, and regulatory requirements (e.g., FDA, UL, or NSF compliance). Our in-house compounding laboratory develops proprietary formulations that balance critical properties such as compression set resistance, tensile strength, hardness (Shore A), and low-temperature flexibility. Each formulation undergoes rigorous simulation testing using ASTM and ISO protocols to predict long-term performance in dynamic or static sealing applications.
Prototyping and Validation
Once the formulation is finalized, we proceed to prototype production using precision molding techniques—typically compression, transfer, or injection molding—depending on complexity and volume requirements. Prototypes are manufactured in controlled batches and subjected to dimensional inspection via coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and optical comparators. Simultaneously, functional testing includes leak rate evaluation, thermal aging, fluid immersion, and dynamic motion trials where applicable. Feedback from this phase informs final adjustments to both material and mold design, ensuring compliance with the client’s performance envelope.
Mass Production and Quality Assurance
Upon client approval of prototypes, we transition to full-scale production. Our automated molding lines, supported by statistical process control (SPC) and 100% visual inspection systems, maintain consistency across large batches. Every production lot is traceable, with material certificates, cure curves, and inspection reports documented per IATF 16949 standards.
The following table summarizes key technical specifications managed during customization:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 50–90 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | 8–25 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | 150–500% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (70h, 100°C) | ≤25% (NBR), ≤20% (FKM) | ASTM D395 |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +230°C (varies by compound) | ISO 1817 |
| Tolerance Class | ISO 3601 Class M or tighter | ISO 3601 |
Through this structured approach, Suzhou Baoshida ensures every custom O-ring meets the highest standards of precision, durability, and application-specific performance.
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision O-Ring Solutions Engineered to Perform
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the intersection of advanced polymer science and industrial reliability, delivering mission-critical O-ring solutions for demanding global applications. Our engineering team possesses deep expertise in elastomer formulation, material compatibility analysis, and precision manufacturing processes essential for sealing integrity under extreme thermal, chemical, and mechanical stress. Selecting the optimal O-ring material is not merely a specification check; it is a fundamental engineering decision impacting system longevity, safety, and operational efficiency. Generic solutions often fail to address the nuanced interplay between fluid dynamics, surface finish, and environmental exposure inherent in modern industrial systems. We bridge this gap through rigorous material science and application-specific validation.
The table below summarizes key performance characteristics of standard elastomer compounds we engineer and manufacture. These values represent typical achievable ranges under controlled test conditions; actual performance in your specific application requires detailed engineering review considering all operational variables.
| Material Type | Continuous Temp Range (°C) | Max Pressure (Bar) | Key Chemical Resistance | Primary Industrial Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR (Nitrile) | -30 to +100 | 300 | Oils, Fuels, Hydraulic Fluids | Automotive Hydraulics, Fuel Systems |
| FKM (Viton®) | -20 to +230 | 400 | Aggressive Chemicals, High-Temp Oils | Aerospace, Petrochemical, Semiconductor |
| EPDM | -50 to +150 | 250 | Water, Steam, Brake Fluids, Polar Solvents | HVAC, Water Treatment, Automotive Cooling |
| Silicone | -60 to +200 | 150 | Ozone, UV, Moderate Chemicals | Medical Devices, Food Processing, Electronics |
| FFKM (Perfluoroelastomer) | -15 to +325 | 500 | Virtually All Chemicals, Plasma | Ultra-High-Purity Semiconductor, Critical Pharma |
Our value extends beyond standard catalog offerings. We specialize in custom compound development for unique challenges—whether requiring extreme low-temperature flexibility, resistance to novel biofuels, or compliance with stringent FDA/USP Class VI or AMS7256 aerospace standards. Every formulation undergoes stringent quality control per ISO 9001 protocols, including Mooney viscosity, tensile strength, compression set, and precise dimensional verification per AS568 or ISO 3601 standards. Our Suzhou-based manufacturing facility integrates automated molding with real-time process monitoring, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency critical for high-volume OEM production. Global logistics partnerships guarantee on-time delivery to assembly lines across North America, Europe, and Asia, mitigating supply chain disruption risks.
Do not compromise sealing performance on generic material data sheets or inadequate supplier technical support. The cost of seal failure—downtime, recalls, safety incidents—far exceeds the investment in precision-engineered elastomer solutions. Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Technical Manager, possesses 15 years of experience resolving complex sealing challenges across automotive, energy, and industrial automation sectors. He will collaborate with your engineering team to analyze application parameters, review fluid compatibility data, and recommend or develop the optimal O-ring solution tailored to your performance and regulatory requirements.
Initiate a direct technical consultation today. Contact Mr. Boyce immediately at [email protected] to discuss your specific sealing challenge. Provide details on operating environment, media exposure, temperature cycles, and dimensional constraints for a rapid, data-driven solution proposal. Suzhou Baoshida transforms material science into operational reliability—one precision O-ring at a time. Your system’s integrity demands engineered excellence; contact us to secure it.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
