Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Compression Moulding Service

Engineering Insight: Material Selection in Compression Moulding Services
The failure of rubber components in demanding applications frequently originates not from mould design flaws or process inconsistencies, but from inadequate material selection. Off-the-shelf rubber compounds present significant risks in compression moulding due to their generic formulations, which lack the molecular precision required for specific operational environments. Compression set, fluid exposure, thermal cycling, and dynamic stress demands vary drastically across industries—from automotive seals enduring brake fluid at 150°C to medical diaphragms resisting ozone sterilization. Standard compounds sacrifice critical performance attributes to achieve broad market compatibility, leading to premature seal extrusion, chemical degradation, or loss of resiliency under sustained load.
Generic solutions ignore the interdependence of polymer backbone architecture, filler dispersion, and cure system chemistry. For instance, a standard NBR compound may meet basic fuel resistance but fail catastrophically when exposed to modern biofuels due to insufficient acrylonitrile content or inadequate antioxidant packages. Similarly, off-the-shelf silicone often lacks the reinforced polymer network needed for low-compression-set applications, resulting in permanent deformation after 72 hours at elevated temperatures. These failures manifest as field leaks, assembly complications, or regulatory non-compliance, incurring costs far exceeding initial material savings.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. addresses this through application-specific polymer formulation. Our engineering process begins with OEM validation of service parameters—including dynamic stress profiles, fluid immersion sequences, and lifetime expectancy—before initiating compound development. Molecular-level customization of base polymers, curatives, and specialty additives ensures performance alignment with real-world demands. Below illustrates the performance gap between standard and engineered compounds under identical compression moulding conditions:
| Performance Parameter | Standard Off-the-Shelf Compound | Baoshida Engineered Compound | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70h, 100°C) | 25% | ≤8% | ASTM D395 |
| Heat Aging (70h, 150°C) | ΔTensile: -45% | ΔTensile: -12% | ASTM D573 |
| Fuel B (ASTM D471) | ΔVolume: +35% | ΔVolume: +8% | ASTM D471 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 12.0 | 18.5 | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200 | 450 | ASTM D412 |
This data underscores how engineered compounds mitigate failure modes inherent in generic materials. Our OEM collaboration framework integrates material science with compression moulding physics—optimizing cure kinetics for complex geometries while ensuring crosslink density resists fluid ingress. Crucially, we validate formulations against actual customer duty cycles, not just baseline industry specs. The result is a component that maintains dimensional stability, sealing force, and chemical integrity throughout its intended service life.
Compression moulding success hinges on recognizing that rubber is not a commodity. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers failure-resistant solutions by treating material selection as a core engineering discipline—not a procurement exercise. Partner with us to transform material specifications from a vulnerability into a competitive advantage.
Material Specifications
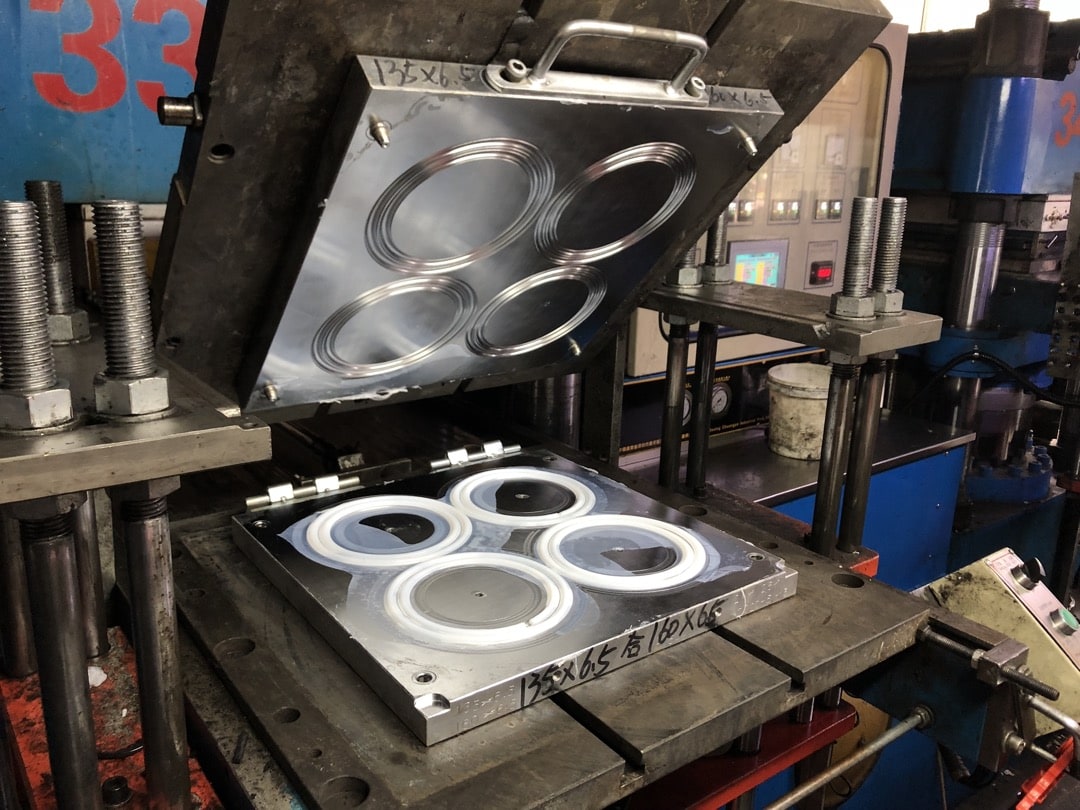

Material selection is a critical factor in compression molding processes, especially when producing custom molded rubber parts for demanding industrial applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision compression molding using high-performance elastomers such as Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone. Each material offers unique chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties that must be aligned with the operational environment of the final component. Understanding these characteristics ensures optimal part performance, longevity, and reliability in service.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber (FKM), is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of chemicals. It performs reliably in continuous service temperatures up to 200°C and can withstand short-term exposure to temperatures as high as 250°C. This makes Viton an ideal choice for aerospace, automotive, and oil & gas applications where exposure to aggressive media and extreme heat is common. Additionally, Viton exhibits low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics, contributing to long-term sealing performance under harsh conditions.
Nitrile rubber, or acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), is one of the most widely used elastomers in industrial sealing due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels. It offers good abrasion resistance and tensile strength, with operational temperatures typically ranging from -30°C to 120°C. Nitrile is cost-effective and well-suited for hydraulic systems, fuel systems, and general-purpose O-rings and gaskets. While it lacks the high-temperature stability of Viton, its balance of performance and affordability makes it a preferred option for many standard applications.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) stands out for its outstanding thermal stability and flexibility across a wide temperature range, from -60°C to 200°C. It also demonstrates excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering, making it ideal for outdoor and high-visibility applications. Silicone is commonly used in food, pharmaceutical, and medical industries due to its compliance with stringent hygiene standards and low toxicity. While it has lower mechanical strength compared to Viton and Nitrile, its electrical insulation properties and biocompatibility are superior.
The following table summarizes key material specifications to assist in the selection process for compression molded rubber components.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Polymer | Fluorocarbon | Acrylonitrile Butadiene | Polysiloxane |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 50–90 | 40–95 | 30–80 |
| Continuous Service Temp. | -20°C to 200°C | -30°C to 120°C | -60°C to 200°C |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 10–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–300 | 200–500 | 200–700 |
| Fluid Resistance | Excellent (oils, fuels, acids) | Excellent (petroleum oils, fuels) | Poor (oils/fuels), Good (water, alcohols) |
| Compression Set | Very Good | Good | Very Good |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Fair | Excellent |
Selecting the appropriate elastomer requires a thorough evaluation of operating conditions, including temperature, media exposure, mechanical stress, and regulatory requirements. Our engineering team at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports clients in material selection to ensure optimal performance and cost efficiency in every compression molding project.
Manufacturing Capabilities
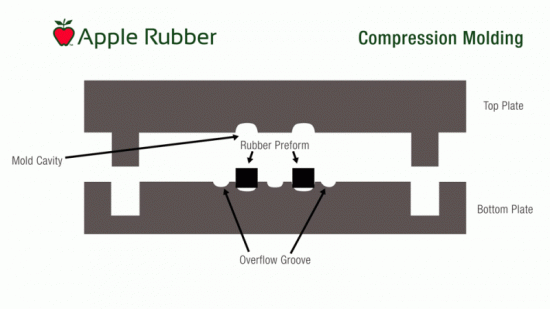
Engineering Capabilities for Precision Compression Moulding Services
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. integrates advanced engineering expertise with rigorous material science to deliver superior custom molded rubber parts via compression moulding. Our core strength lies in the seamless collaboration between dedicated Mold Engineering and Rubber Formulation teams, ensuring every component meets exacting industrial specifications. With five specialized mold engineers and two certified rubber formula engineers, we address complex challenges from initial design through production validation, eliminating common inter-departmental bottlenecks faced by competitors.
Our mold engineers utilize 3D simulation software to optimize cavity design, venting, and material flow, minimizing flash and cure inconsistencies. Concurrently, our formula engineers develop bespoke rubber compounds tailored to application demands—whether extreme temperature resistance, chemical exposure, or dynamic mechanical stress. This dual-engineering approach enables precise control over durometer, compression set, and tensile properties, ensuring performance in precision-critical applications like automotive seals, aerospace gaskets, and medical device components. Unlike standard service providers, we formulate and validate compounds in-house, accelerating prototyping and eliminating third-party dependencies.
OEM partnerships commence with joint design reviews, where our engineers identify manufacturability improvements early in the development cycle. We support full turnkey solutions, including material sourcing, tooling fabrication, and 100% dimensional validation per ISO 3302-1 tolerances. Our facility handles volumes from 100 to 500,000+ units annually, with rapid changeover protocols maintaining agility for urgent reorders.
Key technical capabilities are summarized below:
| Parameter | Capability Range | Typical Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Moulding Force | 50–1500 Tons | ±2% of rated capacity |
| Temperature Control | Ambient to 250°C | ±1°C stability |
| Cavity Count | Single to 16 cavities | Matched flow balancing |
| Part Dimensions | 10 mm to 600 mm diameter | ±0.1 mm (simple geometries) |
| Durometer Range | 30–90 Shore A | ±3 points |
| Production Lead Time | 15–25 days (post-tooling approval) | Customizable per order |
This technical infrastructure enables us to solve persistent industry pain points: reducing scrap rates by 18–22% through predictive cure modeling and extending part lifespan via fatigue-resistant formulations. All compounds undergo ASTM D2000 validation, with traceable batch records for full regulatory compliance. For OEMs, we provide comprehensive documentation packages—including FMEA reports, PPAP submissions, and raw material certifications—to streamline integration into existing supply chains.
Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering-led compression moulding service transforms material limitations into competitive advantages, ensuring your rubber components perform reliably under operational extremes while meeting cost and timeline targets. Partner with us for a seamless transition from prototype to volume production, backed by data-driven process control and unwavering technical accountability.
Customization Process
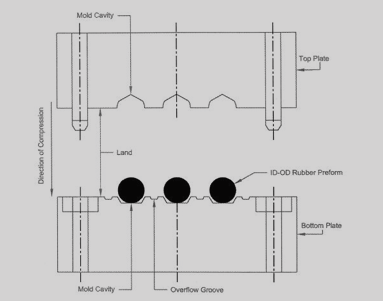
Compression Moulding Service: Customization Process for Rubber Components
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our compression moulding service is engineered to deliver high-performance, custom molded rubber parts tailored to the exacting demands of industrial applications. Our process follows a structured sequence—Drawing Analysis, Formulation Development, Prototyping, and Mass Production—ensuring precision, material compatibility, and long-term reliability.
The process begins with Drawing Analysis, where our engineering team conducts a comprehensive review of customer-provided technical drawings and specifications. We assess critical dimensions, tolerances (typically ±0.1 mm to ±0.5 mm depending on part geometry), parting line placement, draft angles, and expected performance conditions such as temperature exposure, chemical resistance, and mechanical stress. This stage ensures manufacturability and identifies potential design optimizations to reduce flash formation and improve mold longevity.
Following drawing validation, we proceed to Formulation Development. As certified rubber formula engineers, we select and compound elastomers based on application requirements. Common base polymers include NBR (nitrile butadiene rubber), EPDM, silicone (VMQ), FKM (fluoroelastomer), and CR (neoprene). The formulation is adjusted for hardness (Shore A 30–90), compression set, tensile strength, and resistance to oils, ozone, or extreme temperatures. All compounds are mixed in-house under controlled conditions to ensure batch consistency and traceability.
Once the formulation is finalized, we enter the Prototyping phase. A prototype mold—typically made from P20 or H13 tool steel—is fabricated with CNC precision. Small-batch molding runs (10–50 pieces) are conducted under production-equivalent conditions to validate part geometry, material behavior, and process stability. Prototypes undergo dimensional inspection and functional testing, including compression deflection and environmental exposure where applicable. Feedback from this stage informs any necessary mold or material adjustments.
Upon customer approval, we transition to Mass Production. High-precision steel molds are used in hydraulic compression presses with controlled temperature and pressure profiles. Production cycles are monitored for consistency, with in-process quality checks conducted at defined intervals. All finished parts are visually inspected, dimensionally verified, and packaged per customer requirements. Our production line supports volumes from thousands to millions of units annually, with lead times optimized through lean manufacturing practices.
The table below outlines typical technical capabilities for our compression moulding service:
| Parameter | Range / Specification |
|---|---|
| Material Types | NBR, EPDM, Silicone, FKM, CR, NR, SBR |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 30–90 |
| Dimensional Tolerance | ±0.1 mm (critical), ±0.3 mm (standard) |
| Weight Range | 5 g – 1,500 g |
| Temperature Resistance | -60°C to +300°C (material-dependent) |
| Production Capacity | 50,000 – 500,000 units/month |
| Mold Tool Life | 50,000 – 100,000 cycles (steel dependent) |
Through rigorous process control and material science expertise, Suzhou Baoshida ensures every custom rubber component meets both functional and regulatory standards for global industrial use.
Contact Engineering Team
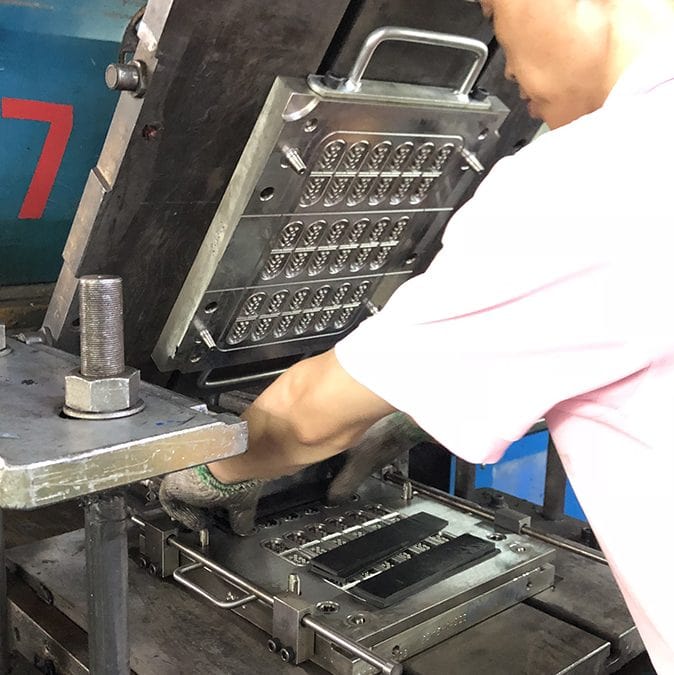

Precision Rubber Compounding and Compression Molding: Engineering Partnership for Critical Applications
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered rubber solutions where material integrity and dimensional accuracy define operational success. Our compression molding services are built upon 15 years of OEM collaboration, serving automotive, aerospace, and industrial sealing sectors with uncompromising adherence to ISO 9001:2015 and IATF 16949 standards. We specialize in transforming complex rubber formulations into mission-critical components, leveraging in-house polymer chemistry expertise to solve challenges in extreme thermal, chemical, and mechanical environments. Our facility integrates real-time process monitoring with statistical process control (SPC), ensuring every molded part meets stringent GD&T requirements and material performance benchmarks.
Material science forms the core of our value proposition. Below are key compound specifications validated through ASTM D2000 and customer-specific protocols. Each formulation undergoes rigorous lot-to-lot validation for consistency:
| Material Type | Durometer Range (Shore A) | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Performance Attributes | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR (Nitrile) | 40–90 | -40 to +125 | Fuel/oil resistance, abrasion durability | Fuel system seals, hydraulic O-rings |
| EPDM | 50–80 | -50 to +150 | Weather/ozone resistance, steam tolerance | Automotive weatherstripping, radiator hoses |
| Silicone | 30–80 | -60 to +230 | Biocompatibility, electrical insulation | Medical devices, high-temp gaskets |
| FKM (Viton®) | 60–90 | -20 to +250 | Chemical resistance (acids, fuels), low gas permeation | Aerospace seals, semiconductor components |
| CR (Neoprene) | 40–70 | -40 to +100 | Flame resistance, flex fatigue strength | Electrical cable jackets, vibration mounts |
Compression molding demands exacting control over cure kinetics, material flow, and post-mold stabilization—factors directly tied to compound formulation and tooling design. Our engineers optimize cure cycles using Mooney viscometry and rheometer data to eliminate flash, voids, and incomplete cross-linking. For high-volume OEM programs, we implement automated material handling and 100% automated vision inspection, reducing defect rates to below 50 PPM. Prototyping lead times are compressed to 15 business days through concurrent engineering, where our team co-develops tooling and material specs alongside your design phase.
OEMs face escalating pressure to mitigate NPI timeline risks while meeting evolving material regulations like REACH and UL 746. Generic rubber suppliers cannot address the interdependencies between compound chemistry, mold design, and end-use performance. Suzhou Baoshida operates as an extension of your engineering department—providing full material traceability, PPAP documentation, and failure mode analysis for critical sealing interfaces. When dimensional drift in a turbocharger gasket or compression set in a medical diaphragm threatens your production line, our rapid-response technical team delivers root-cause resolution within 72 hours.
Initiate a technical dialogue to secure your next-generation rubber component supply chain. Contact Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Relationship Manager, at [email protected]. Specify your application’s environmental stressors, volume requirements, and target GD&T tolerances. Mr. Boyce will coordinate a cross-functional review within 24 hours, including material selection recommendations, DFM feedback, and a validated production timeline. Do not compromise on the compound integrity that safeguards your product’s reliability—partner with engineers who treat rubber formulation as a precision science. Your request triggers immediate access to our application database of 1,200+ validated material-process combinations. Act now to eliminate prototyping iterations and accelerate time-to-market.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
