Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Waterstop For Concrete Joints

Engineering Insight: Material Selection in Waterstops for Concrete Joints
The performance and service life of waterstops in concrete joints are directly governed by material selection. While many contractors and specifiers assume that all waterstops are functionally equivalent, this assumption leads to premature failure, costly repairs, and compromised structural integrity. Off-the-shelf solutions, often mass-produced from generic polymer blends, lack the tailored formulation required to withstand site-specific chemical, thermal, and mechanical stresses.
Waterstops are not passive components. They are dynamic seals subjected to hydrostatic pressure, joint movement, concrete alkalinity, and long-term environmental exposure. Standard PVC or low-grade rubber waterstops degrade when exposed to chlorinated water, UV radiation, or elevated temperatures. Moreover, they exhibit poor elongation and recovery characteristics, leading to cracking under cyclic loading—a common occurrence in expansion and construction joints.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize engineered material performance over cost-driven substitutions. High-performance waterstops must balance flexibility, tensile strength, and chemical resistance. For example, hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) are selected not for cost efficiency but for their proven resilience in aggressive environments. HNBR offers superior resistance to oils, ozone, and elevated temperatures, making it ideal for industrial and wastewater applications. EPDM, with its excellent weathering and steam resistance, is preferred in above-grade or exposed structures.
Equally critical is the compatibility between the waterstop and the surrounding concrete matrix. Poor adhesion or differential thermal expansion can create micro-gaps, initiating water migration. Our formulations include adhesion promoters and controlled durometer profiles to ensure seamless integration with poured concrete. This level of precision cannot be achieved with generic, off-the-shelf products designed for broad applicability rather than engineered performance.
Another overlooked factor is aging behavior. Accelerated aging tests reveal significant performance divergence between premium and commodity-grade materials. After 1,000 hours of UV and moisture exposure, standard PVC waterstops show 40% loss in tensile strength, while reinforced EPDM retains over 85%. These differences are not visible during installation but manifest years later as leaks and joint spalling.
We recommend a project-specific material assessment before selection. Below is a comparative performance matrix for common waterstop materials used in industrial applications.
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Hardness (Shore A) | Resistance to UV | Resistance to Alkali | Max Continuous Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | 10–15 | 250–350 | 65–75 | Low | Moderate | 60 |
| NR (Natural Rubber) | 18–22 | 400–600 | 55–65 | Poor | Low | 70 |
| EPDM | 15–20 | 300–450 | 60–70 | Excellent | Excellent | 135 |
| HNBR | 20–25 | 250–350 | 70–80 | Good | Excellent | 150 |
Material selection is not a commodity decision—it is an engineering imperative. At Suzhou Baoshida, we provide application-driven solutions backed by material science, ensuring long-term watertight integrity in critical concrete structures.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Concrete Joint Waterstops
Selecting the optimal elastomeric material for concrete waterstops is critical to ensuring long-term structural integrity in submerged or chemically aggressive environments. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we engineer waterstops to withstand hydrostatic pressure, joint movement, and environmental degradation while maintaining adhesion to concrete substrates. Our technical analysis focuses on three primary polymers: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ), each offering distinct performance profiles for specialized applications. Material selection must align with project-specific chemical exposure, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical stress parameters to prevent premature failure.
Viton fluorocarbon rubber provides exceptional resistance to hydrocarbons, acids, and high-temperature environments, making it ideal for industrial wastewater treatment plants or chemical processing facilities. Its molecular stability ensures minimal swelling when exposed to aggressive solvents, though it commands a premium cost. Nitrile rubber delivers optimal balance for standard infrastructure projects, exhibiting strong resistance to oils, greases, and aliphatic hydrocarbons at moderate temperatures. It remains cost-effective for highway tunnels, parking structures, and potable water systems where chemical exposure is less severe. Silicone rubber excels in extreme thermal cycling and ozone-rich settings, maintaining flexibility from -60°C to 230°C. Its superior weathering resistance suits above-grade applications like expansion joints in bridges or architectural facades, though it exhibits lower tensile strength compared to hydrocarbon-based elastomers.
The following comparative table details critical mechanical and chemical properties per ASTM D2000 and ISO 37 standards:
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Hardness (Shore A) | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Resistance Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | 15.0 min | 200 min | 70 ±5 | -20 to +250 | Hydrocarbons, acids, solvents, steam |
| Nitrile (NBR) | 18.0 min | 300 min | 60 ±5 | -30 to +120 | Oils, greases, aliphatic hydrocarbons, water |
| Silicone (VMQ) | 8.0 min | 400 min | 50 ±5 | -60 to +230 | Ozone, UV radiation, weathering, extreme cold |
Critical selection criteria include verifying hardness compatibility with joint movement requirements—softer compounds (50–60 Shore A) accommodate greater dynamic displacement, while harder grades (70+ Shore A) resist extrusion under high pressure. Viton’s superior chemical inertness justifies its use in refineries despite higher material costs, whereas NBR remains the industry standard for municipal infrastructure due to its balanced performance-to-cost ratio. Silicone’s low-temperature flexibility prevents brittle fracture in alpine or arctic construction but requires reinforcement for high-load applications. All materials must undergo accelerated aging tests per ASTM C1309 to validate 50+ year service life in concrete matrices.
Suzhou Baoshida prioritizes material traceability and batch certification to ensure compliance with EN 14731 and ASTM C1309 specifications. We collaborate with OEM partners to tailor durometer, tensile properties, and additive packages—such as antimony trioxide for flame retardancy—to project-specific demands. This precision engineering guarantees waterstops perform as the final barrier against water ingress, protecting structural concrete from corrosion and spalling throughout the asset lifecycle.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team forms the backbone of our industrial rubber solutions, delivering precision-engineered waterstops for concrete joints that meet the exacting demands of modern construction and civil infrastructure. Our in-house engineering department comprises five dedicated mould engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, enabling us to control every phase of product development—from concept and material formulation to tooling design and final validation.
Our mould engineers bring over a decade of cumulative experience in precision rubber moulding, focusing on complex profiles required for hydrophilic and hydrophobic waterstop applications. Utilizing advanced CAD/CAM software, they design high-tolerance steel and aluminum tooling optimized for consistent extrusion and vulcanization. Each mould is rigorously tested for dimensional accuracy, flow dynamics, and cycle efficiency, ensuring uniform product quality across large production runs. This technical mastery allows us to produce waterstops with intricate geometries, including bulb-tail configurations, center bulbs, and multi-rib profiles, all critical for reliable water migration resistance in concrete joints.
Complementing our tooling expertise, our two rubber formula engineers specialize in polymer chemistry and material performance under extreme environmental conditions. They develop custom EPDM, SBR, and neoprene-based compounds tailored to specific client requirements such as high elongation, low compression set, ozone resistance, and compliance with ASTM C1309 or EN 14733 standards. Each formulation undergoes accelerated ageing, swelling, and tensile testing in our on-site laboratory to ensure long-term durability in submerged, buried, or chemically aggressive environments.
Our integrated approach enables seamless OEM collaboration. Clients provide technical drawings or performance specifications, and our team conducts a full feasibility analysis, including material selection, tooling strategy, and prototyping timeline. We support low-volume pilot runs and rapid iterations, ensuring design validation before full-scale production. This end-to-end control reduces time-to-market and enhances product reliability.
All waterstop products are manufactured under ISO 9001-certified processes, with full traceability from raw material batch to finished goods. We maintain strict process controls during mixing, extrusion, splicing, and curing to eliminate defects and ensure uniform cross-sectional integrity.
The following table summarizes key technical capabilities and performance parameters of our standard waterstop offerings:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Material Types | EPDM, SBR, Neoprene, PVC, Hydrophilic Rubber |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 50–70 ±5 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥8 MPa (EPDM), ≥7 MPa (SBR) |
| Elongation at Break | ≥400% |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +120°C |
| Joint Movement Capacity | ±25% of joint width |
| Compliance Standards | ASTM C1309, EN 14733, GB/T 18173.3 |
| Customization Lead Time (Mould) | 15–25 days |
| Sample Production | 7–10 days after design approval |
By combining deep materials science with precision engineering, Suzhou Baoshida delivers waterstops that exceed functional and regulatory expectations in tunnels, dams, subways, and wastewater treatment facilities worldwide.
Customization Process

Customization Process for Concrete Joint Waterstops
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. executes a rigorous four-phase customization protocol for concrete joint waterstops, ensuring absolute alignment with structural engineering requirements and environmental exposure conditions. This systematic approach mitigates leakage risks in critical infrastructure while optimizing material performance and lifecycle cost.
Drawing Analysis
Our engineering team initiates the process with comprehensive CAD drawing dissection, focusing on joint geometry, anticipated movement tolerances (compression, extension, shear), and concrete interface specifications. We evaluate substrate conditions, water pressure differentials, and chemical exposure risks per project location. This phase identifies critical parameters such as maximum joint width variation, settlement potential, and installation constraints, forming the technical foundation for subsequent material and design decisions. Non-compliance risks are flagged using ISO 10545-13 simulation protocols.
Formulation Development
Based on drawing analysis outputs, our rubber chemists develop client-specific polymer compounds. We prioritize EPDM for ozone resistance in above-grade structures, PVC for cost-sensitive submerged applications, and chloroprene for hydrocarbon exposure. Key variables include crosslink density adjustments to balance flexibility and recovery, carbon black dispersion for UV stability, and plasticizer selection to prevent migration in alkaline concrete environments. Each formulation undergoes predictive modeling for compression set (ASTM D395) and low-temperature brittleness (ASTM D2137), targeting ≤15% permanent deformation after 22 hours at 70°C.
Prototyping and Validation
Precision extruded prototypes undergo accelerated aging per ISO 188 and cyclic deformation testing per ASTM E1190. We measure tensile strength retention after 500 cycles, hydrostatic integrity at 1.5x design pressure, and adhesion strength to fresh concrete (ASTM C882). Clients receive dimensional conformance reports against their drawings, alongside stress-strain curves and thermal expansion coefficients. Iterations occur within 15 business days until all performance thresholds are met, with material lot traceability maintained via blockchain-enabled batch coding.
Mass Production Oversight
Upon prototype approval, Suzhou Baoshida implements strict production controls under ISO 9001:2015. Extrusion lines operate with real-time rheometry monitoring, while automated vision systems verify profile tolerances to ±0.3mm. Every 500-meter batch undergoes destructive testing for tensile properties and non-destructive hydrostatic validation. Final shipments include material test reports (MTRs) with lot-specific cure characteristics and compliance certificates for ASTM D412, EN 14733, and project-specified standards. OEM packaging with serialized barcoding ensures site-level traceability.
Critical Material Performance Specifications
| Material Type | Shore A Hardness | Tensile Strength | Elongation at Break | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | 55-65 | 18-25 MPa | 450-600% | Bridges, tunnels, potable water structures |
| PVC | 60-70 | 12-18 MPa | 300-450% | Basements, culverts, non-potable systems |
| Chloroprene | 50-60 | 20-28 MPa | 500-700% | Chemical plants, marine environments |
This end-to-end customization framework guarantees waterstops that dynamically accommodate concrete movement while maintaining watertight integrity for 50+ years. Suzhou Baoshida’s integration of polymer science with structural engineering principles delivers failure-proof solutions for global infrastructure projects.
Contact Engineering Team
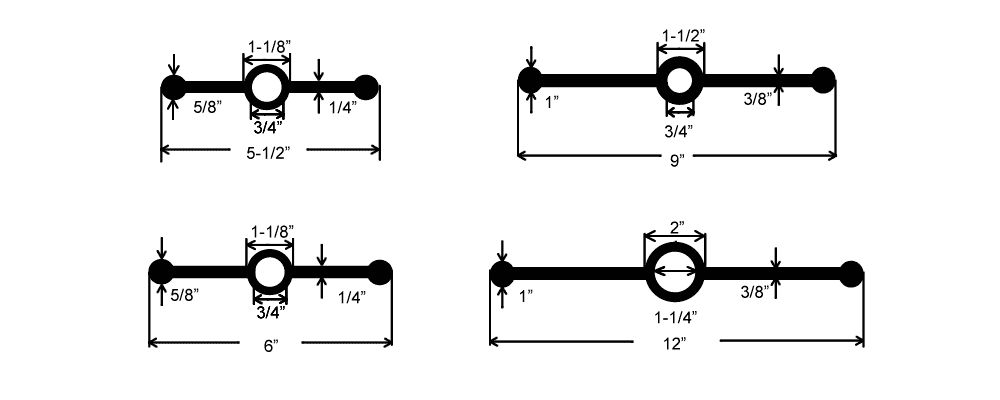
For engineered performance in concrete joint sealing, waterstops are critical components that ensure structural integrity, longevity, and watertight reliability in infrastructure projects. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-performance industrial rubber solutions, with a focused expertise in precision-manufactured waterstops designed for demanding applications in tunnels, subways, reservoirs, foundations, and wastewater treatment facilities. Our waterstops are formulated to resist hydrostatic pressure, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, ensuring long-term durability under extreme environmental conditions.
Our product line includes both center-bulb and P-type waterstops made from high-quality vulcanized rubber compounds, including NR (Natural Rubber), EPDM, and CR (Chloroprene), each selected for optimal elongation, tensile strength, and aging resistance. These materials are compounded and cured using advanced rubber processing techniques to meet international standards such as ASTM C1304, BS 5930, and EN 14705. Every waterstop is manufactured under strict quality control protocols to guarantee dimensional accuracy, consistent cross-sectional profiles, and seamless splice compatibility in the field.
We understand that every construction project presents unique challenges. That’s why Suzhou Baoshida offers custom formulation and extrusion services, allowing us to tailor waterstop profiles, hardness (Shore A), and material composition to match your project’s specific chemical, thermal, and mechanical requirements. Whether you need enhanced resistance to chlorinated water, oil, or UV exposure, our R&D team works closely with clients to develop engineered solutions that exceed performance expectations.
Below are representative technical specifications for our standard waterstop products:
| Property | Test Standard | NR (Natural Rubber) | EPDM | CR (Chloroprene) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 55 ± 5 | 60 ± 5 | 60 ± 5 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ASTM D412 | ≥12 | ≥10 | ≥13 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ASTM D412 | ≥400 | ≥350 | ≥380 |
| Tear Resistance (kN/m) | ASTM D624 | ≥30 | ≥25 | ≥32 |
| Water Absorption (%) | ASTM D471 | ≤2.0 | ≤1.8 | ≤1.5 |
| Operating Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +80°C | -50°C to +120°C | -40°C to +100°C |
All products undergo batch testing, with full traceability and certification available upon request. Installation support, technical data sheets, and 3D profile drawings are provided to ensure seamless integration into your construction workflow.
For project-specific inquiries, material recommendations, or custom extrusion requests, contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Manager and Rubber Formula Engineer at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. With over 15 years of experience in industrial rubber formulation and international project coordination, Mr. Boyce provides technical-first support to engineers, contractors, and procurement teams worldwide.
Reach out today via email at [email protected] to discuss your waterstop requirements. We respond to all technical inquiries within 4 business hours and offer sample submissions, third-party test reporting, and on-site consultation services for large-scale infrastructure programs. Partner with Suzhou Baoshida for engineered rubber solutions that seal performance, safety, and trust into every joint.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
