Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Rubber Edge Protector For Sheet Metal
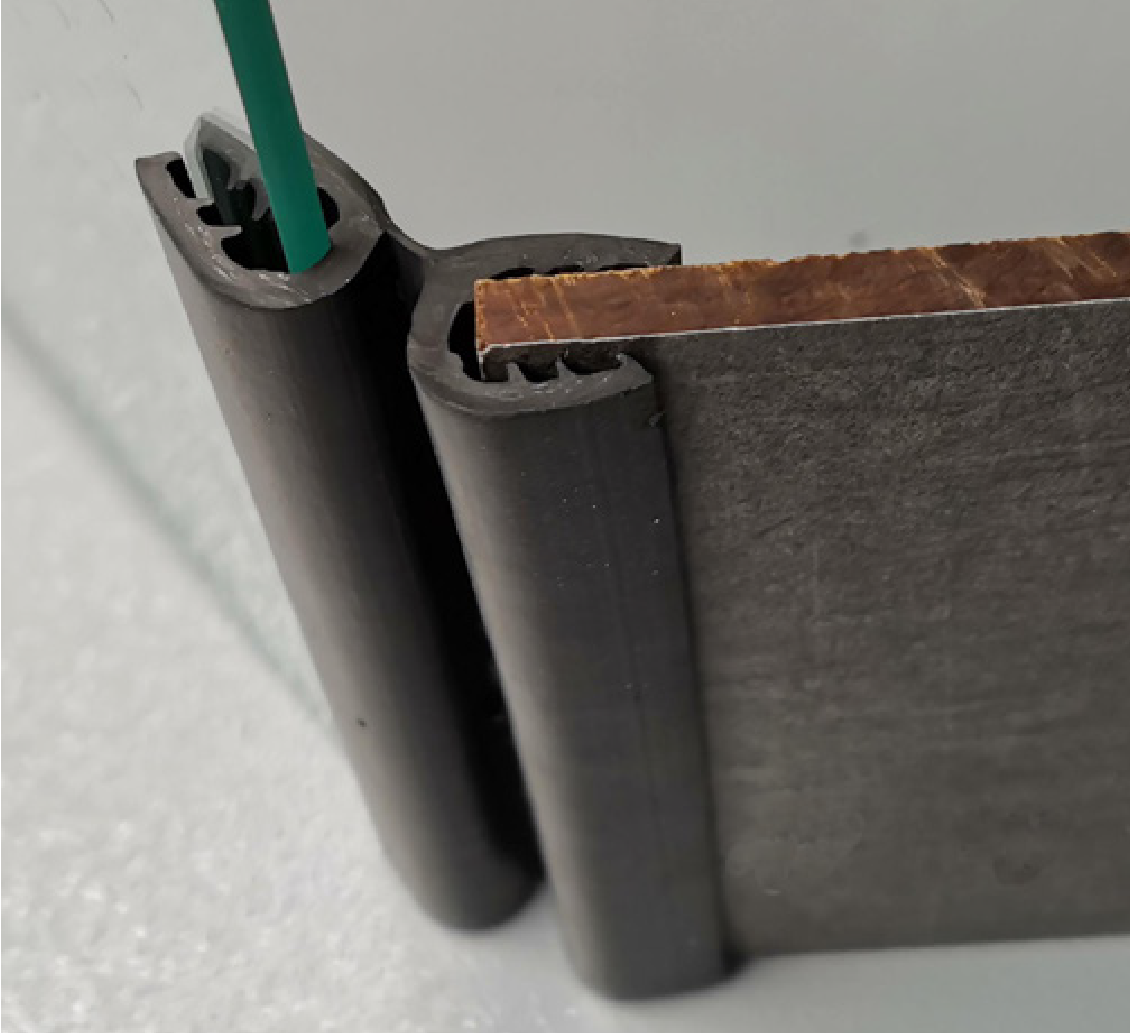
Engineering Insight: The Critical Role of Material Selection in Rubber Edge Protectors for Sheet Metal
In industrial manufacturing and material handling, the integrity of sheet metal components during transport, storage, and processing is paramount. One of the most vulnerable points of failure lies at the edges—exposed surfaces prone to abrasion, impact damage, and environmental degradation. Rubber edge protectors serve as a critical defense mechanism, yet their effectiveness is not guaranteed by generic design or off-the-shelf availability. The true determinant of performance is precise material selection, engineered to match the operational environment and mechanical demands.
Standard rubber edge protectors, often mass-produced from generic elastomers like natural rubber or low-grade SBR, fail under real-world industrial conditions due to inadequate resistance to ozone, UV exposure, temperature extremes, and mechanical stress. These materials degrade rapidly when exposed to outdoor elements or aggressive handling environments, leading to cracking, hardening, or loss of elasticity. In high-throughput facilities, such premature failure results in increased maintenance costs, product damage, and logistical inefficiencies.
At Suzhou Baoshada Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize application-specific formulation. Our engineered rubber compounds—primarily EPDM, neoprene (CR), and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE)—are selected based on three core criteria: environmental exposure, mechanical load, and surface compatibility. EPDM offers superior resistance to weathering and UV radiation, making it ideal for outdoor storage or transportation. Neoprene provides balanced performance with excellent flame resistance and moderate oil resistance, suitable for industrial workshops and automated handling lines. TPEs offer flexibility in design and processing, with enhanced recovery properties for repeated impact scenarios.
Beyond chemical resistance, durometer (hardness) and tensile strength must be optimized. A protector that is too soft may deform under pressure, failing to shield the edge. One that is too rigid may crack upon impact or damage the sheet metal surface during installation. Our formulations target a Shore A hardness range of 60–80, ensuring a balance between flexibility and structural integrity.
The failure of off-the-shelf solutions stems from their one-size-fits-all approach. Without customization to load profiles, temperature cycles, and surface geometry, even well-designed protectors underperform. True reliability comes from integrating material science with application data.
| Material | Shore A Hardness | Temperature Range | Key Properties | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | 65–75 | -50°C to +130°C | Excellent UV/ozone resistance, good weathering | Outdoor storage, construction panels |
| Neoprene (CR) | 70–80 | -40°C to +120°C | Flame retardant, moderate oil resistance | Industrial workshops, electrical enclosures |
| TPE | 60–75 | -40°C to +110°C | High elasticity, recyclable, easy processing | High-volume logistics, automated lines |
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Rubber Edge Protectors in Sheet Metal Handling
Precise material selection for rubber edge protectors is critical in sheet metal fabrication and transport. These components prevent surface marring, edge deformation, and handling damage while enduring rigorous industrial environments. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we engineer protectors using three primary elastomers—Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ)—each offering distinct performance profiles tailored to specific operational demands. The choice directly impacts protector longevity, chemical compatibility, temperature resilience, and mechanical integrity during high-speed production or logistics. Misalignment between material properties and application conditions leads to premature failure, increased scrap rates, and compromised product quality. Understanding the nuanced specifications of each compound ensures optimal protection and cost efficiency for OEM manufacturing lines.
Viton fluorocarbon rubber provides exceptional resistance to high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and oils. Its molecular structure withstands continuous exposure up to 250°C (482°F) and intermittent peaks near 300°C (572°F). Viton excels in environments involving cutting fluids, hydraulic oils, solvents, and ozone, maintaining integrity where other elastomers degrade rapidly. Typical hardness ranges from 70 to 90 Shore A, with tensile strength exceeding 15 MPa. This material is indispensable for automotive stamping lines using synthetic lubricants or aerospace component handling near jet fuels. However, Viton commands a premium cost and exhibits lower flexibility at sub-zero temperatures compared to alternatives.
Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) delivers outstanding resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and aliphatic hydrocarbons at a more economical price point. Standard formulations operate effectively between -40°C (-40°F) and 120°C (248°F), with specialty grades extending the upper limit to 150°C (302°F). NBR typically achieves 60 to 90 Shore A hardness and tensile strengths of 10–25 MPa. Its robust abrasion resistance and moderate compression set make it ideal for general sheet metal stamping, bending, and warehouse racking where mineral oils or hydraulic fluids are present. Limitations include poor resistance to ozone, weathering, and polar solvents like ketones or esters.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) offers the broadest operational temperature range, functioning reliably from -60°C (-76°F) to 230°C (446°F) continuously. It provides excellent flexibility across this spectrum and superior resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering. Silicone maintains stable electrical properties and achieves hardness levels between 30 and 80 Shore A, though its tensile strength (typically 6–12 MPa) is lower than NBR or Viton. Key applications include powder-coated or anodized metal handling requiring non-marking properties, cleanroom environments, and thermal cycling processes. Silicone exhibits poor resistance to concentrated acids, alkalis, and petroleum derivatives.
The following comparative table details critical specifications per ASTM standards for informed material selection:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -20°C to +250°C | -40°C to +120°C | -60°C to +230°C |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 70–90 | 60–90 | 30–80 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥15 | 10–25 | 6–12 |
| Key Chemical Resistance | Fuels, Acids, Ozone | Petroleum Oils, Greases | Ozone, UV, Water |
| Key Limitations | Cost, Low-Temp Flex | Ozone, Polar Solvents | Acids, Petroleum |
| Primary ASTM Standard | D2000 AA Type 5 | D2000 BG Type 2 | D2000 EE Type 1 |
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. rigorously validates all material formulations against OEM production requirements. Our engineering team collaborates directly with manufacturers to match protector specifications to sheet metal grade, processing speed, environmental exposure, and lifecycle cost targets, ensuring seamless integration into high-precision manufacturing workflows. Material datasheets and application testing protocols are available upon request for technical validation.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Excellence in Rubber Edge Protector Development
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering capability forms the backbone of our industrial rubber solutions, particularly in the design and production of rubber edge protectors for sheet metal applications. With a dedicated team of five certified mould engineers and two specialized rubber formulation engineers, we maintain full in-house control over the entire product development lifecycle—from concept to mass production. This integrated approach ensures precision, repeatability, and compliance with the most stringent OEM requirements.
Our mould engineers possess extensive experience in precision tooling for extruded and injection-moulded rubber profiles. They utilize advanced CAD/CAM software, including SolidWorks and AutoCAD, to design robust, high-tolerance steel and aluminum moulds optimized for long service life and dimensional consistency. Each mould undergoes rigorous simulation testing to predict material flow, minimize flash, and eliminate defects before production begins. This proactive engineering strategy reduces time-to-market and ensures first-time-right performance, critical for clients operating in fast-paced manufacturing environments.
Complementing our tooling expertise, our two rubber formula engineers specialize in elastomer chemistry and material performance optimization. They develop custom rubber compounds tailored to specific mechanical, thermal, and environmental demands. For sheet metal edge protectors, this means formulating EPDM, NBR, or SBR-based compounds that deliver superior abrasion resistance, UV stability, and flexibility across temperature ranges from -40°C to +120°C. These formulations are engineered to maintain elasticity under compression, resist oil and ozone exposure, and provide consistent grip without damaging coated or painted metal surfaces.
Our OEM capabilities are built on a foundation of technical collaboration. We work directly with client engineering teams to reverse-engineer legacy parts, validate new designs, and conduct material compatibility testing. All formulations and tooling are documented under strict change control procedures, ensuring full traceability and compliance with ISO 9001 standards. Prototypes are produced in-house using production-intent tooling, enabling accurate performance validation prior to scale-up.
Suzhou Baoshida supports low-volume pilot runs and high-volume continuous production, with automated extrusion and vulcanization lines capable of meeting tight tolerances and consistent surface finish requirements. Our engineering team also conducts regular DFMEA (Design Failure Modes and Effects Analysis) reviews to anticipate and mitigate potential field failures, ensuring long-term reliability of every edge protector supplied.
Typical Technical Specifications for Rubber Edge Protectors
| Property | Standard Value | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 55–75 ±5 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥8 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ≤25% | ASTM D395 |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +120°C | Internal |
| Abrasion Resistance (DIN) | ≤120 mm³ loss | DIN 53516 |
| Color Options | Black, Grey, Red, Blue (custom) | RAL/Pantone Match |
Through the synergy of advanced tooling, scientific material development, and OEM-focused engineering services, Suzhou Baoshida delivers rubber edge protectors that meet exact functional and dimensional requirements—ensuring protection, performance, and longevity in demanding industrial applications.
Customization Process

Customization Process for Rubber Edge Protectors in Sheet Metal Applications
The customization journey for rubber edge protectors begins with rigorous drawing analysis to ensure dimensional and functional alignment with client specifications. Engineering teams at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. dissect CAD files or technical sketches, verifying critical parameters such as cross-sectional geometry, tolerance bands per ISO 2768-mK, and interface requirements with sheet metal substrates. This phase identifies potential stress concentration points and validates compatibility with bending radii, stamping processes, or assembly line constraints. Non-conformities trigger collaborative redesign consultations to prevent downstream production failures, emphasizing precision in edge contour replication to eliminate gap-induced corrosion risks.
Formulation Development
Material science drives the next critical phase. Based on operational demands—exposure to oils, UV, temperature extremes, or mechanical abrasion—our rubber compounders select base polymers (EPDM for outdoor weatherability, NBR for fuel resistance, or silicone for high-heat zones) and engineer bespoke formulations. Key considerations include optimizing Shore A hardness for impact absorption versus ease of installation, filler ratios for cost-performance balance, and additive packages to meet flammability standards (e.g., UL 94 V-0). Each formulation undergoes computational modeling to predict compression set behavior under cyclic loading, ensuring long-term sealing integrity without permanent deformation.
Prototyping and Validation
Precision-molded prototypes are produced using client-approved tooling inserts, followed by exhaustive physical testing. We measure performance against industry benchmarks: tensile strength (ASTM D412), elongation at break, and resilience via rebound resilience tests (ASTM D2632). Critical for sheet metal applications, edge protector prototypes undergo simulated assembly line trials to assess snap-fit retention force and resistance to edge chipping during handling. Accelerated aging tests (e.g., 70°C for 72 hours) validate dimensional stability, while chemical resistance checks confirm compatibility with common metalworking fluids. Client feedback on prototype fit/functionality is integrated within 72 hours to finalize specifications.
Mass Production Execution
Upon sign-off, production transitions to ISO 9001-certified facilities with real-time statistical process control (SPC). Automated injection molding lines maintain ±0.1 mm tolerances, with 100% inline vision inspection for flash defects or voids. Every batch undergoes traceability via serialized lot coding, with third-party lab reports for hardness, density, and tear strength provided per ASTM standards. Suzhou Baoshida implements just-in-time logistics coordination, ensuring seamless integration into OEM assembly sequences while adhering to strict PPAP documentation protocols.
Key Material Specifications for Edge Protectors
| Parameter | Standard Range | Custom Capability | Application Context |
|————————|———————-|—————————|————————————–|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 45–95 | Balances flexibility and edge retention |
| Temperature Resistance | -40°C to +120°C | -60°C to +200°C (Silicone)| Automotive exteriors, industrial ovens |
| Abrasion Resistance | ASTM D5963 ≥ 120 mm³ | ≤ 80 mm³ | High-wear conveyor systems |
| Compression Set (22h) | ≤ 25% (70°C) | ≤ 15% | Long-term sealing under constant load |
| Chemical Resistance | Oils, water, mild acids | Custom fluorocarbon blends | Metal stamping fluid exposure |
This structured methodology guarantees edge protectors that prevent sheet metal burring, reduce workplace injuries, and extend component lifespan through scientifically validated material solutions. Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering-led approach minimizes time-to-market while exceeding OEM durability expectations.
Contact Engineering Team
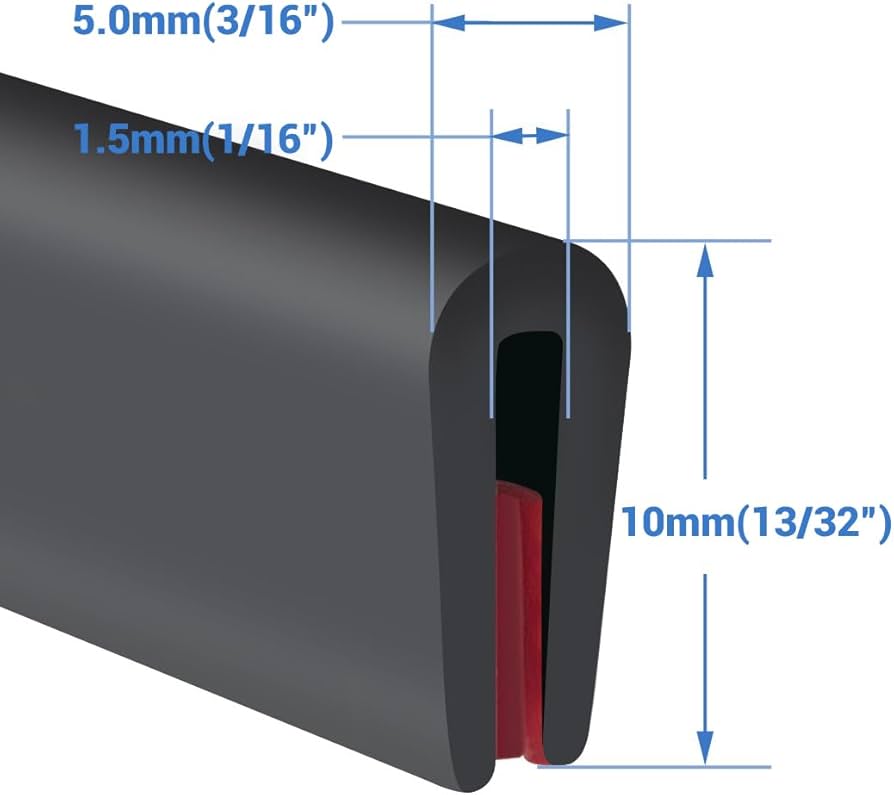
Contact Suzhou Baoshida for High-Performance Rubber Edge Protectors
When sourcing industrial rubber components such as edge protectors for sheet metal, precision, material integrity, and long-term performance are non-negotiable. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in engineered rubber solutions designed to meet the rigorous demands of metal fabrication, automotive assembly, logistics, and industrial packaging. Our rubber edge protectors are formulated to prevent surface damage, reduce handling-related defects, and improve safety across production and transportation workflows.
We invite manufacturers, procurement managers, and engineering teams to contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Manager and Rubber Formula Engineer at Suzhou Baoshida, to discuss custom specifications, volume supply agreements, or technical collaboration. With in-house material development, mold design capabilities, and ISO-compliant production lines, we ensure consistency, durability, and cost-efficiency across every batch.
Our edge protectors are manufactured using advanced EPDM, NBR, and SBR rubber compounds, selected based on environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and compatibility with coated or galvanized sheet metal surfaces. Each product is validated for abrasion resistance, UV stability, temperature tolerance, and adhesion performance under industrial conditions. Whether you require standard profiles or application-specific geometries, we support rapid prototyping and tooling development to accelerate time-to-market.
To facilitate informed decision-making, the table below outlines the standard technical specifications for our most widely deployed rubber edge protector series. These values represent baseline performance; customized Shore hardness, color coding, length tolerances, and anti-slip surface textures are available upon request.
| Property | Test Method | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | — | EPDM / NBR / SBR (custom blends) |
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 55 ± 5 to 85 ± 5 (adjustable) |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥ 8.0 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥ 250% |
| Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +120°C (up to +150°C intermittent) |
| UV and Ozone Resistance | ASTM D1149 | Excellent (Grade 1-2) |
| Density | ASTM D297 | 1.15–1.25 g/cm³ |
| Flame Resistance | UL94 | HB (optional V-0) |
| Adhesion to Steel | Peel Test (ASTM D903) | ≥ 4.5 kN/m (with primer) |
Partnering with Suzhou Baoshida means access to technical expertise grounded in rubber chemistry and industrial application engineering. Mr. Boyce leads a cross-functional team that collaborates directly with OEMs to optimize material selection, reduce total cost of ownership, and resolve field performance challenges.
For technical inquiries, sample requests, or to initiate a vendor qualification process, contact Mr. Boyce at [email protected]. We respond to all inquiries within 12 business hours and support communication in English, Mandarin, and technical German. Let us help you implement a reliable, scalable solution for sheet metal edge protection—engineered to perform, built to last.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
