Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Trim Around Sliding Glass Door

Engineering Insight: Trim Around Sliding Glass Door – The Critical Role of Material Selection
In industrial and commercial construction, the performance of trim components around sliding glass doors is often underestimated until failure occurs. These seals are not merely aesthetic finishes; they serve critical functional roles in weatherproofing, noise reduction, thermal insulation, and structural longevity. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize that off-the-shelf rubber trims frequently fail due to inappropriate material selection for specific environmental and mechanical conditions. Understanding the engineering behind elastomer performance is essential for achieving long-term reliability.
Standard trim solutions are typically formulated using generic rubber compounds such as low-grade EPDM or recycled materials. While cost-effective, these materials lack the resilience required for dynamic applications where repeated door movement, UV exposure, thermal cycling, and moisture ingress are constant challenges. For instance, low-durometer recycled rubber deforms under continuous compression, leading to gaps that compromise sealing integrity. Additionally, poor ozone resistance accelerates surface cracking, particularly in urban or coastal environments.
The optimal trim solution must balance hardness, elasticity, and chemical resistance. High-purity EPDM with controlled cross-link density offers superior weather resistance and maintains sealing force over thousands of cycles. Silicone-based compounds are preferable in extreme temperature ranges, while thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) provide excellent extrudability and mechanical strength for complex profiles. At Baoshida, we customize formulations based on OEM specifications, ensuring compatibility with aluminum framing systems, glass tolerances, and regional climate data.
Another overlooked factor is adhesion performance. Many pre-fabricated trims rely on weak pressure-sensitive tapes that degrade within months. Our engineered solutions integrate co-extruded adhesive layers or mechanical interlocks that bond permanently to substrates, eliminating delamination risks. Furthermore, precise dimensional control during extrusion ensures consistent compression set—typically below 20% after 1,000 hours at 70°C—critical for maintaining door operability and seal integrity.
Below is a comparative analysis of common elastomers used in door trim applications:
| Material | Hardness (Shore A) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Compression Set (%) | UV Resistance | Operating Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled Rubber | 50–60 | 4.5 | 35–50 | Poor | -10 to +70 |
| Standard EPDM | 60–70 | 8.0 | 25–30 | Good | -40 to +120 |
| High-Purity EPDM | 65–75 | 11.0 | 15–20 | Excellent | -50 to +150 |
| Silicone | 45–60 | 6.5 | 20–25 | Excellent | -60 to +200 |
| TPV | 55–80 | 12.5 | 18–22 | Good | -40 to +135 |
Selecting the right material is not a one-size-fits-all decision. It requires a systems-level approach that considers installation method, substrate type, expected lifespan, and environmental stressors. Off-the-shelf trims often fail because they prioritize cost over engineering rigor. At Baoshida, we partner with OEMs to develop application-specific solutions that outperform generic alternatives in both durability and functional precision.
Material Specifications
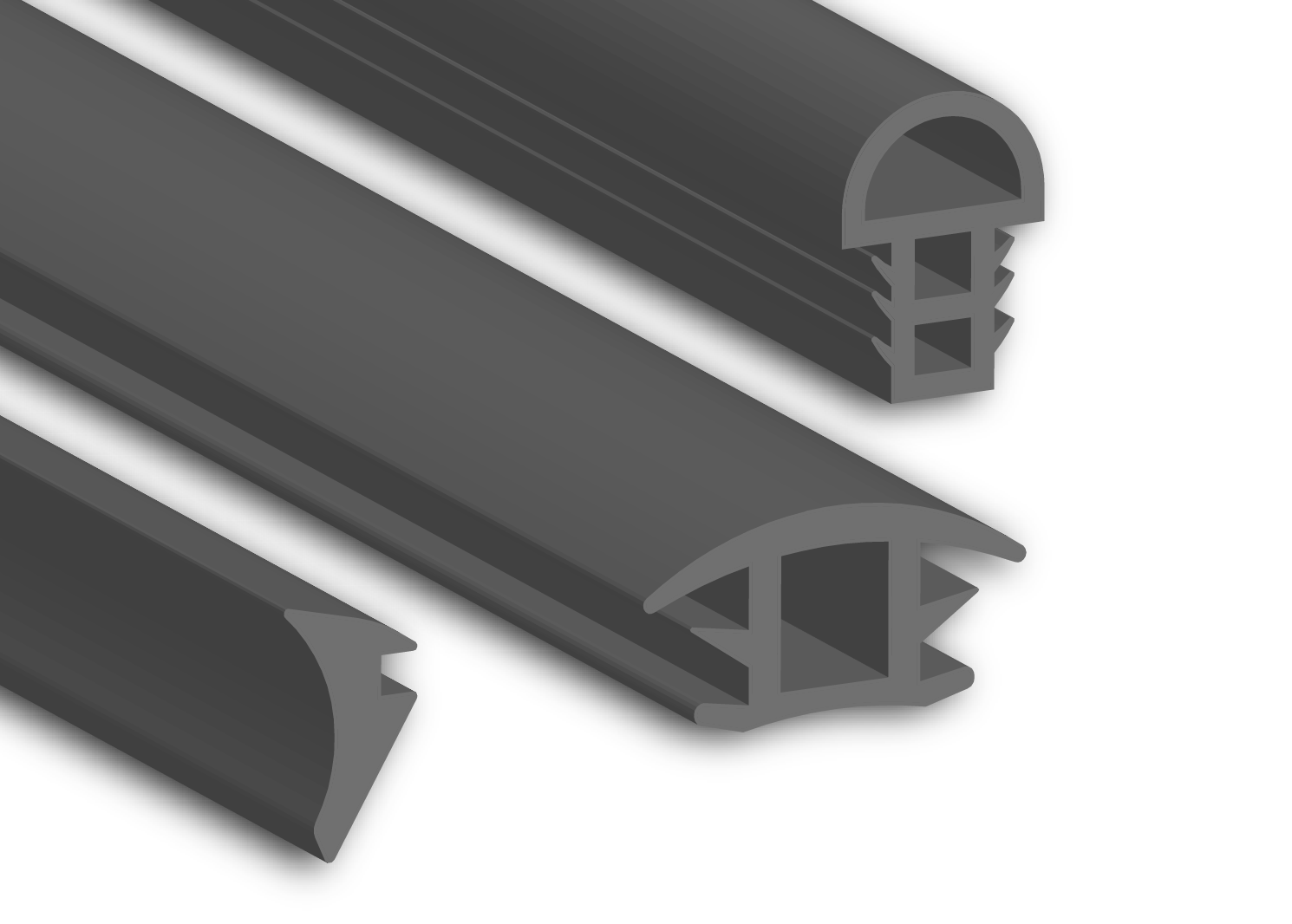
Material Specifications for Sliding Glass Door Trim Seals
Sliding glass door trim seals operate under demanding environmental and mechanical conditions, requiring precise material selection to ensure longevity, weather resistance, and consistent sealing performance. Key stressors include thermal cycling (-40°C to +150°C), UV exposure, ozone degradation, compression set under continuous load, and resistance to cleaning agents or incidental chemical contact. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we rigorously evaluate elastomers for dimensional stability, recovery force, and extrusion durability to prevent air/water infiltration and maintain OEM functional integrity. Below, we detail three primary materials engineered for this application: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ).
Viton fluorocarbon rubber offers superior resistance to extreme temperatures, ozone, and aggressive chemicals, including solvents and automotive fluids. Its molecular stability ensures minimal compression set (≤20% per ASTM D395) even after prolonged exposure to 200°C, making it ideal for high-end architectural applications in harsh climates. However, its high fluorine content increases material cost and reduces flexibility at sub-zero temperatures compared to alternatives. Nitrile butadiene rubber provides an optimal balance of oil/fuel resistance (critical for doors near garages or industrial zones) and cost efficiency. With acrylonitrile content tailored between 33-50%, NBR achieves tensile strengths of 15-25 MPa (ASTM D412) and operational ranges from -30°C to +120°C. Its vulnerability to ozone cracking necessitates protective additives for outdoor use. Silicone rubber excels in extreme temperature resilience (-60°C to +230°C) and UV stability, with low compression set (≤25%) ensuring long-term seal retention. While inherently ozone-resistant, its lower tensile strength (6-10 MPa) and susceptibility to tearing require reinforced formulations for high-traffic sliding mechanisms.
Critical performance metrics are summarized in the comparative table below, reflecting standardized test protocols per ISO 37 and ASTM specifications:
| Material | Key Chemical Composition | Temperature Range (°C) | Compression Set (%), 70h/150°C (ASTM D395) | Tensile Strength (MPa) (ASTM D412) | Critical Application Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | Fluorocarbon | -20 to +250 | ≤20 | 8-15 | Optimal for chemical-rich environments; higher cost; moderate low-temp flexibility |
| Nitrile (NBR) | Acrylonitrile-Butadiene | -30 to +120 | 25-35 | 15-25 | Cost-effective for urban/residential use; requires anti-ozonants for outdoor exposure |
| Silicone (VMQ) | Polysiloxane | -60 to +230 | ≤25 | 6-10 | Unmatched UV/heat resistance; prone to abrasion; requires tear-resistant additives |
Material selection must align with geographic and operational parameters. For coastal installations with high salt/ozone exposure, reinforced NBR with 45% acrylonitrile content provides economical durability. Viton is reserved for premium projects demanding chemical inertness, such as hospitality facilities with intensive cleaning protocols. Silicone suits extreme climates but mandates co-extruded fabric reinforcement to counteract tear vulnerability during door operation. Suzhou Baoshida prioritizes application-specific compound engineering, ensuring each trim seal meets OEM dimensional tolerances (±0.1mm) and 10-year service life expectations under ISO 1817 immersion testing. Partner with our technical team to validate material performance against your regional environmental stressors and lifecycle requirements.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision-Driven Development for Industrial Rubber Seals
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering capability forms the backbone of our industrial rubber solutions, particularly in the design and production of custom trims for sliding glass doors. With a dedicated team comprising five experienced mould engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, we deliver technically advanced, application-specific sealing systems that meet the rigorous demands of modern architectural and industrial applications.
Our mould engineers bring over a decade of cumulative experience in precision tooling design, utilizing advanced CAD/CAM software to develop high-tolerance moulds that ensure dimensional accuracy and consistent part geometry. Each mould is engineered to accommodate complex cross-sectional profiles commonly required in perimeter sealing for sliding glass assemblies, including dual-durometer configurations, bulb seals, and multi-ribbed designs. Finite element analysis (FEA) is routinely applied during the design phase to simulate material flow, optimize gate placement, and minimize defects such as flash or knit lines—ensuring rapid prototyping and first-time-right production.
Complementing our tooling expertise, our two in-house rubber formula engineers specialize in elastomer compounding tailored to performance requirements. For trims used in sliding glass door applications, this includes formulating EPDM and TPE compounds with enhanced UV resistance, low compression set, and stable mechanical properties across a wide temperature range (–40°C to +120°C). Custom additives are integrated to improve ozone resistance and surface finish, critical for both functional durability and aesthetic integration in architectural settings. Our formulation process is supported by an on-site laboratory equipped for tensile testing, hardness profiling, aging studies, and weathering simulations, enabling data-driven adjustments and full traceability.
We operate as a full-service OEM partner, offering end-to-end development from concept to mass production. Our clients benefit from integrated project management, where design, material selection, tooling, and process validation are aligned under one technical roof. This vertical integration reduces time-to-market and ensures consistency across batches, even for complex co-extruded or insert-moulded trim components.
The following table outlines key technical capabilities and material performance specifications relevant to our sliding glass door trim solutions:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Material Types | EPDM, TPE, Silicone (on request) |
| Durometer Range (Shore A) | 40–90 ±5 |
| Temperature Resistance | –40°C to +120°C (continuous) |
| Tensile Strength | ≥8 MPa (EPDM, ASTM D412) |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% |
| Compression Set (22h @ 100°C) | ≤25% |
| UV/Ozone Resistance | Excellent (ASTM D1149, ASTM D4797) |
| Mould Tolerance | ±0.1 mm (critical dimensions) |
| Production Process | Injection Moulding, Compression Moulding, Co-extrusion |
Through the synergy of advanced tooling design and scientific material engineering, Suzhou Baoshida delivers robust, high-performance rubber trims that exceed industry standards. Our OEM framework ensures complete confidentiality, scalability, and technical ownership for global partners seeking reliable, custom-engineered sealing solutions.
Customization Process
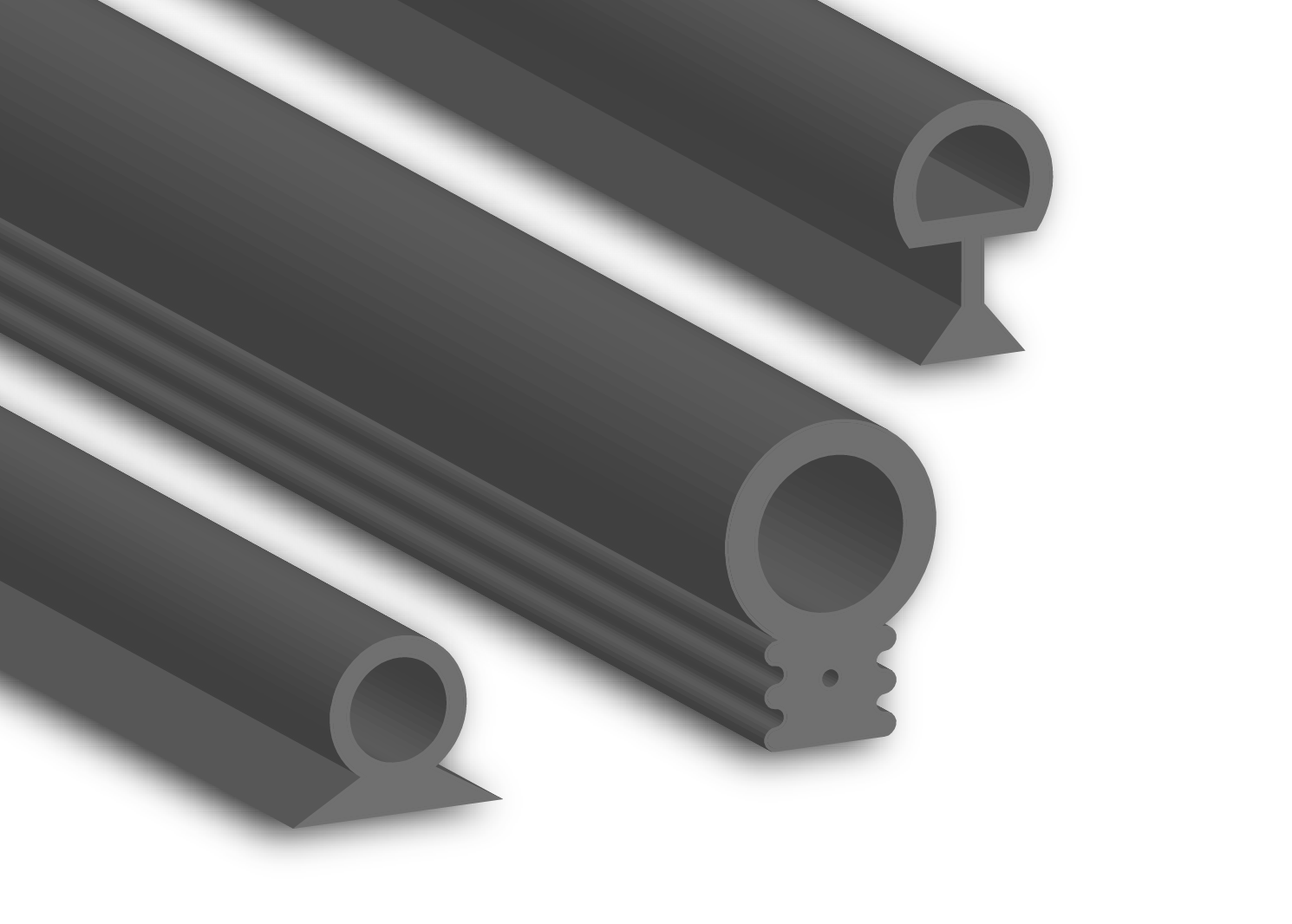
Customization Process for Sliding Glass Door Trim: Precision Engineering Pathway
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. executes a rigorously defined customization sequence for industrial rubber trim solutions, specifically engineered for sliding glass door applications. This systematic approach ensures dimensional accuracy, environmental resilience, and seamless integration with client assembly lines, directly addressing the demanding performance requirements of modern architectural hardware.
The process commences with Drawing Analysis. Our engineering team conducts a meticulous review of the client-supplied CAD drawings or technical specifications. Critical parameters scrutinized include cross-sectional geometry, dimensional tolerances (ISO 2768-mK standard minimum), installation groove compatibility, and dynamic movement requirements. We identify potential stress concentration points and assess material feasibility against specified operating temperatures (-40°C to +120°C typical range) and UV exposure levels. Any ambiguities or potential manufacturability conflicts are resolved collaboratively with the client’s design team prior to progression.
Formulation Development represents the core technical phase. Based on the validated drawing requirements and environmental factors, our rubber chemists select the optimal base polymer. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) is predominantly specified for its exceptional ozone, UV, and thermal stability essential for exterior door applications. The precise compound formulation is engineered, balancing critical properties: Shore A hardness for compression sealing force, tensile strength for installation durability, elongation for flexibility, and low-temperature flexibility. Key additives are incorporated to enhance weather resistance, reduce compression set, and ensure color stability. Material selection strictly adheres to relevant industry standards and client-specific regulatory mandates.
Prototyping & Validation follows formulation finalization. Short-run prototypes are manufactured using precision extrusion tooling, replicating the intended production process. These samples undergo comprehensive in-house testing per the parameters outlined in the specification table below. Crucially, physical prototypes are submitted to the client for real-world fitment trials within their door assembly system and environmental exposure testing. Client feedback on handling, installation force, and initial sealing performance is integrated, triggering iterative compound or profile adjustments if necessary. Only upon formal client sign-off does the project advance.
Mass Production initiates with full-scale tooling validation and process parameter optimization. Production runs are executed under stringent ISO 9001-controlled conditions, featuring real-time Statistical Process Control (SPC) monitoring of critical dimensions and physical properties. Each batch undergoes rigorous final inspection against the approved prototype and drawing specifications, with full material traceability maintained. Optimized cycle times and minimized scrap rates are achieved through our deep process expertise, ensuring cost-effective delivery of high-integrity trim components meeting the exacting demands of global door manufacturers.
Critical Performance Specifications for Sliding Door Trim
| Property | Target Range | Test Standard | Significance for Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | 65 – 75 | ASTM D2240 | Optimal balance of sealing force & flexibility |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥ 10.0 | ASTM D412 | Resistance to tearing during installation/use |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ≥ 150 | ASTM D412 | Accommodates door movement without fracture |
| Compression Set (B) | ≤ 25% (22h, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | Maintains sealing force over long-term use |
| Low Temp Flexibility | Pass (-50°C) | ISO 812 | Prevents cracking in freezing climates |
| Accelerated Weathering | ≥ 5000 hrs (QUV) | ASTM G154 | Ensures color stability & surface integrity |
Contact Engineering Team
For industrial manufacturers and OEM partners seeking high-performance rubber trim solutions for sliding glass door applications, Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. stands at the forefront of precision engineering and material innovation. Our expertise in industrial rubber formulations ensures that every trim component delivers optimal sealing, durability, and resistance to environmental stressors such as UV exposure, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical wear. As a trusted supplier in the global market, we specialize in custom extruded rubber profiles tailored to meet exact dimensional, durometer, and performance specifications.
Our rubber trims are engineered for seamless integration into sliding glass door systems used in commercial buildings, transportation, and high-end residential applications. Whether you require EPDM for superior weather resistance, silicone for extreme temperature stability, or TPE for enhanced flexibility and recyclability, our formulations are rigorously tested to ensure long-term performance. Each product is manufactured under strict quality control protocols, adhering to international standards for dimensional accuracy, compression set, and aging resistance.
To support our clients from concept to production, we offer comprehensive technical consultation, rapid prototyping, and scalable manufacturing solutions. Our team collaborates directly with engineers and design teams to optimize profile geometry, material selection, and installation methods—ensuring that the final product not only meets but exceeds functional and regulatory requirements.
Below are key technical specifications for our standard sliding door rubber trim offerings:
| Property | EPDM | Silicone | TPE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 50–80 | 40–80 | 60–90 |
| Temperature Range | -50°C to +135°C | -60°C to +200°C | -40°C to +120°C |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥8.0 | ≥6.5 | ≥10.0 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ≥300 | ≥250 | ≥400 |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ≤25% | ≤20% | ≤30% |
| UV and Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
| Color Options | Black, Gray, Custom | Any Color | Any Color |
| Standard Lengths | 1m, 2m, 5m, or Continuous Spool | 1m, 2m, 5m | 1m, 2m, 5m |
All profiles can be produced with adhesive backing, co-extruded stiffening inserts, or conductive fillers upon request. We also support custom tooling for unique cross-sectional designs and low-to-high volume production runs.
For technical inquiries, material samples, or to discuss a custom project, contact Mr. Boyce, Rubber Formula Engineer and OEM Manager, directly at [email protected]. Our team is prepared to provide engineering data sheets, compliance documentation, and on-time global logistics support. Partner with Suzhou Baoshida to integrate scientifically formulated rubber solutions into your next generation of sliding glass door systems. Your application demands precision—our formulations deliver it.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
