Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Flexible Plastic Edge Trim
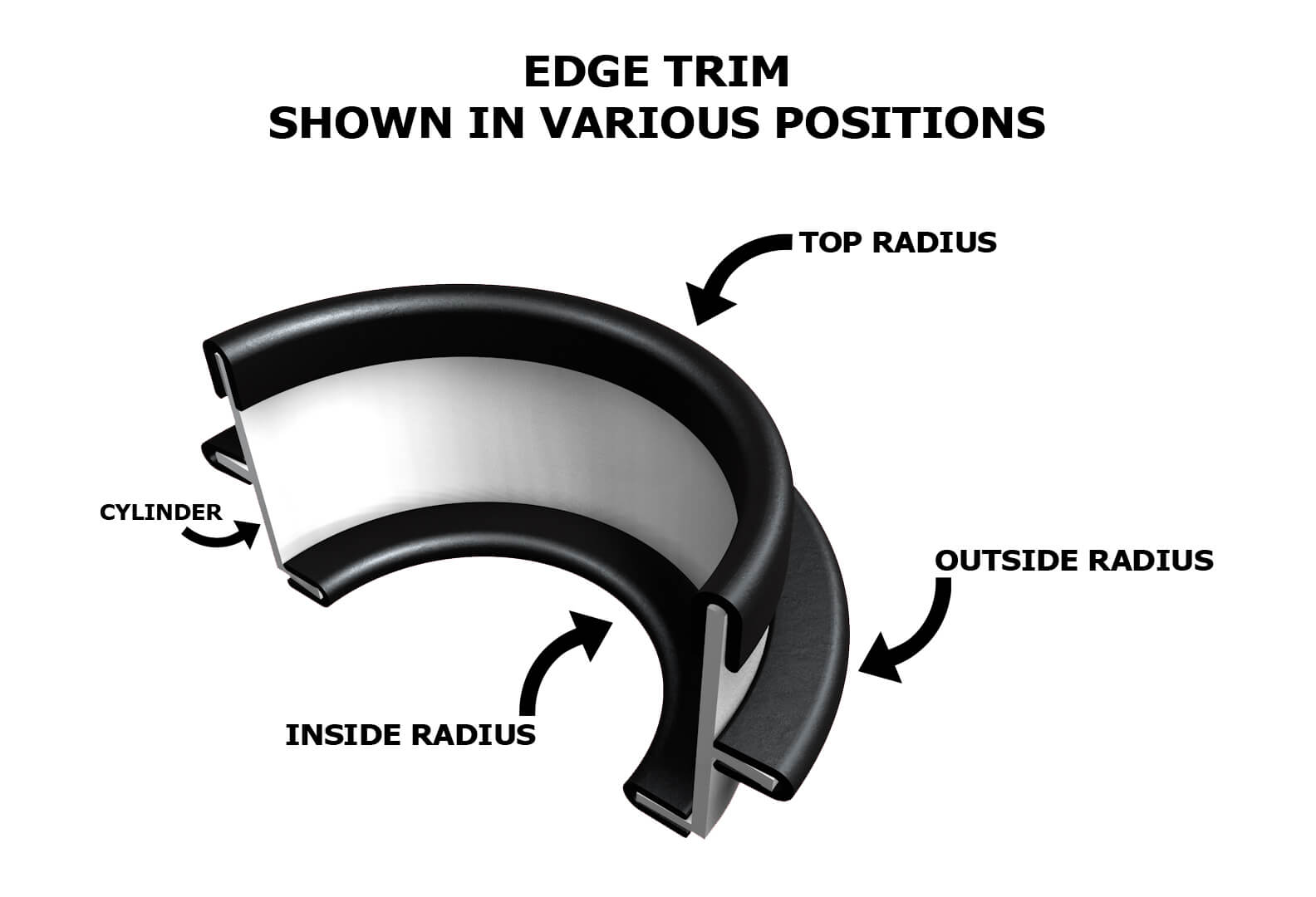
Engineering Insight: The Critical Role of Material Selection in Flexible Plastic Edge Trim
In industrial applications, flexible plastic edge trim serves as a vital component for edge protection, sealing, noise dampening, and aesthetic finishing. Despite its seemingly simple function, the performance and longevity of edge trim are directly tied to precise material selection. Off-the-shelf solutions, while cost-attractive initially, frequently fail under real-world operating conditions due to inadequate material compatibility, environmental exposure, or mechanical stress. This underscores the necessity for engineered material solutions tailored to the specific demands of the application.
Standard edge trims are typically manufactured using generic thermoplastics or elastomers such as low-grade PVC or unmodified TPEs. These materials often lack the resilience required for demanding environments involving temperature extremes, UV exposure, chemical contact, or continuous flexing. For instance, in automotive or rail transit applications, edge trims exposed to prolonged sunlight undergo photodegradation, leading to cracking and embrittlement. Similarly, industrial machinery housings using generic trims may experience premature failure when exposed to oils or cleaning solvents, resulting in swelling, deformation, or loss of sealing integrity.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our approach emphasizes material science-driven design. We evaluate the operational environment—thermal range, chemical exposure, mechanical loading, and regulatory requirements—to recommend or develop edge trims using high-performance polymers such as thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV), ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), or UV-stabilized TPU. These materials offer superior weather resistance, elasticity retention, and chemical inertness, ensuring functional reliability over extended service life.
Custom compounding allows for fine-tuning of hardness, tensile strength, and friction coefficient, enabling optimal performance in sealing, snap-fit retention, or abrasion resistance. For example, a TPV-based edge trim with 70 Shore A hardness demonstrates excellent balance between flexibility and structural integrity, making it ideal for dynamic sealing applications in outdoor enclosures.
Below is a comparative analysis of common flexible trim materials used in industrial applications:
| Material | Hardness (Shore A) | Temp Range (°C) | UV Resistance | Chemical Resistance | Typical Failure Mode in Off-the-Shelf Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard PVC | 60–80 | -10 to 60 | Low | Poor | Cracking, plasticizer leaching, discoloration |
| Unmodified TPE | 55–75 | -20 to 90 | Moderate | Moderate | Compression set, softening in oils |
| EPDM | 60–85 | -50 to 150 | High | Excellent | Rare (when properly formulated) |
| TPV | 50–80 | -40 to 135 | High | Good to Excellent | Minimal (highly durable in dynamic applications) |
| TPU | 70–95 | -30 to 100 | Moderate | Very Good | Hydrolysis in humid environments (unstabilized) |
The data illustrates why generic trims fail: they operate near or beyond their material limits under routine stress. In contrast, engineered solutions from Suzhou Baoshida are formulated to exceed application-specific thresholds, reducing downtime and lifecycle costs. Material selection is not a commodity decision—it is an engineering imperative.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Flexible Plastic Edge Trim
Selecting the optimal elastomer for flexible plastic edge trim requires precise evaluation of operational demands. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we engineer compounds to withstand mechanical stress, chemical exposure, and thermal cycling inherent in industrial assembly. Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ) represent three critical material families, each offering distinct performance profiles. Understanding their inherent properties ensures compatibility with automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery applications where edge trim seals, protects, and enhances structural integrity.
Viton fluorocarbon rubber delivers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, aggressive fuels, and hydraulic fluids. Its molecular stability maintains integrity between -20°C and +230°C continuous service, with short-term peaks to 300°C. Viton excels in aerospace fuel systems and engine compartments where exposure to aromatic hydrocarbons or chlorinated solvents would degrade lesser elastomers. However, its higher cost necessitates strategic application in critical sealing zones.
Nitrile butadiene rubber provides an optimal balance of oil resistance, abrasion tolerance, and cost efficiency for general industrial use. Operating effectively from -40°C to +120°C, NBR formulations withstand prolonged contact with petroleum derivatives, greases, and water-based fluids. Its robust tensile strength (15–25 MPa) and tear resistance make it ideal for automotive door seals, hydraulic equipment gaskets, and machinery edge protection where moderate thermal loads occur.
Silicone rubber dominates applications requiring extreme temperature flexibility and biocompatibility. With a service range spanning -60°C to +200°C, VMQ retains elasticity in cryogenic environments while resisting oxidation at elevated temperatures. Its inert composition meets FDA and USP Class VI standards, suiting medical device edge trim and food processing equipment. Limitations include lower tensile strength (5–10 MPa) and susceptibility to concentrated acids, necessitating careful chemical compatibility review.
The comparative specifications below outline critical parameters for informed material selection. All values reflect standard ASTM D2000 classification for M3BG material types, with hardness measured in Shore A scale.
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Key Resistance Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | -20 to +230 | 12–18 | 150–250 | 60–90 | Fuels, oils, acids, ozone, steam |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -40 to +120 | 15–25 | 200–400 | 50–90 | Petroleum oils, aliphatic hydrocarbons, water, abrasion |
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 to +200 | 5–10 | 200–600 | 30–80 | Extreme temperatures, ozone, UV, water, steam, biological fluids |
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages proprietary compounding techniques to enhance base polymer performance. Our OEM team tailors filler systems, cure chemistry, and additive packages to address specific edge trim challenges—including dynamic flex fatigue, compression set, and adhesion to thermoplastic substrates. Material validation follows ISO 37 tensile testing and ASTM D471 fluid immersion protocols, ensuring compliance with global automotive OEM specifications. For mission-critical applications, we recommend accelerated aging studies to confirm long-term dimensional stability under end-use conditions.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision-Driven Development for Flexible Plastic Edge Trim
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering capability forms the backbone of our industrial rubber solutions, particularly in the design and production of high-performance flexible plastic edge trim. With a dedicated team of five certified mould engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, we deliver technically advanced, application-specific products tailored to the rigorous demands of global OEMs. Our integrated engineering approach ensures seamless development from concept to mass production, with full control over material formulation, tooling design, and process optimization.
Our mould engineers bring over 60 combined years of experience in precision tooling for extrusion and injection applications. They utilize advanced CAD/CAM software, including SolidWorks and AutoCAD, to develop robust, high-tolerance moulds that support complex geometries and tight dimensional specifications. Finite element analysis (FEA) is routinely applied to simulate flow dynamics, thermal distribution, and stress points, ensuring optimal performance during high-volume manufacturing. This proactive design validation reduces time-to-market and minimizes production risks.
Complementing our tooling expertise, our two in-house rubber formula engineers specialize in polymer science and elastomer compounding. They formulate custom rubber blends that precisely match the mechanical, thermal, and environmental requirements of each edge trim application. Whether resistance to UV degradation, extreme temperatures (-40°C to +120°C), or compliance with RoHS and REACH standards is required, our formulations are engineered for long-term durability and regulatory compliance. This vertical integration of material science and mechanical design allows us to solve complex engineering challenges that generic suppliers cannot address.
As an OEM partner, we offer full turnkey solutions—from prototype development and DFM (Design for Manufacturability) feedback to serial production and quality assurance. Our clients benefit from IP-protected designs, batch traceability, and rigorous in-process testing using calibrated metrology equipment. We support low-volume custom runs as well as high-volume contracts with automated production lines, ensuring scalability without compromise on consistency.
The following table outlines key engineering specifications and capabilities relevant to our flexible plastic edge trim production:
| Parameter | Capability Range |
|---|---|
| Material Types | TPE, PVC, EPDM, Silicone, NBR, CR |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 40–90 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +120°C (up to +180°C for silicone) |
| Tensile Strength | 6–18 MPa (material-dependent) |
| Elongation at Break | 200–800% |
| Mould Tolerance | ±0.1 mm |
| Production Lead Time (Mould) | 15–25 days (depending on complexity) |
| OEM Design Support | Full CAD/FEA, DFM, sample validation |
| Compliance Standards | RoHS, REACH, FDA (on request), UL (on request) |
Our engineering team operates under a continuous improvement framework, leveraging real-time production data and customer feedback to refine both product performance and manufacturing efficiency. This scientific, data-driven methodology ensures that every flexible plastic edge trim we produce meets the highest standards of industrial reliability and functional precision.
Customization Process

Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. Technical Guide: Flexible Plastic Edge Trim Customization Process
The customization process for industrial flexible plastic edge trim at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. adheres to a rigorous, four-stage methodology ensuring precise alignment with client specifications and operational demands. This structured approach minimizes iteration cycles while guaranteeing material integrity and functional reliability in end-use applications.
Drawing Analysis
Initial engagement commences with comprehensive technical drawing review. Our engineering team validates dimensional tolerances, critical radius specifications, and interface requirements against ISO 3302-1 and ISO 2768-mK standards. Part geometry, stress concentration zones, and assembly constraints are evaluated to identify potential molding challenges. Material compatibility with adjacent substrates (e.g., metals, composites) is assessed, alongside environmental exposure factors such as UV, ozone, or chemical contact. This phase culminates in a formal tolerance conformance report, highlighting deviations requiring client consultation prior to formulation.
Formulation Development
Based on drawing analysis outcomes, our rubber compounding specialists design a proprietary elastomer blend. Key parameters include Shore A hardness (typically 40–90), elongation at break (>300%), and compression set resistance (<25% per ASTM D395). Plasticizer selection is optimized for low-temperature flexibility (down to -40°C) and long-term migration resistance. Flame retardancy (UL94 HB/V-0), color stability (Pantone matching), and surface finish (gloss/matte) are integrated per application needs. All formulations undergo accelerated aging simulations and regulatory screening (REACH, RoHS) before prototyping.
Prototyping & Validation
Precision injection-molded prototypes are produced using client-approved tool steel cavities. Each sample undergoes mechanical validation: tensile strength (ASTM D412), tear resistance (ASTM D624), and dynamic flex testing (10,000+ cycles). Dimensional accuracy is verified via CMM against original CAD data, with critical features held to ±0.15mm tolerance. Client feedback on fit, aesthetics, and functional performance triggers iterative refinements. Final sign-off requires documented conformance to all performance criteria and assembly line compatibility.
Mass Production Execution
Upon prototype approval, production transitions to our ISO 9001-certified facility. Statistical Process Control (SPC) monitors key variables: melt temperature consistency (±2°C), injection pressure stability, and cure time accuracy. Every production batch undergoes first-article inspection and in-process sampling for hardness, density, and visual defects. Finished rolls are serialized, vacuum-sealed, and palletized per logistics specifications. Full traceability—from raw material lot numbers to operator IDs—is maintained via our ERP system, ensuring seamless quality audits and rapid root-cause analysis if required.
Critical material specifications for flexible edge trim are summarized below:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Customization Capability | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | 40–90 | ±5 points precision | ASTM D2240 |
| Temperature Resistance | -40°C to +120°C | Up to +150°C (specialty) | ISO 188 |
| Elongation at Break | 300%–600% | Application-specific | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set | <25% (70°C, 22h) | <15% achievable | ASTM D395 Method B |
| Color Options | Pantone RAL standard | Custom matching (ΔE<1.0) | ISO 11664-4 |
| Customization Lead Time | 4–6 weeks | Expedited options | N/A |
This end-to-end process guarantees that Suzhou Baoshida delivers edge trim solutions engineered for dimensional precision, environmental resilience, and seamless integration into client assembly lines—reducing total cost of ownership through minimized scrap and field failures.
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Premium Flexible Plastic Edge Trim Solutions
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in delivering high-performance industrial rubber and polymer components tailored to the rigorous demands of modern manufacturing. As a trusted OEM partner in the field of flexible plastic edge trim production, we combine advanced material science with precision extrusion technologies to serve industries ranging from automotive and construction to consumer electronics and industrial equipment. Our engineering team is dedicated to developing edge protection solutions that offer superior durability, weather resistance, and aesthetic consistency across diverse operating environments.
Flexible plastic edge trim is more than a cosmetic component—it plays a critical role in impact absorption, edge reinforcement, noise reduction, and user safety. Whether you require trims for panel enclosures, door frames, display units, or machinery guards, our formulations are engineered to meet exact mechanical and environmental specifications. We utilize thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and modified ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) compounds, each selected for optimal flexibility, UV stability, and adhesion properties. Our extrusion and co-extrusion capabilities allow for multi-durometer profiles, integrated sealing lips, and custom color matching to align with your brand or functional requirements.
To ensure seamless integration into your production line, we offer comprehensive technical support—from initial profile design and tooling development to batch validation and long-term supply chain management. Our quality control protocols follow ISO 9001 standards, with in-house testing for tensile strength, elongation, compression set, and resistance to ozone, oil, and temperature extremes.
For OEM clients seeking a reliable, scalable source of high-integrity edge trim solutions, direct engagement with our technical team is the next step toward optimized performance and cost efficiency.
The following table outlines typical material specifications available for flexible plastic edge trim:
| Property | TPE | PVC | EVA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–95 | 70–90 | 40–80 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 8–15 | 10–18 | 5–12 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 400–700 | 250–400 | 400–600 |
| Operating Temperature Range (°C) | -40 to +120 | -20 to +80 | -30 to +90 |
| UV Resistance | Excellent | Good | Moderate |
| Flame Rating | UL94 HB/V-2 | UL94 V-2 | UL94 HB |
All materials are RoHS and REACH compliant, and custom formulations can be developed to meet specific flame, smoke, toxicity (FST), or food-contact requirements.
To discuss your flexible plastic edge trim needs, contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Account Manager at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. He will coordinate technical evaluation, sample provision, and volume production planning tailored to your project timeline. Reach Mr. Boyce directly via email at [email protected] for prompt, professional support. Partner with us to ensure your edge protection components meet the highest standards in performance, consistency, and industrial reliability.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
