Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Sponge Protector
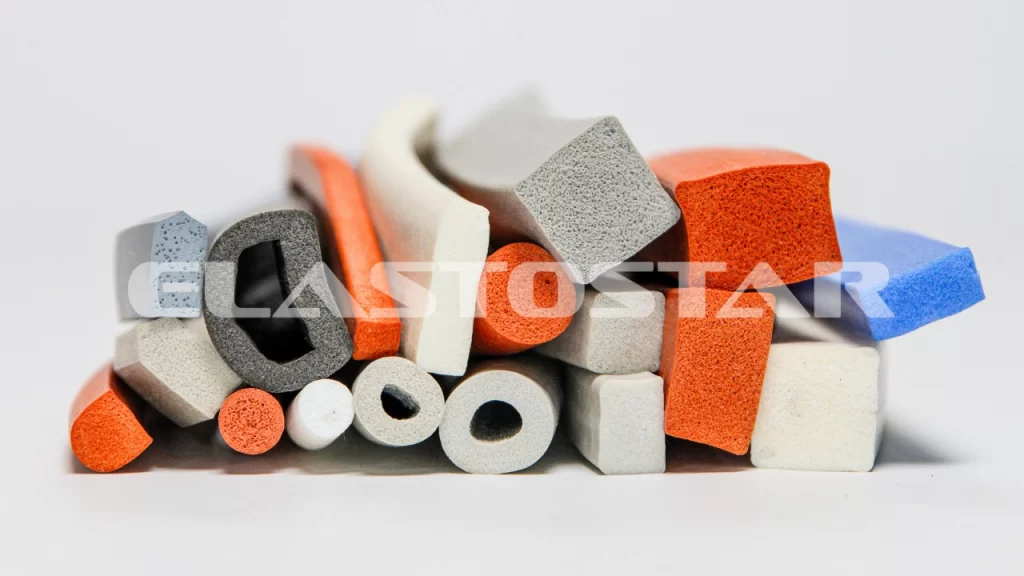

Engineering Insight: Material Selection Criticality in Industrial Sponge Protectors
Sponge protectors, specifically engineered cellular rubber components, serve as vital barriers against environmental ingress, vibration damping, and sealing in demanding industrial applications. Their performance is not inherent to the “sponge” form alone but is critically dependent on the precise elastomeric compound formulation. Off-the-shelf solutions frequently fail because they utilize generic, cost-optimized materials lacking the tailored polymer chemistry required for specific operational stresses. Standard commercial foams prioritize initial cost and basic cushioning, neglecting the complex interplay of compression set resistance, chemical compatibility, and thermal stability essential for long-term industrial reliability. This oversight leads to premature degradation, compromising system integrity and incurring significant downstream costs from leaks, contamination, or equipment failure.
The core failure mechanism in generic sponge protectors is excessive compression set. Under sustained load or elevated temperatures, poorly formulated compounds permanently deform, losing their ability to rebound and maintain a seal. This is particularly critical in dynamic applications like automotive door seals or HVAC flanges where cyclic compression occurs. Furthermore, inadequate resistance to oils, solvents, ozone, or UV exposure causes surface cracking, hardening, or dissolution – vulnerabilities absent in compounds designed with specific additive packages and saturated polymer backbones. Temperature extremes also expose material limitations; many standard foams become brittle below -20°C or soften excessively above 70°C, rendering them ineffective outside narrow ambient ranges. Suzhou Baoshida addresses these failure modes through rigorous material science, selecting base polymers (EPDM, NBR, silicone, or specialty blends) and compounding with precision-engineered fillers, curatives, and stabilizers validated against the exact application profile.
Material selection directly dictates the protector’s functional lifespan and total cost of ownership. Investing in a compound engineered for the specific environmental and mechanical demands prevents costly field failures, unplanned downtime, and warranty claims. Below is a comparison highlighting the critical performance gap between generic market offerings and Suzhou Baoshida’s engineered solutions:
| Critical Property | OEM-Grade Specification (Suzhou Baoshida Standard) | Generic Market Average | Primary Failure Consequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (ASTM D395, 22h/70°C) | ≤ 20% | 35% – 45%+ | Permanent seal loss, leakage paths |
| Operating Temperature Range | -50°C to +150°C (Polymer Dependent) | -20°C to +80°C | Brittleness at low T, creep at high T |
| Resistance to Hydraulic Oils (ASTM D471) | Volume Swell ≤ 15% | Volume Swell 25% – 40% | Seal extrusion, loss of mechanical strength |
| Ozone Resistance (ASTM D1149) | No Cracks @ 50 pphm, 40°C, 20% Strain, 96h | Severe Cracking | Surface degradation, premature failure |
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. rejects the “one-size-fits-all” approach. Our engineering process begins with a detailed analysis of the operational environment – fluid exposure, temperature cycles, compression load, and required service life. We then formulate custom cellular rubber compounds, leveraging advanced polymer science and stringent in-house testing protocols (ASTM, ISO, OEM-specific) to ensure the sponge protector performs reliably throughout its intended lifecycle. Material selection is not a cost line item; it is the foundational engineering decision determining system resilience. Partnering with a specialist focused on elastomeric compound performance, rather than merely foam geometry, is imperative for eliminating preventable failures in critical industrial sealing applications.
Material Specifications
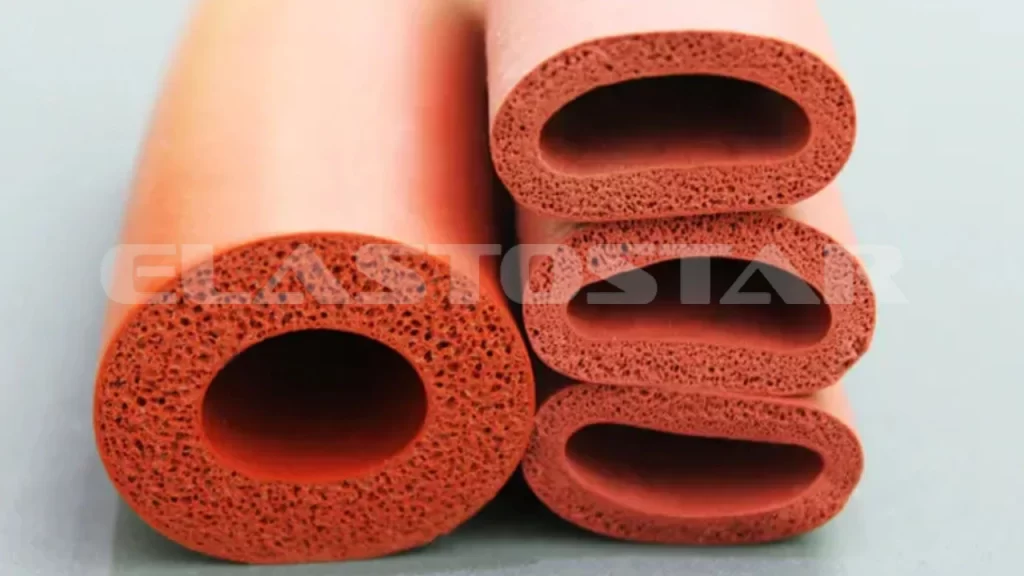

The selection of appropriate elastomeric materials for sponge protector applications in industrial environments requires a comprehensive understanding of chemical resistance, temperature stability, mechanical performance, and long-term durability. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-performance rubber solutions tailored to meet rigorous OEM standards. Our sponge protectors are engineered using three primary elastomers: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each material offers distinct advantages depending on operational conditions, ensuring optimal sealing, cushioning, and environmental protection.
Viton sponge rubber is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of aggressive chemicals. With continuous service capabilities up to 230°C and intermittent exposure tolerance exceeding 260°C, Viton is ideal for aerospace, automotive, and oil & gas applications where thermal degradation is a critical concern. Its low gas permeability and outstanding aging characteristics further enhance reliability in demanding sealing environments. However, Viton exhibits lower flexibility at sub-zero temperatures and higher material cost compared to alternatives.
Nitrile sponge rubber offers a balanced performance profile with superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, hydraulic fluids, and aliphatic hydrocarbons. It maintains good mechanical strength and compression set resistance across a service range of -30°C to 120°C, making it a cost-effective choice for industrial machinery, automotive gaskets, and fluid-handling systems. While Nitrile is less resistant to ozone, UV radiation, and polar solvents than Viton or Silicone, its compatibility with common industrial fluids and ease of fabrication make it a widely adopted solution.
Silicone sponge rubber excels in extreme temperature applications, functioning reliably from -60°C to 200°C, with short-term exposure up to 230°C. It demonstrates excellent resistance to ozone, UV light, and weathering, making it ideal for outdoor enclosures, electrical insulation, and food-grade environments. Silicone also offers high purity and low toxicity, meeting FDA and USP Class VI requirements. However, it has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Nitrile and Viton, necessitating careful design considerations in high-stress applications.
The following table summarizes key material properties to guide selection for sponge protector applications:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Moderate to Good |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 8–12 | 10–18 | 5–9 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–250 | 200–400 | 200–350 |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 40–90 | 40–80 | 30–80 |
| FDA Compliant Grades Available | Yes | Limited | Yes |
Material selection must align with application-specific stressors including fluid exposure, thermal cycling, mechanical load, and regulatory requirements. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides customized formulation and manufacturing services to ensure optimal performance across diverse industrial sectors.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision Development for Industrial Sponge Protectors
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages integrated material science and precision tooling expertise to deliver mission-critical sponge protector solutions for demanding industrial applications. Our dedicated engineering cohort comprises five specialized mold engineers and two advanced rubber formula engineers, operating under a unified development protocol. This dual-discipline structure ensures seamless alignment between compound performance and geometric integrity from initial concept to量产 validation.
Our formula engineers focus on optimizing elastomer matrix properties for sponge protectors, tailoring cellular structure density, rebound resilience, and chemical resistance to client-specific operational environments. Utilizing proprietary vulcanization kinetics modeling, we achieve precise control over cross-link density and closed-cell morphology, directly influencing compression set performance and service longevity. Concurrently, our mold engineering team employs 3D flow simulation and thermal gradient analysis to design tooling that eliminates knit lines, ensures uniform cell distribution, and maintains dimensional tolerances within ±0.15 mm. This cross-functional collaboration eliminates traditional handoff inefficiencies, reducing prototyping cycles by 40% compared to industry benchmarks.
OEM partnerships benefit from our closed-loop development system, where material formulations are validated against mold dynamics in virtual environments prior to physical tooling. Clients provide functional requirements—such as dynamic sealing pressures, fluid exposure profiles, or thermal cycling ranges—and our team reverse-engineers the optimal compound architecture and mold topology. All sponge protectors undergo rigorous in-house validation per ASTM D395 (compression set), ISO 188 (heat aging), and ISO 815 (low-temperature flexibility), with full traceability from raw material lot to finished part certification.
Critical performance specifications for our standard industrial sponge protectors are summarized below:
| Property | Test Standard | Typical Range | Industrial Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | ASTM D3574 | 0.25–0.65 g/cm³ | Weight-sensitive sealing applications |
| Hardness (Shore 00) | ASTM D2240 | 15–45 | Balance of conformability and recovery |
| Compression Set (22h/70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% | Long-term sealing force retention |
| Temperature Range | ISO 188 | -40°C to +120°C | Automotive/industrial fluid exposure |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | 0.8–2.5 MPa | Durability during installation |
This technical foundation enables Suzhou Baoshida to execute complex OEM projects with zero tooling rework in 92% of engagements. Our engineers co-develop failure-mode analyses with clients during the FMEA phase, embedding reliability into the material and mold design rather than relying on post-production corrections. For applications requiring extreme fluid resistance or flame retardancy, we formulate custom EPDM, silicone, or chloroprene-based sponge systems with accelerated aging validation data provided within 15 business days. Partnering with us guarantees sponge protectors engineered not merely to specification sheets, but to the unspoken demands of real-world machinery fatigue and environmental stressors.
Customization Process
Customization Process for Sponge Protectors at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our sponge protector customization process is engineered for precision, durability, and performance consistency across industrial applications. We follow a structured four-stage workflow—Drawing Analysis, Formulation, Prototyping, and Mass Production—ensuring that every sponge protector meets the exact mechanical, environmental, and dimensional requirements of our clients.
The process begins with Drawing Analysis, where our rubber formula engineers evaluate technical schematics provided by the client. This includes assessing critical dimensions, tolerance ranges, sealing interfaces, and installation conditions. We verify compliance with international standards such as ISO 2768 for general tolerances and ISO 3302 for rubber dimensional accuracy. Special attention is given to compression set requirements, load-bearing zones, and environmental exposure zones (e.g., UV, ozone, temperature extremes). Any ambiguities or design risks are flagged early through formal engineering feedback.
Next, our team initiates Formulation Development, selecting the optimal elastomer base based on application demands. Our primary compounds include EPDM for weather resistance, NBR for oil and fuel exposure, and silicone for extreme temperature ranges. Additives such as blowing agents, cross-linking accelerators, and reinforcing fillers are precisely balanced to achieve target hardness (typically 20–60 Shore A), cell structure uniformity, and compression deflection characteristics. The formulation is validated through rheometric testing (ASTM D5289) and thermal stability analysis (TGA/DSC).
Once the compound is finalized, we proceed to Prototyping. Using CNC-machined molds or die-cutting tools, we produce small-batch samples for functional evaluation. Prototypes undergo rigorous in-house testing, including compression set (ASTM D395), tensile strength (ASTM D412), and aging resistance (ASTM D573). Clients receive physical samples along with material test reports for approval. Iterations are conducted if performance deviations are identified, ensuring design and material alignment before scale-up.
Upon prototype validation, the project transitions into Mass Production. We deploy automated sponge vulcanization lines with continuous monitoring of temperature, pressure, and curing time. Each batch is subject to statistical process control (SPC) and first-article inspection. Final products are packaged per client specifications, with traceability maintained through batch coding and QC documentation.
Our end-to-end process ensures sponge protectors deliver consistent sealing, cushioning, and environmental protection in demanding industrial environments.
| Property | Test Standard | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 20–60 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | 2.5–6.0 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | 150–300% |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤30% |
| Operating Temperature | — | -40°C to +150°C (varies by compound) |
| Cell Density | Internal Method | 0.35–0.55 g/cm³ |
Contact Engineering Team

Technical Specifications and Engineering Support for Industrial Sponge Protectors
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered sponge rubber solutions designed for critical sealing, cushioning, and environmental protection in demanding industrial applications. Our sponge protectors mitigate failure risks in automotive, aerospace, construction, and heavy machinery sectors by addressing compression set, thermal degradation, and chemical exposure. Precision compounding ensures consistent cellular structure integrity, directly impacting service life and operational reliability. Below are core technical parameters for standard formulations, all validated per ASTM D2000 and ISO 188 testing protocols.
| Material Type | Density Range (kg/m³) | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | 80–150 | 20–60 | -50 to +150 | Ozone/weather resistance, low compression set |
| NBR | 100–180 | 30–70 | -40 to +120 | Fuel/oil resistance, high resilience |
| Silicone | 70–120 | 15–50 | -60 to +230 | Extreme temp stability, FDA-compliant options |
These specifications reflect baseline performance; Suzhou Baoshida specializes in OEM-driven customization. Our formula engineering team modifies cell morphology, additive packages, and polymer blends to meet exact application stressors—such as dynamic load cycling in hydraulic systems or UV exposure in outdoor enclosures. For instance, aerospace clients require sponge protectors with ≤8% compression set after 70 hours at 150°C, achieved through peroxide-cured EPDM with nano-reinforced fillers. Similarly, automotive battery sealing demands flame-retardant NBR variants with UL 94 V-0 certification.
As your OEM manufacturing partner, we integrate technical collaboration from prototype to volume production. Initial engagement includes material compatibility testing against customer-specified fluids, thermal profiling via DMA analysis, and dimensional tolerance validation using CMM equipment. This eliminates field failures caused by unverified material substitutions. Our Suzhou facility operates under IATF 16949 quality management, with batch traceability to raw material lot codes and real-time process monitoring during continuous vulcanization.
Industrial buyers face escalating pressure to reduce downtime and warranty costs. Generic sponge products often lack the accelerated aging data or formulation transparency needed for mission-critical applications. Suzhou Baoshida provides full material disclosure reports, including DSC thermograms and compression force-deflection curves, ensuring your engineering team can validate performance against design specifications.
To initiate a technical consultation for your sponge protector requirements, contact Mr. Boyce directly. With 12 years of compound development experience in closed-cell elastomers, he will coordinate application analysis, sample provisioning, and feasibility assessment within 48 hours. Provide your sealing challenge parameters—such as media exposure, load duration, and environmental conditions—and receive a tailored solution proposal with accelerated lifecycle projections.
Mr. Boyce
Rubber Formula Engineer & OEM Manager
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
Email: [email protected]
Response Time: Within 2 business hours for technical inquiries
Partner with Suzhou Baoshida to convert sealing vulnerabilities into engineered reliability. Our data-driven approach transforms sponge protector performance from a cost factor into a strategic asset for your manufacturing resilience.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
