Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Freezer Door Plastic
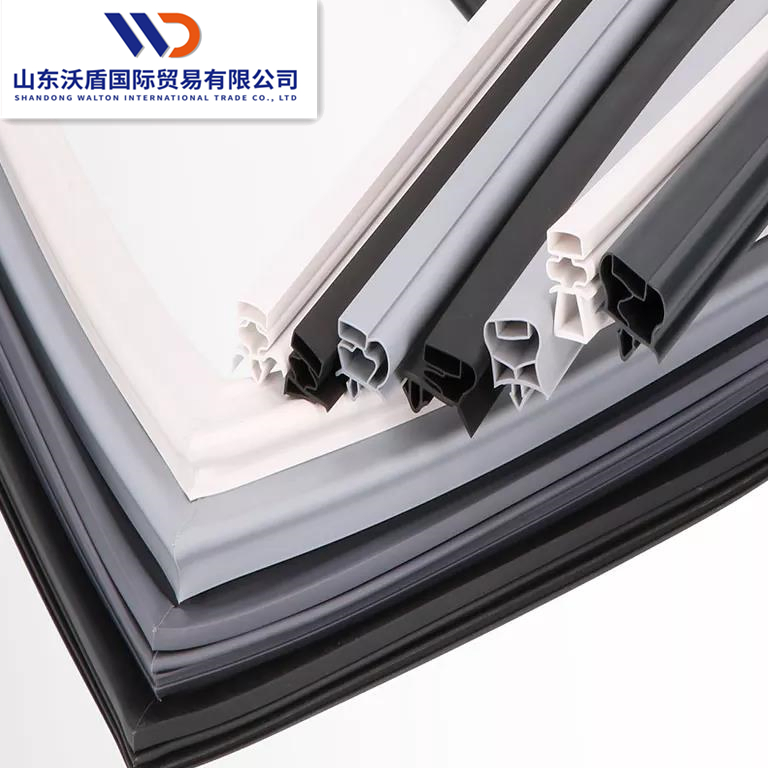
Engineering Insight: Material Selection for Freezer Door Plastic Seals
In the design and manufacturing of freezer door seals, material selection is not merely a component of the process—it is the foundation of performance, durability, and energy efficiency. Freezer environments subject sealing materials to extreme thermal cycling, constant compression, and prolonged exposure to moisture and cleaning agents. Off-the-shelf plastic or generic elastomeric seals often fail prematurely under these conditions, leading to air leakage, increased energy consumption, frost buildup, and compromised product integrity. These failures stem from inadequate material formulation and a lack of application-specific engineering.
Standard thermoplastics such as PVC or low-grade TPEs may appear cost-effective initially but lack the necessary resilience for sustained sub-zero operation. At temperatures below -30°C, many conventional plastics undergo glass transition, becoming brittle and losing elasticity. This results in cracking, compression set, and seal failure. Furthermore, repeated door cycling accelerates wear in materials not engineered for dynamic performance, compromising the integrity of the cold chain.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in advanced rubber formulations tailored for extreme cold environments. Our engineered solutions leverage high-performance elastomers such as EPDM, silicone, and specialty nitrile (NBR) compounds, each selected and modified to meet the exact thermal, mechanical, and chemical demands of freezer applications. These materials maintain flexibility at ultra-low temperatures, resist microbial growth, and exhibit superior compression recovery—critical factors in maintaining a consistent seal over thousands of door cycles.
A key differentiator lies in compound customization. Generic seals use standardized formulations optimized for broad markets, not specific operational conditions. In contrast, our approach integrates OEM requirements—such as door weight, closure force, ambient humidity, and cleaning protocols—into the material design phase. This ensures optimal durometer, tensile strength, and low-temperature flexibility tailored to the application.
The following table outlines comparative performance characteristics of common freezer door seal materials:
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Compression Set (22 hrs, 70°C) | Hardness (Shore A) | Key Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | -50 to +150 | ≤ 25% | 60–75 | Excellent low-temp flexibility, ozone resistance | Poor oil resistance |
| Silicone | -60 to +200 | ≤ 20% | 40–80 | Ultra-low temp performance, food-safe | Lower tensile strength |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -30 to +100 | ≤ 30% | 55–70 | Good abrasion resistance, moderate cold flexibility | Limited below -30°C |
| PVC | -10 to +60 | ≤ 40% | 70–90 | Low cost, rigid | Brittle at low temps, poor recovery |
As demonstrated, material behavior diverges significantly under operational stress. Relying on off-the-shelf solutions risks system-level inefficiencies that outweigh initial savings. At Baoshida, we advocate for engineered material selection as a strategic imperative—ensuring reliability, compliance, and long-term cost savings in industrial refrigeration systems.
Material Specifications
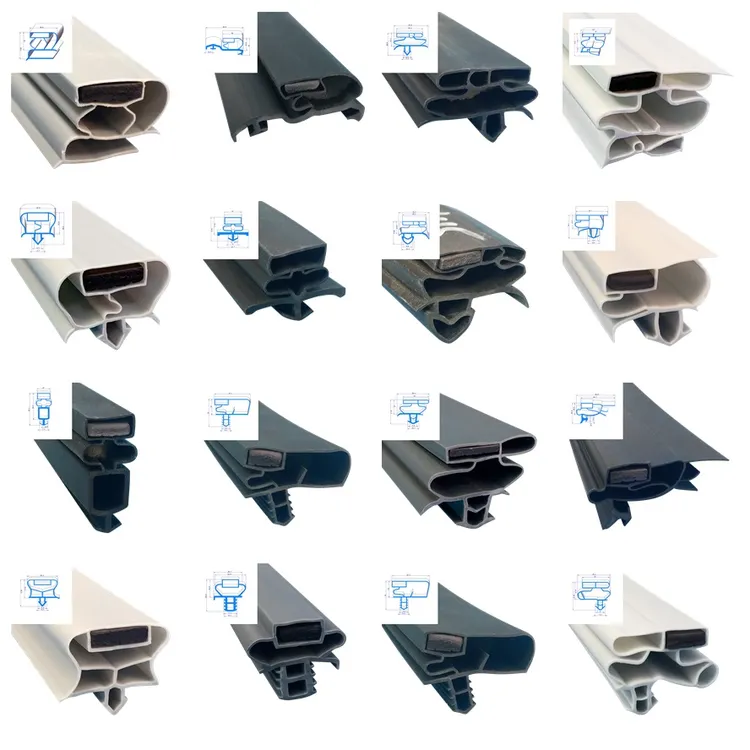

Material Specifications for Freezer Door Elastomeric Seals
Selecting the optimal elastomer for freezer door sealing profiles demands rigorous evaluation of low-temperature resilience, compression set resistance, and mechanical durability. Freezer environments impose extreme thermal cycling down to -40°C, coupled with constant flex fatigue from door operation. Material failure manifests as hardening, cracking, or permanent set, directly compromising thermal efficiency and energy compliance. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we validate all formulations against ASTM D2000 and ISO 3384 standards under simulated operational stress. Three polymers dominate this application: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ), each exhibiting distinct performance boundaries.
Viton fluorocarbon elastomers deliver unparalleled stability in ultra-low-temperature freezers (-50°C continuous exposure). Their saturated backbone resists chain scission below -40°C, maintaining flexibility where hydrocarbon rubbers embrittle. Critical for pharmaceutical or cryogenic storage, Viton seals exhibit compression set values below 20% after 72 hours at -40°C (ASTM D395 Method B). However, raw material costs are 3-4x higher than alternatives, necessitating justification for non-critical applications. Nitrile rubber (NBR) remains the cost-optimized solution for commercial freezers operating above -30°C. High-acrylonitrile grades (45% ACN) balance oil resistance and low-temperature performance, with glass transition temperatures (Tg) reaching -35°C. Its compression set typically ranges 25-30% at -30°C, acceptable for retail or warehouse environments where door cycling frequency is moderate. Silicone (VMQ) offers the broadest operational range (-60°C to +200°C) and exceptional flexibility at temperature extremes. Its low Tg (-120°C) prevents stiffening, but tensile strength degrades significantly below -40°C. Silicone’s 15-20% compression set at -40°C suits intermittent-use freezers, though its lower abrasion resistance requires protective design features in high-traffic installations.
Our engineering validation confirms no universal solution exists; material selection hinges on the freezer’s operational class, regulatory requirements (FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 for food contact), and lifecycle cost analysis. The comparative performance data below guides evidence-based specification.
| Material | Continuous Temp Range (°C) | Compression Set @ -40°C (72h, %) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | -50 to +200 | <20 | 12-18 | Ultra-low temp freezers (-40°C), pharmaceutical storage, military cold chain |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -30 to +100 | 25-30 | 15-22 | Commercial freezers (-25°C), refrigerated transport, retail display cases |
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 to +200 | 15-20 | 6-10 | Laboratory freezers, medical sample storage, intermittent-use environments |
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides OEMs with accelerated aging data and finite element analysis (FEA) modeling to predict seal performance over 100,000+ door cycles. Partnering early in the design phase ensures material properties align with thermal dynamics and mechanical loading profiles, eliminating costly field failures. Precision compounding for freezer applications requires balancing compound cost against the total cost of ownership—where premature seal degradation incurs exponentially higher energy and maintenance expenses than initial material investment.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. maintains a highly specialized engineering team dedicated to the development and production of advanced rubber components, including precision-engineered seals for freezer door applications. Our technical capabilities are anchored by a team of five dedicated mould engineers and two certified rubber formulation engineers, enabling us to deliver fully integrated OEM solutions from concept to mass production. This internal engineering synergy ensures rigorous control over material performance, dimensional accuracy, and long-term durability under extreme cold environments.
Our mould engineers possess extensive experience in designing and optimizing injection, compression, and transfer moulds specifically for low-temperature elastomer applications. Each design undergoes finite element analysis (FEA) and thermal cycle simulation to verify performance under sustained sub-zero conditions, typically ranging from -40°C to +80°C. Tooling is fabricated using hardened P20 or H13 steel with precision tolerances held to ±0.05 mm, ensuring consistent part geometry and sealing integrity across high-volume production runs. Mold flow analysis is standard practice to eliminate defects such as short shots or weld lines, which are critical in maintaining the homogeneity of the final seal.
Complementing our mould design expertise, our two in-house rubber formulation engineers specialize in developing custom EPDM, silicone, and TPE compounds tailored for freezer door performance. These formulations are engineered to resist compression set, maintain elasticity at low temperatures, and exhibit excellent resistance to moisture, ozone, and repeated mechanical stress. All formulations are developed and tested in our on-site laboratory, where we conduct accelerated aging, tensile strength analysis, hardness profiling, and low-temperature flexibility testing (ASTM D1329 and ISO 2231). This vertical integration of material science and tooling design allows us to rapidly prototype and validate new solutions aligned with OEM specifications.
We provide full OEM support including 3D CAD modeling, DFM analysis, first article inspection (FAI) reports, and PPAP documentation. Our engineering team collaborates directly with client R&D departments to ensure seamless integration of our seals into existing door assemblies, meeting stringent energy efficiency and safety standards required in commercial and residential refrigeration systems.
The following table outlines the typical technical specifications achievable for our freezer door rubber seals:
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 55–70 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥8.0 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥250% |
| Compression Set (22 hrs, -20°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% |
| Operating Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +80°C |
| Aging Resistance (70°C x 168 hrs) | ASTM D573 | Max 20% change in properties |
| Ozone Resistance | ASTM D1149 | No cracking (200 pphm, 20%) |
Through the combined expertise of our mould and formulation engineers, Suzhou Baoshida delivers technically robust, application-specific sealing solutions that meet the demanding requirements of modern freezer door systems.
Customization Process
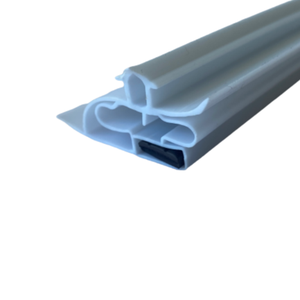
Customization Process for Freezer Door Seals
Freezer door seals operate under extreme thermal cycling and constant mechanical stress, demanding precision-engineered elastomer solutions. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our customization process ensures optimal performance through rigorous scientific methodology. We begin with Drawing Analysis, where engineering teams dissect client CAD files to assess dimensional tolerances, cross-sectional geometry, and interface requirements. Critical parameters include thermal contraction coefficients at -40°C to -50°C, compression deflection forces, and adhesion compatibility with door substrates. Finite element analysis (FEA) simulates real-world stress distribution, identifying potential weak points before material selection. This phase validates feasibility against ISO 1307 dimensional standards and client-specific mechanical benchmarks.
The Formulation stage leverages our 15 years of cold-chain material expertise. We select base polymers—typically EPDM, silicone, or chloroprene—based on the required temperature range, ozone resistance, and cost targets. Key additives include cryogenic plasticizers to maintain flexibility below -40°C, high-purity carbon black for UV stability, and peroxide curing systems to minimize compression set. Each compound undergoes iterative lab testing per ASTM D2000 standards, with adjustments to crosslink density and filler ratios to achieve target hardness (50–70 Shore A) and tensile strength (>10 MPa). Critical validation includes 72-hour compression set tests at -40°C, targeting <25% permanent deformation.
Prototyping involves low-volume production using client-approved tooling. Samples undergo accelerated aging in climate chambers (-50°C to +70°C cycling), door cycle testing (10,000+ operations), and leak integrity checks via helium mass spectrometry. We provide detailed test reports including force-deflection curves and thermal conductivity data. Client feedback drives final compound refinements, typically within 15 business days.
Mass Production commences only after formal sign-off. Our ISO 9001-certified facility employs automated mixing with real-time rheometer monitoring to ensure batch consistency. Every production run includes in-process checks for Mooney viscosity (±3 points) and cure characteristics. Final inspection uses laser micrometers for dimensional accuracy (±0.1 mm) and 100% visual screening for surface defects. Traceability is maintained via batch-coded RFID tags, with full material test reports (MTRs) supplied with each shipment.
Material performance is defined by critical specifications, as shown below for common freezer seal compounds:
| Property | EPDM Standard | EPDM Cryo-Grade | Silicone High-Temp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -45 to +120 | -60 to +150 | -70 to +230 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60 ± 5 | 55 ± 5 | 50 ± 5 |
| Compression Set @ -40°C | 35% max | 22% max | 18% max |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 12 | 10 | 8 |
| Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
This structured approach ensures freezer door seals deliver 10+ years of reliable service in cold storage environments. Suzhou Baoshida’s integration of material science and industrial manufacturing guarantees solutions that prevent energy leakage, reduce maintenance costs, and comply with global cold-chain integrity standards.
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for High-Performance Freezer Door Plastic Solutions
When it comes to industrial-grade freezer door plastic components, precision, durability, and material consistency are non-negotiable. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in engineered rubber and plastic solutions tailored for extreme cold environments, including commercial and industrial freezer applications. Our expertise in thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), silicone, EPDM, and PVC-based compounds ensures that every freezer door seal or trim delivers long-term performance under repeated thermal cycling and mechanical stress.
We understand that OEMs and industrial manufacturers require materials that maintain flexibility at sub-zero temperatures, resist microbial growth, and offer excellent compression set resistance. Our formulations are developed in alignment with international standards for food safety, flame retardancy, and environmental compliance. Whether you are designing walk-in cold storage units, refrigerated transport doors, or medical-grade freezers, our team provides customized material solutions backed by rigorous testing and quality control protocols.
For technical collaboration or material sourcing, we invite you to contact Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Manager and Rubber Formula Engineer. With over 15 years of experience in polymer formulation and industrial sealing applications, Mr. Boyce leads technical consultations, custom compound development, and production scaling for global clients. He ensures seamless integration of our freezer door plastic components into your manufacturing workflow, from prototype to mass production.
To initiate a technical discussion, request samples, or obtain a material data sheet, please reach out directly via email at [email protected]. We respond to all inquiries within 24 business hours and offer virtual or on-site technical support for qualified partners.
Below is a representative specification table for our standard freezer door plastic profile, commonly used in commercial refrigeration systems. Custom dimensions, durometers, and additives (e.g., antimicrobial agents, UV stabilizers) are available upon request.
| Property | Test Method | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | — | EPDM + TPE Blend |
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 65 ± 5 |
| Operating Temperature Range | — | -50°C to +100°C |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥ 10 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥ 300% |
| Compression Set (22h at -20°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤ 25% |
| Color Options | — | Black, White, Gray (custom on request) |
| Food Contact Compliance | FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 | Yes |
| Flame Resistance | UL94 | HB Rated |
| Density | ASTM D792 | 1.15 g/cm³ |
Partnering with Suzhou Baoshida means access to advanced material science, consistent production quality, and responsive technical service. We support clients across North America, Europe, and Southeast Asia with reliable logistics and documentation, including COA, RoHS, and REACH compliance reports.
For immediate assistance with your freezer door plastic requirements, contact Mr. Boyce at [email protected]. Let us help you engineer a sealing solution that performs under pressure and over time.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
