Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Bottom Door Jamb Seal

Engineering Insight: Material Selection for Bottom Door Jamb Seals
Premature bottom door jamb seal failure directly compromises vehicle integrity, leading to water ingress, noise vibration harshness (NVH) issues, and accelerated corrosion. This critical interface demands a sealant engineered beyond generic rubber profiles. Off-the-shelf solutions, predominantly standard EPDM compounds, consistently underperform due to inadequate material science alignment with the unique operational stresses encountered in this specific location. Understanding these failure mechanisms is paramount for OEM durability targets.
The bottom door jamb seal operates under extreme conditions: constant dynamic compression fatigue from door closure cycles, prolonged exposure to road splash containing oils, fuels, and de-icing salts, and significant thermal cycling from ambient to underhood temperatures. Standard commercial EPDM formulations prioritize low cost over performance in these areas. They typically exhibit excessive compression set – often exceeding 30% per ASTM D395 – after prolonged compression at elevated temperatures. This loss of recovery force creates permanent gaps, allowing water and contaminants to breach the cabin. Furthermore, standard grades possess insufficient resistance to non-polar fluids like engine oils and transmission fluids prevalent in underbody environments, leading to swelling, hardening, and eventual cracking. Their usable temperature range is frequently limited, becoming brittle below -40°C or losing resilience above 120°C, failing to cover the full operational spectrum of modern vehicles.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. addresses these challenges through precision rubber compounding. Our engineered EPDM solutions incorporate high-purity, saturated backbone polymers with tailored cure systems and specialized additives. This achieves significantly lower compression set, superior fluid resistance, and extended thermal stability. Critical properties are rigorously validated against automotive OEM specifications, not generic industry standards. Partnering with a specialist rubber formula engineer ensures the material properties are intrinsically matched to the door jamb’s mechanical duty cycle and environmental exposure profile, preventing costly warranty claims and reputational damage.
Critical Material Property Comparison: Standard vs. Engineered Bottom Door Jamb Seal
| Property | Test Standard | Standard Off-the-Shelf EPDM | Baoshida Engineered EPDM | Significance for Door Jamb Seal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (22h, 100°C) | ASTM D395 B | ≥ 30% | ≤ 15% | Maintains sealing force over years of door cycling; prevents gap formation |
| Fluid Resistance (IRM 903) | ASTM D471 | Swell: +25% to +40% | Swell: +8% to +15% | Resists degradation from oils, fuels, road chemicals; prevents hardening/cracking |
| Low Temperature Flexibility | ASTM D2137 | -40°C (Pass/Fail) | -50°C (Pass/Fail) | Ensures seal integrity and recovery in extreme cold climates |
| Heat Aging (70h, 150°C) | ASTM D573 | Tensile Retention: ≤ 60% | Tensile Retention: ≥ 85% | Maintains mechanical properties near hot underhood components |
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 60 ± 8 | 65 ± 5 | Optimized balance of sealing force and ease of door closure |
Material selection is not a commodity decision for the bottom door jamb. It is a fundamental engineering parameter requiring deep compound expertise. Generic solutions sacrifice long-term performance for initial cost savings, inevitably failing the vehicle’s service life requirements. Precision-formulated rubber, validated against the specific demands of this application, is the only viable path to achieving the required 10+ year durability and maintaining cabin integrity under all operational conditions.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Bottom Door Jamb Seals
The selection of elastomeric materials for bottom door jamb seals is critical to ensuring long-term performance, environmental resistance, and mechanical integrity in demanding industrial and automotive applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision-engineered rubber seals tailored to OEM specifications, with a focus on Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ) compounds. Each material offers distinct advantages based on temperature range, chemical exposure, compression set resistance, and durability.
Viton (FKM) is a fluorocarbon-based rubber renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and aggressive chemicals. With a continuous service temperature range of -20°C to +230°C, Viton is ideal for underhood automotive environments and industrial enclosures exposed to hydrocarbons or ozone. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics make it a premium choice for applications requiring long service life under thermal and chemical stress. However, Viton exhibits lower flexibility at sub-zero temperatures compared to other elastomers and carries a higher material cost, which must be weighed against performance requirements.
Nitrile (NBR) remains one of the most widely used elastomers in sealing applications due to its superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and hydraulic fluids. Operating effectively from -30°C to +120°C, it offers a balanced performance profile for general-purpose use in automotive, machinery, and industrial equipment. NBR demonstrates good abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it suitable for dynamic sealing environments. While it outperforms many rubbers in oil resistance, it is less effective in ozone, UV, and extreme high-temperature conditions, limiting its use in outdoor or high-heat applications without special compounding.
Silicone (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature environments, with a service range from -60°C to +200°C, and short-term resistance up to +250°C. It maintains flexibility at cryogenic temperatures and offers excellent resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and weathering. These properties make silicone ideal for exterior door seals exposed to sunlight and temperature cycling. However, standard silicone formulations have lower tensile and tear strength compared to NBR or Viton and exhibit poor resistance to petroleum-based fluids, requiring careful application evaluation.
The following table summarizes key physical and chemical properties of these materials for comparative analysis:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +230 | -30 to +120 | -60 to +200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 12–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–300 | 200–500 | 200–600 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
Material selection must be aligned with the operational environment, sealing force requirements, and lifecycle expectations. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports OEMs with custom compounding, rigorous testing, and full traceability to ensure optimal material performance in every bottom door jamb seal.
Manufacturing Capabilities
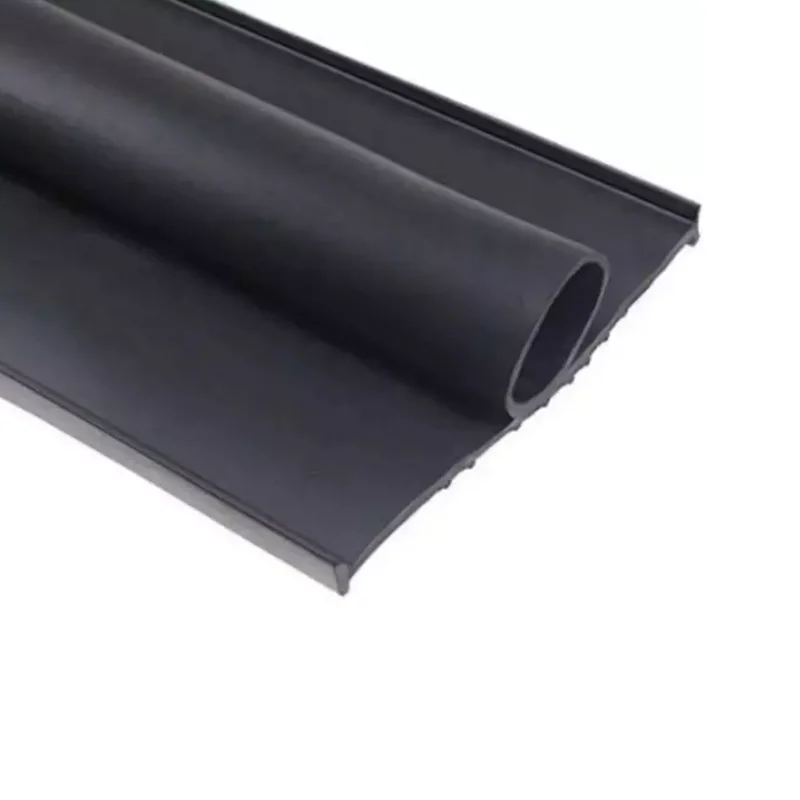

Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Formulation and Mold Design for Bottom Door Jamb Seals
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered bottom door jamb seals through advanced rubber science and precision tooling. Our dedicated team of five Mold Engineers and two Rubber Formula Engineers ensures every component meets stringent automotive and architectural OEM requirements. This integrated expertise allows us to solve complex sealing challenges, including thermal cycling resistance, compression set stability, and material durability under dynamic load conditions. We prioritize material integrity and geometric accuracy to prevent air/water infiltration while maintaining consistent door closure force.
Our Mold Engineering team utilizes 3D simulation software to optimize cavity design, runner systems, and venting for zero flash and minimal parting line defects. Each mold undergoes rigorous validation for cycle time efficiency and dimensional repeatability within ±0.1 mm tolerances. This precision ensures uniform sealing pressure across the entire door threshold interface, critical for noise reduction and energy efficiency in end applications. Tooling iterations are minimized through finite element analysis (FEA) of material flow and shrinkage behavior, reducing time-to-market for new programs.
The Rubber Formula Engineering division develops proprietary EPDM and TPE compounds tailored to extreme environmental exposure. We balance Shore A hardness, elongation at break, and low-temperature flexibility to achieve -40°C to +120°C operational resilience. Critical additives are precisely dosed to enhance UV resistance, ozone stability, and resistance to road salts and cleaning agents. Every formulation undergoes accelerated aging tests per ASTM D2240 and ISO 188, ensuring 15+ years of service life without hardening or cracking. This scientific approach eliminates trial-and-error, delivering first-pass material approval for global OEMs.
As an OEM partner, we manage full program lifecycles from CAD data to PPAP submission. Our Suzhou facility supports rapid prototyping, DFM analysis, and serial production with automated inspection systems. We maintain IATF 16949-certified processes for traceability, including lot-specific compound certificates and 100% inline dimensional checks via vision systems. This end-to-end control guarantees compliance with GMW14125, VW 50180, and JASO D612 standards.
Key performance specifications for our bottom door jamb seals are validated across all production batches:
| Parameter | Test Standard | Typical Value | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 60 ± 5 | Optimal sealing force without door drag |
| Compression Set (22h/70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤ 15% | Long-term shape recovery after compression |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥ 10 MPa | Resistance to tearing during installation |
| Low-Temperature Flex | ISO 1432 | Pass at -45°C | Prevents brittle fracture in cold climates |
| Density | ASTM D297 | 1.15–1.25 g/cm³ | Weight optimization for door mechanisms |
This engineering rigor enables Suzhou Baoshida to deliver bottom door jamb seals that exceed OEM durability benchmarks while supporting just-in-time logistics. Our formula-mold synergy ensures material properties are never compromised by manufacturing variables, providing clients with a single-source solution for mission-critical sealing performance.
Customization Process
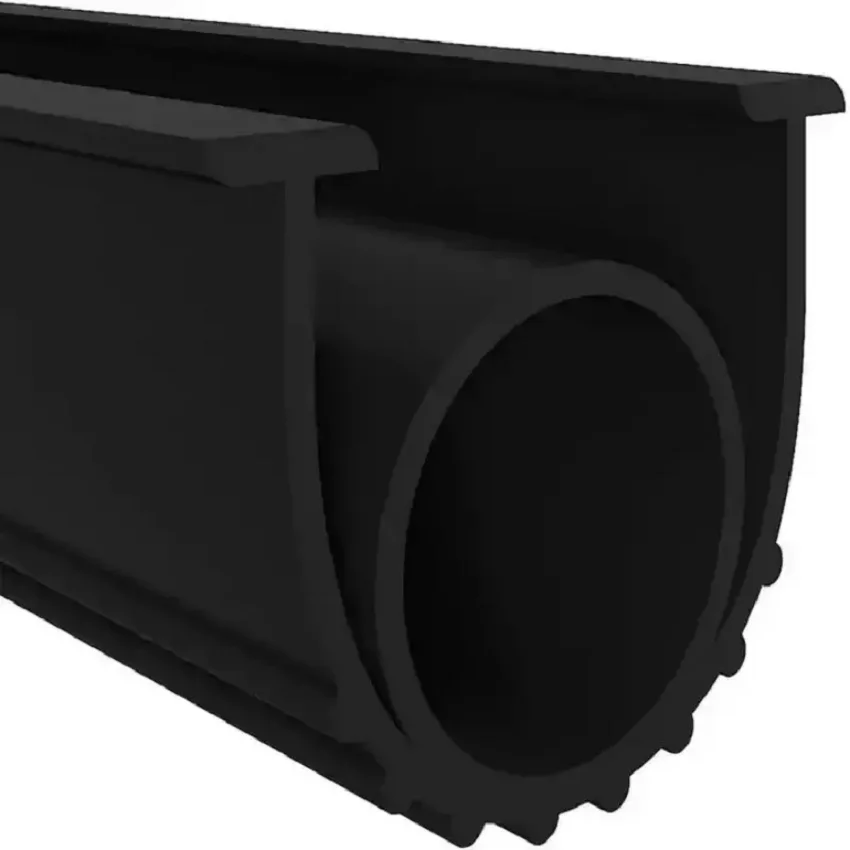
Drawing Analysis
The customization process for bottom door jamb seals begins with rigorous drawing analysis, a foundational step that ensures dimensional accuracy and functional compatibility. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team conducts a comprehensive review of customer-provided technical drawings, focusing on critical parameters such as cross-sectional profile, overall length, compression set requirements, and installation clearances. We validate geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) specifications in accordance with ISO 1101 standards, ensuring alignment with OEM design intent. Any ambiguities or potential manufacturing constraints are flagged during this phase, and we engage in direct technical consultation with the client to resolve discrepancies. This proactive approach minimizes rework and accelerates time-to-market.
Rubber Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, our Rubber Formula Engineers develop a compound tailored to the operational environment of the bottom door jamb seal. Material selection is driven by performance criteria including temperature resistance, UV stability, ozone exposure, and compression deflection characteristics. We primarily utilize EPDM for its superior weather resistance in exterior applications, though silicone or neoprene may be specified for extreme thermal or chemical environments. The formulation process includes precise control over polymer base, filler loading (e.g., carbon black or silica), plasticizers, and vulcanizing agents to achieve target hardness (Shore A 55–75), elongation at break (>200%), and low-temperature flexibility (down to -40°C). Each compound is documented under a proprietary formula code and subjected to preliminary lab testing for consistency.
Prototyping and Validation
Once the formulation is finalized, we produce functional prototypes using precision extrusion and splice molding techniques. Prototypes are manufactured in small batches to simulate real production conditions and are inspected for dimensional conformity using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and optical comparators. Sealing performance is evaluated through compression force-deflection (CFD) testing and air leakage trials under simulated door closure cycles. Clients receive physical samples along with a full test report detailing material certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH) and performance data. Feedback is integrated into final design adjustments before release for mass production.
Mass Production Readiness
With approved prototypes, we transition to high-volume manufacturing under ISO 9001-certified processes. Production lines are equipped with real-time monitoring systems to ensure lot-to-lot consistency in extrusion diameter, splice strength, and surface finish. Each batch undergoes in-process quality checks and final inspection before packaging. We maintain traceability through serialized batch coding and provide full material documentation upon shipment.
Typical Material and Performance Specifications
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Material | — | EPDM, Black |
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 65 ± 5 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥ 9.0 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥ 250% |
| Compression Set (25%, 70°C/24h) | ASTM D395 | ≤ 20% |
| Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +125°C |
| Specific Gravity | ASTM D297 | 1.35 ± 0.05 |
| Color | — | Black (custom colors on request) |
Contact Engineering Team

Technical Engagement for Precision Bottom Door Jamb Seals
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the convergence of advanced polymer science and industrial manufacturing rigor, delivering bottom door jamb seals that meet the exacting demands of global automotive and heavy equipment OEMs. Our engineering team specializes in formulating elastomeric compounds resistant to ozone degradation, extreme thermal cycling, and compression set—critical factors for seals ensuring cabin integrity, acoustic insulation, and longevity in dynamic door mechanisms. Unlike generic suppliers, we integrate material science with precision extrusion and vulcanization control, validated through ISO/TS 16949 protocols and real-world environmental testing. Each seal undergoes dimensional verification via CMM systems, guaranteeing ±0.15mm tolerance adherence to complex cross-sectional profiles.
The table below summarizes core technical specifications achievable through our custom formulation process, reflecting baseline capabilities for standard automotive applications. All parameters are adjustable per OEM material specifications and functional requirements.
| Property | Standard Range | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material Compound | EPDM, ACM, Silicone | ASTM D2000 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 55–85 ±5 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥8.0 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22h/70°C) | ≤25% | ASTM D395 |
| Temperature Range | -50°C to +150°C (EPDM) | ISO 188 |
| Fluid Resistance (Brake Fluid) | Volume Swell ≤15% | ASTM D471 |
Partnering with Suzhou Baoshida means access to dedicated compound development resources. Our engineers collaborate directly with your design teams to resolve challenges such as low-temperature flexibility retention, extrusion die flow optimization, or adhesion promotion for multi-material assemblies. We maintain in-house labs for rapid iteration of durometer gradients, filler dispersion analysis, and dynamic fatigue simulation—reducing time-to-prototype by up to 40% versus industry averages. Production scalability is ensured through automated extrusion lines with real-time rheometry monitoring, supporting volumes from 5,000 to 500,000 units monthly without compromising batch consistency.
Initiate a technical dialogue to resolve your specific bottom door jamb seal challenges. Contact Mr. Boyce, our OEM Technical Account Manager, who possesses 12 years of experience in automotive sealing systems and material compatibility validation. Mr. Boyce will coordinate a structured engineering review covering your dimensional schematics, environmental exposure profiles, and performance targets. He facilitates direct access to our formulation chemists and process engineers for collaborative problem-solving, ensuring seamless integration of our seals into your assembly line with zero NPI delays.
Email [email protected] with subject line “Technical Query: Bottom Door Jamb Seal – [Your Company Name]” to receive a tailored compound proposal within 48 business hours. Include your current material specification codes, cross-section drawings, and critical failure mode data for immediate technical assessment. Suzhou Baoshida commits to providing not merely a component, but a validated engineering solution backed by material traceability, PPAP documentation, and lifetime performance support. Your next-generation door sealing performance begins with precise molecular design—contact us to activate this capability.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
