Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for crankshaft seal oil
Crankshaft seal oil may seem like a minor component in the complex machinery of global industry, but for international B2B buyers, its impact on performance, reliability, and long-term operational costs is immense. Whether operating in heavy-duty automotive, agriculture, maritime, or industrial power generation sectors, businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly recognizing the necessity of sourcing high-quality crankshaft seal oil to ensure equipment longevity and minimize unplanned downtime. A single seal’s failure can result in oil leaks, contamination, and costly machinery repairs—repercussions that no forward-looking operation can afford.
Understanding the nuances behind crankshaft seal oil—its types, materials, optimized manufacturing processes, and global supplier networks—is crucial in a market shaped by rapidly evolving technology and diverse operational environments. Regional factors such as climate, infrastructure, and varying equipment standards further complicate selection, placing unique demands on sourcing strategies for buyers in Brazil, Egypt, and beyond. This comprehensive guide demystifies the technical landscape, examining:
- Key types of crankshaft oil seals and their specific applications
- Material innovations and resistance properties vital for harsh conditions
- Manufacturing and quality control benchmarks to safeguard reliability
- Supplier assessment for trustworthy global partnerships
- Cost drivers and negotiation tactics to optimize your procurement budget
- Emerging market trends, logistical challenges, and regulatory considerations
- Frequently asked questions to address real-world buyer concerns
Equipped with actionable insights and comparative analysis, this guide empowers procurement leaders and technical teams to make informed, strategic decisions. The result: enhanced performance, improved cost efficiency, and a robust, future-proof supply chain for crankshaft seal oil across diverse industrial landscapes.
Understanding crankshaft seal oil Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Lip Crankshaft Oil Seal | One sealing edge, simple construction | Standard automotive engines, trucks | Cost-effective, easy to install; less protection from contaminants |
| Double-Lip (Dual-Lip) Seal | Extra dust lip for debris exclusion | Off-road, agricultural, industrial | Improved contamination control; may require more installation care |
| PTFE (Teflon) Crankshaft Seal | Made from polytetrafluoroethylene, low friction, no spring | High-speed, modern, luxury vehicles | Superior durability, works in aggressive media; higher price |
| Spring-Loaded Rubber (NBR/FKM) | Elastomeric seal with integrated tensioning spring | General automotive, diesel engines | Excellent sealing force, widely available; moderate temperature range |
| Metal-Cased Crankshaft Seal | Metal outer casing, rubber sealing lip | Heavy-duty, high-pressure engines | Enhanced structural integrity, robust; difficult to retrofit |
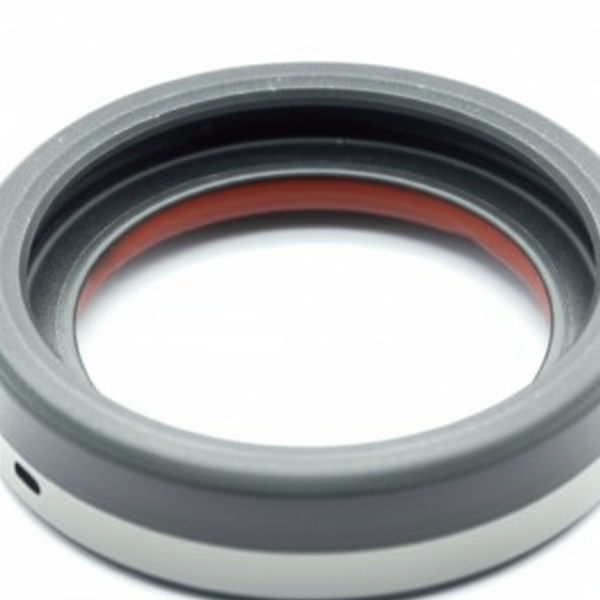
Single-Lip Crankshaft Oil Seal
Single-lip seals feature a single edge responsible for retaining oil and excluding basic contaminants. Their straightforward design makes them a popular choice for standard automotive engines and light trucks operating in stable environments. Buyers often select single-lip seals for cost-sensitive projects or refurbishment operations where exposure to heavy contamination is limited. The main consideration is balancing cost versus the potential need for more advanced contamination control in harsher environments, which these seals may lack.
Double-Lip (Dual-Lip) Seal
Double-lip seals incorporate a secondary dust lip, effectively providing an additional barrier against the ingress of dirt, mud, and other contaminants. This feature is especially valuable for applications in agriculture, mining, off-road vehicles, and environments where particle contamination is a concern. For B2B buyers, these seals offer a strategic edge for prolonging equipment life and reducing unplanned maintenance in challenging conditions. The installation must be precise to ensure both lips contact surfaces correctly; otherwise, performance can decline.
PTFE (Teflon) Crankshaft Seal
PTFE crankshaft seals use advanced engineered polymer technology, resulting in extremely low friction and outstanding thermal resistance. These seals are springless, reducing wear mechanisms, and can handle aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures demanded by modern, high-performance engines—such as those found in premium cars, export markets, and critical industrial machinery. Buyers benefit from reduced downtime and extended maintenance intervals but should weigh the higher upfront cost and ensure compatibility with specific crankshaft surfaces and lubricants prior to procurement.
Spring-Loaded Rubber (NBR/FKM)
Spring-loaded rubber seals (commonly crafted from nitrile (NBR) or fluoroelastomer (FKM/Viton)) use a metal spring for consistent radial tension atop a resilient rubber sealing element. This design is renowned for its versatility, making it suitable for a broad array of machinery, including commercial vehicles and generators. These seals strike an excellent cost-performance balance and are widely available in global markets, fitting most engines used in African, South American, and Middle Eastern vehicle fleets. It is important to match material grade with temperature and chemical exposure requirements during purchase.
Metal-Cased Crankshaft Seal
Metal-cased seals provide robust structural stability, with a metallic exterior that enables tight press-fit into housings under high pressure or vibration. They are favored in heavy-duty or industrial engines—such as those powering construction equipment or stationary generators—where reliability under mechanical stress is paramount. Such seals can be more challenging to retrofit or replace due to increased rigidity, so buyers must confirm fit and compatibility, especially for legacy or region-specific machinery. Nevertheless, they deliver an advanced solution for demanding B2B operational environments.
Related Video: how to change crankshaft oil seal/ how to replace front crankshaft oil seal
Key Industrial Applications of crankshaft seal oil
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of crankshaft seal oil | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive & Transport | Engine assembly and maintenance of vehicles | Minimizes downtime, reduces oil leakage, extends engine life | Resistance to high temperatures, compatibility with seal materials, availability in bulk quantities |
| Industrial Machinery | Lubrication and sealing for compressors, pumps, and turbines | Prevents contaminant ingress, ensures consistent performance | Chemical stability, longevity under continuous operation, certification for industrial standards |
| Marine & Shipping | Crankshaft protection in ship engines | Maintains operational safety, reduces maintenance frequency | Resistance to saltwater corrosion, availability at major ports, compliance with maritime regulations |
| Power Generation | Sealing and lubricating generators and turbine assemblies | Reduces unplanned outages, supports high-load conditions | High thermal resistance, supplier reliability, ability to meet high-volume needs |
| Agriculture & Construction Equipment | Protection for heavy-duty engine crankshafts | Increases machinery uptime, handles dusty/high-load environments | Performance in harsh environments, effective sealing under vibration, support for on-site delivery |
Automotive & Transport
Crankshaft seal oil is fundamental for automotive and heavy vehicle manufacturers, assembly lines, and fleet maintenance operations worldwide. It forms a lubricating barrier around engine crankshafts, shielding against oil leaks that can cripple engine performance and lead to costly repairs. For buyers in regions like Brazil and Egypt, where transport logistics are vital and cost containment is critical, selecting crankshaft seal oils compatible with local climate temperatures and common seal materials (such as fluorocarbon or nitrile rubber) is essential. Bulk availability and access to technical support further streamline maintenance and minimize vehicle downtime.
Industrial Machinery
Industrial sectors rely on compressors, pumps, and turbines that often run continuously in demanding environments. Crankshaft seal oil plays a central role by both lubricating and preserving the integrity of dynamic seals, preventing wear and ingress of dust or process chemicals. Consistent use reduces unscheduled maintenance and equipment failure, directly impacting production efficiency. International buyers from Africa and South America must ensure oil selection matches not only machine specifications but also endures long run-times and variable power quality, with consideration for quality assurance certificates and compliance with industrial regulations.
Marine & Shipping
Maritime operations involve high-performance engines where crankshaft seal oil guards critical components against harsh marine conditions, including saltwater corrosion and thermal cycling. Effective sealing solutions reduce unscheduled dry-dock stops and extend time between overhauls, directly affecting profit margins for shipping lines. Buyers, especially in major shipping hubs across Europe and the Middle East, should prioritize oils with proven resistance to saline exposure and those readily supplied to ports, along with assurance of regulatory compliance for marine equipment.
Power Generation
Within power generation facilities, especially where turbines and large generators are present, crankshaft seal oil ensures rotating assemblies remain tightly sealed and well-lubricated. Proper application helps handle both high thermal loads and prolonged operational cycles, resulting in fewer unexpected outages and stable energy supply—a critical consideration in regions with growing energy infrastructure demands. Sourcing strategies should emphasize product reliability, high-temperature performance, and the ability to fulfill large recurring orders in line with plant maintenance schedules.
Agriculture & Construction Equipment
In agriculture and construction sectors, engines are routinely exposed to dust, vibration, and extreme loads. Crankshaft seal oil is essential for sealing these rough-running crankshafts, providing robust protection from external contaminants and ensuring continued lubrication even under severe operating conditions. Buyers in developing markets must account for variations in field conditions, prioritize products that maintain efficacy in harsh environments, and rely on suppliers offering prompt, flexible delivery to rural or remote job sites. These strategic decisions support higher equipment utilization rates and lower lifetime maintenance costs.
Related Video: 2012-2017 equinox 2.4 engine oil leak diagnosis and crankshaft seal repair.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for crankshaft seal oil
Understanding Material Choices for Crankshaft Seal Oil Applications
Selecting the right material for crankshaft oil seals is essential for ensuring operational reliability and long seal life, particularly in demanding markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The chosen material must balance chemical compatibility, temperature and pressure resistance, ease of manufacturing, and compliance with local and international regulations. Below, we analyze the four most commonly used materials in crankshaft seal oil applications: Nitrile Rubber (NBR), Fluoroelastomer (FKM/Viton®), Polyacrylate Rubber (ACM), and Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
1. Nitrile Rubber (NBR, Buna-N)
Key Properties:
NBR is highly valued for its resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels. It has a typical operating temperature range from -40°C to +120°C, with moderate resistance to abrasion and good mechanical stability.
Pros:
– Good performance in standard lubrication and oil environments
– Cost-effective and widely available
– Simple manufacturing processes and flexible form factor
Cons:
– Lower resistance to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals compared to premium materials
– Prone to degradation by ozone and weathering, which can be challenging in harsh outdoor environments
Impact on Application:
NBR is suitable for engines operating under standard temperatures and pressures, often found in general automotive, agricultural, and light industrial applications. However, it may not suffice for engines exposed to elevated heat or aggressive synthetic or bio-based oils.
International B2B Considerations:
NBR seals are commonly available in compliance with standards such as ASTM D2000, DIN 3771, and others. For regions like Africa and Brazil, where cost sensitivity is high and standard petroleum lubricants dominate, NBR is a pragmatic, easily sourced choice.
2. Fluoroelastomer (FKM, Viton®)
Key Properties:
FKM offers exceptional resistance to high temperatures (up to +200°C) and an extensive range of chemicals, including aggressive synthetic oils and fuels.
Pros:
– Outstanding heat, chemical, and oil resistance
– Durable and maintains elasticity over long periods, even in harsh engine environments
Cons:
– Significantly higher cost than most other elastomers
– More complex manufacturing, sometimes requiring specialized equipment and skilled labor
Impact on Application:
FKM is ideal for heavy-duty, high-performance engines and equipment exposed to aggressive media, such as synthetic lubricants or biofuels. It’s favored in demanding industrial, automotive, and power generation contexts.
International B2B Considerations:
FKM materials often meet stringent standards (e.g., ASTM D1418, DIN ISO 1629) required by OEMs in Europe and the Middle East. In regions with higher ambient temperatures or stricter emission standards, the investment in FKM provides enhanced reliability and compliance with service expectations.
3. Polyacrylate Rubber (ACM)
Key Properties:
ACM provides intermediate resistance to heat (up to +150°C) and good performance in the presence of oxidized oils and automatic transmission fluids.
Pros:
– Better heat and oil resistance than NBR
– Good balance between cost and performance for mid-range applications
Cons:
– Inferior low-temperature flexibility (typically brittle below -20°C)
– Limited resistance to fuels and more aggressive chemicals
Impact on Application:
ACM is well-suited for mass-market vehicles and machinery where moderate heat and oil resistance is necessary. However, it’s less suitable for extremely cold environments found in parts of Europe or for engines using more aggressive fluids.
International B2B Considerations:
ACM seals conform to international standards like ISO 1629 and are widely used by global OEMs in affordable vehicle segments. They are often found in applications across South America and North Africa, balancing cost and performance.
4. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE, Teflon®)
Key Properties:
PTFE delivers the broadest chemical compatibility and withstands continuous service temperatures from -60°C to +220°C. It’s nearly inert, with extremely low friction.
Pros:
– Virtually universal chemical resistance: compatible with synthetic, mineral, and bio-based oils
– Exceptional temperature tolerance and low wear under dynamic loads
Cons:
– High cost relative to elastomers
– Additional manufacturing complexity (requires precision machining or molding)
Impact on Application:
PTFE seals are chosen for critical applications, such as heavy industrial engines or in environments with frequent temperature cycling and aggressive lubricants.
International B2B Considerations:
PTFE seals meet rigorous standards like ASTM D4894 and have growing demand in regions prioritizing high technology or where seal replacement is difficult (such as remote oil and gas or mining industries in the Middle East and Africa). Their reliability offsets higher upfront costs in these scenarios.
Material Selection Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for crankshaft seal oil | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Standard automotive, light industry, agriculture | Cost-effective; resists oils well | Not suitable for high temperatures or aggressive media | Low |
| Fluoroelastomer (FKM) | High-temp, high-performance, synthetic oil engines | Superior heat and chemical resistance | High initial cost; complex manufacturing | High |
| Polyacrylate Rubber (ACM) | Mid-range engines, mass-market vehicles | Good heat/oil resistance and value | Limited low-temp/fuel resistance; brittle when cold | Medium |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Heavy-duty/industrial, aggressive fluid, critical reliability applications | Extreme chemical/temperature durability | Highest cost; manufacturing complexity | High |
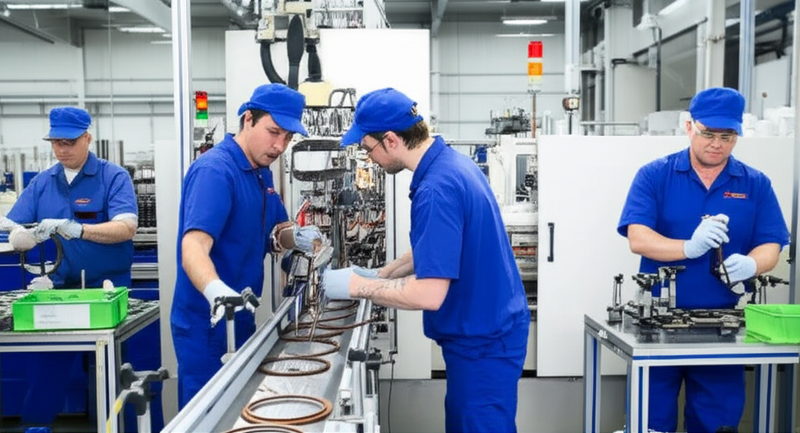
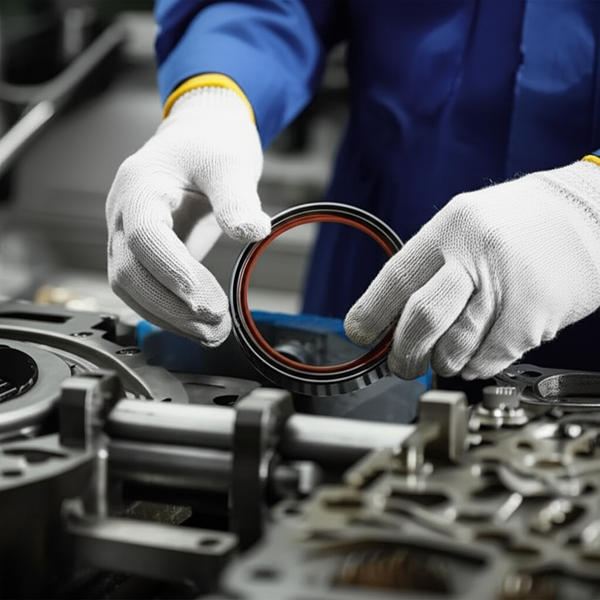
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for crankshaft seal oil
Core Manufacturing Stages of Crankshaft Seal Oil
International B2B buyers seeking high-performance crankshaft seal oil products should understand the typical manufacturing flow, as robust processes directly impact durability and performance in demanding environments. Most reputable suppliers adhere to a multi-stage production line that includes material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is critical for creating seals that can withstand pressure, temperature, and chemical exposure over extended use periods.
Material Preparation
Quality begins with raw material selection. Manufacturers source specialized elastomers and polymers—such as nitrile rubber (NBR), fluoroelastomer (FKM/Viton®), or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)—chosen for their resistance to oil, heat, and aggressive chemicals. The chosen material’s specification sheet should be validated against the intended operating environment (temperature range, oil composition, rotation speed).
During preparation, raw materials are blended with reinforcing fillers, antioxidants, and plasticizers according to proprietary compound recipes. B2B buyers should note that leading suppliers maintain batch traceability—a key aspect for downstream quality tracking, especially important for global buyers facing regulatory or warranty-compliance requirements.
Forming and Molding Techniques
Most crankshaft seal oils are manufactured via compression molding, transfer molding, or injection molding. Each method has merits:
- Compression Molding: Preferred for low-to-medium volume runs and complex geometries, offering high material integrity.
- Injection Molding: Enables high-volume automation with excellent repeatability, critical for large-scale procurement.
- Transfer Molding: Often used for integrating seals into metal cases or with composite carriers.
Sophisticated manufacturers use computer-controlled parameters to guarantee optimal temperature, pressure, and curing time, ensuring consistent physical properties throughout production batches.
Assembly and Metal Inserts
High-stress applications often require a seal design that integrates metal stiffeners, springs, or PTFE lips. Metal inserts (usually carbon steel or stainless steel) are prepared via degreasing, grit blasting, and anti-corrosive coating before bonding with rubber components. Automated assembly lines minimize human error and promote uniformity—key for multinational buyers demanding consistent SKU performance.
Finishing and Surface Treatment
Post-molding, seals are flash-trimmed, deburred, and—if required—subjected to surface treatments such as plasma coating or PTFE lips application. These finishing steps enhance chemical resistance and reduce friction, prolonging seal life. Stringent cleaning protocols are followed to eliminate contaminants that could compromise sealing performance.
Quality Control Frameworks and Certifications
For B2B buyers, a supplier’s commitment to repeatable quality matters as much as engineering prowess. Leading manufacturers of crankshaft seal oil typically operate under an umbrella of international certifications and continuous quality control (QC) monitoring processes.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: Virtually mandatory for reputable suppliers, this standard assures robust quality management systems across all manufacturing processes.
- IATF 16949: Specifically relevant for automotive applications, aligning with the strict requirements of OEM buyers in Europe and South America.
- CE Mark (Europe): Indicates compliance with EU directives for safety and environmental impact.
- API Standards: For suppliers serving the oil & gas sector in the Middle East or Africa.
Ask suppliers for up-to-date digital certificates. For cross-border buyers, ensure these are recognized locally (some markets may require additional certification or customs documentation).
In-Process and Final Quality Control (QC) Checkpoints
Leading producers employ multi-stage QC:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are tested for physical and chemical conformity. B2B buyers should inquire about the presence of incoming batch records and material certification (such as MSDS or RoHS compliance) for risk mitigation.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During molding and assembly, automated cameras and statistical process controls (SPC) continuously monitor dimension accuracy, hardness (Shore A scale), and curing completeness.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished seals undergo sample-based and 100% inspections before shipment. Common methods include:
– Visual and surface defect inspection under high-magnification cameras or human operators.
– Dimensional measurement with CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines).
– Hardness and tensile strength testing (ASTM D2240, D412).
– Oil resistance and chemical compatibility testing (ASTM D471).
– Dynamic leak tests and high/low temperature cycling.
Seals generally leave the factory with traceable lot numbers for post-sale troubleshooting—a non-negotiable for B2B buyers managing distributed aftersales service networks.
Independent Verification and Supplier Audits
Procurement teams should not rely solely on supplier-provided QC documents. Implementing a third-party inspection or requesting sample testing through independent labs (such as SGS, TÜV, or Intertek) is standard, especially for international orders or initial batch deliveries.
Consider these verification mechanisms:
- On-site Audits: Evaluate the robustness of the QC system and inspect batch records, calibration logs, and staff training certifications.
- First Article Inspection (FAI): Review a comprehensive dimensional and property report from a pilot lot, particularly when launching new models for regional markets.
- Continuous Re-qualification: Request periodic random sample testing, especially for long-term supply agreements.
Key Considerations for International Markets
Africa
Buyers in Africa should be mindful of challenging logistics and infrastructure. Favor suppliers providing robust packaging that preserves quality during transit. Verify supplier awareness of prevailing local standards or customs requirements, such as SONCAP in Nigeria or KEBS in Kenya.
South America (e.g., Brazil)
The Mercosur region has its own sets of import regulations, such as INMETRO certification alongside ISO-based documentation. Language support (Portuguese, Spanish) for training and technical documentation is valuable when coordinating after-sales service, which can help reduce return rates and warranty disputes.
Middle East
High ambient temperatures and dust require seals with enhanced heat and abrasion resistance. Demand documented evidence of suitability for these conditions—such as extended heat aging (ASTM D573) or sand/dust ingress tests. For oil & gas projects, API and local regulatory compliance (such as SASO) is mandatory.
Europe
CE Marking and REACH compliance are prerequisites for market access. European buyers often require full traceability and detailed RoHS declarations due to strict environmental rules.
Actionable Tips for B2B Buyers
- Request Comprehensive Dossiers: Insist on material certifications, dimensional inspection reports, and test results with each shipment.
- Prioritize Traceability: This enables easier root-cause analysis in the event of failure—essential for distributed networks.
- Perform Risk-Based Audits: Direct resources to higher-risk suppliers or those with repeat non-conformances.
- Insist on Written QC Protocols: These should describe how non-conformances are managed, records retention periods, and escalation procedures.
By demanding and understanding these manufacturing and QC fundamentals, B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can minimize supply chain risks and secure high-performing, reliable crankshaft seal oil products tailored to local market and regulatory needs.
Related Video: ⛽️Crude Oil Manufacturing Production Process – Extraction and Refining Crude Oil – Petrol Factory
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for crankshaft seal oil Sourcing
Key Cost Elements in Crankshaft Seal Oil Procurement
When sourcing crankshaft seal oil for international markets, understanding the granular breakdown of costs is crucial for effective planning and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
- Raw Materials: The base materials—typically nitrile rubber (NBR), fluorocarbon elastomers (FKM/Viton), silicone, or PTFE—account for a significant portion of unit cost. Price varies by material, dictated by chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and end-use specifications.
- Manufacturing Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for precision manufacturing, especially for high-performance or custom-designed seals. Labor costs can fluctuate by region, with lower costs typically found in Asia and select Eastern European markets.
- Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses factory utilities, equipment depreciation, and indirect labor—typically bundled into supplier quotes. Higher automation and modern processes may lower overhead per piece, particularly at higher volumes.
- Tooling & Molds: Initial procurement of custom or OEM-specific seals usually requires investment in molds or dies. For high-MOQs or repeat orders, tooling costs are amortized over the volume, but for smaller orders, these can inflate unit pricing.
- Quality Control (QC) & Testing: Certifications (e.g., ISO, TS16949) and rigorous QC protocols add to the cost but are often non-negotiable for buyers demanding reliability and international compliance.
- Logistics & Freight: Costs for crating, shipping, insurance, and customs handling can be non-trivial—especially for Africa and South America, where supply chains can be more complex or where import duties are significant.
- Supplier Margin: Margin structures vary by supplier size, region, and value-add (such as engineering or inventory services).
Primary Pricing Drivers and Market Dynamics
The final price quoted to a B2B buyer will depend on several interrelated variables:
- Order Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger, consolidated orders unlock major price reductions due to economies of scale. Small, irregular, or sample orders incur higher per-unit prices.
- Customization & Specifications: Non-standard sizes, unique profiles, or proprietary material blends increase cost due to special tooling, extra engineering, or lower production efficiencies.
- Material Grade & Compliance: More chemically resistant or heat-resilient grades, as well as compliance with industry standards (e.g., automotive OEM specs, FDA/NSF), command price premiums.
- Quality Certifications: Suppliers with robust certification portfolios offer higher price points but can be essential for regulated or safety-critical industries.
- Supplier Location & Capacity: Proximity to raw material sources and access to advanced manufacturing affect base costs. High-capacity, integrated suppliers often offer more competitive pricing for scale.
- Incoterms: Whether price includes delivery to port (FOB), direct to buyer’s warehouse (DDP), or ex-works, will shift the logistics cost and risk burden.
- Currency Volatility: Especially relevant for buyers in Africa and South America; exchange rate shifts can materially impact landed costs.
Actionable Strategies for International B2B Buyers
International buyers from Brazil, Egypt, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, and the EU can leverage several best practices to optimize cost and procurement:
- Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just unit price but lifetime performance, installation costs, failure risk, and logistics. A slightly higher-priced, certified seal may reduce downtime, warranty costs, or labor outlays over time.
- Negotiate Based on Volume and Commitment: Secure tiered pricing for annual forecasts or aggregated orders across multiple business units or regions. Suppliers may offer improved terms for multi-year deals.
- Clarify All-In Pricing: Know exactly what is included—customs duties, transport, import VAT, and whether the quote is FOB, CIF, or DDP.
- Request Dual Sourcing and Local Stocking: For critical SKUs or hard-to-source sizes, explore dual sourcing (e.g., Asia plus regional EU supplier) or local vendor-managed inventory to minimize disruption, delivery lead times, and emergency freight costs.
- Insist on Quality and Supply Chain Transparency: For buyers operating in regions with variable import quality (notably parts of Africa and LATAM), require batch test reports, traceable lot numbers, and, if possible, on-site supplier audits ahead of large commitments.
- Beware of Low-Quality Alternatives: Products that underperform or fail prematurely can dramatically elevate operating costs and jeopardize equipment warranties, especially in extreme climates.
Regional Pricing Trends and Considerations
- Africa & South America: Import duties, forex fluctuations, and last-leg logistics often make up a higher proportion of landed cost. Collaborate with suppliers experienced in these regions, and factor in local warehousing or customs brokerage fees.
- Middle East: Consolidated shipments, local agents, or free-zone warehousing can optimize pricing. Oil & gas sector buyers should pay close attention to international certifications and high-performance materials.
- Europe: Buyers here can often negotiate better pricing on larger, ongoing contracts, and benefit from proximity to certified, reputable European manufacturers. However, minimums and regulatory compliance can drive up initial costs.
Disclaimer: All prices, cost structures, and indicative figures are subject to market fluctuation, material price trends, and supplier-specific factors. Always validate pricing and contractual terms with qualified suppliers before finalizing
Spotlight on Potential crankshaft seal oil Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘crankshaft seal oil’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
5 best oil seal manufacturers (iquality.techinfus.com)
Corteco, a division of the global Freudenberg Group, stands out among European oil seal manufacturers for its extensive range of crankshaft seal oil solutions. The company’s products are noted for high elasticity and resistance to extreme temperature fluctuations, ensuring reliable engine sealing even in demanding conditions. Corteco maintains rigorous inspection protocols and meticulous packaging, contributing to its reputation for supplying consistently high-quality products that meet or exceed industry standards. With a strong presence across Europe and active export channels, Corteco has established trust with B2B buyers seeking both OEM-quality performance and competitive pricing—attributes especially valued in markets like Africa, South America, and the Middle East. Its crankshaft oil seals are designed to compete directly with premium brands, offering robust service life and minimal maintenance requirements.
Parjetseals (www.parjetseals.com)
Parjetseals is recognized as a key manufacturer and supplier of industrial seals, including crankshaft seal oil solutions for automotive and heavy machinery applications. The company emphasizes high-quality materials and innovative sealing technologies tailored to demanding environments, supporting OEMs and aftermarket requirements alike. Parjetseals’ product range is engineered for durability, efficiency, and leak prevention, catering to industries where component reliability is critical. While comprehensive public information is limited, Parjetseals is noted among global leaders in sealing, indicating substantial experience in international B2B markets—particularly relevant for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Buyers can expect products developed to rigorous industry standards, with a focus on supporting uptime and reducing maintenance costs across diverse operating conditions.
How to Choose the Best Auto Oil Seal Manufacturer (drorubber.com)
Based in Asia and recognized globally, this supplier focuses on the design and production of auto oil seals, including crankshaft seal oil solutions tailored for demanding automotive applications. With a reputation cited among the Top 10 global oil seal manufacturers, the company emphasizes long-standing technical expertise, advanced material selection (such as rubber and fluorocarbon compounds), and custom-engineered products for superior leakage prevention and durability. Production is aligned with strict international quality standards (such as ISO 9001), and the company invests in both automated manufacturing and in-house testing for performance assurance.
Serving diverse B2B markets—including buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—the company provides both OEM and aftermarket solutions, supporting various industry certifications. Key strengths include flexible order quantities, responsive logistics tailored for international partners, and the ability to develop seals suited to harsh operating environments or unique client specifications.
Quick Comparison of Profiled Manufacturers
| Manufacturer | Brief Focus Summary | Website Domain |
|---|---|---|
| 5 best oil seal manufacturers | European standard, robust performance, excellent value | iquality.techinfus.com |
| Parjetseals | Durable, innovative crankshaft oil seals for OEMs worldwide | www.parjetseals.com |
| How to Choose the Best Auto Oil Seal Manufacturer | Global supplier, certified custom crankshaft oil seals | drorubber.com |
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for crankshaft seal oil
Key Technical Specifications for Crankshaft Seal Oil
International B2B buyers, particularly those operating in automotive, heavy machinery, or industrial sectors, must understand the technical specifications that determine the performance and compatibility of crankshaft seal oil. Assessing these properties is essential for ensuring reliability, reducing operational risks, and increasing equipment longevity.
1. Material Grade
– The composition of crankshaft seal oil must be compatible with various seal materials such as nitrile rubber (NBR), fluoroelastomer (FKM/Viton®), or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). The right oil minimizes chemical degradation, swelling, or hardening of the seals, especially in engines exposed to high temperatures or aggressive fuels. Certification or documentation of the oil’s compatibility with seal compounds is crucial to prevent premature seal failure.
2. Viscosity Index
– The viscosity index indicates how much the oil’s thickness changes with temperature. A high viscosity index ensures stable lubrication across a wide temperature range, which is particularly relevant in regions with hot climates (e.g., the Middle East, Africa) or equipment operating in extreme conditions. Reliable viscosity performance reduces leakage risk and supports consistent engine protection.
3. Thermal Stability
– Crankshaft seal oil must withstand prolonged exposure to high temperatures without oxidizing or breaking down. Good thermal stability prevents acid formation, deposits, or sludge that can damage seals and crankshaft surfaces. International buyers should request data sheets detailing heat resistance to align with local operating environments.
4. Additive Package
– Carefully formulated additives (such as anti-wear, anti-oxidation, and anti-foam agents) enhance oil performance and contribute to seal health. Some additives protect against corrosion or inhibit deposit formation, which is crucial for machinery running in humid, salty, or highly contaminated conditions found in various global markets.
5. Compatibility and OEM Approval
– Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) approvals or cross-reference guarantees that the crankshaft seal oil meets or exceeds equipment standards. Compatibility checks with both local and international OEMs ensure the oil will not void warranties or cause performance issues, reducing costly downtime or disputes.
6. Contaminant Resistance
– The ability of seal oil to resist contamination from dirt, water, or chemicals is vital, especially for buyers in environments prone to dust or harsh conditions (e.g., mining in South America, agriculture in North Africa). Superior protection minimizes maintenance frequency and operational interruptions.
Common B2B Trade Terminology
International procurement in the crankshaft seal oil segment often involves specific trade jargon. Understanding these terms enables B2B buyers to communicate precisely, negotiate effectively, and avoid costly misunderstandings.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Refers to the company that originally manufactured the engine or machinery. OEM-grade products meet the exact specifications required by the original maker, ensuring proper fit, performance, and warranty compliance. Always clarify if oil meets OEM standards relevant to your application.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– The smallest quantity a supplier will accept in an order. For international buyers, negotiating the lowest feasible MOQ is critical for inventory efficiency and cash flow management, particularly when consolidating shipments or testing new suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– A formal inquiry issued to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products. A well-structured RFQ should specify technical requirements (like viscosity, material compatibility, or certifications) to receive accurate and comparable quotations.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Standardized trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define buyer and seller responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, customs clearance, and delivery risk. Common Incoterms relevant to oil and seals include FOB (Free On Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight), and DDP (Delivered Duty Paid).
5. Lead Time
– The period between order placement and delivery. Buyers should confirm lead times for crankshaft seal oil, considering local customs clearance, shipping routes, and potential supply chain disruptions, especially with cross-continental logistics.
6. MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
– A detailed document outlining the safety, handling, and environmental properties of the oil. Ensuring that MSDS documents comply with local regulations in Africa, the Middle East, South America, or Europe is required for imports and workplace safety audits.
Actionable Insights:
Request comprehensive technical data and traceability documents from suppliers. Confirm local and international compliance—including OEM approvals, MSDS, and Incoterm agreements. Evaluate supplier responsiveness to RFQs and ability to meet MOQ and lead time requirements. This diligence helps B2B buyers minimize risk, optimize total cost of ownership, and ensure supply chain resilience in diverse regions.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the crankshaft seal oil Sector
Global Market Drivers and Current Sourcing Dynamics
The crankshaft seal oil sector, vital to both automotive and industrial equipment manufacturing, is experiencing steady growth propelled by increased vehicle production, stringent emission standards, and demand for improved machinery uptime. Emerging economies across Africa, South America, and the Middle East are witnessing robust expansion in transport, construction, and agricultural activities, directly influencing demand for high-performance engine parts such as crankshaft seals. European markets remain focused on vehicle electrification and advanced industrial maintenance, sparking interest in seals with greater durability and thermal resilience.
Key trends shaping sourcing strategies include:
- Material Innovation: There is a marked shift toward advanced elastomers (such as FKM/Viton, HNBR, and PTFE) to combat higher engine temperatures, aggressive lubricants, and extended service intervals. These materials are particularly important for buyers in regions with harsh climates or heavy-duty usage profiles.
- Supplier Diversification: Ongoing supply chain disruptions have pushed B2B buyers to diversify their supplier base, combining established global manufacturers with quality-driven regional players. This is especially relevant for importers in Africa and South America seeking reliable and timely delivery.
- Digital Procurement Platforms: The adoption of e-sourcing portals and direct-to-manufacturer online channels continues to accelerate. These platforms offer real-time inventory data, product customization options, and transparent compliance documentation, streamlining the supplier selection process for buyers in markets like Brazil or Egypt.
- Quality Assurance and Aftermarket Support: B2B purchasers are placing increased emphasis on suppliers who provide robust technical documentation (e.g., ISO/TS 16949, ISO 9001 certifications), warranty terms, and localized post-sales support—crucial for reducing downtime and managing total cost of ownership.
- Regulatory Compliance: Heightened attention to environmental and safety compliance is shaping purchase decisions, notably in Europe but increasingly in African and Middle Eastern import markets as environmental regulations tighten.
Sustainability Considerations and Ethical Sourcing
Sustainability is fast becoming a non-negotiable criterion in crankshaft seal oil procurement strategies, affecting purchasing decisions across global B2B landscapes. Environmental impact assessments focus on both the material lifecycle (from raw sourcing to disposal) and the manufacturing processes used by upstream suppliers.
Critical sustainability trends and best practices include:
- Eco-friendly Materials: Sourcing officers are prioritizing seals made from low-VOC elastomers, recyclable thermoplastic composites, and materials with certified reduced environmental footprints (such as those bearing RoHS or REACH compliance). Some European and Middle Eastern organizations now explicitly demand suppliers that minimize hazardous content.
- Green Manufacturing Certification: Look for vendors that operate under internationally recognized standards (ISO 14001 Environmental Management, for example). Such certifications assure buyers that suppliers are actively mitigating their environmental footprint across energy use, water management, and emissions.
- Transparency and Traceability: Ethical sourcing is underpinned by full traceability of material origins and supplier practices—important for buyers in regions where illegal mining or unethical labor practices might otherwise taint supply chains. Comprehensive supplier audits and digital traceability platforms are now vital components of larger tenders.
- Waste Reduction Initiatives: Suppliers that incorporate remanufacturing, circular economy principles, or take-back programs for used seals are gaining favor with sustainability-driven buyers.
- Global Certifications: Be aware of and request documentation pertaining to widely recognized standards, including ISO 9001 for quality assurance, ISO 14001 for environmental management, and regional eco-labels where applicable.
Market Evolution and Historical Context
Originally, crankshaft seals were rudimentary leather or felt components offering basic functionality and requiring frequent maintenance. With the rapid evolution of internal combustion engines in the mid-20th century, new synthetic materials and precision manufacturing techniques entered the market. The last two decades have been defined by a shift toward specialty elastomers and PTFE-based seals, dramatically enhancing longevity and thermal resistance. This transformation allows today’s seals to support far higher speeds, pressures, and oil retentions than their predecessors, positioning modern crankshaft seals as critical, high-value components within global supply chains. For international B2B buyers, this evolution underscores the importance of technical specification when evaluating suppliers—and the need to stay attuned to ongoing innovations poised to reduce total lifecycle costs and environmental impact.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of crankshaft seal oil
-
How do I effectively vet international suppliers of crankshaft seal oil to ensure product quality and reliability?
When selecting suppliers, request detailed company profiles, including years of operation, references, and export experience to markets similar to yours (e.g., Africa, the Middle East, or Europe). Insist on third-party audited certifications (such as ISO 9001 or IATF 16949), and review sample quality reports. Conduct video factory tours or arrange third-party inspections. Check trade references and verify if the supplier holds OEM approvals or works with reputable global brands. An initial small trial order can help assess responsiveness and ongoing support. -
Can suppliers provide customized formulations or packaging for crankshaft seal oil to meet regional or application-specific needs?
Many reputable manufacturers offer formulation adjustments to suit specific machinery, climate, or compliance requirements—crucial for buyers in regions with extreme heat (e.g., the Middle East) or humidity (e.g., Brazil). Engage suppliers early to discuss viscosity, additives, material compatibility, and desired temperature range. For packaging, request customization in container type, labeling (multilingual or local language), and volume (drums, IBCs, pails). Closely communicate technical specs and regulatory standards to ensure your supplied product is fit for purpose. -
What are typical Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) and lead times for bulk orders, and how can they be negotiated?
MOQs can vary significantly depending on manufacturer scale and your location—often starting from 1,000-5,000 liters or full pallet quantities, but flexible on request. Lead times for production and export typically range from 2-6 weeks. To negotiate lower MOQs (ideal when testing new suppliers or markets), leverage firm future order commitments or consolidated shipments. For urgent needs, explore supplier stock levels or regional distributors. Always formalize timelines and penalties for late shipments in the purchase agreement. -
Which quality assurance measures and certifications should buyers require when sourcing crankshaft seal oil internationally?
Insist on robust QA protocols, including batch traceability, Certificates of Analysis (COA) for each shipment, and adherence to ISO or automotive industry standards. Request Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS), and check for REACH, RoHS, or region-specific compliance (especially for the EU). Third-party lab testing results or sample retention policies add further assurance. For critical applications, ensure the oil’s formulation aligns with OEM specifications or industry benchmarks. -
What international payment terms are commonly accepted, and how can buyers minimize risks when dealing with overseas suppliers?
Popular payment terms include Telegraphic Transfer (T/T), Letters of Credit (L/C), and, for established relationships, Open Account or Documentary Collections. For first-time purchases, consider L/C or Escrow services to secure funds until confirmed shipment or product inspection. Always clarify incoterms (FOB, CIF, DAP) to avoid hidden costs. Use contracts drafted with clear dispute and jurisdiction clauses, and establish a pre-shipment inspection milestone before full payment. -
How can buyers manage shipping logistics, customs clearance, and delivery, particularly to Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
Partner with suppliers experienced in exporting to your region—this ensures proper documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, Certificate of Origin), knowledge of import duties, and compliance with local environmental regulations. Consider working with global freight forwarders who offer both sea and air options and can advise on port congestion or last-mile delivery solutions. For African, Middle Eastern, and South American destinations, verify if your supplier provides assistance with import licenses or local certifications. -
What steps should buyers take to resolve disputes over product quality, shipment delays, or incorrect documentation?
Maintain detailed written records at every stage—contract terms, communication logs, and evidence of discrepancies. Address issues immediately with the supplier’s designated contact. Most reputable suppliers include dispute mechanisms in their contracts, such as mediation or arbitration clauses valid in internationally recognized venues. For large-value shipments, consider trade credit insurance or involve your chamber of commerce. Timely reporting and documentation make claims resolution much smoother. -
Are there seasonal, regional, or regulatory factors that international buyers of crankshaft seal oil should anticipate?
Yes, plan for seasonal demand spikes (e.g., agricultural or construction peak seasons in Brazil or northern Africa) which can affect lead times and price volatility. In the EU, REACH compliance is mandatory; Egypt and other countries may require specific import permits or conformity certificates. Logistics can be affected by holidays (e.g., Ramadan, Carnival, or European summer holidays). Proactive ordering and regular regulatory monitoring help prevent delays and ensure continuous supply.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for crankshaft seal oil
For international B2B buyers, the sourcing of crankshaft seal oil is not just a matter of procurement—it is a strategic imperative affecting cost control, reliability, and long-term operational efficiency. Markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe face distinct demands and regulatory environments, which makes a tailored approach to supplier selection and quality assurance crucial. Key takeaways from this guide include the importance of prioritizing premium-grade materials, ensuring compatibility with local conditions, and partnering with suppliers who offer strong technical support and consistent lead times.
Strategic sourcing delivers multiple advantages:
– Risk mitigation: By vetting suppliers for material quality and production standards, buyers reduce the likelihood of premature seal failure and costly downtime.
– Total cost of ownership: Investing in superior crankshaft seal oil minimizes maintenance needs and avoids expensive repairs, outpacing the perceived savings from lower-cost, lower-quality alternatives.
– Operational resilience: Regularly reviewing and diversifying your supplier network ensures steady access to critical components even amid global supply chain fluctuations.
As global markets grow more interconnected and demand for high-performance crankshaft seals rises, proactive and informed sourcing will define future success. Buyers are encouraged to leverage data-driven decision-making, invest in supplier relationships, and continuously monitor product performance. Now is the time to elevate sourcing strategies—ensuring reliability, sustainability, and scalability in every market you serve.