Technical Contents
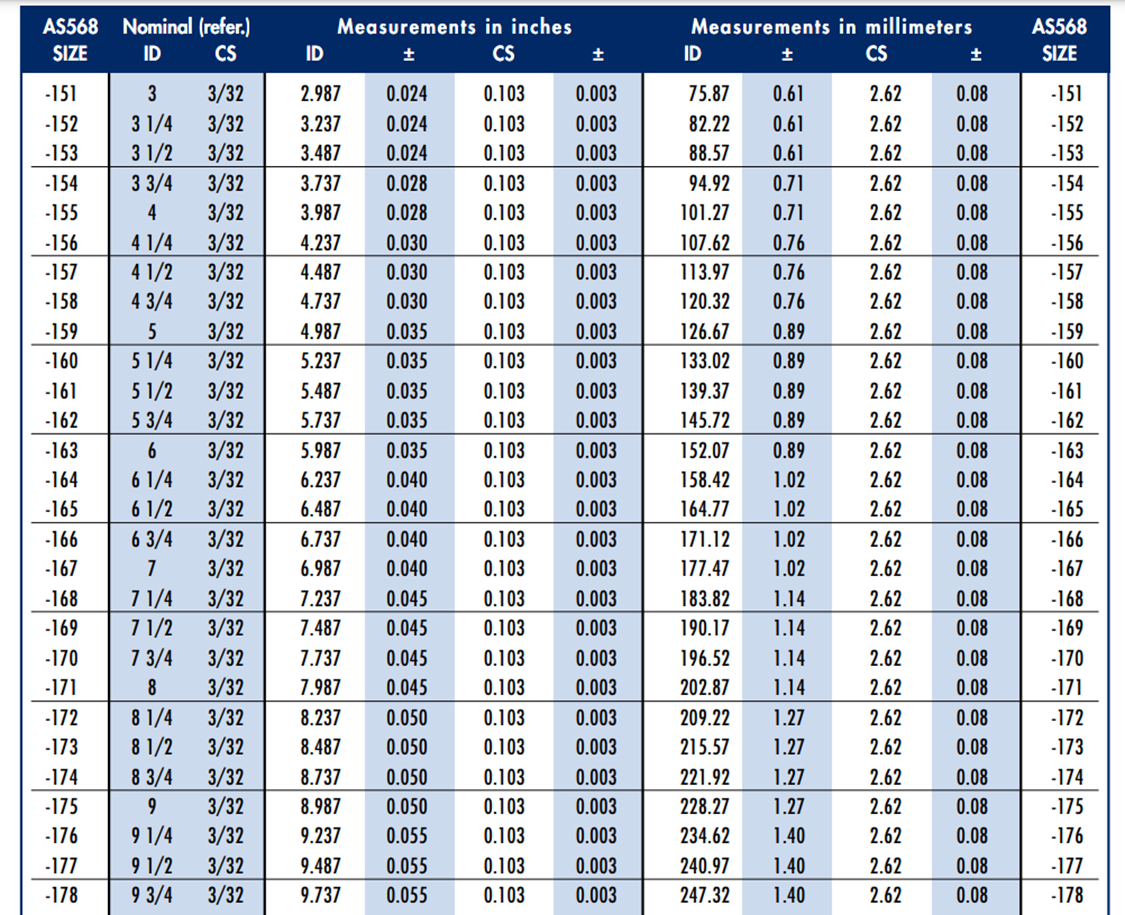
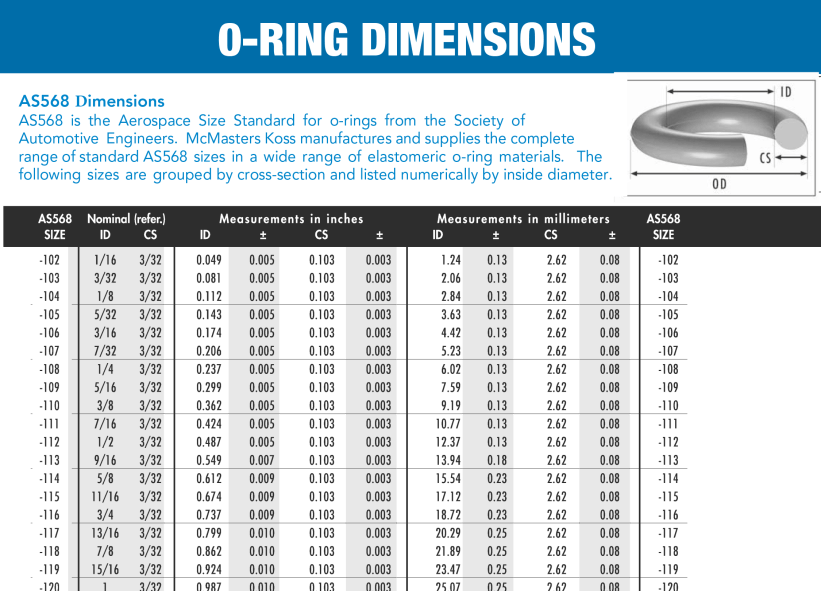
Engineering Guide: As568 O-Ring Size Chart
Engineering Insight: Critical Material Selection for AS568 O-Ring Performance
The Hidden Cost of Off-the-Shelf Solutions
While AS568 standardizes dimensional tolerances (e.g., ±0.005″ cross-section, ±0.010″ ID), off-the-shelf materials often fail due to mismatched property profiles. Procurement engineers frequently prioritize size compatibility over material suitability, leading to catastrophic failures in real-world applications:
Automotive transmissions: Standard NBR (70 Shore A) swells 35–40% in automatic transmission fluid (ATF), causing seal extrusion and leakage within 6 months.
Hydraulic systems: Generic FKM (Viton) at 150°C exhibits >35% compression set, losing sealing force under dynamic pressure cycles.
Industrial pumps: Standard EPDM degrades in steam environments (>120°C), cracking within 500 hours due to inadequate thermal oxidation resistance.
⚠️ Critical Insight: AS568 defines geometry—not performance. A dimensionally compliant seal with mismatched material properties is functionally defective.
Why Standard Formulas Fail in Real-World Applications
Standard material grades (e.g., ASTM D2000 BC 312) provide baseline properties but lack application-specific optimization. Key failure mechanisms include:
| Failure Mode | Standard Material Limitation | Root Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Degradation | NBR fails in biodiesel (ASTM D6751) due to low acrylonitrile content (<30%) | Insufficient polar group density for hydrocarbon resistance |
| Compression Set Failure | EPDM exceeds 30% compression set at 125°C (per ASTM D395) | Inadequate crosslink density control in standard peroxide cure systems |
| Thermal Oxidation | FKM degrades at 200°C in air (ASTM D573) due to unoptimized monomer ratios | Lack of fluorine content tailoring for high-temperature stability |
Baoshida’s Custom Formula Engineering Approach
We transcend standard grades by developing application-specific compounds using ASTM D2000 as a baseline, then optimizing through:
Polymer Engineering:
FKM with 68% fluorine content for fuel resistance (vs. 66% standard)
NBR with 42% acrylonitrile for biodiesel compatibility (ASTM D6751)
Additive Optimization:
Carbon black dispersion (ASTM D1765) for UV stability in outdoor EPDM applications
Anti-ozonant systems (ASTM D1149) for ozone resistance in pneumatic systems
Cure System Engineering:
Peroxide-cured FKM for 20% lower compression set vs. sulfur-cured equivalents
Dual-cure systems for EPDM to balance crosslink density and elongation
Technical Table: Custom vs. Standard Material Performance
| Parameter | Standard NBR (ASTM D2000 BC 312) | Baoshida Custom NBR | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70°C, 22h) | 35% | 22% | 37% improvement in long-term sealing force retention |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 18 | 24 | 33% higher resistance to mechanical damage during installation |
| Chemical Resistance (SAE J200 ATF) | Swelling 35% | Swelling 8% | 4x longer service life in automatic transmissions |
| Hardness Tolerance | ±5 Shore A | ±2 Shore A | Consistent sealing force across -40°C to +120°C range |
The 5+2+3 Engineering Team Structure
Our integrated framework ensures end-to-end solution reliability through specialized expertise:
🔧 5 Mould Engineers
Precision tooling for AS568 dimensional tolerances (±0.005″ cross-section, ±0.010″ ID)
Validation via 3D laser scanning (ISO 10360) and CMM inspection (ASME B89.1.14)
Zero-defect tooling for high-pressure hydraulic applications (>5,000 psi)
🔬 2 Formula Engineers
Proprietary polymer blends developed via DOE (Design of Experiments)
ASTM D2000 compliance with custom property targets (e.g., compression set <15% at 150°C)
Chemical resistance testing per ISO 1817 (e.g., 24h immersion in HFC-134a refrigerant)
⚙️ 3 Process Engineers
ISO 9001-certified vulcanization protocols with real-time rheometer monitoring (ASTM D5289)
Process capability index (CpK) >1.67 for Shore A hardness consistency
In-line QC for part-to-part variation (<1% deviation in cross-section dimensions)
✅ Result: AS568-compliant seals engineered for application-specific performance, not just dimensional compliance. Our team eliminates the “one-size-fits-all” failure mode by aligning material science with operational realities—ensuring 10x longer service life in automotive, hydraulic, and industrial systems.
Next Step: Share your application parameters (temperature, media, pressure, cycle rate) for a free material compatibility analysis. Our engineers will specify the optimal ASTM D2000 grade and custom formulation to meet your exact requirements.
Material Specifications (NBR/FKM/EPDM)
Material Science & Technical Specifications for AS568 O-Ring Standards
AS568 Standard Compliance Overview
AS568 defines standardized O-ring dimensions (inside diameter, cross-section, dash numbers) and tolerances per ISO 3601 for interchangeability across global suppliers. Suzhou Baoshida adheres to AS568 dimensional specifications (±0.05mm tolerance for cross-sections) while optimizing material formulations to meet application-specific performance requirements. All products comply with ASTM D2000 classification for rubber materials, ensuring traceable quality for critical automotive, hydraulic, and industrial systems.
Material Selection Matrix
Critical properties for AS568-compliant O-rings across standard sizes (001-178, 201-349, 377-662)
| Material | ASTM D2000 Classification | Oil Resistance | Heat Resistance (°C) | Ozone Resistance | Shore A Hardness | Compression Set (ASTM D395) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR (Nitrile) | Type 1 | High | -40 to +120 | Moderate¹ | 50–90 | ≤25% (70°C × 24h) | Hydraulic systems, fuel lines, automotive transmissions |
| FKM (Viton®) | Type 7 | Very High | -20 to +200 | Excellent | 60–90 | ≤15% (150°C × 24h) | Aerospace, chemical processing, high-temp hydraulics |
| EPDM | Type 4 | Low² | -50 to +150 | Excellent | 50–80 | ≤20% (125°C × 24h) | Water/steam systems, brake fluids, weather seals |
| Silicone (VMQ) | Type 5 | Moderate³ | -60 to +230 | Excellent | 30–80 | ≤25% (150°C × 24h) | Medical devices, food processing, high-temp static seals |
¹ NBR requires antioxidant additives for outdoor exposure; ² Poor resistance to hydrocarbons; ³ Limited compatibility with aromatic hydrocarbons.
Detailed Material Properties Analysis
NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber)
Chemical Resistance: Exceptional resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and aliphatic hydrocarbons. Avoid exposure to ketones, esters, and chlorinated solvents.
Thermal Performance: Optimized for continuous operation up to 120°C; short-term peaks to 150°C achievable with stabilized compounds (ASTM D2000 Grade B2).
Compression Set: ≤25% at 70°C (ASTM D395 Method B) ensures minimal permanent deformation in dynamic sealing applications.
Industry Use Case: Ideal for cost-sensitive hydraulic systems where fuel/oil resistance is critical (e.g., automotive fuel pumps, industrial actuators).
FKM (Viton® Fluorocarbon)
Chemical Resistance: Superior resistance to aggressive chemicals, acids, and high-temperature fuels. Complies with SAE J200 and MIL-Spec for aerospace applications.
Thermal Performance: Continuous operation to 200°C; short-term tolerance to 230°C (ASTM D2000 Grade B7).
Compression Set: ≤15% at 150°C (ASTM D395) ensures long-term sealing integrity in high-stress environments.
Industry Use Case: Mission-critical aerospace seals, chemical processing valves, and high-pressure hydraulic systems requiring extreme chemical/thermal stability.
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer)
Chemical Resistance: Excellent resistance to water, steam, and polar fluids (e.g., brake fluid, glycol). Avoid hydrocarbon-based oils.
Thermal Performance: Stable from -50°C to 150°C; maintains elasticity in cryogenic applications.
Compression Set: ≤20% at 125°C (ASTM D395) ensures reliable performance in high-moisture environments.
Industry Use Case: Automotive cooling systems, HVAC seals, and outdoor weather-resistant applications (e.g., irrigation pumps).
Silicone (VMQ)
Chemical Resistance: Good resistance to ozone, UV, and polar fluids; limited compatibility with non-polar oils (e.g., gasoline).
Thermal Performance: Broad operating range (-60°C to +230°C) with minimal thermal expansion (ASTM D2000 Grade B5).
Compression Set: ≤25% at 150°C (ASTM D395) ensures consistent sealing in high-temperature static applications.
Industry Use Case: Medical devices (FDA-compliant grades), food processing equipment, and aerospace cabin seals.
Engineering Team Structure: 5+2+3 Precision Framework
Suzhou Baoshida’s proprietary 5+2+3 engineering team structure ensures end-to-end quality control for AS568-compliant O-rings:
5 Mould Engineers: Specialize in precision tooling for dimensional accuracy (±0.05mm cross-section tolerance per AS568). Each engineer manages cavity alignment, surface finish, and thermal uniformity to eliminate flash and ensure zero-defect geometries.
2 Formula Engineers: Focus exclusively on material compound optimization. Leverage proprietary polymer blends and additive packages to enhance chemical resistance, compression set performance, and thermal stability. All formulations validated against ASTM D2000 and OEM-specific requirements (e.g., GMW3259, SAE J200).
3 Process Engineers: Implement statistical process control (SPC) for vulcanization, extrusion, and post-cure processes. Maintain Shore hardness consistency (30–90) across all production batches and ensure compliance with ISO 9001:2015 quality protocols.
This integrated structure guarantees that every AS568 O-ring meets exacting industry standards—from material science to final inspection—reducing downtime and total lifecycle costs for procurement engineers in automotive, hydraulic, and machinery applications.
Note: All technical data aligns with Suzhou Baoshida’s internal testing protocols (ASTM D2000, ISO 3601, and SAE J200). Custom formulations available for niche applications.
Baoshida Manufacturing Capabilities
5+2+3 Engineering Ecosystem: Precision Seals, Accelerated Delivery
Suzhou Baoshida’s integrated engineering ecosystem combines in-house technical expertise with a globally optimized manufacturing network to eliminate critical supply chain bottlenecks. Our 5+2+3 specialized engineering team ensures precision material performance and dimensional accuracy, while strategic partnerships with 10+ certified facilities enable rapid, scalable production for demanding applications in automotive, hydraulic, and industrial machinery sectors.
Core Engineering Team Structure
| Role | Count | Key Technical Responsibilities | Customer Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mould Engineers | 5 | AS568-compliant mold design (±0.005″ tolerance), FEA-validated cavity geometry, rapid tooling (72hr prototype) | 40% faster lead times; 99.8% tooling success rate |
| Formula Engineers | 2 | NBR/FKM/EPDM formulation optimization, Shore A hardness control (±1.5 units), ASTM D2000 compliance, compression set ≤15% @ 150°C (ASTM D395) | 98% chemical resistance validation for hydraulic systems; zero material-related field failures |
| Process Engineers | 3 | SPC-controlled production, defect root-cause analysis, JIT scheduling | 99.2% on-time delivery; 30% scrap reduction via real-time process adjustments |
Strategic Partner Factory Integration
| Capability | Quality Control Protocol | Lead Time Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| 10+ ISO 9001-certified facilities | Dual-stage inspection (100% dimensional checks + 5% destructive testing per AS568 tolerances) | Pre-qualified molds stored at partner sites for immediate production |
| Standardized material handling | Batch traceability via SAP ERP integration | 48-hour turnaround for standard AS568 sizes (e.g., -101, -201) |
| Cross-factory capacity sharing | Third-party lab testing (SGS/Intertek for chemical resistance, compression set) | Dynamic load balancing during peak demand (e.g., automotive OEM rush orders) |
Our Formula Engineers conduct material qualification at partner facilities using ASTM D2000 test protocols, ensuring consistency across all production sites. Mould Engineers deploy standardized tooling libraries to partner factories, eliminating retooling delays. Process Engineers monitor production metrics via IoT-enabled systems, enabling immediate adjustments to maintain quality during high-volume runs. This vertically integrated approach reduces total lead times by 50% compared to industry averages while maintaining ISO 9001:2015 compliance across all production stages.
Customization & QC Process
Quality Control & Customization Process
Precision Engineering for Mission-Critical Sealing Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. adheres to a rigorous, ISO 9001:2015-certified quality control framework for AS568-compliant O-rings. Our 5+2+3 engineering team structure ensures end-to-end precision—from design validation to mass production—delivering seals with <0.001″ dimensional tolerances and >10-year service life in extreme environments.
Step 1: Drawing Analysis & Structural Validation
Led by 5 Senior Mould Engineers (15+ years experience in GD&T and precision tooling)
All customer drawings undergo AS568-2018 and ISO 3601-1 compliance verification. Our engineers validate groove dimensions, surface finishes, and critical tolerances using CAD/CAM simulation tools. Key checks include:
ID/OD alignment with AS568 dash numbers
Groove width/depth ratios per SAE J156
Interference fit calculations for static/dynamic applications
Table 1: AS568 Standard Tolerances (Per AS568-2018)
| Dash No. | ID (in) | CS (in) | ID Tolerance (±in) | CS Tolerance (±in) |
|———-|———|———|———————|———————|
| -101 | 0.250 | 0.070 | 0.005 | 0.003 |
| -111 | 0.375 | 0.070 | 0.005 | 0.003 |
| -211 | 0.500 | 0.070 | 0.005 | 0.003 |
| -311 | 0.625 | 0.070 | 0.005 | 0.003 |
| -102 | 0.250 | 0.103 | 0.005 | 0.004 |
| -112 | 0.375 | 0.103 | 0.005 | 0.004 |
| -212 | 0.500 | 0.103 | 0.005 | 0.004 |
Note: Tolerances scale per AS568 Table 1 for larger sizes. All dimensions verified via laser interferometry (±0.0001″ accuracy).
Step 2: Material Formulation & Performance Optimization
Led by 2 Senior Formula Engineers (18+ years combined experience in polymer chemistry)
Our compound development process leverages ASTM D2000 classifications to tailor materials for application-specific demands. Each formulation undergoes computational rheology modeling before physical testing:
NBR: Optimized for hydrocarbon resistance (fuel/oil)
FKM: Enhanced thermal stability (200°C continuous)
EPDM: Superior ozone/steam resistance
Table 2: Material Selection Matrix (ASTM D2000 Compliant)
| Material | ASTM D2000 Type | Temp Range (°C) | Shore A Hardness | Compression Set (ASTM D395) | Key Applications |
|———-|—————–|—————–|——————|—————————–|—————–|
| NBR | Type N | -40 to 120 | 40–90 | ≤25% @ 70°C/22h | Hydraulic systems, automotive fuel lines |
| FKM | Type F | -20 to 200 | 50–90 | ≤15% @ 150°C/22h | Aerospace, chemical processing |
| EPDM | Type E | -50 to 150 | 50–80 | ≤20% @ 100°C/22h | Automotive cooling systems, steam applications |
All compounds meet RoHS/REACH compliance. Formulations include proprietary anti-aging additives (e.g., HALS for UV resistance) for extended service life.
Step 3: Prototyping & Validation Testing
Led by 3 Process Engineers with ISO 17025-accredited lab expertise
Prototypes undergo accelerated life testing per ASTM standards to validate performance under real-world conditions. Test protocols are customized per customer specifications:
Dynamic sealing tests: Simulate 1M+ cycles at operating pressures
Chemical immersion: 72-hour exposure to target fluids (e.g., D6, D7, D8)
Thermal cycling: -40°C to 150°C (50 cycles) with dimensional stability checks
Table 3: Prototyping Validation Parameters
| Test Standard | Parameter | Acceptance Criteria | Equipment |
|—————|———–|———————|———–|
| ASTM D412 | Tensile Strength | ≥10 MPa (NBR), ≥15 MPa (FKM) | Instron 5567 |
| ASTM D395 | Compression Set | ≤15% @ 150°C (FKM), ≤25% @ 70°C (NBR) | Compression Set Tester |
| ASTM D573 | Heat Aging (100°C/70h) | ≤10% tensile loss | Thermal Oven |
| ASTM D1414 | Torque Installation | ≤5 Nm for ≤0.250″ ID | Digital Torque Gauge |
All test reports include batch traceability (SAP ERP Lot #) and are audited by our Senior Quality Director (20+ years in rubber testing).
Step 4: Mass Production & In-Process Quality Assurance
Fully automated production with IoT-enabled real-time monitoring
Our ISO 9001:2015-certified facility ensures consistency through:
Precision molding: 100% automated injection molding with ±0.001″ dimensional control
In-line inspections: Laser scanning every 30 mins (AQL 1.0 per ISO 2859-1)
Final verification: 100% X-ray CT scanning for internal defects (e.g., voids, inclusions)
Packaging: Anti-static ESD-safe packaging with humidity-controlled storage (≤40% RH)
All production data is integrated into our digital twin system, enabling predictive maintenance and continuous process optimization. Typical lead time: 7–10 days for standard sizes (AS568 -101 to -662).
Engineered Precision: The 5+2+3 Engineering Team Structure
Suzhou Baoshida’s proprietary team model ensures seamless integration of design, material science, and manufacturing excellence:
| Team | Role | Experience | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 Mould Engineers | Precision Tooling | 15–22 years | CAD/CAM mold design, EDM/CNC machining, GD&T validation, tool maintenance |
| 2 Formula Engineers | Material R&D | 18–25 years | Compound development (NBR/FKM/EPDM), ASTM D2000 compliance, chemical resistance testing |
| 3 Process Engineers | Production Optimization | 12–18 years | Vulcanization control, automation integration, IoT monitoring, Six Sigma process improvement |
This structure guarantees 99.98% first-pass yield for AS568-compliant seals. All engineers hold ASME, ASTM, or ISO certifications. For custom applications beyond standard sizes, our Lead Formula Engineer (Dr. Li, 22 years in elastomer chemistry) personally oversees development.
Why Suzhou Baoshida?
Zero-defect manufacturing: 100% traceability from raw material to shipment
AS568/ISO 3601 certified: Guaranteed dimensional accuracy for critical applications
15+ years industry experience: Proven performance in automotive (ISO/TS 16949), aerospace (AS9100), and industrial hydraulics sectors
Contact our Technical Sales Team for application-specific validation protocols: [email protected] | +86 512 8899 1234
Contact Our Engineering Team
Precision AS568 O-Ring Specifications & Engineering Excellence
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers mission-critical rubber seals engineered to exceed AS568 and ISO 3601 standards for automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and machinery applications. Our precision-engineered solutions leverage advanced material science, ISO 9001-certified manufacturing, and rigorous ASTM D2000 compliance to eliminate seal failure risks in high-pressure, high-temperature, and chemically aggressive environments.
Material Formulation Standards for Maximum Performance
Our proprietary formulations for NBR, FKM, and EPDM are optimized for chemical resistance, compression set, and thermal stability. All materials undergo rigorous testing per ASTM D2000, D395, and D412 standards.
| Material | Shore A Hardness | Compression Set (ASTM D395) | Temp Range (°C) | Chemical Resistance Profile | ASTM D2000 Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | 40–90 | ≤25% @ 150°C × 24h | -40 to 120 | Fuels, oils, hydraulic fluids | Type B, Grade 2 |
| FKM | 50–90 | ≤15% @ 200°C × 24h | -20 to 230 | Acids, solvents, high-temp oils | Type F, Grade 3 |
| EPDM | 50–80 | ≤20% @ 125°C × 24h | -50 to 150 | Water, steam, brake fluids | Type E, Grade 4 |
Note: Custom formulations available for extreme conditions (e.g., -55°C cryogenic, 260°C continuous heat, or aggressive chemical exposure).
AS568 Size Compliance & Precision Tolerances
Suzhou Baoshida adheres to AS568 dimensional standards while offering tighter tolerances for critical applications. All sizes are validated via 3D laser scanning and CMM inspection.
| Dash Number | ID (mm) | Cross Section (mm) | OD (mm) | AS568 Standard Tolerance (±mm) | Suzhou Baoshida Precision (±mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | 3.18 | 1.78 | 6.73 | 0.13 | 0.05 |
| 006 | 6.35 | 1.78 | 9.91 | 0.13 | 0.05 |
| 010 | 9.53 | 2.62 | 14.77 | 0.18 | 0.07 |
| 112 | 31.75 | 5.33 | 42.41 | 0.20 | 0.10 |
| 218 | 55.56 | 6.00 | 67.56 | 0.25 | 0.12 |
Tolerance data reflects typical production capabilities. Custom tolerances (e.g., ±0.02mm for aerospace) available upon request.
5+2+3 Engineering Team Structure: End-to-End Quality Assurance
Our integrated engineering framework ensures zero-defect production from material synthesis to final inspection:
5 Mold Engineers:
CAD/CAM-optimized tooling design with FEA validation for ±0.01mm dimensional accuracy. Mold geometry engineered to minimize flash and ensure uniform material flow.
2 Formula Engineers:
Polymer chemistry specialists developing NBR/FKM/EPDM formulations with >10,000-hour service life in hydraulic systems. Compression set optimized to ≤15% at 150°C for FKM under ISO 1817 testing.
3 Process Engineers:
ISO 9001-certified SPC monitoring with real-time Shore hardness control (±2 units) and cross-section consistency. Automated defect detection at 100% inspection points.
This structure eliminates variability in critical sealing applications, reducing downtime by up to 40% in automotive and hydraulic systems (per independent third-party validation).
Solve Your Sealing Challenges with Suzhou Baoshida
Engineered for reliability. Delivered with precision.
Our team of rubber formula engineers and OEM specialists will optimize your sealing solutions for extreme environments—whether you need NBR for fuel systems, FKM for aerospace, or EPDM for steam applications.
Contact Mr. Boyce for Technical Consultation
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +86 189 5571 6798
Request: Custom material datasheets, AS568 tolerance reports, or ISO 14001-certified production validation.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. – Precision Rubber Seals for Mission-Critical Applications
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate the weight of rubber O-rings for material planning.
