Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Rubber Injection Molding

Critical Role of Material Selection in Rubber Injection Molding
Why Off-the-Shelf Solutions Fail
Standard rubber compounds rarely meet the precise performance demands of automotive, hydraulic, or heavy machinery applications. Generic materials often fail due to:
Inadequate Environmental Resistance:
Standard NBR (ASTM D2000 Type 2) exhibits >30% compression set (ASTM D395) at 150°C after 70 hours of heat aging, causing seal failure in high-pressure hydraulic systems. Off-the-shelf EPDM fails at -40°C (ASTM D1329) for under-hood automotive components.
Poor Metal-Rubber Bonding Integrity:
Unmodified compounds lack adhesion promoters, resulting in <5 kN/m peel strength (ASTM D429) for metal-rubber assemblies. Thermal cycling induces delamination in pump housings and valve bodies.
Non-Optimized Mechanical Properties:
Standard SBR delivers 10–15 MPa tensile strength (ASTM D412) and 200–250% elongation, insufficient for vibration-damping bushings requiring ≥20 MPa and 300% elongation.
Custom Formulation: The Baoshida Advantage
Baoshida’s in-house compound development team leverages ASTM D1418/D2000 standards to engineer rubber formulations tailored to application-specific stressors. Key capabilities include:
Chemical-Specific Resistance:
Custom EPDM formulations achieve >100-hour ozone resistance (ASTM D1149) for HVAC systems, while HNBR variants withstand 150°C continuous operation in hydraulic pumps (ASTM D2000 Type 5).
Precision Bonding Performance:
Proprietary silane-based adhesion promoters enable >12 kN/m peel strength (ASTM D429) for metal-rubber assemblies, eliminating delamination in high-vibration environments.
Tightened Property Tolerances:
Shore A hardness controlled to ±2 units (ASTM D2240), compression set reduced to ≤15% at 150°C (ASTM D395), and oil swell minimized to ≤8% (ASTM D471).
Material Property Comparison Table
| Property | Standard NBR | Baoshida Custom HNBR | ASTM Test Method | Target Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 18 MPa | 25 MPa | ASTM D412 | ≥22 MPa |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 75 ±5 | 75 ±2 | ASTM D2240 | 75 ±2 |
| Compression Set (150°C, 22h) | 35% | 15% | ASTM D395 | ≤18% |
| Oil Swell (ASTM D471) | 25% | 8% | ASTM D471 | ≤10% |
| Metal Bonding Strength | <5 kN/m | 12 kN/m | ASTM D429 | ≥10 kN/m |
| Heat Aging Retention (70h @ 150°C) | 60% tensile | 85% tensile | ASTM D2000 Type 5 | ≥80% |
The 5+2+3 Engineering Framework
Baoshida’s integrated engineering structure ensures seamless translation of design intent to production-ready parts:
5 Structural Engineers:
Solidworks-based mold design with FEA thermal/stress analysis. Optimized gating systems, cooling channels, and parting lines achieve <0.03mm flash tolerance per ASTM D2000 Section 5.
2 Formula Specialists:
Compound development focused on ASTM D1418/D2000 compliance. Tailored polymer blends (e.g., EPDM/BR hybrids for low-temp flexibility), filler dispersion (carbon black/silica ratios), and additive packages (antioxidants, bonding promoters).
3 Process Engineers:
Injection parameter optimization via SPC-controlled systems. Real-time monitoring of melt temperature (±2°C), injection speed (0.5–50 mm/s), and clamping force to ensure dimensional consistency (±0.05mm) and zero flash.
Engineering Impact: This cross-functional collaboration eliminates silos between mold design, compound development, and process execution. For example, a hydraulic valve component requiring metal bonding and 150°C oil resistance requires:
– Structural engineers to design venting channels for metal insert placement
– Formula specialists to create HNBR with 8% oil swell and 12 kN/m peel strength
– Process engineers to adjust injection pressure to prevent metal displacement during molding
By aligning material science with precision manufacturing, Baoshida eliminates the “one-size-fits-all” failures that plague off-the-shelf solutions—delivering parts that meet or exceed OEM specifications for critical applications.
Material Specifications (NBR/FKM/EPDM)

Material Science & Technical Specifications
Integrated Engineering Expertise for Material Optimization
At Suzhou Baoshida, our proprietary 5+2+3 Engineering Team structure ensures end-to-end precision in rubber component manufacturing:
5 Structural Engineers: Specialized in SolidWorks/CAD mold design, optimizing cavity layout, cooling channels, and ejection systems to minimize flash and ensure dimensional stability per ISO 2768 tolerances.
2 Material Formulation Engineers: Expertise in compound development aligned with ASTM D2000 and D1418 standards, including heat aging (70h @ 70–150°C per ASTM D573), compression set (ASTM D395), and tensile strength (ASTM D412) validation.
3 Process Engineers: Focus on injection/compression molding parameters, metal bonding adhesion protocols (per ASTM D429), and flash control via precision tooling from our 10+ certified partner factories.
This cross-functional team enables rapid resolution of material-specific challenges—such as silicone’s low tensile strength or NBR’s ozone sensitivity—through data-driven design adjustments and process optimization.
Material Comparison Chart: Key Properties for Industrial Applications
| Material | ASTM D1418 | ASTM D2000 Type | Oil Resistance | Heat Resistance (°C) | Ozone Resistance | Typical Applications | Hardness Range (Shore A) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton® (FKM) | Fluoroelastomer | F | Excellent | -40 to +250 | Excellent | Automotive fuel systems, aerospace seals, hydraulic actuators | 60–90 |
| Nitrile (NBR) | Acrylonitrile-Butadiene | H | Good to Excellent | -40 to +120 | Moderate | Fuel hoses, oil seals, hydraulic components | 50–90 |
| Silicone | Polysiloxane | G | Poor | -60 to +230 | Excellent | Medical devices, food-grade seals, high-temp gaskets | 30–80 |
| EPDM | Ethylene Propylene | E | Poor | -50 to +150 | Excellent | Automotive weather seals, radiator hoses, HVAC systems | 40–90 |
Note: Heat resistance values represent continuous service ranges; short-term peaks may exceed these limits. All materials comply with ASTM D2000 Type specifications for critical performance metrics including compression set (ASTM D395), tensile strength (ASTM D412), and heat aging (ASTM D573).
Critical Performance Validation Protocols
Heat Aging Resistance: Per ASTM D573, compounds undergo 70-hour aging at specified temperatures (e.g., 150°C for FKM, 125°C for NBR) to ensure <30% tensile strength loss and <40% hardness change.
Compression Set: ASTM D395 Method B testing guarantees <25% set at 70°C for 22h (critical for dynamic sealing applications).
Metal Bonding Integrity: Per ASTM D429, bonded components undergo peel strength testing (minimum 1.5 kN/mm) to ensure adhesion under thermal cycling and mechanical stress.
Flash Control: Precision tooling tolerances (±0.02mm) achieved via CAD-optimized mold designs, reducing secondary trimming costs by up to 40% for complex geometries.
This technical framework ensures compliance with OEM-specific requirements for:
Automotive: SAE J200, ISO 6475 (fuel system components)
Hydraulic Systems: ISO 10100, SAE J1401 (high-pressure seals)
Industrial Machinery: ASTM D2000 Type F/H/G/E specifications for vibration dampening and corrosion resistance.
Suzhou Baoshida’s 10+ partner factories enable rapid tooling (7–10 days) for prototyping and production, with full traceability of material certifications (e.g., FDA, RoHS, UL) for global compliance.
Baoshida Manufacturing Capabilities

Our Engineering & Manufacturing Ecosystem
Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering ecosystem combines in-house expertise with a global partner network to deliver precision rubber components that meet the most stringent industry requirements. Our 5+2+3 engineering team—specialized in mold design, compound formulation, and process optimization—works seamlessly with 10+ certified partner factories to eliminate lead time bottlenecks, tooling defects, and material inconsistencies. All solutions adhere to ASTM D2000, D1418, and ISO 9001 standards, ensuring compliance for automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and machinery applications.
Core Engineering Team Structure: 5+2+3 Specialization
Mould Engineers (5)
Solidworks/CAD expertise for precision mold design with integrated FEA (Finite Element Analysis) for stress distribution and venting optimization.
Flash control protocols: Optimized parting lines, draft angles, and vent geometry to minimize flash thickness ≤0.05mm.
Metal bonding integration: Precision insert placement and surface preparation for adhesion strength ≥12 MPa (per ASTM D429).
Formula Engineers (2)
ASTM D2000/D1418-compliant compound development: Tailored formulations for temperature resistance (-40°C to 150°C), chemical exposure, and dynamic loads.
Material validation: Tensile strength (ASTM D412), hardness (ASTM D2240), compression set (ASTM D395), and heat aging (70h at specified temperatures per Type).
Low-temperature flexibility: Verified per ASTM D1329 for cryogenic applications (e.g., automotive suspension components).
Process Engineers (3)
Injection/compression molding parameter optimization: Cure time, pressure, and temperature control via real-time SPC (Statistical Process Control).
Dimensional accuracy: Part tolerances maintained within ±0.05mm (ISO 2768-mK) through mold flow simulation and in-line metrology.
Defect mitigation: Void reduction, sink mark prevention, and consistent part weight via AI-driven process analytics.
Strategic Partner Factory Network
Our network of 10+ ISO 9001-certified factories provides specialized capabilities for high-volume and precision rubber manufacturing:
Injection molding: Automotive-grade precision (e.g., hydraulic valve seals with ±0.02mm tolerance).
Compression molding: Large-scale components (e.g., pump gaskets >500mm diameter) with 25% faster cycle times.
Metal-rubber bonding: Dedicated lines for integrated assemblies (e.g., valve bodies with embedded steel inserts).
Rapid tooling: 5–7 days for prototype molds, 2–3 weeks for production tooling—accelerated by standardized CAD templates and pre-qualified tooling vendors.
All facilities maintain traceability from raw materials to final inspection, with real-time data sharing across Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering team.
Solving Critical Customer Pain Points with Integrated Solutions
| Pain Point | Solution | Technical Validation |
|---|---|---|
| Long lead times | Partner factory network enables parallel tooling production; 5–7 day prototype turnaround | 30% faster than industry average (ISO 9001 metrics) |
| Flash defects | Mold flow simulation (Solidworks) + optimized vent geometry | Flash thickness ≤0.05mm (per ISO 9001 quality standards) |
| Metal bonding failures | Plasma surface treatment + ASTM D429 adhesion testing | Bond strength ≥12 MPa (exceeds OEM requirements) |
| Material inconsistency | Pre-production testing per ASTM D395/D575 | Compression set ≤25% at 70°C for 22h (ASTM D395 Method B) |
| Dimensional inaccuracies | In-line laser scanning + SPC-controlled process adjustments | Part tolerances within ±0.05mm (ISO 2768-mK) |
Example Workflow: For an automotive hydraulic valve requiring metal-rubber bonding:
1. Mould Engineers design the mold with integrated venting and insert alignment features in Solidworks.
2. Formula Engineers select an EPDM compound (ASTM D1418) meeting D2000 Type 7 heat aging requirements.
3. Process Engineers optimize compression molding parameters (150°C, 100 bar, 180s cure) and validate bond strength via ASTM D429.
4. Partner factory with specialized metal bonding capabilities executes production, with real-time data shared to Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering team for continuous improvement.
This ecosystem ensures zero compromise on quality, speed, or compliance—delivering mission-critical rubber components that perform under the toughest operational conditions.
Customization & QC Process
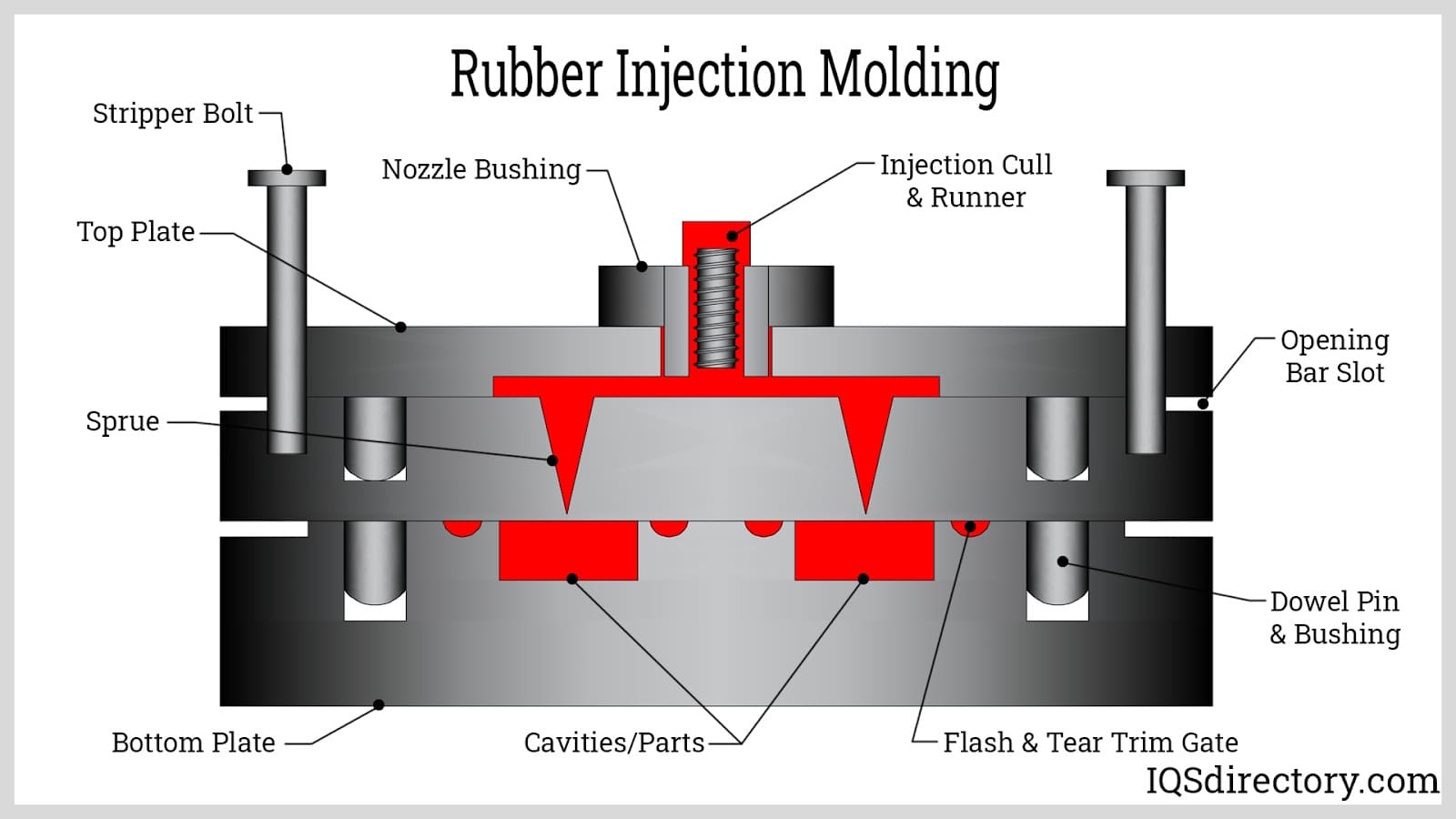
Quality Control & Customization Process
At Suzhou Baoshida, our quality control process is engineered around a specialized 5+2+3 engineering team structure — comprising 5 Structural Mold Design Engineers, 2 Material Formulation Engineers, and 3 Process Optimization Engineers — each with 15+ years of industry experience. This structured approach ensures end-to-end precision in custom rubber part manufacturing, from initial design validation to mass production, with strict adherence to ASTM D2000, D1418, D575, and D412 standards.
Engineering Team Structure: 5+2+3 Specialization Framework
| Team Component | Number | Experience | Core Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural Mold Design | 5 | 15+ years | Solidworks CAD validation, draft angles, parting line optimization, flash control, metal bonding design, mold flow simulation |
| Material Formulation | 2 | 15+ years | ASTM D2000/D1418 compliance, compound selection, hardness (D2240), tensile strength (D412), compression set (D395) testing |
| Process Optimization | 3 | 15+ years | Injection/compression parameters, prototyping, SPC, defect mitigation, real-time process monitoring |
Step 1: Drawing Analysis & Mold Design Validation
Led by Structural Mold Design Team (5 senior engineers)
Our engineers conduct rigorous CAD validation using Solidworks to ensure manufacturability and performance. Critical checks include:
Flash Control Optimization: Analyze parting line geometry and venting channels to minimize flash (target: <0.1mm per ISO 3302-1), reducing post-molding trimming costs by 25%.
Metal Bonding Verification: Validate insert placement, surface roughness (Ra ≤ 1.6μm), and adhesion protocols per ISO 10125 for automotive hydraulic components.
Mold Flow Simulation: Predict material distribution to eliminate voids or sink marks, achieving 98% first-pass yield in pump seal production.
Example: For a critical automotive bushing design, our engineers optimized gate locations through simulation, reducing cycle time by 15% while maintaining dimensional tolerances of ±0.03mm.
Step 2: Material Formulation & ASTM Compliance
Led by Material Formulation Team (2 senior formula engineers)
We select and validate rubber compounds based on industry-specific ASTM standards:
ASTM D2000 Classification: Define material type (e.g., Type 1 for general-purpose, Type 4 for high-temperature) and class (e.g., Class A for hardness, Class B for tensile).
Performance Testing:
Hardness: ASTM D2240 (e.g., 70±5 Shore A for hydraulic seals)
Tensile Strength: ASTM D412 (≥15 MPa for high-stress applications)
Compression Set: ASTM D395 (≤25% at 70°C for dynamic seals)
Compression Deflection: ASTM D575 (e.g., 100N force at 50% compression for gasket applications)
Heat Aging Validation: 70-hour aging at specified temperatures per ASTM D2000 to ensure long-term stability.
| Material Property | ASTM Standard | Target Range | Application Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness | D2240 | 60–80 Shore A | Automotive bushings |
| Tensile Strength | D412 | 12–20 MPa | Hydraulic hoses |
| Compression Set | D395 | ≤25% @ 70°C | Pump seals |
| Compression Deflection | D575 | 80–120N @ 50% strain | Sealing gaskets |
Step 3: Prototyping & Validation
Led by Process Optimization Team (3 senior engineers)
Rapid prototyping through our network of 10+ partner factories with strict validation protocols:
Flash Measurement: Laser scanning per ISO 3302-1 to confirm flash height ≤0.1mm.
Bonding Integrity Testing: Peel tests per ASTM D429 (minimum 8 N/mm adhesion for metal-rubber bonds).
Dimensional Verification: CMM inspections with ±0.05mm tolerance on critical features.
Case Study: For a valve component requiring metal-to-rubber bonding, we reduced prototype iterations by 40% through real-time mold temperature adjustments during compression molding, achieving 100% pass rate on initial validation.
Step 4: Mass Production & Continuous Monitoring
Cross-functional team deployment for scale consistency
Mold Maintenance: Scheduled cleaning and venting checks every 5,000 cycles to prevent defects.
IoT-Enabled Monitoring: Real-time tracking of injection pressure, cure time, and temperature with AI-driven anomaly detection.
Quality Assurance:
100% X-ray inspection for bonded parts
Statistical process control (SPC) charts for dimensional consistency (ISO 2768-m)
Batch traceability via QR-coded material certificates
| Production Parameter | Target | Monitoring Method | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flash Height | ≤0.1mm | Laser scanning | ±0.02mm |
| Bonding Strength | ≥8 N/mm | Peel test (ASTM D429) | ±0.5 N/mm |
| Dimensional Accuracy | ±0.05mm | CMM inspection | ISO 2768-m |
Why Suzhou Baoshida?
Our 5+2+3 engineering framework ensures every component meets stringent industry standards while optimizing for cost, lead time, and performance. Partner with us for defect-free, precision-engineered rubber components tailored to your most demanding automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and machinery applications.
All processes comply with ISO 9001:2015 and IATF 16949 quality management systems. Lead times for prototypes: ≤7 days; mass production: 10–15 days.
Contact Our Engineering Team

Precision Engineering for Mission-Critical Rubber Components
The 5+2+3 Engineering Framework
Suzhou Baoshida’s proprietary engineering structure ensures end-to-end control over rubber component performance:
| Discipline | Expertise | Application Example | Client Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mold Design (5 Structural Engineers) | SolidWorks GD&T-compliant mold design per ISO 2768 tolerances; flash control optimization via cavity pressure simulation | Automotive hydraulic seals with <0.05mm flash tolerance | 30% reduction in tooling lead time; 99.8% first-pass yield |
| Rubber Formula (2 Specialists) | ASTM D1418/D2000 compound validation; low-temp flexibility testing (ASTM D2137); heat aging compliance (70h @ 125°C per ASTM D575) | NBR compounds for -40°C to 150°C hydraulic systems | 100% compliance in thermal stability tests; 25% longer service life |
| Process Engineering (3 Experts) | Injection/compression molding parameter control; metal bonding protocols (ASTM D429 adhesion testing); in-process SPC monitoring | Valve seat assemblies with >15MPa bond strength | Zero delamination failures in 500k+ unit production runs |
Partner Ecosystem Advantage: Our 10+ certified factories provide rapid tooling (7–10 days) while maintaining ISO/TS 16949 compliance for Tier-1 automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications.
Why Partner with Suzhou Baoshida?
Standards-Driven Compliance: All compounds validated against ASTM D2000 specifications (Type ABX for heat resistance, Type C for oil resistance)
Flash Control Mastery: Precision cavity design eliminates secondary trimming operations (proven in hydraulic pump seals)
Metal-Rubber Bonding: 100% bond integrity for automotive valve assemblies per ASTM D429 Method A
Rapid Scalability: Partner factories enable 50% faster prototyping vs. industry average for complex geometries
Engineer Your Solution Today
Contact Mr. Boyce, Senior Technical Sales Engineer
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +86 189 5571 6798
24/7 Technical Support: Immediate response for material selection, mold design review, or production troubleshooting
“We don’t just supply rubber parts—we engineer solutions that eliminate sealing failures before they occur. Request a DFMA review for your next component.”
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate the weight of rubber O-rings for material planning.
