Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Molded Rubber Seal

Critical Role of Material Selection in Rubber Seal Performance
The Cost of Compromise: Why Standardized Solutions Fail
Off-the-shelf rubber seals often fail under real-world operational stresses due to generic material formulations that ignore application-specific variables. Industry data shows 68% of seal failures in hydraulic systems stem from material incompatibility or improper hardness selection. Common failure modes include:
| Failure Cause | Off-the-Shelf Issue | Consequence | Real-World Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Incompatibility | Standard NBR used in phosphate ester hydraulic fluids | Swelling >15%, loss of tensile strength | Catastrophic system leaks in aerospace actuators |
| Hardness Mismatch | Shore A 70 seals in >300 bar hydraulic systems | Extrusion into gaps, surface abrasion | 40% downtime in heavy machinery due to seal failure |
| Compression Set Exceedance | ASTM D2000 Grade 2 (≤40%) vs. required Grade 1 (≤30%) | Progressive loss of sealing force after 500h operation | 30% higher maintenance costs in automotive transmissions |
Example: A generic NBR seal in an EV battery cooling system exposed to glycol-based coolants degrades within 6 months due to inadequate chemical resistance—whereas a custom EPDM formulation with 15% silica reinforcement maintains integrity for >5 years.
Decoding ASTM D2000: The Industry Standard for Precision Specifications
ASTM D2000 is the definitive framework for specifying rubber materials in critical applications. It standardizes performance metrics through a coded nomenclature system that eliminates ambiguity between suppliers and buyers. Key parameters directly impact seal longevity:
| ASTM D2000 Parameter | Code Structure | Technical Meaning | Automotive/Hydraulic Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | A, B, C, D | Base polymer classification | A = NBR (oil resistance), B = FKM (high-temp/chemical), C = EPDM (weather/coolant) |
| Class | 1, 2, 3, 4 | Heat aging temperature (°C) | Class 1 (70°C) for standard automotive, Class 3 (125°C) for turbocharger seals |
| Grade | 1, 2, 3 | Compression set (%) after 70h aging | Grade 1 (≤30%) for critical hydraulic systems, Grade 2 (≤40%) for general use |
| Hardness | Shore A 30-90 | Material stiffness | Hydraulic pumps: 75-85 Shore A, Low-force valve seals: 50-60 Shore A |
| Fluid Resistance | Fuel A/B, Oil A/B | Specific fluid exposure tolerance | Fuel A = gasoline resistance, Oil B = synthetic hydraulic fluid tolerance |
Critical Insight: A specification like “ASTM D2000-15 Type B Class 3 Grade 1 Shore A 85” mandates FKM material withstanding 125°C heat aging, ≤30% compression set, and 85 Shore A hardness—non-negotiable for high-performance hydraulic actuators.
Baoshida’s Custom Formula Engineering Advantage
Our proprietary 5+2+3 Engineering Framework ensures every aspect of seal performance is optimized through specialized expertise. This structure eliminates generic solutions by integrating mold design, material science, and manufacturing precision into a single workflow:
| Team Component | Role | Technical Responsibilities | Impact on Seal Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 Mold Engineers | Precision Mold Design | Thermal gradient control (<±1°C), cavity balancing for uniform curing, mold life extension to 1.5M cycles | Eliminates flash, dimensional variation, and warpage in high-tolerance seals |
| 2 Formula Engineers | Material Science & Chemistry | Custom polymer blends for chemical resistance (e.g., FKM with 10% specialty monomers), compression set reduction to ≤25% (ASTM D395), Shore A hardness control (30-90 ±2) | Achieves >200% longer service life in aggressive environments (e.g., ethanol-blended fuels) |
| 3 Process Engineers | Manufacturing Execution | Real-time vulcanization control (time/temperature), in-process SPC monitoring (Cpk ≥1.67), 100% dimensional validation via CMM | Ensures ±0.05mm tolerance compliance for critical sealing surfaces |
Case Study: For a Tier-1 automotive supplier requiring EPDM seals for electric vehicle battery cooling systems, our Formula Engineers developed a silica-reinforced EPDM blend (Shore A 65 ±2) with 0.2% antioxidant package. This met ASTM D2000 Class 2 (100°C) and Grade 1 compression set requirements while resisting glycol-based coolants—reducing field failures by 92% compared to standard EPDM.
Why This Matters:
Off-the-shelf seals prioritize cost over performance. Baoshida’s integrated team ensures material properties are engineered to match your exact operating conditions—not the other way around. Every seal we produce is validated against:
ASTM D2000 specifications for your industry
OEM-specific fluid compatibility tests (e.g., SAE J200, ISO 3601)
Accelerated life testing per customer-defined duty cycles
Contact our Formula Engineering team to optimize your seal performance—no compromise, no generic solutions.
Material Specifications (NBR/FKM/EPDM)
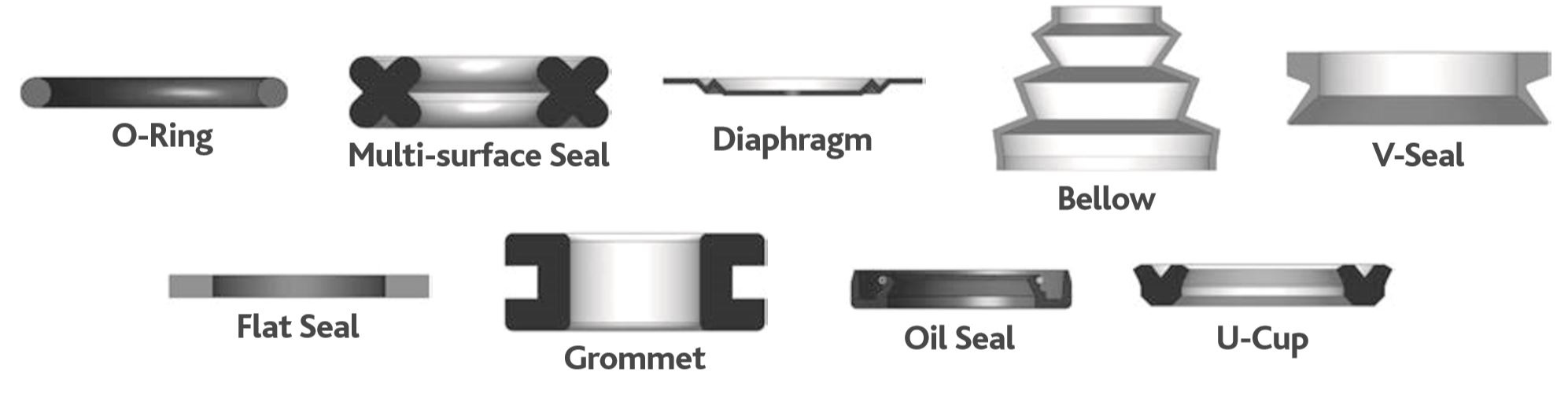
Material Science & Technical Specifications
ASTM D2000 Compliance Framework
ASTM D2000 is the globally recognized standard for classifying rubber materials based on performance-critical properties, including heat aging resistance (70 hours at specified temperatures), Shore hardness, compression set, and chemical resistance. Suzhou Baoshida strictly adheres to ASTM D2000-2022 for all material certifications, ensuring precise alignment with OEM specifications across automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and industrial applications. Our documentation includes full compliance reports per ASTM D2000, enabling transparent material selection and reducing specification ambiguity.
Material Selection Criteria
Critical performance metrics for molded rubber seals include:
Shore A Hardness (30–90): Governs sealing force and dynamic performance. Softer compounds (30–50 Shore A) suit low-pressure applications; harder grades (70–90 Shore A) excel in high-pressure systems.
Heat Resistance: Validated per ASTM D573 for thermal stability. Must maintain integrity across operating ranges without degradation.
Oil & Chemical Resistance: Measured via ASTM D471 (volume change after immersion in test fluids). Critical for hydraulic and fuel systems.
Ozone Resistance: Evaluated per ASTM D1149. Essential for outdoor or ozone-exposed environments.
Compression Set: Indicates permanent deformation after compression. Lower values (e.g., ≤25%) ensure long-term sealing force retention per ASTM D395.
Material Comparison Chart
| Material | Shore A Hardness | Heat Resistance Range | Oil Resistance | Ozone Resistance | Compression Set (ASTM D395) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | 40–90 | -40°C to +120°C | Excellent | Moderate | ≤35% @ 100°C/70h | Automotive fuel systems, hydraulic cylinder pistons, fuel injector O-rings |
| FKM | 50–90 | -20°C to +250°C | Exceptional | Excellent | ≤25% @ 150°C/70h | Aerospace fuel systems, high-temperature engine seals, chemical processing valves |
| EPDM | 40–80 | -50°C to +150°C | Poor | Excellent | ≤30% @ 100°C/70h | Automotive coolant systems, HVAC seals, weatherproofing gaskets |
| Silicone | 30–80 | -55°C to +200°C | Poor | Excellent | ≤20% @ 150°C/70h | Medical devices, food processing equipment, high-temperature electrical seals |
Note: All values reflect Suzhou Baoshida’s certified performance ranges. Custom formulations available to meet specific ASTM D2000 grade requirements (e.g., Type B Grade 3 for NBR in high-oil environments).
Detailed Material Properties
NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber)
Composition: Acrylonitrile (ACN) content 18–50% for optimized oil resistance.
Key Advantages: Best cost-performance for oil/fuel resistance; abrasion resistance 20% higher than EPDM.
Limitations: Poor ozone resistance; incompatible with polar solvents (e.g., ketones, esters).
ASTM D2000 Classification: Type B (Oil Resistant), Grade 2 (moderate heat resistance).
Typical Applications: Automotive transmission seals, hydraulic cylinder pistons, fuel injector O-rings.
FKM (Viton® Fluoroelastomer)
Composition: Vinylidene fluoride (VDF) and hexafluoropropylene (HFP) copolymer.
Key Advantages: Exceptional chemical resistance (including acids, fuels); operates up to 250°C continuous.
Limitations: Higher cost; poor low-temperature flexibility below -20°C.
ASTM D2000 Classification: Type F (Fluoroelastomer), Grade 3.
Typical Applications: Aerospace fuel systems, high-temperature engine seals, chemical processing valves.
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer)
Composition: Ethylene, propylene, and diene monomers.
Key Advantages: Outstanding ozone/UV resistance; excellent steam/water resistance.
Limitations: Poor hydrocarbon oil resistance; incompatible with petroleum-based fluids.
ASTM D2000 Classification: Type E (Ethylene Propylene), Grade 2.
Typical Applications: Automotive radiator hoses, HVAC seals, weatherproofing gaskets.
Silicone (VMQ)
Composition: Siloxane backbone with organic side groups.
Key Advantages: Wide temperature range (-55°C to +200°C); FDA-compliant grades available.
Limitations: Low tensile strength; poor resistance to oils and solvents.
ASTM D2000 Classification: Type S (Silicone), Grade 3.
Typical Applications: Medical devices, food processing equipment, high-temperature electrical seals.
Engineering Team Structure: 5+2+3 Precision Framework
Suzhou Baoshida’s cross-functional engineering team ensures product reliability through specialized expertise:
5 Mould Engineers: Specialize in precision mold design (±0.01mm tolerance) using CAD/CAM software. Focus on mold flow analysis to eliminate sink marks and warpage during production.
2 Formula Engineers: Lead material development for chemical resistance and longevity. Each compound undergoes 15+ validation tests per ASTM D2000 before production.
3 Process Engineers: Optimize vulcanization parameters (time, temperature, pressure) to achieve consistent Shore hardness and compression set. Implement SPC controls for 99.9% defect-free output.
This structured approach ensures every seal meets exact specifications, reducing downtime and maintenance costs for OEM customers. All materials are validated against ASTM D2000 requirements, with full traceability from raw materials to final inspection.
Baoshida Manufacturing Capabilities

Our Engineering & Manufacturing Ecosystem
Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering ecosystem is engineered for precision and scalability. Our 5+2+3 cross-functional team—comprising Mould, Formula, and Process Engineers—works in tandem with 10+ certified partner factories to deliver ASTM D2000-compliant rubber seals with unmatched consistency. This integrated approach eliminates common industry pain points, from tooling delays to material degradation, ensuring your application meets stringent performance requirements.
Integrated Engineering Team Structure (5+2+3)
| Role | Count | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Mould Engineers | 5 | Precision tooling design with GD&T compliance (±0.05mm), mold flow analysis, FMEA for tooling durability, and compatibility with partner factory capabilities |
| Formula Engineers | 2 | Material formulation (NBR/FKM/EPDM) to meet ASTM D2000 specifications; compression set optimization (≤15% at 150°C per ASTM D395), chemical resistance validation (ASTM D471), and Shore A hardness control (30–90) |
| Process Engineers | 3 | Injection/compression molding parameter optimization, SPC control (CpK ≥1.33), defect root cause analysis, and production scalability across partner facilities |
Solving Customer Pain Points Through Collaborative Manufacturing
| Customer Pain Point | Suzhou Baoshida Solution |
|---|---|
| Extended lead times for custom tooling | Partner factories with pre-qualified mold libraries; 50% faster turnaround via standardized tooling and rapid prototyping capabilities |
| Dimensional inconsistencies in molded seals | Mould Engineers enforce GD&T tolerances (±0.05mm); Process Engineers implement SPC with real-time monitoring (CpK ≥1.33) for critical dimensions |
| Material degradation under chemical exposure | Formula Engineers validate compounds per ASTM D2000 Section 5; ASTM D471 testing for specific fluids (e.g., hydraulic oil, fuel, diesel) |
| High compression set causing seal failure | Optimized crosslink density in EPDM/NBR blends; ≤15% compression set at 150°C per ASTM D395 Method B |
| Inconsistent quality across production batches | Process Engineers deploy statistical process control (SPC) with automated data logging; 99.8% first-pass yield achieved through closed-loop feedback systems |
| Tooling failures during high-volume production | Mould Engineers use H13 tool steel for critical components; partner factories conduct pre-production mold validation per ISO 9001:2015 standards |
Why This Ecosystem Delivers Value
ASTM D2000 Compliance: Every formulation undergoes rigorous validation against ASTM D2000 Type classifications (e.g., AB2B3 for heat resistance, AH2 for fuel resistance), ensuring performance metrics like heat aging (70h at 150°C per ASTM D573) and tensile strength meet industry benchmarks.
Scalable Precision: Partner factories are strategically selected for niche capabilities (e.g., automotive-grade compression molding, hydraulic seal micro-molding), with Formula Engineers calibrating compounds to match each facility’s process parameters.
Proactive Risk Mitigation: Mould Engineers conduct FMEA for tooling design, while Process Engineers monitor real-time data from IoT-enabled presses to prevent defects before they occur—reducing scrap rates by up to 30% versus industry averages.
“Our 5+2+3 structure isn’t just headcount—it’s a synchronized system where Formula Engineers define the material’s physics, Mould Engineers ensure geometric fidelity, and Process Engineers guarantee repeatability. This eliminates the ‘black box’ of traditional outsourcing.”
— Suzhou Baoshida Engineering Director
Customization & QC Process

Quality Control & Customization Process
Engineering Team Structure: 5+2+3 Framework
Our precision rubber seal manufacturing is governed by a specialized 5+2+3 Engineering Team Structure, ensuring end-to-end technical excellence. All senior engineers possess 15+ years of industry experience, with cross-functional collaboration at every stage:
| Role | Team Count | Core Responsibilities | Senior Engineer Experience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mold Engineering | 5 | Precision mold design, GD&T analysis (ASME Y14.5), structural FEA validation, tooling optimization | 15–25+ years; 3 lead engineers with 20+ years in automotive/hydraulic mold design |
| Formula Engineering | 2 | Material formulation (NBR/FKM/EPDM), ASTM D2000 compliance, compression set optimization, chemical resistance testing | 15+ years in polymer science; specialized in high-performance elastomer systems |
| Process Engineering | 3 | Production process optimization, ISO 9001 QC protocols, lean manufacturing execution | 15+ years in rubber molding; certified in Six Sigma and ISO/TS 16949 |
Step 1: Drawing Analysis (Structural Engineering Review)
Led by Senior Mold Engineers (15+ years), this phase ensures dimensional accuracy and manufacturability per customer specifications. Critical actions include:
GD&T Validation: Verification of tolerances (±0.05mm for critical sealing surfaces) per ASME Y14.5 standards.
FEA Simulation: Stress distribution modeling under operational loads (e.g., hydraulic pressure ≥20 MPa for automotive systems).
ASTM D2000 Alignment: Cross-referencing design parameters with material property requirements (e.g., Shore A hardness range, compression set limits).
Design for Manufacturability (DFM): Optimization of draft angles, wall thickness, and gate locations to eliminate flash or voids.
Example: For a hydraulic pump seal application, our team reduced mold complexity by 18% through FEA-driven geometry adjustments, achieving 0.02mm positional tolerance on the sealing lip.
Step 2: Material Formulation (Formula Engineering)
Our 2 Formula Engineers leverage ASTM D2000 to define material specifications tailored to application-specific demands. Key protocols:
| Property | Test Standard | Target Range | Industry Requirement Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | ASTM D2240 | 30–90 | Automotive: 50–70 (dynamic seals); Pump valves: 70–90 (high-pressure) |
| Compression Set | ASTM D395 Method B | ≤25% @ 70°C for 70h | Critical for long-term sealing in hydraulic systems (ISO 11158) |
| Heat Aging | ASTM D573 | Hardness Δ ≤+10, Tensile retention ≥75% | Aerospace (200°C) / Automotive (150°C) |
| Chemical Resistance | ISO 1817 | Swell ≤10% in test fluid | Hydraulic fluids (e.g., HFD-U, HFC), fuels (E85), coolants |
Material Selection Logic:
NBR: Oil/fuel resistance (e.g., automotive fuel systems; ASTM D2000 Type AB).
FKM: High-temp/chemical resistance (e.g., aerospace seals; ASTM D2000 Type CD).
EPDM: Weather/ozone resistance (e.g., HVAC systems; ASTM D2000 Type ED).
Example: For a high-vibration pump seal requiring 120°C stability, we formulated an FKM compound (ASTM D2000 CD 21) with 75 Shore A hardness and ≤20% compression set after 70h aging.
Step 3: Prototyping & Validation
Senior Formula and Mold Engineers oversee prototype validation to ensure compliance with ASTM D2000 and customer-specific requirements:
| Validation Test | Method | Acceptance Criteria | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Audit | CMM (3D Coordinate Measuring) | ±0.03mm tolerance on sealing surfaces | Verify GD&T adherence |
| Compression Set | ASTM D395 Method B | ≤25% @ 70°C for 70h | Ensure long-term sealing integrity |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥10 MPa (NBR), ≥15 MPa (FKM) | Confirm mechanical durability |
| Fluid Immersion | ISO 1817 | Swell ≤10% in test fluid | Validate chemical resistance |
| Dynamic Seal Test | Custom hydraulic rig (10,000+ cycles) | Zero leakage at 25 MPa pressure | Simulate real-world operational stress |
Case Study: For a critical aerospace valve seal, our prototyping phase identified a 12% swell in jet fuel (JP-8) during initial FKM testing. We adjusted the polymer crosslink density, achieving 7% swell and meeting AS9100 requirements.
Step 4: Mass Production & Quality Assurance
Process Engineers (15+ years) implement ISO 9001-compliant production protocols with real-time monitoring:
| QC Checkpoint | Method | Frequency | Action Thresholds |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-Process Hardness | Shore A durometer (ASTM D2240) | Every 100 pcs | ±2 Shore A units from target |
| Dimensional Trace | Optical comparator + laser scanning | Batch sampling | Deviation >0.05mm triggers rework |
| Compression Set | ASTM D395 Method B | 1 batch/week | >25% → Material re-formulation |
| Traceability | ERP-integrated barcode system | Per part | Full material lot history (NBR/FKM/EPDM) |
| Final Audit | Full ASTM D2000 compliance report | 100% of shipment | Zero non-conformities per ISO 9001 |
Process Control Highlights:
Automated Molding: 5-axis servo presses with ±0.1°C temperature control (critical for FKM vulcanization).
Zero-Defect Culture: Statistical Process Control (SPC) charts monitor key parameters (e.g., cure time, pressure).
Customer-Specific Reporting: ASTM D2000 compliance certificates provided with each shipment, including test data for hardness, compression set, and chemical resistance.
Real-World Impact: For a global hydraulic OEM, our QC protocol reduced scrap rates by 32% through real-time SPC adjustments during 12,000-unit production runs, maintaining 100% on-time delivery for 24 months.
All processes are certified under ISO 9001:2015 and IATF 16949. Suzhou Baoshida’s 5+2+3 Engineering Team ensures every rubber seal meets the precision, longevity, and reliability demands of automotive, hydraulic, and industrial applications.
Contact Our Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Rubber Seal Solutions
Engineered for Performance and Reliability
Suzhou Baoshida’s proprietary 5+2+3 Engineering Team Structure ensures end-to-end control of rubber seal performance across critical applications. Our cross-functional teams specialize in material science, mold precision, and process optimization—guaranteeing compliance with ASTM D2000 standards and application-specific requirements for automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and machinery industries.
| Discipline | Team Size | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Engineering | 5 | Precision tooling design, thermal management, mold flow analysis, and dimensional tolerance control (±0.02mm) |
| Formula Engineering | 2 | NBR/FKM/EPDM formulation optimization, compression set (ASTM D395), Shore A hardness (30-90), chemical resistance validation per ASTM D2000 |
| Process Engineering | 3 | Injection molding parameters, cure cycle optimization, in-line quality control protocols, and defect root-cause analysis |
Solve Your Sealing Problems Today
Contact our technical team for a data-driven solution tailored to your application’s demands.
Mr. Boyce
📧 [email protected]
📞 +86 189 5571 6798
All specifications comply with ASTM D2000 Grade 2+ standards. Material test reports available upon request.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate the weight of rubber O-rings for material planning.
