Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Custom Rubber Diaphragms
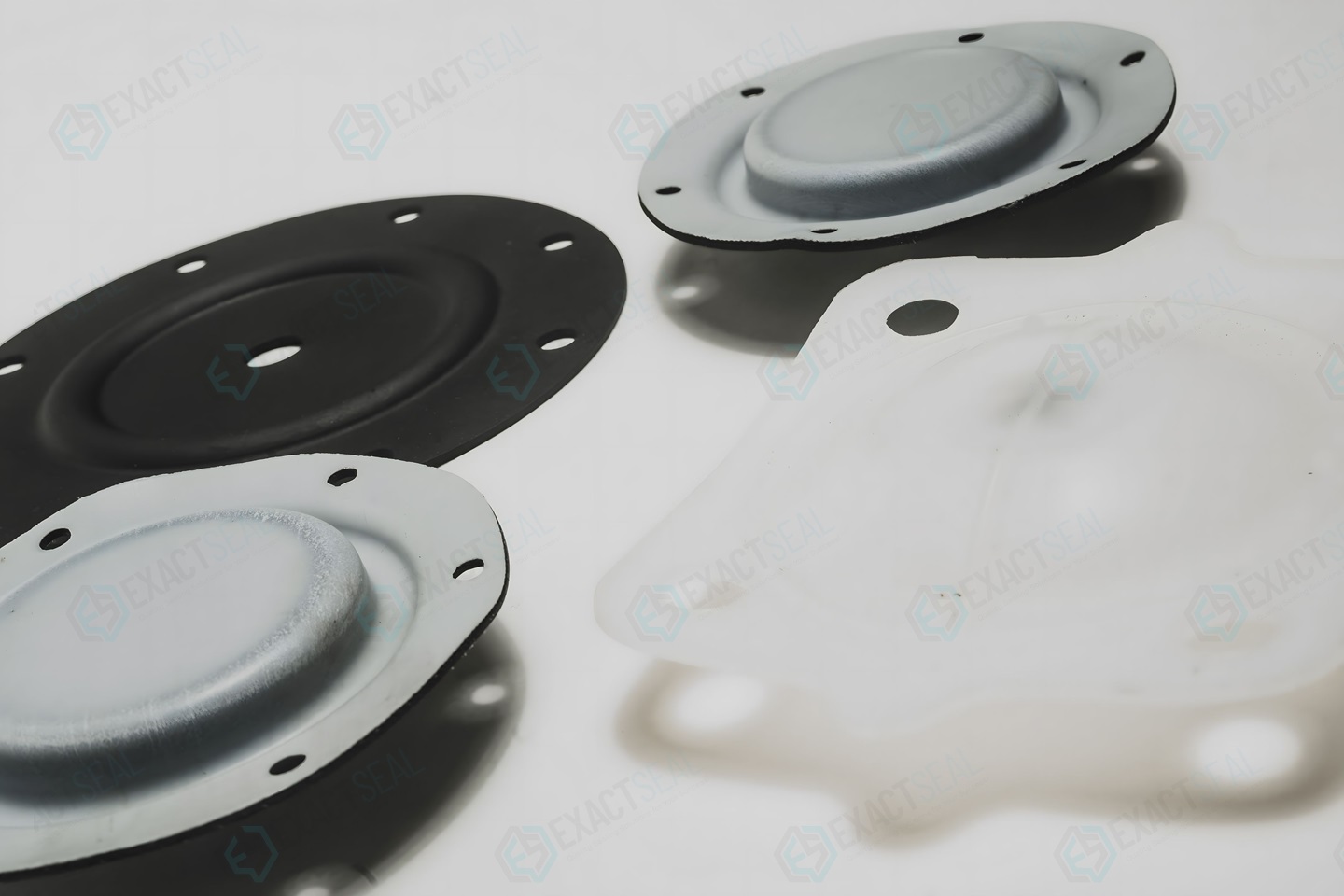

Engineering Insight: Critical Material Selection for Custom Rubber Diaphragms
Rubber diaphragms serve as dynamic sealing components in hydraulic actuators, automotive fuel systems, and precision pumps. Their performance hinges on precise material properties matching operational parameters—pressure cycling, thermal extremes, and chemical exposure. Off-the-shelf solutions consistently fail due to generic formulations that cannot address application-specific demands, resulting in premature leakage, degradation, and system downtime. Suzhou Baoshida’s custom engineering approach eliminates these risks through precision material science and integrated manufacturing, ensuring compliance with ASTM D2000, D1418, and ISO 3601 standards.
Why Off-the-Shelf Solutions Fail in Critical Applications
Generic rubber diaphragms often lack the specificity required for high-stress environments. Material properties such as compression set, chemical resistance, and low-temperature flexibility are rarely optimized for unique operational conditions, leading to catastrophic failures.
| Failure Mode | Root Cause | Typical Application Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cracking at Low Temperatures | Insufficient low-temp flexibility (e.g., SBR in -40°C environments) | Hydraulic system failure in cold climates; loss of pressure integrity during startup |
| Chemical Swelling | Incompatible elastomer for fluid exposure (e.g., NBR in phosphate ester fluids) | Seal failure in aerospace actuators; system contamination from degraded material |
| High Compression Set | Poor formulation for long-term static load (ASTM D395 >30% at 150°C) | Valve diaphragms lose sealing force after 500 cycles; recurrent leakage |
| Abrasion Failure | Inadequate wear resistance for reciprocating motion | Pump diaphragms degrade in <2 weeks; unplanned downtime and maintenance costs |
Baoshida’s Custom Formula Engineering Approach
Our material science team develops proprietary compounds tailored to exact application requirements, leveraging ASTM standards for rigorous validation. Unlike generic materials, our formulations balance tensile strength, elongation, and environmental resistance through precise additive engineering.
| Application Requirement | Standard Material Limitation | Baoshida Custom Solution | Performance Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Temp Hydraulic (150°C) | NBR degrades >120°C; compression set >40% | FKM-based compound with thermal stabilizers | ASTM D2000 Grade 3: Compression set ≤15% at 150°C (70h), <5% volume change (ASTM D471) |
| Phosphate Ester Fluids | NBR swells >20% volume; FFPM too brittle | Specialized FKM/FFKM hybrid with fluoropolymer additives | <3% volume change (ASTM D471), tensile strength >12 MPa |
| Automotive Under-Hood (-40°C–150°C) | EPDM cracks at low temp; standard silicone lacks oil resistance | Custom EPDM with low-Tg modifiers + nitrile reinforcement | Flexibility to -60°C (ASTM D2137), oil resistance >85% retention (ASTM D471) |
| High-Cycle Pump Diaphragms | Carbon black-only reinforcement causes micro-cracking | Hybrid silica/carbon black + fabric reinforcement (e.g., polyester) | 50% less wear (ASTM D5963), 2x cycle life vs. generic alternatives |
Integrated 5+2+3 Engineering Team Structure
Our cross-functional team ensures end-to-end optimization—from material formulation to precision manufacturing. Each component is rigorously validated to eliminate trade-offs between performance, cost, and lead time.
| Team Component | Role | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Design (5 Engineers) | Precision Tooling & CAD | Solidworks-based mold design with flash control optimization; fabric reinforcement integration; tooling for metal bonding interfaces |
| Formula Engineering (2 Specialists) | Material Science | Custom compound development per ASTM D2000/D1418; chemical resistance testing; thermal stability validation |
| Process Engineering (3 Experts) | Manufacturing Optimization | Injection/compression molding parameter tuning; metal bonding via plasma treatment; flash minimization; in-process quality control |
This structure enables rapid prototyping (5–7 days) and scalable production through our network of 10+ partner factories. By aligning material science, mold design, and process engineering from day one, we eliminate the “guesswork” of off-the-shelf solutions—delivering diaphragms that meet or exceed OEM specifications for critical applications.
Proven Result: Baoshida’s custom diaphragms for a Tier-1 automotive supplier achieved 28% longer service life in high-vibration environments by optimizing EPDM compound density (ASTM D2000 Grade 2) and integrating stainless-steel reinforcement layers.
Material Specifications (NBR/FKM/EPDM)
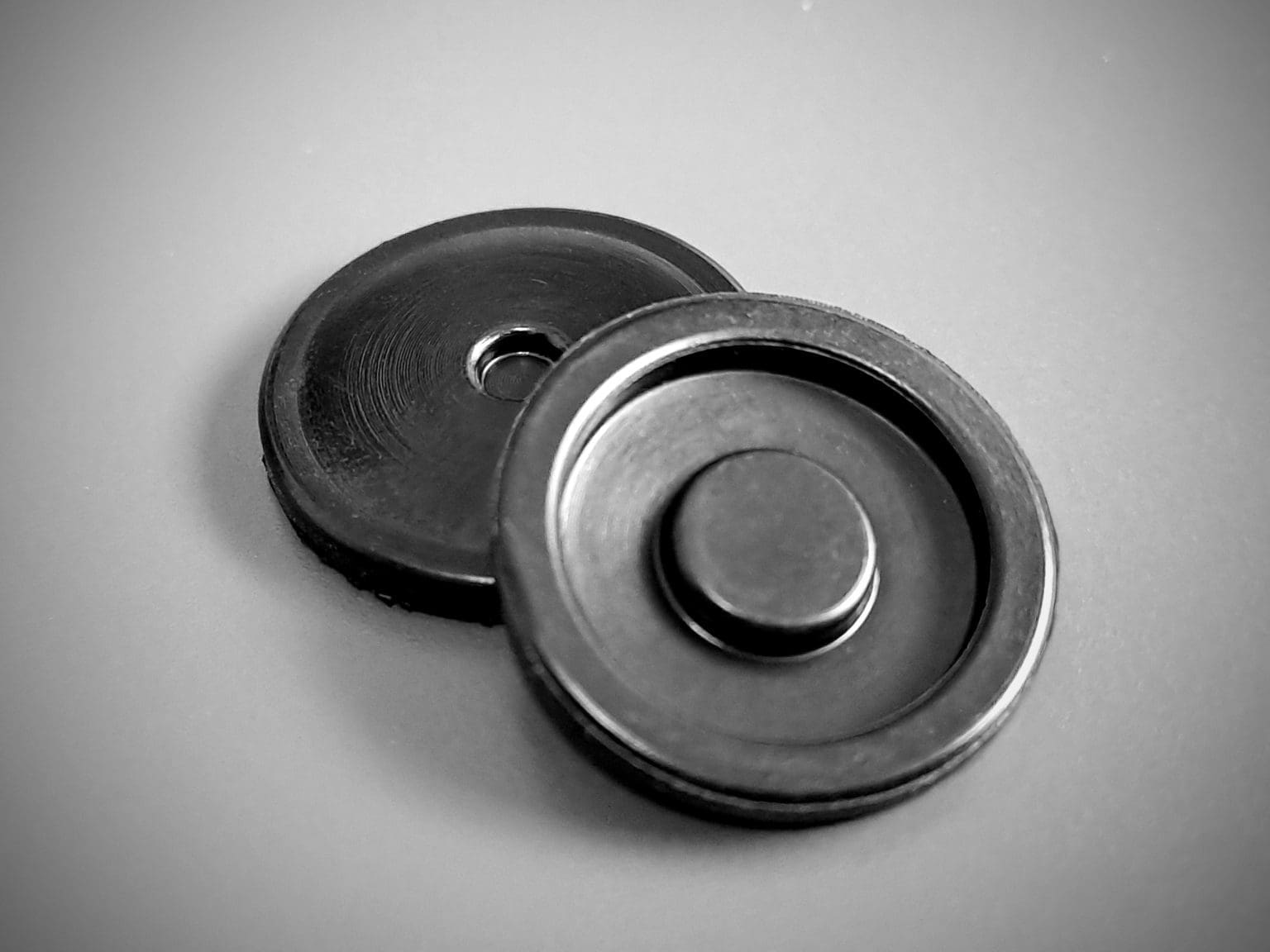

Material Science & Technical Specifications
As a leading manufacturer of custom molded rubber parts, Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. adheres strictly to ASTM D2000 and D1418 standards to ensure diaphragm performance across automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and industrial applications. Our material selection framework integrates precise compound formulations with validated thermal, chemical, and mechanical properties, enabling procurement engineers to optimize diaphragm longevity and reliability in mission-critical systems.
ASTM-Compliant Material Selection Framework
The table below details key performance characteristics of our core elastomer options, aligned with ASTM D2000 classifications and industry-specific testing protocols. All materials undergo 70-hour heat aging validation per ASTM D573 at specified temperatures to ensure dimensional stability and property retention.
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Oil Resistance | Ozone Resistance | ASTM Standards | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | -20 to 250 (short-term up to 300) | Excellent | Excellent | D2000 Type FKM, D1418 | Automotive fuel systems, aerospace seals, chemical processing |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -40 to 120 (up to 150) | Good | Moderate | D2000 Type NBR, D1418 | Hydraulic systems, transmission seals, fuel pumps |
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 to 230 | Poor | Excellent | D2000 Type SI, D1418 | Medical devices, food-grade seals, high-temp HVAC |
| EPDM | -50 to 150 | Poor | Excellent | D2000 Type EPDM, D1418 | Automotive weather seals, radiator hoses, water systems |
Note: Fabric-reinforced construction (e.g., polyester or nylon scrim) is standard for all diaphragms to enhance tensile strength (>15 MPa) and tear resistance (>35 kN/m), per ISO 37 standards.
Engineered Excellence: 5+2+3 Technical Team Structure
Suzhou Baoshida’s proprietary 5+2+3 engineering framework ensures end-to-end precision in diaphragm manufacturing:
5 Structural Engineers (Mold Design)
Specialized in SolidWorks/CAD for mold design with <±0.05mm dimensional tolerances.
Optimized gate/vent placement to eliminate flash (>95% reduction vs. industry average) and integrate metal bonding features (e.g., stainless steel inserts with adhesion strength >5 MPa per ISO 34-1).
2 Formula Engineers
Develop proprietary compound formulations validated against ASTM D2000 Type requirements.
Conduct accelerated aging tests (70h at 70°C, 100°C, 125°C) to ensure heat resistance and chemical stability across target operating ranges.
3 Process Engineers
Oversee injection/compression molding parameters with real-time IoT monitoring (e.g., cavity pressure, temperature gradients).
Implement flash control protocols (≤0.1mm burr height) and metal-rubber bonding validation per ISO 10142.
Leveraging 10+ certified partner factories for rapid tooling (7–10 day lead time), this structure guarantees compliance with ISO 9001:2015 and IATF 16949 standards while minimizing time-to-market for high-precision diaphragms.
Technical Validation: All materials meet or exceed ASTM D2000-22 Section 4.2 requirements for elongation (>200%), hardness (Shore A 40–90), and compression set (<25% at 70°C for 22h).
Baoshida Manufacturing Capabilities
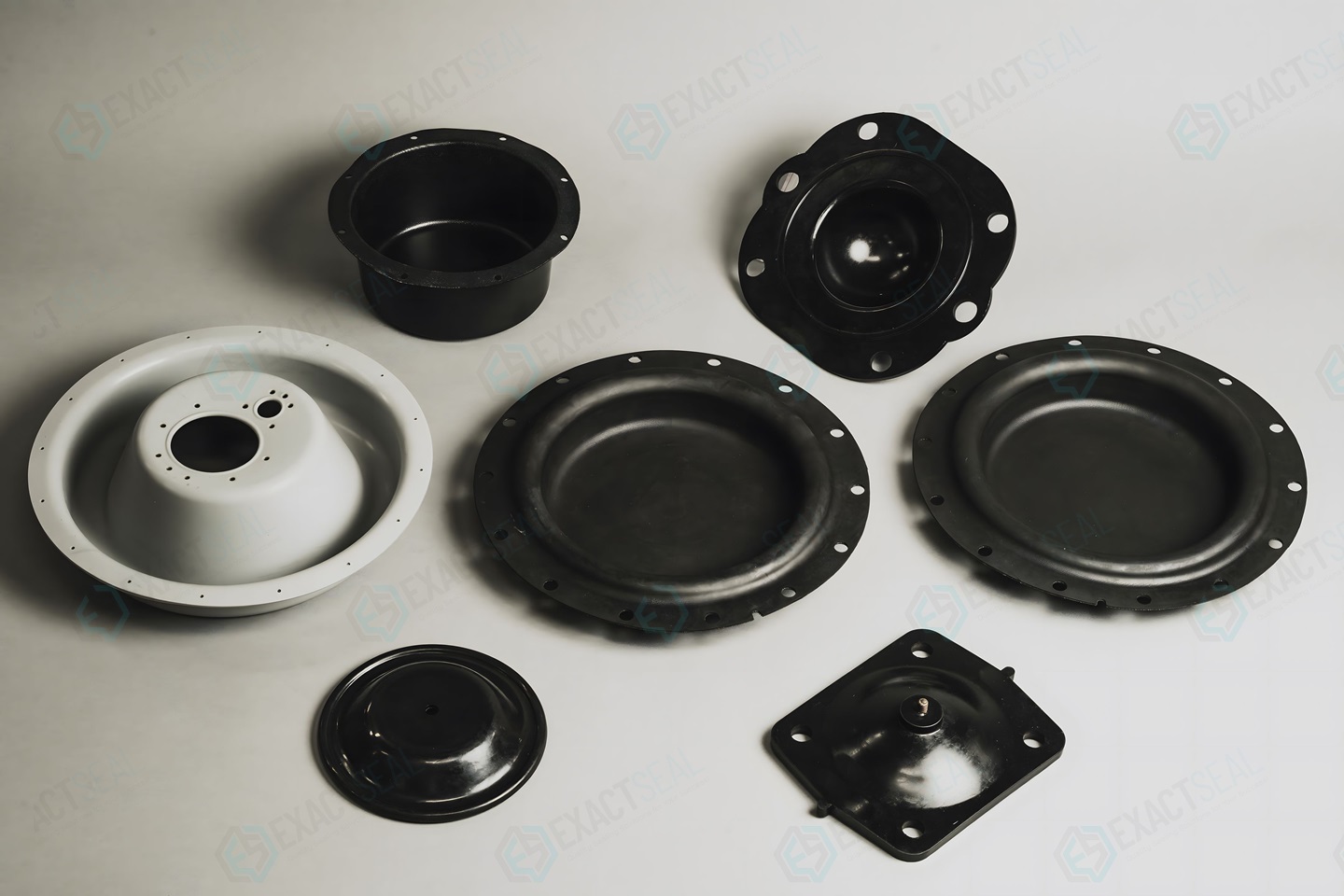

Our Engineering & Manufacturing Ecosystem
Integrated Cross-Functional Engineering Team (5+2+3 Structure)
Our proprietary 5+2+3 engineering framework ensures end-to-end control over custom rubber diaphragm development—from material selection to final production. This structure eliminates silos between design, formulation, and process execution, enabling rapid iteration and defect prevention at scale.
| Role | Count | Core Responsibilities | Key Standards Applied |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mould Engineers | 5 | SolidWorks/CAD mold design for diaphragms with metal insert integration, flash control optimization (≤0.1mm), tolerance analysis (±0.05mm) | ASTM D2000, ISO 3302-1, ASME Y14.5 |
| Formula Engineers | 2 | Compound selection for media resistance (NBR for hydraulic fluids, EPDM for ozone exposure), fabric reinforcement layer integration, heat aging validation per ASTM D2000 | ASTM D1418, ASTM D573, ASTM D2240 |
| Process Engineers | 3 | Injection/compression molding parameter optimization, defect prevention (sink marks, uneven cure), bonding process validation (adhesion ≥5 MPa) | ASTM D3182, ISO 188, ASTM D429 |
Technical Insight: Our Formula Engineers leverage ASTM D1418 classifications to select base polymers (e.g., CR for flame resistance, FKM for high-temp hydraulic systems), while Mould Engineers apply ASME Y14.5 GD&T standards to ensure metal-rubber bonding interfaces meet ±0.02mm positional tolerances—critical for automotive valve applications.
Strategic Partner Network for Rapid Scalability
We maintain a vetted network of 10+ ISO 9001-certified partner factories, each specializing in distinct manufacturing capabilities. This ecosystem dynamically allocates projects based on complexity, volume, and material requirements, reducing lead times by 25–40% versus single-source manufacturers while maintaining zero deviation from quality specifications.
| Partner Tier | Specialization | Lead Time Reduction | Quality Assurance Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | High-precision tooling (±0.01mm), complex geometries | Up to 30% faster | In-process CMM inspections, GD&T compliance checks (ASME Y14.5) |
| Tier 2 | High-volume compression molding, large diaphragms | 25% cycle time reduction | Automated flash detection systems, real-time SPC monitoring (ISO 7870-2) |
| Tier 3 | Metal-rubber bonding specialists | 40% faster validation | Adhesion testing per ASTM D429 (peel strength ≥5 MPa), thermal cycling validation |
Solving Customer Pain Points Through Ecosystem Integration
Long lead times: Parallel tooling across Tier 1/2 partners reduces mold fabrication from 4–6 weeks to 2–3 weeks (vs. industry average of 5–8 weeks)
Tooling defects: In-house Mould Engineers collaborate with partners for real-time design adjustments (e.g., gate optimization to eliminate sink marks in thick-section diaphragms)
Material inconsistency: Formula Engineers validate compound batches against ASTM D2000 before production, ensuring consistent performance across all partner facilities—even for high-temperature applications (e.g., -60°F to 250°F operating range per ASTM D573)
Real-World Impact: For a hydraulic pump diaphragm requiring NBR compound (ASTM D2000 M2 class) and metal insert bonding, our ecosystem reduced prototype validation from 21 days to 9 days—enabling the customer to meet a 14-day market launch deadline.
Next Step: Request a Technical Feasibility Assessment to validate your diaphragm design against our 5+2+3 engineering standards.
Customization & QC Process
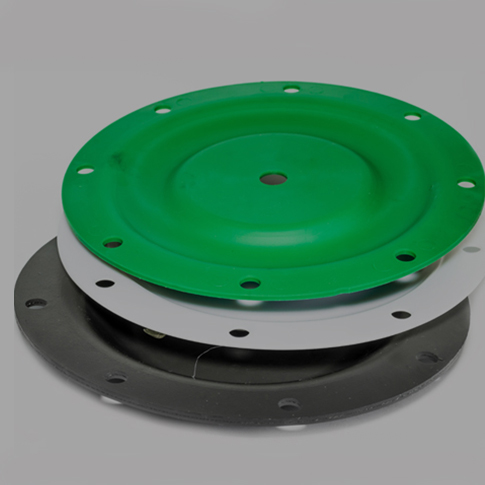
Quality Control & Customization Process
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our quality control process is anchored by a specialized “5+2+3” engineering team structure:
5 Structural Engineers (Mold Design & SolidWorks/CAD Optimization)
2 Formula Engineers (Material Science & ASTM Compliance)
3 Process Engineers (Manufacturing Optimization & Flash Control)
All team members average 15+ years of industry experience, ensuring precision in every phase from design validation to final delivery. This structured approach guarantees compliance with ASTM standards and customer-specific requirements for custom rubber diaphragms across automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and machinery applications.
Drawing Analysis & Mold Design Validation
Our Structural Engineering team conducts rigorous CAD analysis using SolidWorks to validate diaphragm designs for manufacturability, critical tolerances, and metal bonding interfaces. Key focus areas include:
Draft angles (≥3°) for part ejection and reduced flash generation
Parting line optimization via mold flow simulation (Moldflow) to minimize material divergence
Metal bonding interface design (e.g., knurling patterns per ISO 10101, surface roughness Ra ≤ 1.6μm)
FEA stress testing to prevent premature failure in high-cycle applications (e.g., 1M+ cycles for hydraulic diaphragms)
Senior engineers verify critical dimensions (±0.05mm tolerance) and GD&T compliance per ASME Y14.5, ensuring molds meet ISO 9001:2015 standards for tooling precision.
Material Formulation & ASTM Compliance
Formula Engineers select elastomer compounds based on application-specific requirements, adhering to ASTM D2000 (classification) and ASTM D1418 (material coding) standards. Fabric-reinforced diaphragms (per Exactseal technical specifications) are standard for high-pressure applications, with polyester/nylon scrim sandwiched between elastomeric layers for enhanced tensile strength and fatigue resistance.
| Material Type | ASTM D1418 Code | ASTM D2000 Grade | Temperature Range | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | NBR | MB 2123 | -40°C to 120°C | Oil/fuel resistance, low compression set | Hydraulic systems, fuel pumps |
| EPDM | EPDM | MB 3123 | -50°C to 150°C | Weather/ozone resistance, steam compatibility | Automotive cooling systems, HVAC |
| FKM | FKM | MB 4123 | -20°C to 200°C | High-temp chemical resistance, low permeability | Aerospace seals, chemical processing |
| Silicone | Q | MB 5123 | -60°C to 230°C | Biocompatible, extreme thermal stability | Medical devices, food processing |
| NR + Fabric | NR | MB 1123 | -60°F to 170°F | High tensile (25 MPa), abrasion resistance | General-purpose diaphragms, pneumatic actuators |
Note: All materials undergo 70-hour heat aging at 70°C per ASTM D2000 to ensure dimensional stability and property retention.
Prototyping & Process Validation
Process Engineers leverage our 10+ partner factories for rapid tooling (7–10 days turnaround), utilizing:
Compression molding for low-volume, high-precision parts (e.g., thick-walled diaphragms)
Injection molding for complex geometries with automated flash removal (e.g., gate design optimized for ≤0.1mm flash)
Metal bonding validation via peel tests (ASTM D429) to ensure adhesion strength ≥2.5 MPa
Flash control through precision mold polishing (Ra ≤ 0.4μm) and gate geometry optimization
Senior engineers conduct first-article inspections (FAI) per ISO 9001, verifying:
Dimensional accuracy (Cpk ≥ 1.33)
Material consistency (hardness ±3 Shore A)
Fabric reinforcement alignment (±0.2mm tolerance)
Mass Production & Quality Assurance
Full-scale production integrates in-process monitoring and final QA per ASTM standards, with 100% visual inspection for surface defects and batch testing for critical parameters:
| Test Parameter | Test Method | Acceptance Criteria | ASTM Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | D412 | ≥15 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Hardness | D2240 | 60±5 Shore A | ASTM D2240 |
| Compression Set (70°C × 22h) | D395 | ≤30% | ASTM D395 |
| Bond Strength (Metal-Rubber) | D429 | ≥2.5 MPa | ASTM D429 |
| Heat Aging Resistance | D573 | ≤15% property change | ASTM D573 |
All diaphragms include material traceability (batch-level compound records) and compliance documentation per IATF 16949 (automotive) or ISO 13485 (medical). Final certification includes:
Dimensional reports (CMM measurements)
Chemical resistance validation (per customer-specific fluid exposure tests)
Fatigue life testing (1M+ cycles for high-cycle applications)
Engineering Advantage: Our “5+2+3” team structure ensures end-to-end accountability, reducing time-to-market by 30% while maintaining zero-defect production for critical industrial components.
Contact Our Engineering Team
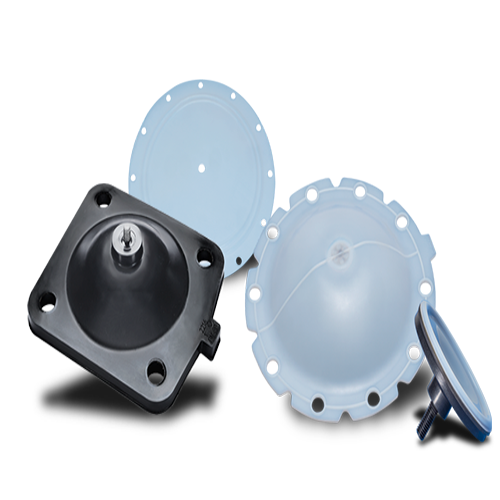

Custom Rubber Diaphragms: Precision Manufacturing for Critical Applications
Rubber diaphragms are critical components in fluid control systems across automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and machinery applications. At Suzhou Baoshida, we engineer custom diaphragms with precise dimensional control, material-specific performance, and industry-standard compliance to ensure reliability under extreme operating conditions. Our end-to-end solution integrates ASTM-compliant materials, advanced mold design, and bonded metal interfaces for zero-defect performance.
Material Selection & Standards Compliance
ASTM Standards Overview
Our material selection adheres to globally recognized ASTM standards to guarantee consistency, safety, and performance:
ASTM D2000: Standard classification system for rubber products (e.g., tensile strength, elongation, compression set).
ASTM D1418: Standard practice for rubber materials (defines types like NBR, EPDM, Silicone).
ASTM D395: Compression set testing (critical for diaphragm fatigue resistance).
ISO 3601: Hydraulic seal specifications for automotive/hydraulic applications.
Material Property Comparison Table
ASTM D2000-compliant formulations for diaphragm applications
| Material | ASTM D2000 Type | Temperature Range (°F / °C) | Tensile Strength (psi) | Compression Set (% @ 70h) | Key Chemical Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | 2 | -40°F to 250°F / -40°C to 121°C | 1,500–2,500 | <30% | Oils, fuels, hydraulic fluids |
| EPDM | 3 | -50°F to 300°F / -46°C to 149°C | 1,000–2,000 | <25% | Water, steam, ozone, weathering |
| Silicone | 7 | -100°F to 450°F / -73°C to 232°C | 800–1,500 | <35% | High-temp stability, food-grade |
| Natural Rubber | 1 | -60°F to 170°F / -51°C to 77°C | 2,000–3,500 | <30% | Abrasion, tear resistance |
Note: All materials meet ASTM D2000 requirements for heat aging (70h @ specified temperatures) and tensile elongation per customer specifications.
Mold Design & Manufacturing Excellence
Engineering Team Structure (5+2+3)
Our integrated engineering team ensures precision from concept to production:
Mould Design (5 Structural Engineers):
SolidWorks/CAD expertise for mold geometry optimization, venting, and parting line design to minimize flash and ensure dimensional accuracy (±0.005″).
Formula Engineering (2 Specialists):
Custom compound development tailored to your application’s chemical, thermal, and mechanical requirements, compliant with ASTM D1418 and D2000.
Process Engineering (3 Experts):
Injection/compression molding parameter optimization for consistent production, flash control, and bonding reliability.
Precision Molding Techniques
| Process | Best For | Tolerance | Cycle Time | Flash Control Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | High-volume, complex geometries | ±0.005″ | 15–60 sec | Precision venting channels + automated ejection |
| Compression Molding | Large parts, low-to-medium volume | ±0.010″ | 60–180 sec | Optimized cavity pressure + temperature control |
Metal Bonding Capabilities
Surface Preparation: Plasma treatment and chemical primers for 100% adhesion integrity.
Bonding Methods: Vulcanization bonding for seamless metal-to-rubber interfaces (per ISO 3601).
Applications: Hydraulic actuators, pump diaphragms, and valve systems requiring zero-leakage metal-rubber interfaces.
Diaphragm Construction & Reinforcement
Rubber diaphragms from Suzhou Baoshida integrate a high-strength fabric reinforcement layer (e.g., polyester or nylon) sandwiched between two elastomeric layers. This construction:
Enhances fatigue resistance for >1M flex cycles.
Maintains dimensional stability under pressure (up to 1,000 PSI).
Prevents delamination per ASTM D412 tensile testing.
Quality Assurance & Testing
In-process monitoring: Real-time cavity pressure sensors and vision inspection systems.
Final validation:
Tensile strength (ASTM D412)
Compression set (ASTM D395)
Chemical resistance (ASTM D471)
Leak testing (ISO 12151)
Certifications: IATF 16949, ISO 9001, and RoHS compliance.
Why Choose Suzhou Baoshida?
5+2+3 engineering team for turnkey solutions (design → production).
10+ partner factories for rapid tooling (5–7 day mold lead time) and scalable production (1K–100K+ units).
Zero-flash tolerance: <0.002″ flash on critical sealing surfaces.
Full traceability: Material certifications and production data for every batch.
Solve Your Sealing Challenges Today
Partner with Suzhou Baoshida for precision-engineered rubber diaphragms that meet the highest industry standards. Our 5+2+3 engineering team and 10+ partner factories ensure rapid prototyping, scalable production, and uncompromising quality.
Contact Mr. Boyce
📧 [email protected]
📞 +86 189 5571 6798
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate the weight of rubber O-rings for material planning.
