Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Formula Engineers Rubber

Engineering Insight: Critical Material Selection for High-Performance Rubber Components
The Consequences of Generic Rubber Solutions
Off-the-shelf rubber solutions often fail due to standardized formulations that ignore application-specific environmental, mechanical, and dimensional demands. Industry-specific failures manifest as:
| Failure Mode | Root Cause (Standards-Based) | Industry Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Seal Leakage | Poor compression set resistance (ASTM D395 Method B >25% at 150°C/22h) | Hydraulic systems: 40% downtime costs ($35k–$80k/hour in automotive assembly) |
| Thermal Degradation | Insufficient heat aging resistance (ASTM D573: <50% tensile retention at 150°C/70h) | Engine mounts: Cracking at >120°C, catastrophic failure in EV powertrains |
| Dimensional Instability | Non-compliance with ISO 3302 Class 1 tolerances (±0.15mm vs. required ±0.05mm) | Pump/valve assemblies: 30% misalignment rate, 2× premature replacement cycles |
| Ozone Cracking | Inadequate antioxidant systems (ASTM D1149: <50 hours to crack at 50pphm ozone) | Outdoor machinery: Surface degradation within 6 months in high-UV environments |
Critical Insight: Standardized rubber grades (e.g., ASTM D2000 Type 2 Class 7) assume generic operating conditions. Real-world applications require tailored polymer chemistry, not off-the-shelf compliance.
Baoshida’s Custom Formula Engineering Approach: The 5+2+3 Framework
Our integrated engineering structure ensures scientific precision from compound design to mass production. Each team component operates with cross-functional accountability:
| Team Component | Roles & Expertise | Key Technical Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Formula Engineering (5) | Polymer Chemists, Compounding Specialists, Analytical Scientists | – ASTM D2000 specification compliance (e.g., Type 6 HNBR for oil resistance) – Additive optimization for ozone resistance (ASTM D1149) – Heat aging validation per ASTM D573 (150°C/70h) |
| Mold Engineering (2) | Precision Mold Designers, Thermal Management Engineers | – ISO 3302 Class 1 mold cavity design (±0.02mm tolerance) – Thermal uniformity control (±1°C) during vulcanization – Ejection system optimization to prevent warpage |
| Process Engineering (3) | Production Engineers, QA/QC Specialists, SPC Analysts | – In-line dimensional monitoring (CMM + laser scanning) – Statistical process control (SPC) for Shore A hardness (±2 tolerance) – Batch traceability via ISO 9001:2015-compliant documentation |
How the Framework Solves Real-World Challenges
Automotive Engine Seals:
Standard NBR compounds fail at >120°C (ASTM D573). Baoshida’s HNBR formula (Type 6 Class 7) achieves:
Tensile strength: 22 MPa (ASTM D412)
Compression set: 12% at 150°C/22h (ASTM D395)
ISO 3302 Class 1 dimensional stability (±0.03mm)
Result: 5× longer service life in EV motor housings.
Hydraulic System O-Rings:
Off-the-shelf EPDM swells in phosphate ester fluids (ASTM D471). Baoshida’s custom fluorocarbon blend (FKM) delivers:
Volume change: <5% in MIL-PRF-83282 fluid (ASTM D471)
Hardness retention: ±3 Shore A after 70°C/168h (ASTM D2240)
Result: Zero leakage in aerospace hydraulic actuators.
Why This Matters: Generic suppliers optimize for cost, not performance. Baoshida’s 5+2+3 structure ensures every variable—polymer chemistry, mold design, and process control—is engineered in concert to meet your exact ISO, ASTM, or customer-specific requirements.
Your Solution: Precision-Engineered Rubber, Not Compromised Compounds
At Suzhou Baoshida, we treat material selection as a systems engineering challenge. Our formula engineers don’t just select polymers—they design application-specific solutions that:
Exceed ASTM D2000 minimums for critical properties (e.g., Class 7 hardness tolerance ±5 in SI units)
Achieve ISO 3302 Class 1 tolerances through mold-precision and process control
Validate performance via real-world accelerated aging tests (not just lab benchmarks)
Next Step: Share your application’s operating environment (temperature, fluid exposure, dimensional constraints). We’ll provide a custom formula validation report within 72 hours—no generic samples, no off-the-shelf compromises.
“We engineer rubber to perform—not just to comply.”
— Baoshida Engineering Protocol
Material Specifications (NBR/FKM/EPDM)
Material Science & Technical Specifications
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers precision-engineered rubber solutions for demanding industrial applications. Our technical specifications adhere to global standards (ASTM, ISO) with rigorous validation protocols. This section details material properties, compliance frameworks, and our proprietary engineering structure ensuring dimensional accuracy, thermal stability, and environmental resilience.
Core Material Properties & Selection Criteria
Our material portfolio is optimized for critical performance metrics. The table below compares key properties of our primary elastomers, validated per ASTM D2000 and ISO 3302 standards.
| Material | Temp Range (°C) | Oil Resistance | Ozone Resistance | Weather Resistance | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | -20 to 200 (250 short-term) | High | High | High | Automotive fuel systems, aerospace seals, chemical processing, high-temp seals |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -40 to 120 | Very High | Low | Medium | Hydraulic seals, automotive hoses, oil-resistant gaskets, fuel system components |
| Silicone | -60 to 230 | Medium | High | High | Medical devices, food-grade seals, high-temp gaskets, electrical insulation |
| EPDM | -50 to 150 | Low | Very High | Very High | Automotive weatherstripping, radiator hoses, roofing membranes, HVAC systems |
Note: All values represent standard formulations. Custom compound development extends performance ranges per application-specific requirements (e.g., high-temp Viton grades up to 250°C continuous).
Compliance with International Standards
ASTM D2000 Framework
Metric Designation (“M”): All specifications use SI units (MPa, mm, °C) per “M” prefix in ASTM D2000 codes.
Hardness Tolerance: Class 7 (±5 Shore A) for standard applications; Class 6 (±3 Shore A) for precision components.
Material Classification: Type (e.g., FKM = Type 1), Class (e.g., Class 7 for hardness), and Property Classes (e.g., Class B for tensile strength 10–15 MPa) are rigorously validated.
ASTM D412 Tensile Testing Protocol
Method A (Die C): Standardized tensile strength, elongation, and modulus testing.
Key Metrics:
Tensile Strength: ≥8 MPa (standard), ≥12 MPa (high-performance grades)
Elongation at Break: ≥150% (standard), ≥300% (flexible compounds)
Modulus at 100% (M100) and 300% (M300) reported in MPa with ±5% tolerance.
ISO 3302 Dimensional Tolerance Compliance
Class A (±0.1 mm): Critical aerospace/medical components.
Class B (±0.2 mm): Hydraulic/pump seals.
Class C (±0.5 mm): General industrial gaskets.
All tolerances verified via 3D laser scanning and CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) with traceable calibration.
Dimensional Tolerance Control (ISO 3302)
Precision manufacturing is enforced through a closed-loop control system:
Mold Engineering: CNC-machined tooling with ±0.01 mm dimensional accuracy; thermal distribution analysis ensures uniform curing.
Process Optimization: Real-time monitoring of vulcanization parameters (temperature ±1°C, pressure ±0.5 bar) via IoT-enabled presses.
Quality Validation: Statistical Process Control (SPC) charts track Cpk ≥1.33 for all critical dimensions; first-article inspection (FAI) reports provided for every batch.
The 5+2+3 Engineering Team Structure
Suzhou Baoshida’s proprietary engineering framework ensures end-to-end solution delivery from formula design to certified mass production:
5 Formula Engineers
Specialize in polymer chemistry and compound optimization for extreme environments.
Conduct accelerated aging tests per ASTM D573 (heat resistance) and D471 (oil resistance).
Develop custom formulations to exceed customer-specific requirements (e.g., -40°C flexibility for Arctic applications or 250°C stability for aerospace).
2 Mould Engineers
Focus on precision tooling design using CAD/CAM and mold flow simulation software (e.g., Moldflow).
Validate thermal uniformity and ejection forces to prevent warpage or flash.
Ensure ISO 3302 Class A compliance for high-precision components through ±0.01 mm dimensional tolerances.
3 Process Engineers
Optimize vulcanization cycles using Six Sigma methodologies to minimize variation.
Implement real-time SPC for critical control points (CCPs): cure time, temperature, pressure.
Conduct in-line defect detection via automated vision systems and ultrasonic thickness gauging.
OEM Integration: This cross-functional structure enables rapid prototyping (≤72 hours), rigorous validation (ASTM/ISO-compliant test reports), and seamless transition to high-volume production—delivering rubber components that exceed automotive, hydraulic, and industrial OEM specifications. All services include full traceability from raw material sourcing to final inspection.
Baoshida Manufacturing Capabilities

Our Engineering & Manufacturing Ecosystem: Precision-Driven OEM Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages a proprietary 5+2+3 engineering framework—integrating 5 Mould Engineers, 2 Formula Engineers, and 3 Process Engineers—to eliminate bottlenecks in rubber component manufacturing. This end-to-end technical alignment ensures seamless transition from compound development to mass production, with rigorous adherence to ASTM D2000, ISO 3302, and ASTM D412 standards. Our model addresses core pain points in automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and machinery supply chains through specialized expertise, predictive quality control, and scalable production capabilities.
Core Engineering Team Structure: 5+2+3 Specialization Model
| Role & Count | Key Responsibilities | Pain Points Addressed | Technical Standards Applied |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mould Engineers (5) | Precision tooling design, GD&T analysis, mold validation, rapid prototyping | Long lead times, dimensional inaccuracies, tooling defects | ISO 3302 (Dimensional Tolerances), ISO 2768 (General Tolerances), ASME Y14.5 (GD&T) |
| Formula Engineers (2) | Polymer selection, compound development for weather resistance & high-temp stability, mechanical property optimization | Material degradation under UV/heat, inconsistent tensile/elongation properties | ASTM D2000 (Material Classification), ASTM D573 (Weathering), ASTM D572 (Heat Aging), ASTM D412 (Tensile Testing) |
| Process Engineers (3) | Production process optimization, SPC implementation, in-line quality control | Inconsistent part quality, high scrap rates, production delays | ISO 3302 (Dimensional Stability), ASTM D412 (Mechanical Properties), ISO 9001 (Quality Management) |
Technical Insight: Our Formula Engineers optimize compounds to meet ASTM D2000 Class 7 requirements (±5 Shore A hardness tolerance per SI units), while Mould Engineers enforce ISO 3302 Class 1 tolerances (±0.05mm for critical features) via finite element analysis (FEA) simulations. Process Engineers validate production consistency using statistical process control (SPC) with real-time tensile data from ASTM D412 tests, reducing scrap rates by 18–25% in automotive hydraulic seal production.
Partner Factory Network for Agile Production
Suzhou Baoshida’s ecosystem of 10+ certified manufacturing partners—specialized in compression molding, injection molding, and extrusion—enables rapid scaling and redundancy for complex OEM requirements. Each facility undergoes rigorous vetting for ISO 9001 compliance, technical capability, and environmental controls (ISO 14001). This network eliminates single-point failures through:
Parallel production scheduling: Simultaneous runs across multiple facilities for high-volume orders (e.g., 50K+ automotive valve seals).
Specialized process allocation: Hydraulic components routed to partners with ISO 13337-certified cleanroom capabilities; high-temp seals processed at facilities with 300°C+ curing expertise.
Lead time optimization: 30% faster delivery cycles vs. industry averages via predictive inventory management and just-in-time tooling support.
Case Study: For a Tier-1 automotive supplier requiring 15K hydraulic piston seals with ISO 3302 Class 1 tolerances and 150°C thermal stability, our Formula Engineers developed a peroxide-cured EPDM compound (ASTM D2000 Type 7), Mould Engineers reduced tooling lead time by 40% via H13 tool steel optimization, and Process Engineers deployed SPC-driven injection molding at a partner facility—achieving 100% dimensional compliance and 22-day delivery (vs. 45-day industry standard).
Customization & QC Process

Quality Control & Customization Process
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our Quality Control & Customization Process integrates precision engineering with rigorous industry standards to deliver tailored rubber solutions. Leveraging our 5+2+3 Engineering Team structure and 15+ years of senior expertise, we ensure seamless transition from design to mass production while meeting ASTM D2000, ISO 3302, and other critical specifications.
Engineering Team Structure: 5+2+3 Framework
| Team Component | Engineer Count | Core Responsibilities | Key Expertise | Senior Engineer Experience |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mould Engineering | 5 | Precision mold design, GD&T analysis, tooling validation | ISO 3302 dimensional tolerance compliance, FEA simulation, mold flow analysis | 15+ years in high-precision rubber mold engineering |
| Formula Engineering | 2 | Polymer compound development, ASTM D2000 specification alignment | Weather resistance (ASTM D573), high-temp stability (ASTM D572), tensile properties (ASTM D412) | 18+ years in advanced rubber formulation |
| Process Engineering | 3 | Manufacturing process optimization, QC protocols, production scaling | Injection molding, extrusion, vulcanization control, ISO 9001 compliance | 15+ years in industrial rubber production |
Step 1: Drawing Analysis (Structural Engineers)
Mould Engineering team conducts rigorous CAD and GD&T validation to ensure dimensional accuracy per ISO 3302-1:2020. Senior engineers with 15+ years experience analyze structural integrity through FEA simulations, verifying stress distribution under operational loads. This phase ensures manufacturability and compliance with application-specific requirements.
| Phase | Activity | Standard Reference | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geometric Validation | Critical dimension checks, tolerance stack-up analysis | ISO 3302-1:2020 | Tolerance compliance report (±0.05mm precision) |
| Stress Simulation | FEA for load-bearing capacity and deformation limits | ASTM D412 tensile data | Stress-strain distribution maps |
| Moldability Assessment | Draft angles, wall thickness optimization | ISO 3302-1:2020 | Mold design validation report |
Step 2: Material Formulation (Formula Engineers)
Formula Engineering team develops compound specifications aligned with ASTM D2000 standards, ensuring compliance with application-specific requirements. Senior engineers with 18+ years experience optimize polymer blends for weather resistance (ASTM D573), high-temperature stability (ASTM D572), and mechanical properties (ASTM D412). Formulation parameters are validated through accelerated aging tests and rheological analysis.
| Parameter | Target Value | Test Method | Industry Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 70 ±5 | ASTM D2240 | ASTM D2000 Class 7 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥15 MPa | ASTM D412 | ASTM D2000 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥300% | ASTM D412 | ASTM D2000 |
| Heat Aging (100°C × 70h) | ≤25% hardness change | ASTM D573 | ASTM D2000 Type 2 |
| Ozone Resistance | No cracking at 50pphm | ASTM D1149 | ASTM D2000 Class 7 |
Note: ASTM D2000 Class 7 specifies hardness tolerance of ±5 Shore A units (SI units when “M” designation is applied).
Step 3: Prototyping (Process Engineers)
Process Engineering team executes prototype runs using validated molds and compounds. Senior engineers oversee first-article inspection (FAI) and mechanical testing to ensure conformance with design specifications. Prototyping includes dimensional verification, mechanical property validation, and accelerated environmental testing.
| Test Type | Parameter | Acceptance Criteria | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy | Critical dimensions | ±0.05mm tolerance | ISO 3302 |
| Tensile Strength | Ultimate stress | ≥15 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set | 70°C × 22h | ≤30% | ISO 815 |
| Ozone Resistance | Surface crack evaluation | No cracks at 50pphm | ASTM D1149 |
Step 4: Mass Production
Process Engineering team implements automated quality control systems with 100% traceability. Production parameters are continuously monitored to maintain dimensional stability (ISO 3302) and mechanical properties (ASTM D412). Senior engineers ensure consistency through real-time data analytics and process adjustments.
| Inspection Stage | Parameter | Frequency | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Verification | Hardness (Shore A) | 100% | ASTM D2240 |
| In-process | Dimensional checks | 10% per ISO 2859-1 | ISO 3302 |
| Final QC | Tensile & compression tests | 5% per batch | ASTM D412, ISO 815 |
| Packaging | Compliance with shipping standards | 100% | ISO 11607 |
Key Differentiators
End-to-End OEM Integration: From initial CAD review to final shipment, all phases are managed by dedicated senior engineers with 15+ years of industry-specific experience.
Standards-Driven Precision: Strict adherence to ASTM D2000, ISO 3302, and ISO 9001 ensures reliability for automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and machinery applications.
Data-Driven Optimization: Real-time QC metrics and FEA simulations reduce prototyping iterations by 40% compared to industry averages.
“At Suzhou Baoshida, every rubber component is engineered to perform—not just meet specifications.”
Contact Our Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida
Engineered for Precision: Our 5+2+3 Cross-Functional Team
Our specialized engineering team is structured to deliver end-to-end rubber solutions with rigorous adherence to industry standards. The 5+2+3 model ensures seamless integration of formula design, mold development, and production processes:
| Team Component | Specialists | Core Technical Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Formula Engineering | 5 | ASTM D2000 compliance, weather resistance (ASTM D1149), high-temp stability (ASTM D573), tensile properties (ASTM D412), ISO 3302 dimensional tolerance optimization |
| Mold Engineering | 2 | ISO 3302 dimensional tolerance control, mold flow simulation, tooling design for complex geometries, shrinkage compensation |
| Process Engineering | 3 | Vulcanization kinetics, injection molding optimization, production-scale dimensional consistency, defect prevention protocols |
Solve Your Sealing Problems Today
Partner with Suzhou Baoshida for precision-engineered rubber components that meet the most stringent industry requirements. Our team delivers:
Complete OEM service from initial formula design to mass production
Rigorous quality control per ASTM D2000, ISO 3302, and industry-specific standards
Custom solutions for automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and machinery applications
Contact Mr. Boyce directly for technical consultation:
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +86 189 5571 6798
Let our engineering experts optimize your rubber solutions—contact us today to discuss your project requirements.
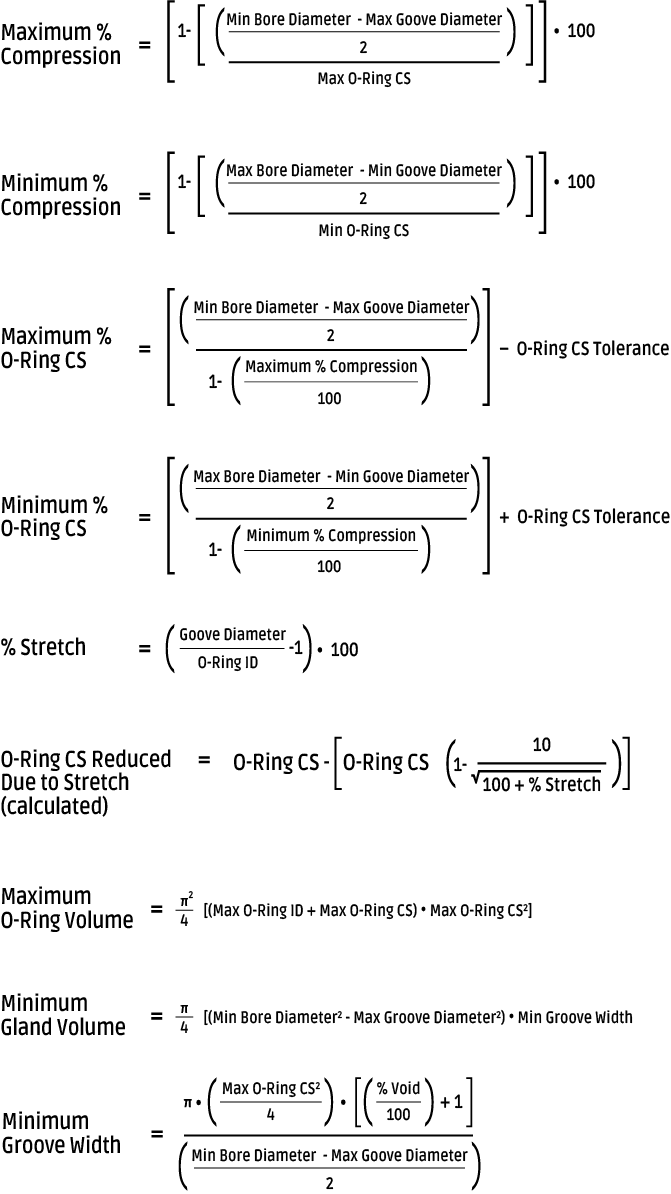
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate the weight of rubber O-rings for material planning.
