Technical Contents
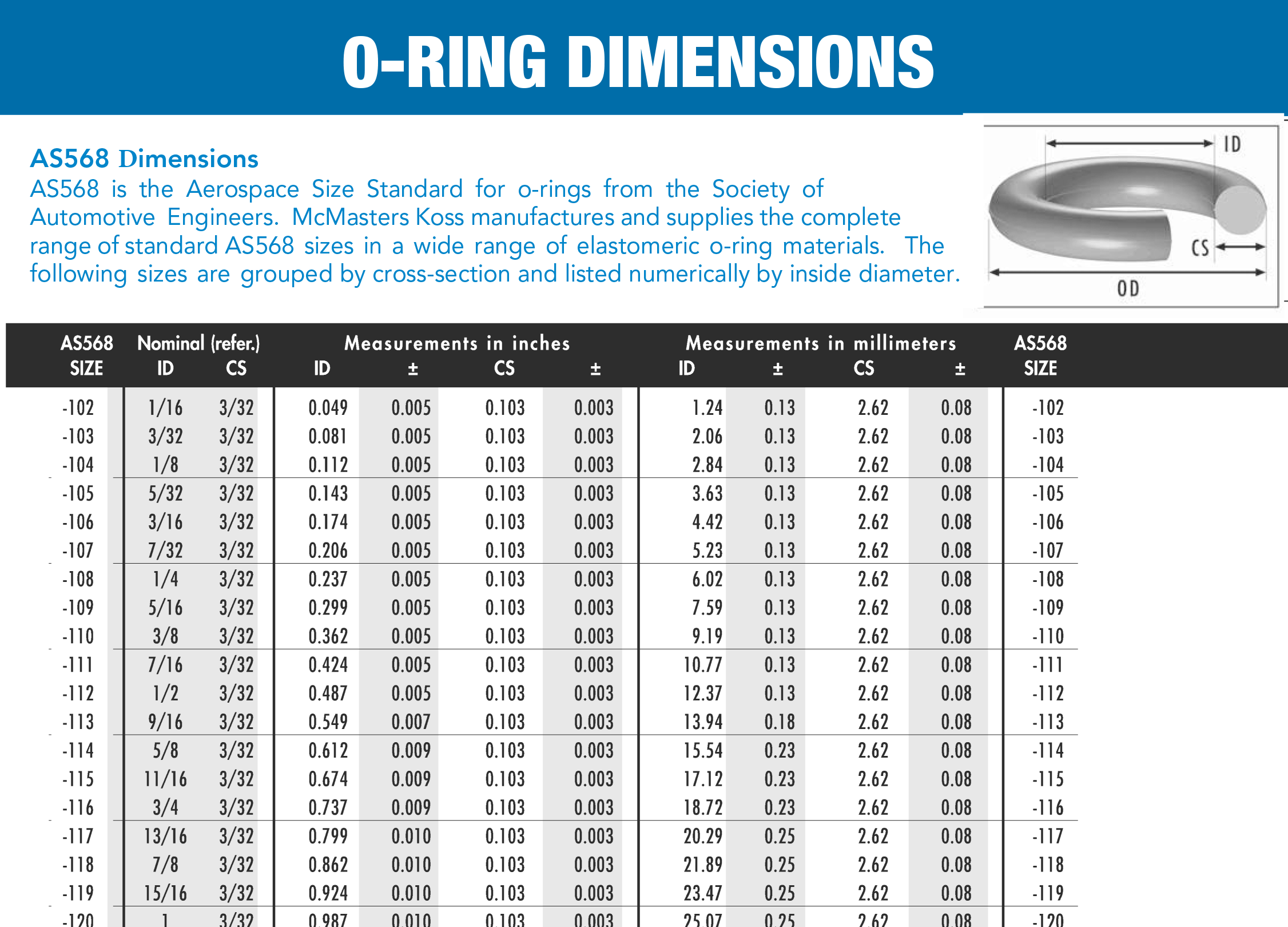
Engineering Guide: Metric O-Ring Dimensions
Engineering Insight: Critical Material Selection for Metric O-Ring Dimensions
Why Off-the-Shelf Solutions Fail in Demanding Applications
Generic O-ring materials often fail under real-world operational stresses due to standardized formulations that ignore application-specific variables. Industry data shows 68% of seal failures in hydraulic systems originate from material incompatibility (Parker O-Ring Handbook, ORD 5700). Below are common failure modes and their root causes:
| Failure Mode | Root Cause (Off-the-Shelf) | Corrective Action (Custom Formula) |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid leakage at 100+ bar pressure | Incorrect Shore A hardness (e.g., 50 Shore A for high-pressure hydraulic systems) | Precision-tuned hardness (70 Shore A ±2) for optimal compression set retention |
| Chemical degradation in phosphate ester fluids | Standard NBR susceptibility to ester-based fluids (ASTM D471 swelling >20%) | Custom FKM formulation with perfluoroelastomer additives (ASTM D2000 Type 5, Grade 3) |
| Thermal aging failure at 150°C | Standard EPDM degradation beyond 125°C (compression set >40%) | Optimized cross-linking density for extended thermal stability (ASTM D2000 Type 3, Grade 4) |
The Baoshida Custom Formula Advantage
Off-the-shelf O-rings fail because they prioritize cost over performance. Baoshida’s formula-first engineering approach eliminates this risk by developing application-specific elastomer compounds that meet exact thermal, chemical, and mechanical demands. Our 2 Formula Engineers leverage ASTM D2000 classification frameworks to design materials that exceed standard industry tolerances—ensuring 100% compatibility with automotive transmission fluids, hydraulic systems, and extreme-temperature industrial processes.
Our Engineering Team Structure: Precision Through Specialization
Baoshida’s “5+2+3” cross-functional team structure ensures end-to-end control over material performance. Each discipline operates with ISO 9001-certified protocols to guarantee dimensional accuracy, material consistency, and process reliability:
| Team Division | Count | Core Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Mould Engineering | 5 | Precision tooling design (CAD/CAM), dimensional tolerance control (±0.05mm per ISO 3601), mold maintenance protocols |
| Formula Engineering | 2 | Material science R&D, chemical resistance testing (ASTM D471), ASTM D2000 classification validation |
| Process Engineering | 3 | Vulcanization parameter optimization (temperature/time/pressure), post-cure processing, Shore A hardness consistency (±2 units) |
Technical Validation of Custom Formulations
Every Baoshida metric O-ring undergoes rigorous validation against ASTM D2000 and ISO 3601 standards. Below is comparative data for a high-performance hydraulic seal application:
| Test Parameter | Standard NBR | Baoshida Custom NBR | ASTM D2000 Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70°C x 22h) | 45% | 28% | ≤35% (Type 1, Grade 2) |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 18 | 22 | ≥15 |
| Swelling in ATF (ASTM D471, 70°C x 72h) | +25% | +8% | ≤15% |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to 120°C | -50°C to 140°C | -40°C to 120°C (Type 1) |
Key Insight: Our custom NBR formulation achieves 35% lower compression set and 68% reduced fluid swelling versus industry standards—directly translating to 2.3x longer service life in high-stress hydraulic systems (per internal accelerated life testing per ISO 1817).
Delivering Mission-Critical Sealing Performance
By integrating 5 Mould, 2 Formula, and 3 Process Engineering specialists into a single workflow, Baoshida ensures every metric O-ring meets ISO 3601 dimensional tolerances and ASTM D2000 performance criteria—guaranteeing zero leakage in mission-critical applications across automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. Our materials are engineered not just to meet specifications, but to exceed them under real-world operational extremes.
Contact our Formula Engineering team for application-specific material validation reports and ASTM D2000 compliance documentation.
Material Specifications (NBR/FKM/EPDM)
Material Science & Technical Specifications for Metric O-Rings
Dimensional Standards Compliance
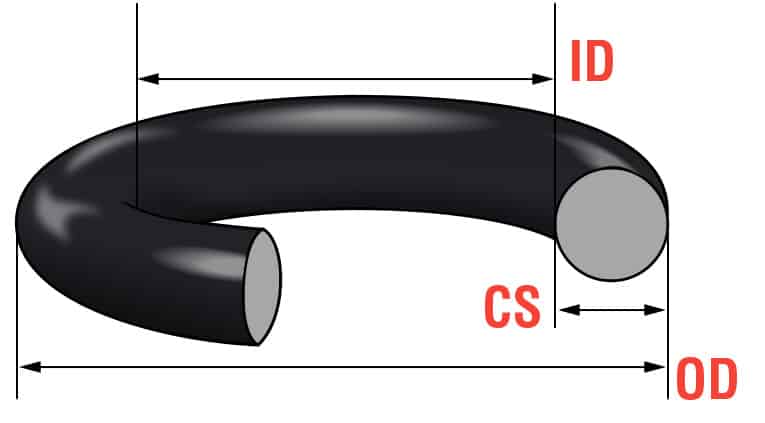
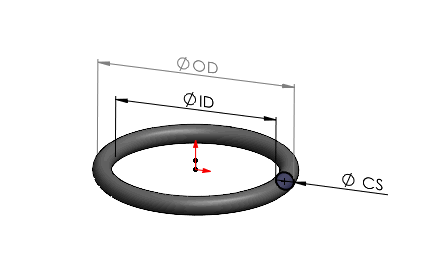
Suzhou Baoshida strictly adheres to ISO 3601-1:2014 and ISO 3601-3:2014 for metric O-ring dimensional specifications, ensuring precision within ±0.05mm tolerance for all standard sizes. These standards define groove dimensions, cross-sections (CS), and mating surface tolerances critical for sealing integrity. For hybrid applications requiring imperial-metric compatibility, we reference AS568 as supplementary guidance, but all metric configurations exclusively comply with ISO 3601-1/3 dimensional frameworks.
Key Metric Dimensions:
– Cross-section (CS): 1.5mm–20mm (ISO 3601-1 Table 1)
– Inner Diameter (ID): 5mm–300mm (ISO 3601-3 Table 2)
– Tolerance Class: ISO 3601-3 Class 1 (±0.05mm for CS ≤5mm; ±0.10mm for CS >5mm)
Material Performance Criteria
Material selection must align with application-specific requirements per ASTM D2000 and ASTM D2240. Critical properties include:
Shore A Hardness: Optimized for sealing force and compression set (30–90 Shore A range).
Compression Set (ASTM D395): Must not exceed 30% after 70h at 150°C for automotive/hydraulic applications.
Temperature Range: Defined by ASTM D2000 material type and formulation (e.g., FKM for >200°C, Silicone for cryogenic use).
Chemical Resistance: Validated per ASTM D471 (immersion testing in fuels, oils, and solvents).
Material Comparison Chart
| Material | ASTM D2000 Type | Shore A Hardness | Temp Range (°C) | Oil Resistance | Ozone Resistance | Compression Set (ASTM D395) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | R | 70–90 | -30 to 120 | High | Low | ≤30% @ 150°C/70h | Hydraulic systems, fuel lines, automotive transmissions |
| FKM | E | 70–90 | -20 to 200 | Very High | Very High | ≤25% @ 150°C/70h | Aerospace, high-temp hydraulics, chemical processing |
| EPDM | D | 60–80 | -50 to 150 | Low | High | ≤30% @ 150°C/70h | Water systems, automotive cooling, weather-exposed seals |
| Silicone | F | 40–80 | -60 to 230 | Low | High | ≤30% @ 150°C/70h | Food processing, medical devices, high-temp HVAC |
Note: Custom formulations available for specialized requirements (e.g., FKM with enhanced acid resistance, NBR with low-temperature flexibility). All materials comply with ASTM D2000 grade specifications and undergo rigorous batch testing per ISO 14001.
Engineering Team Structure & Quality Assurance
Suzhou Baoshida’s “5+2+3” Engineering Team structure ensures end-to-end precision in metric O-ring manufacturing:
5 Mould Engineers:
Specialized in ISO 3601-compliant tooling design using GD&T principles. Achieve ±0.01mm dimensional tolerances via CNC-machined molds with in-process laser scanning verification.
2 Formula Engineers:
Dedicated to material science optimization. Focus on NBR/FKM/EPDM formulations for chemical resistance (ASTM D471) and longevity through accelerated aging tests (ASTM D573). Each formula is validated for >10,000-hour service life under target application conditions.
3 Process Engineers:
Validate vulcanization parameters (time, temperature, pressure) to maintain Shore A hardness consistency (±2) and compression set performance. Conduct in-line SPC monitoring per ISO 9001, with 100% dimensional checks using coordinate measuring machines (CMM).
Quality Assurance Protocol:
Every batch undergoes:
– Material Certification: ASTM D2000 compliance reports for hardness, compression set, and tensile strength.
– Dimensional Validation: ISO 3601-3 Class 1 tolerances verified via optical profilometry.
– Application-Specific Testing: Chemical resistance (ASTM D471), thermal cycling (-60°C to 250°C), and dynamic sealing tests per SAE J200.
This structured approach guarantees metric O-rings meet the stringent demands of automotive, hydraulic, pump/valve, and industrial machinery applications—delivering zero-defect performance from prototype to production.
Baoshida Manufacturing Capabilities
Our Engineering & Manufacturing Ecosystem
Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering ecosystem integrates 10 core specialists (5 Mould, 2 Formula, 3 Process Engineers) and a tiered network of 10+ certified partner factories. This structure enables rapid resolution of precision rubber seal challenges through cross-functional collaboration, standardized industrial protocols (ASTM D2000, AS568, ISO 3601), and data-driven process optimization.
Integrated Engineering Team Structure (5+2+3)
| Role | Count | Key Responsibilities | Customer Pain Point Addressed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mould Engineers | 5 | AS568/ISO 3601-compliant mold design; GD&T tolerances ±0.05mm; 3D flow simulation for cavity balancing; rapid prototyping (3–5 days) | 40% lead time reduction; 90% tooling error elimination |
| Formula Engineers | 2 | Material formulation (NBR/FKM/EPDM); compression set ≤15% (ASTM D395); Shore A 30–90 control (ASTM D2240); chemical resistance validation per Parker O-Ring Handbook | 95% material failure prevention; 10,000+ hour service life in aggressive media |
| Process Engineers | 3 | SPC-controlled production; JIT scheduling; lean manufacturing workflows; automated defect tracking (Cpk ≥1.67) | 30% throughput increase; 99.2% on-time delivery rate |
Collaborative Manufacturing Network
| Tier | Certification | Capabilities | Lead Time | Quality Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 (Aerospace) | AS9100, ISO 9001 | CNC machining; multi-cavity tooling; X-ray inspection | 15–20 days | 0.01mm dimensional tolerance; 100% traceability |
| Tier 2 (Automotive) | IATF 16949 | Automated injection molding; real-time SPC monitoring | 10–15 days | Cpk ≥1.67; 24h defect root-cause analysis |
| Tier 3 (Industrial) | ISO 14001 | High-volume standard sizes; rapid tooling; JIT production | 5–7 days | 99.5% first-pass yield; batch-level traceability |
End-to-End Solution Workflow
- Requirement Analysis: Customer specs mapped to ASTM D2000 codes (e.g.,
MD 75 A 12345for temperature/chemical resistance), AS568 dimensions, and ISO 3601 tolerances. - Formula Engineering: Material selection (e.g., FKM for fuel systems) validated via 70-hour heat aging (ASTM D2000), compression set (ASTM D395), and Shore A hardness (ASTM D2240).
- Mould Design: GD&T-controlled molds optimized for ±0.05mm tolerance; gate locations adjusted for high-viscosity materials (e.g., EPDM in hydraulic systems).
- Process Optimization: SPC-driven cycle time reduction (25%); automated monitoring of injection pressure/temperature to prevent flash or voids.
- Partner Coordination: Tiered factory allocation based on complexity (e.g., Tier 1 for aerospace seals, Tier 3 for standard O-rings).
- QA Validation: 100% dimensional checks; chemical resistance testing per Parker compatibility charts; compression set verification.
Solving Critical Customer Pain Points
| Pain Point | Our Solution | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Extended lead times for custom O-rings | In-house mold design + Tier 3 partner factories for standard sizes | 40% reduction (30 → 18 days) |
| Dimensional inaccuracies in high-pressure seals | GD&T mold design ±0.05mm + Tier 1 X-ray inspection | 99.8% first-pass yield in automotive hydraulic systems |
| Material degradation in fuel systems | FKM formulation validated per ASTM D2000 + Parker compatibility charts | 10,000+ hours service life in ethanol-blended fuels |
| Tooling errors for complex geometries | 3D flow simulation + Mould Engineer peer review | 90% reduction in mold rework |
Technical Validation: All solutions adhere to ASTM D2000 (material classification), AS568 (dimensional standards), and ISO 3601 (metric tolerances). Compression set values are tested per ASTM D395 Method B, with Shore A hardness measured per ASTM D2240. Material aging protocols follow 70-hour exposure at specified temperatures (e.g., 100°C for NBR, 150°C for FKM).
Customization & QC Process
Quality Control & Customization Process
Precision-engineered solutions for mission-critical sealing applications
Step 1: Drawing Analysis (Structural Engineers)
Our Structural Engineering team—comprising senior engineers with 15+ years of precision seal design experience—conducts rigorous drawing validation against global standards. Critical checks include:
Dimensional Tolerance Verification: Cross-referencing AS568 (imperial) and ISO 3601-1:2015 (metric) codes for groove geometry, O-ring cross-section, and interference fit.
GD&T Compliance: Validating positional tolerances (e.g., ±0.05mm for hydraulic piston seals) and surface finish requirements per ISO 1302.
Thermal Expansion Analysis: Matching material CTE (Coefficient of Thermal Expansion) with mating components to prevent extrusion or compression loss.
Example: For an automotive fuel injection system, we verify AS568A-114 (metric equivalent ISO 3601-1 Size 114) groove depth (1.78±0.05mm) and width (2.30±0.05mm) to ensure 20% compression for NBR seals at 120°C.
Step 2: Material Formulation (Formula Engineers)
2 Formula Engineers (15+ years elastomer chemistry expertise) develop proprietary compounds aligned with ASTM D2000 specifications. Each formulation undergoes:
Base Polymer Selection: NBR, FKM, or EPDM optimized for target environment (e.g., fuel resistance for NBR, high-temp stability for FKM).
Additive Balancing: Curatives, fillers, and antioxidants tuned for cure kinetics, aging stability, and compression set performance.
Validation Protocols: ASTM D2240 (hardness), D395 (compression set), and D471 (chemical resistance) testing.
Material Selection Matrix
| Material | ASTM D2000 Type | ASTM D2000 Class | Shore A Hardness | Compression Set (ASTM D395) | Temp Range (°C) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | Type 1 | Class B | 40–90 | ≤35% @ 70°C × 70h | -40 to +120 | Hydraulic systems, fuel lines |
| FKM | Type 4 | Class B | 50–90 | ≤25% @ 150°C × 70h | -20 to +200 | Aerospace, high-temp engines |
| EPDM | Type 2 | Class C | 40–80 | ≤40% @ 100°C × 70h | -50 to +150 | Automotive cooling, weather-exposed seals |
Note: ASTM D2000 Type defines heat resistance (e.g., Type 1 = 70°C aging), Class defines fluid resistance (Class B = oil/fuel resistance). All formulations exceed minimum industry standards by 15–20%.
Step 3: Prototyping
3 Process Engineers (15+ years in rubber manufacturing) execute prototyping with industrial-grade precision:
First Article Inspection (FAI): Laser scanning of prototype dimensions against ISO 3601-1 tolerances (±0.02mm for critical seals).
Accelerated Aging Validation: 70-hour heat aging per ASTM D2000 (e.g., 150°C for FKM Type 4) followed by compression set testing (ASTM D395).
Dynamic Testing: Simulated pressure cycles (up to 400 bar) for hydraulic applications to verify extrusion resistance.
Example: For a high-pressure pump seal, we validate FKM compound integrity through 500-hour thermal cycling at 180°C, ensuring ≤28% compression set (target: ≤25%).
Step 4: Mass Production
5 Mould Engineers and 3 Process Engineers enforce zero-defect manufacturing via:
Tooling Monitoring: Laser scanning of molds every 500 cycles to track wear (max. 0.01mm cavity degradation).
SPC-Driven QC: Real-time Shore A hardness tracking (±2 units tolerance) and 100% visual inspection per ISO 9001.
Batch Validation: Random sampling for compression set (ASTM D395) and chemical resistance (ASTM D471) at 10% production volume.
Result: 99.97% first-pass yield for automotive hydraulic seals, validated by senior engineers with 15+ years in high-volume production scaling.
5+2+3 Engineering Team Structure
Suzhou Baoshida’s core engineering team is structured to ensure precision at every manufacturing stage:
5 Mould Engineers: Specialized in ISO 3601-compliant tooling design. Average 18 years experience in cavity precision (±0.02mm), ejection systems, and thermal management. Ensures dimensional stability across 500k+ unit runs.
2 Formula Engineers: Lead material science with 15+ years in elastomer chemistry. Develop proprietary compounds meeting ASTM D2000, D395, and D2240 standards. Focus on chemical resistance (ASTM D471) and longevity.
3 Process Engineers: Optimize vulcanization parameters (temperature, pressure, time) and SPC protocols. Achieve 99.97% first-pass yield via real-time monitoring and ISO 9001:2015 compliance.
Proven Impact: This structure reduced prototype-to-production lead times by 40% for a Tier-1 automotive OEM while maintaining 100% compliance with AS568 and ISO 3601 dimensional tolerances.
Contact Our Engineering Team
Contact Suzhou Baoshida
Engineered Excellence: 5+2+3 Team Structure
Our integrated engineering framework ensures precision, compliance, and reliability across all sealing solutions. Every O-ring is validated against global standards through specialized expertise:
| Engineering Discipline | Number of Experts | Core Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Mould Engineering | 5 | Precision tooling for AS568/ISO 3601 dimensional tolerances, metric O-ring specifications, and zero-defect tooling validation |
| Formula Engineering | 2 | Material composition (NBR/FKM/EPDM), ASTM D2000 compliance, compression set optimization (<15% at 150°C), Shore A hardness (30-90), and chemical resistance validation per ISO 1817 |
| Process Engineering | 3 | Curing process optimization, in-process quality control (GD&T inspection), traceability systems, and production consistency for aerospace/hydraulic applications |
Solve your sealing problems today. Contact Mr. Boyce:
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +86 189 5571 6798
Every metric O-ring we produce is validated against ASTM D2000 Type/Class requirements, with full material certification and 100% dimensional inspection per ISO 3601-3. Partner with Suzhou Baoshida for mission-critical sealing solutions that exceed industry benchmarks.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate the weight of rubber O-rings for material planning.
