Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Entrance Doormat
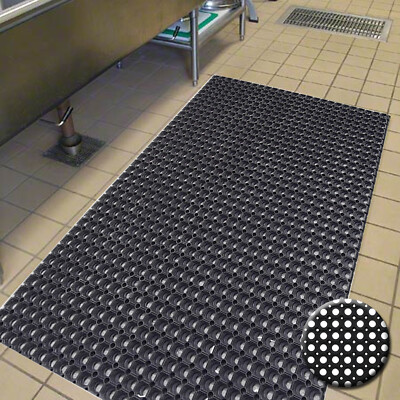

Engineering Insight: Material Science as the Foundation of Commercial Entrance Doormat Performance
The premature failure of entrance doormats in high-traffic commercial environments represents a significant, often underestimated, operational and financial burden. Off-the-shelf solutions, frequently sourced from generic suppliers prioritizing low initial cost, consistently underperform due to fundamental deficiencies in material science and compounding precision. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our OEM engineering approach centers on the critical understanding that the polymer matrix composition and reinforcement strategy directly dictate longevity, safety, and total cost of ownership. Standard recycled rubber mats, prevalent in the market, suffer from inconsistent feedstock quality, excessive non-reinforcing filler content (often exceeding 40% by weight), and inadequate vulcanization control. This results in rapid surface degradation, loss of structural integrity under thermal cycling, and catastrophic failure under abrasive pedestrian traffic – particularly problematic in climates with freeze-thaw cycles or intense UV exposure. The consequence is not merely aesthetic decline but increased slip hazards, frequent replacement costs, and damage to facility reputation.
Virgin synthetic rubber compounds, specifically engineered for this demanding application, provide the necessary performance baseline. Key requirements include exceptional abrasion resistance to withstand constant foot traffic, dimensional stability across wide temperature ranges (-30°C to +70°C), and robust UV resistance to prevent surface cracking and embrittlement. Crucially, the compound must maintain flexibility to effectively scrape dirt while resisting permanent deformation under load. Achieving this balance requires precise control over polymer type (typically high-purity SBR or EPDM), reinforcing filler selection (surface-treated silica replacing carbon black for superior weatherability), curative systems, and protective additive packages. Generic mats lack this tailored formulation, leading to accelerated wear, permanent set (mat flattening), and detachment of the rubber from backing materials. Our OEM process involves rigorous material qualification against defined performance thresholds, ensuring compounds meet the specific abrasion, tensile, and environmental demands of the intended installation site, whether a high-rise lobby or an industrial facility entrance.
The following table compares critical material properties between standard off-the-shelf solutions and Suzhou Baoshida’s engineered OEM compounds:
| Property | Standard Recycled Rubber Mat | Virgin SBR/EPDM OEM Compound (Baoshida Spec) | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High filler (>40%), variable recycled content | Virgin polymer, optimized silica reinforcement | Visual/FTIR |
| Shore A Hardness | 55-65 (inconsistent) | 68 ± 3 (stable) | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 6.0 – 8.0 | ≥ 12.0 | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150 – 250 | ≥ 350 | ASTM D412 |
| Abrasion Loss (mm³) | 180 – 250 | ≤ 90 | ASTM D5963 |
| UV Resistance (QUV hrs) | < 200 (severe cracking) | ≥ 500 (minimal change) | ASTM G154 Cycle 1 |
| Permanent Set (%) | 25 – 40 | ≤ 12 | ASTM D395 Method B |
Material selection is not a commodity decision but a core engineering requirement. Suzhou Baoshida’s focus on scientifically validated rubber formulations ensures entrance mats function reliably as the first line of defense for building interiors, translating directly into reduced lifecycle costs, enhanced safety compliance, and sustained aesthetic performance for our OEM partners and end-users. The initial investment in precision-engineered material yields significant operational savings through extended service life and minimized maintenance disruption.
Material Specifications
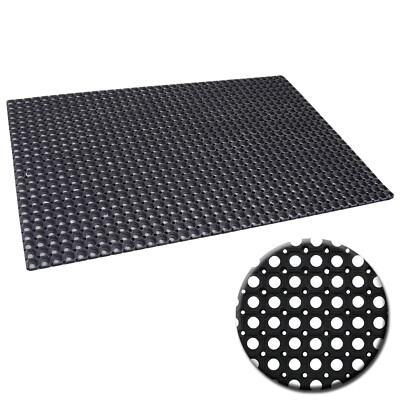
For industrial-grade entrance doormats, material selection is critical to ensure long-term performance under variable environmental and mechanical stress. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-performance rubber compounds engineered for durability, chemical resistance, and weather stability. Our primary elastomers—Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone—are each formulated to meet distinct operational demands in commercial and industrial settings. Understanding the technical characteristics of these materials enables optimal selection based on application-specific requirements such as temperature exposure, oil resistance, and mechanical resilience.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber (FKM), offers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, oils, and ozone. With continuous service capabilities up to 250°C and intermittent peaks reaching 300°C, Viton is ideal for environments exposed to automotive fluids, industrial solvents, and extreme thermal cycling. Its low gas permeability and outstanding aging characteristics make it a premium choice for heavy-duty doormats in manufacturing plants, garages, and chemical processing facilities. However, due to its higher raw material cost, Viton is typically specified where performance outweighs budget constraints.
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a cost-effective solution offering excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and aliphatic hydrocarbons. With a standard operating temperature range of -30°C to 120°C, NBR provides reliable performance in moderate thermal environments. It exhibits good abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, making it suitable for entrance mats in automotive workshops, logistics centers, and industrial warehouses where oil and fluid exposure is frequent. While less resistant to ozone and UV degradation compared to Viton or Silicone, NBR can be compounded with stabilizers to enhance outdoor durability.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature applications, functioning reliably from -60°C to 230°C. It offers superior UV and ozone resistance, ensuring long-term stability in outdoor installations without cracking or embrittlement. Silicone is non-toxic, highly flexible, and maintains its physical properties across wide thermal swings, making it ideal for cleanroom environments, food processing facilities, and exterior commercial entrances. However, it has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance than NBR or Viton, which must be considered in high-traffic or mechanically demanding areas.
The following table compares key technical parameters of these materials to guide material selection for industrial entrance doormats:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 250 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 230 |
| Oil & Fuel Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Ozone & UV Resistance | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Very Good | Moderate |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–8 |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Chemical Resistance | Broad spectrum | Aliphatic oils only | Limited |
| Typical Applications | Chemical plants, refineries | Automotive, warehouses | Outdoor entrances, cleanrooms |
Each elastomer presents distinct advantages, and selection should align with the operational environment and performance priorities. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports OEM partners with custom compounding, precise molding, and full technical documentation to ensure material integrity across production batches.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Excellence in Entrance Doormat Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep technical expertise to deliver high-performance industrial rubber entrance doormats. Our dedicated engineering team comprises five specialized mould engineers and two advanced rubber formula engineers, ensuring end-to-end precision from concept to量产. This integrated capability allows us to solve complex material and structural challenges inherent in high-traffic commercial and industrial applications. Our mould engineers utilize CAD/CAM systems and finite element analysis (FEA) to optimize flow dynamics, cooling channels, and ejection mechanisms, minimizing cycle times while maximizing dimensional stability and surface detail replication. Concurrently, our formula engineers develop proprietary polymer matrices tailored to specific environmental and functional demands, moving beyond standard compound formulations.
Rubber formulation is central to doormat longevity and functionality. Our formula engineers meticulously balance natural rubber (NR), styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) with reinforcing fillers, anti-degradants, and processing aids. This scientific approach achieves critical performance attributes: exceptional abrasion resistance for heavy foot traffic, optimal Shore A hardness for debris retention without user discomfort, and superior UV/ozone stability to prevent cracking and fading in outdoor exposure. We rigorously control vulcanization kinetics to ensure consistent cross-link density, directly impacting rebound resilience and permanent set resistance—key factors in maintaining the mat’s scraping profile over years of service.
The following table details core material properties achievable through our engineered compounds for entrance doormats:
| Property | Test Standard | Typical Value Range | Significance for Doormats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | ASTM D2240 | 55–75 | Balances debris scraping & user comfort |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | 12–18 MPa | Resists tearing under foot traffic |
| Abrasion Loss (Rotary Drum) | ASTM D5963 | ≤ 120 mm³ | Ensures long-term surface profile integrity |
| Compression Set (22h/70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤ 25% | Maintains thickness & resilience after compression |
| UV Resistance (300h QUV) | ASTM G154 | ΔE < 3.0 | Prevents surface degradation & color fade |
Our OEM capabilities transform client specifications into manufacturable reality. We collaborate closely with partners to co-develop custom tread patterns, color systems, and backing integrations (e.g., fabric-reinforced or anti-slip foam). The formula team adjusts compound viscosity for complex mould geometries, while mould engineers validate tooling feasibility through rapid prototyping. This synergy enables rapid iteration—clients receive physical samples within 15 working days for validation. Crucially, our ISO 9001-certified process includes full material traceability, batch-specific certificates of conformance (CoC), and in-house testing for hardness, tensile properties, and density. For global OEM partners, we support regional compliance requirements including REACH, RoHS, and specific fire safety standards (e.g., ASTM E648 for critical surface burning). Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering rigor ensures every doormat meets exacting functional, aesthetic, and durability benchmarks demanded by architectural specifiers and facility managers worldwide.
Customization Process
Drawing Analysis
The customization process for industrial rubber doormats begins with precise drawing analysis, a critical phase that ensures dimensional accuracy and functional compliance. Upon receiving the client’s technical blueprint or CAD file, our engineering team conducts a comprehensive review of key parameters including overall dimensions, tread pattern depth, edge profiles, and any embedded features such as metal inserts or drainage channels. Special attention is given to tolerance specifications—typically ±0.5 mm for molded rubber components—to ensure compatibility with installation environments. We evaluate draft angles and parting lines to optimize mold design for clean demolding and minimal flash. This phase also includes a feasibility assessment for production scalability, identifying any design modifications that may enhance manufacturability without compromising performance. Client feedback is integrated at this stage to finalize the design before tooling proceeds.
Formulation Development
Following drawing approval, our rubber formulation engineers develop a compound tailored to the intended application environment. The selection of base polymer—typically SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber), EPDM, or natural rubber—is determined by performance requirements such as abrasion resistance, UV stability, and temperature tolerance. For entrance doormats exposed to outdoor conditions, EPDM is preferred due to its superior weatherability and ozone resistance. The compound is further enhanced with reinforcing fillers (e.g., carbon black or silica), plasticizers for flexibility, and anti-aging agents. Shore A hardness is customized between 50 and 70 based on desired underfoot feel and durability. All formulations are documented under internal batch standards and subjected to preliminary lab testing for tensile strength, elongation at break, and compression set. This ensures the material meets both functional and regulatory standards prior to prototyping.
Prototyping and Validation
A functional prototype is produced using precision steel molds fabricated in-house, allowing for rapid iteration. The prototype undergoes rigorous physical testing, including slip resistance (measured via DIN 51130 ramp test), wear simulation, and dimensional verification against the original drawing. Color matching is performed under controlled lighting (D65 standard) to ensure consistency with client specifications. Clients receive a sample kit with test reports for approval. Any required adjustments—such as modifying tread depth or adjusting compound stiffness—are implemented before final mold validation.
Mass Production
Once the prototype is approved, the project transitions to mass production. Our automated rubber compression molding lines ensure consistent part quality at scale, with real-time monitoring of cure time, temperature, and pressure. Each batch undergoes quality control checks for visual defects, dimensional accuracy, and physical properties. Finished doormats are packaged per client logistics requirements, with traceability maintained through batch coding.
| Parameter | Standard Range | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | 50–70 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥10 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ≤25% | ASTM D395 |
| Slip Resistance (R9–R11) | R10 typical | DIN 51130 |
Contact Engineering Team

Technical Partnership for Industrial-Grade Entrance Doormat Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the forefront of precision rubber engineering, specializing in high-performance elastomeric compounds for demanding industrial applications. Our entrance doormat formulations are engineered beyond conventional standards, leveraging proprietary polymer matrix optimization to deliver exceptional durability, weather resistance, and functional longevity. As your dedicated OEM partner, we prioritize material science rigor to ensure every mat withstands rigorous commercial foot traffic, extreme temperature fluctuations, and continuous exposure to abrasive particulates without compromising structural integrity. Our solutions are validated through accelerated lifecycle testing, simulating 5+ years of real-world use in controlled laboratory environments. This scientific approach eliminates guesswork, translating directly to reduced replacement costs and sustained aesthetic performance for end-users.
Critical performance metrics define the efficacy of industrial doormats. Below are the core specifications achieved through our SBR-NR hybrid compound, tailored for heavy-duty applications:
| Property | Test Standard | Performance Value | Industrial Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | ASTM D2240 | 65 ± 3 | Optimal balance: debris retention without foot fatigue |
| Abrasion Resistance | ISO 4649 | ≤ 120 mm³ loss | Withstands >10M cycles on steel drum |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥ 18 MPa | Resists tearing under dynamic loading |
| Density | ISO 2781 | 1.15 ± 0.02 g/cm³ | Ensures stability without excessive weight |
| Compression Set (70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤ 22% | Maintains shape integrity after prolonged compression |
These metrics are not theoretical benchmarks but production-relevant outcomes. Our rubber compounds integrate advanced filler dispersion technology and vulcanization control systems, ensuring uniform cross-link density across complex geometries. This eliminates common failure points such as edge delamination or pigment migration seen in commodity-grade mats. Furthermore, our formulations comply with REACH and RoHS directives, with optional certifications for LEED v4.1 Material Ingredient Reporting to support sustainable building initiatives.
Customization is intrinsic to our OEM methodology. We collaborate with manufacturers to adjust compound viscosity for seamless integration into existing extrusion or compression molding lines, minimizing production downtime. Surface texture profiles—from aggressive diamond patterns to ADA-compliant tactile indicators—are precisely engineered to maximize dirt-scraping efficiency while meeting slip-resistance thresholds (ASTM F2913). Thermal stability profiles are calibrated for regional climate extremes, preventing hardening in sub-zero conditions or softening above 80°C.
Initiate your next-generation doormat project with Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering team. Mr. Boyce, our Technical OEM Manager, will conduct a comprehensive material suitability assessment based on your production parameters, volume requirements, and performance targets. He provides actionable data on compound processing windows, mold flow analysis, and lifecycle cost projections—enabling informed sourcing decisions. Contact Mr. Boyce directly at [email protected] to schedule a technical consultation. Include your target specifications, annual volume, and current pain points for immediate compound optimization recommendations. Partner with precision-engineered rubber solutions where material science drives manufacturing excellence.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
