Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Door Draft Seals

Engineering Insight: Material Selection for Door Draft Seals
Field failures of standard door draft seals represent a critical yet preventable cost center in building envelope performance. Generic off-the-shelf solutions frequently degrade within 12–18 months due to inadequate material science alignment with operational stressors. These failures manifest as compression set-induced gaps, ozone cracking, thermal hardening, or chemical swelling—compromising energy efficiency, acoustic insulation, and weatherproofing. The root cause lies in the misapplication of commodity elastomers formulated for low-cost production rather than the multi-variable demands of dynamic door interfaces.
Door seals endure cyclic compression, UV exposure, extreme temperature fluctuations (-40°C to +100°C), airborne pollutants, and incidental contact with cleaning agents or lubricants. Standard EPDM compounds, while economical, lack tailored polymer architecture to resist these combined factors. Their high unsaturation accelerates ozone degradation, while insufficient co-agent crosslinking leads to permanent set under sustained load. In cold climates, generic formulations exceed glass transition temperature (Tg), causing embrittlement and seal fracture. Petroleum-based contaminants further extract plasticizers, accelerating hardening. These material limitations directly correlate with premature air infiltration and costly callbacks.
Suzhou Baoshida addresses this through precision-engineered EPDM and specialty terpolymer formulations. Our compounds integrate controlled diene content for ozone resistance, co-agents for stable crosslink density, and engineered fillers to maintain resilience across thermal cycles. Critical additives mitigate plasticizer migration in chemical exposure scenarios, while optimized cure systems ensure ≤15% compression set after 1,000 hours at 70°C—far exceeding industry baselines. This molecular-level customization prevents the dimensional instability that renders off-the-shelf seals ineffective within demanding OEM applications.
The table below quantifies performance differentials between standard and engineered solutions under accelerated aging protocols:
| Performance Parameter | Standard EPDM Seal | Baoshida Engineered Seal | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70°C/22h) | 42–55% | 8–12% | ASTM D395 Method B |
| Low-Temperature Flex | -40°C (brittle) | -60°C (flexible) | ASTM D1329 |
| Ozone Resistance (50pphm) | Severe cracking (>100h) | No cracking (>300h) | ASTM D1149 |
| Fluid Resistance (SAE 2) | Swell: +25% | Swell: +8% | ASTM D471 |
| Shore A Hardness Shift | Δ +15 points | Δ +3 points | ASTM D2240 |
Material selection is not a cost line item but a system reliability determinant. Generic seals sacrifice long-term performance for initial price reduction, ultimately increasing total cost of ownership through warranty claims and reputational damage. Baoshida’s OEM-engineered compounds deliver dimensional stability and environmental resistance calibrated to specific door system dynamics—ensuring draft elimination over 10+ year service life. This precision approach transforms seals from failure points into silent contributors to building integrity. Partnering with a material science-focused supplier mitigates the hidden risks of commoditized solutions, securing both operational efficiency and end-customer satisfaction.
Material Specifications
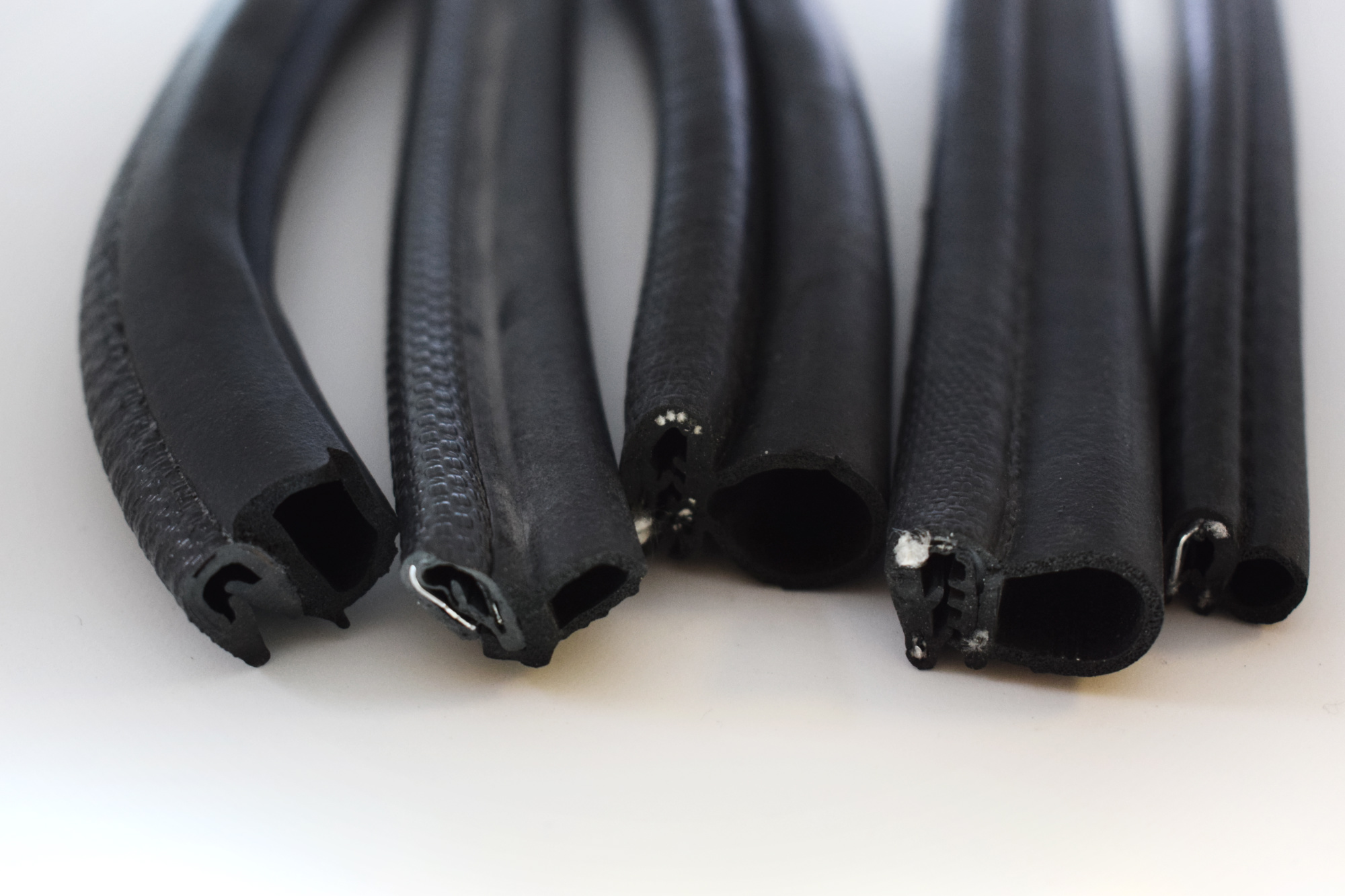

Material Specifications for Door Draft Seals
The performance and longevity of door draft seals are fundamentally determined by the elastomeric material selected for the application. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we engineer precision rubber seals using three primary compounds: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each material offers distinct chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties, enabling optimal performance across diverse environmental and operational conditions. Selecting the appropriate material requires a thorough understanding of exposure factors such as temperature extremes, fluid contact, UV/ozone exposure, and compression set resistance.
Viton (FKM) is a fluorocarbon-based elastomer renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of aggressive chemicals. This makes Viton an ideal candidate for door draft seals used in industrial enclosures, automotive engine compartments, and aerospace applications where exposure to hydrocarbons and continuous operating temperatures up to 200°C are common. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics further enhance long-term sealing integrity. However, Viton exhibits higher material cost and reduced flexibility at low temperatures compared to alternatives.
Nitrile (NBR) remains one of the most widely used elastomers in sealing applications due to its excellent balance of performance and cost. It demonstrates superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and water, making it well-suited for general industrial, automotive, and HVAC door seals. NBR performs reliably within a temperature range of -30°C to +100°C, with short-term excursions up to 120°C. While it offers good abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, its performance degrades under prolonged exposure to ozone, UV radiation, and polar solvents.
Silicone (VMQ) is selected for applications requiring extreme temperature stability and flexibility. It maintains elastic properties from -60°C to +200°C, making it ideal for environments subject to severe thermal cycling. Silicone also offers excellent resistance to UV light, ozone, and weathering, which is critical for exterior-facing door seals in transportation and outdoor equipment. However, silicone has relatively low tensile strength and poor resistance to hydrocarbon fluids, limiting its use in oil-rich environments. Additionally, it is more prone to tearing under mechanical stress.
The selection of the appropriate elastomer must align with the operational profile of the end-use application. Below is a comparative summary of key physical and chemical properties.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +200 | -30 to +100 | -60 to +200 |
| Fluid Resistance (Oils/Fuels) | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Ozone/UV Resistance | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Tensile Strength | High | High | Moderate |
| Flexibility at Low Temp | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
| Cost Level | High | Low to Moderate | Moderate |
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Excellence in Door Draft Seal Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers precision-engineered door draft seals through integrated material science and advanced tooling expertise. Our technical foundation rests on a dedicated team of five mould engineers and two rubber formula specialists, ensuring seamless convergence of design integrity and compound performance. This dual-engineering capability enables us to solve complex sealing challenges while adhering to stringent automotive and architectural industry standards.
Our mould engineering team employs 3D simulation software to optimize cavity design, runner systems, and venting configurations. This preemptive analysis minimizes flash, reduces material waste, and guarantees dimensional stability across production cycles. Each tool undergoes rigorous validation via coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to maintain tolerances within ±0.1 mm, critical for consistent compression deflection and long-term sealing efficacy. Concurrently, our formula engineers develop proprietary EPDM and TPE compounds tailored to operational demands. By manipulating polymer backbone structures, filler dispersion, and crosslink density, we achieve superior resistance to UV degradation, ozone exposure, and extreme temperature fluctuations without compromising flexibility.
OEM collaboration forms the cornerstone of our manufacturing philosophy. We implement a closed-loop development protocol where customer specifications directly inform material formulation and tool geometry. This includes rapid prototyping of seals with custom durometer profiles (55–85 Shore A), multi-cavity production tooling, and batch-specific traceability through integrated ERP systems. Our ISO 9001-certified facility enforces real-time process monitoring, with statistical process control (SPC) tracking critical parameters like cure time, hardness deviation, and compression set at every production stage.
The following table compares standard material properties against our premium formulations, validated per ASTM/ISO test methods:
| Property | Standard EPDM | Baoshida Premium EPDM | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 65 ± 5 | 60 ± 3 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥ 8.0 | ≥ 11.5 | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ≥ 250 | ≥ 350 | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (%) | ≤ 35 (70°C, 22h) | ≤ 22 (70°C, 22h) | ASTM D395 |
| Temp Range (°C) | -40 to +120 | -55 to +140 | ISO 188 |
| Ozone Resistance | Moderate | Excellent (500 pphm) | ASTM D1149 |
This technical synergy between mould design and rubber chemistry directly translates to extended product lifecycle and reduced field failures. We partner with global OEMs to refine sealing interfaces through iterative testing, including dynamic door slam simulations and environmental chamber validation under -40°C to +85°C thermal cycling. Our engineers provide full documentation packages—material certifications, PPAP submissions, and DFMEA reports—to accelerate customer approval cycles. By embedding scientific precision into every development phase, Suzhou Baoshida ensures door draft seals that consistently exceed performance benchmarks while optimizing total cost of ownership for volume manufacturing.
Customization Process
Customization Process for Precision Door Draft Seals at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., the customization of door draft seals follows a rigorous, science-driven engineering workflow designed to meet exact OEM specifications and environmental performance criteria. Our four-phase process—Drawing Analysis, Formulation Development, Prototyping, and Mass Production—ensures dimensional accuracy, material resilience, and long-term sealing integrity under real-world operating conditions.
The process begins with Drawing Analysis, where our rubber formula engineers conduct a comprehensive review of customer-provided technical drawings. Critical parameters such as cross-sectional profile, tolerance class (±0.1 mm to ±0.5 mm), installation groove dimensions, and compression set requirements are evaluated. We assess sealing interface angles, substrate materials (aluminum, steel, or composite), and expected deflection under closure force. This phase ensures the design is manufacturable via extrusion or injection molding and identifies potential stress concentration zones that may affect service life.
Following drawing validation, our team advances to Formulation Development. Based on application-specific demands—including temperature range, UV/ozone exposure, chemical contact, and flame resistance—we engineer proprietary EPDM, silicone, or TPE compounds. Each formulation is optimized for Shore A hardness (typically 40–70), tensile strength (>6 MPa), elongation at break (>200%), and low-temperature flexibility (down to -50°C). Accelerated aging tests (150°C for 72h) and compression set evaluations (<25% at 70°C for 24h) are conducted to validate long-term performance.
Prototyping is executed using pilot-scale extrusion or molding equipment to produce functional samples within ±0.3 mm dimensional tolerance. These prototypes undergo rigorous in-house testing, including air leakage assessment under 200 Pa differential pressure, cycle durability (5,000–10,000 door operations), and adhesion strength measurement (≥3.5 kN/m for co-extruded variants). Customer feedback is integrated iteratively until final approval is obtained.
Upon prototype sign-off, we transition to Mass Production under ISO 9001-certified protocols. Automated extrusion lines with laser-based diameter control ensure consistency, while 100% visual inspection and statistical sampling (AQL 1.0) guarantee quality. Production batches are traceable via lot numbering, and material certifications (RoHS, REACH, UL) are provided upon request.
Below are typical technical specifications achievable through our customization pipeline:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material | EPDM, Silicone, TPE | ASTM D2000 |
| Shore A Hardness | 40–70 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥6 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥200% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (70°C, 24h) | ≤25% | ASTM D395 |
| Temperature Range | -50°C to +150°C (EPDM) | ASTM D1329 |
| Dimensional Tolerance | ±0.1 mm to ±0.5 mm | ISO 3302 |
| Flame Resistance | UL94 HB or VO (custom) | UL 94 |
This structured approach enables Suzhou Baoshida to deliver high-precision door draft seals tailored to automotive, architectural, and industrial applications with uncompromised reliability.
Contact Engineering Team

Precision Engineering for Critical Sealing Applications: Partner with Suzhou Baoshida
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. specializes in the development and manufacturing of high-performance rubber door draft seals engineered for demanding industrial and automotive environments. Our technical team leverages advanced polymer science and decades of OEM collaboration experience to deliver seals that exceed ISO 3302 and ASTM D2000 standards. Generic solutions often fail under thermal cycling, compression fatigue, or chemical exposure—compromising energy efficiency and safety. We address these challenges through proprietary EPDM and silicone formulations optimized for longevity, resilience, and precise dimensional stability. Our seals maintain consistent performance across -50°C to +150°C operational ranges, with compression set values consistently below 25% after 70 hours at 70°C, ensuring decades of reliable service life even in harsh conditions.
Technical Specifications: Door Draft Seal Performance Comparison
| Parameter | Suzhou Baoshida Standard Seal | Industry Average Seal | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Custom EPDM (50±5 Shore A) | Generic EPDM | ASTM D2240 |
| Compression Set (70°C/70h) | ≤22% | ≤35% | ASTM D395 Method B |
| Temperature Range | -50°C to +150°C | -40°C to +120°C | ISO 188 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥12.0 MPa | ≥9.0 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Ozone Resistance | 100 pphm, 200 hrs, no cracks | 50 pphm, 100 hrs, cracks | ASTM D1149 |
| Customization Lead Time | 15–25 days | 30–45 days | N/A |
Our value extends beyond material science. As your dedicated OEM partner, we integrate seamlessly into your supply chain with IATF 16949-certified production, real-time quality traceability via QR-coded batch tracking, and collaborative engineering support from concept to量产. We prioritize rapid prototyping using 3D-printed tooling jigs, reducing development cycles by 40% compared to conventional methods. Every seal undergoes rigorous in-house validation for compression force deflection (CFD), extrusion resistance, and adhesion integrity—ensuring zero field failures.
For mission-critical applications where seal failure risks product recalls or warranty liabilities, generic suppliers cannot match our technical accountability. We require precise understanding of your operational stresses: door cycle frequency, mating surface tolerances, and environmental contaminants. This enables us to tailor compound additives—such as peroxide curing systems for elevated heat resistance or nano-silica reinforcement for low-temperature flexibility—without compromising cost efficiency.
Initiate Your Engineering Partnership Today
Contact Mr. Boyce, our OEM Technical Manager, for an engineer-to-engineer consultation to specify your exact requirements. Mr. Boyce holds 18 years of experience in automotive sealing systems and will review your dimensional drawings, material specifications, and performance validation protocols within 24 business hours. Provide your target compression load, cross-section tolerances (±0.1mm achievable), and lifecycle expectations to receive a validated material recommendation with accelerated aging test data.
Direct your technical inquiry to [email protected] with subject line: “Door Draft Seal OEM Request – [Your Company Name]”. Include applicable standards (e.g., GMW14125, VW 50180), annual volume projections, and critical failure modes observed with current suppliers. Suzhou Baoshida guarantees confidential IP handling and non-disclosure upon engagement. Do not rely on off-the-shelf catalog parts for critical sealing interfaces—demand engineered solutions backed by material batch certification and lifetime performance analytics. Partner with us to eliminate draft infiltration, reduce acoustic leakage, and achieve uncompromised environmental sealing in your next-generation product line.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
