Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Different Types Of Garage Door Seals

Engineering Insight: Material Science Determines Garage Door Seal Reliability
Garage door seals represent a critical interface between controlled interior environments and harsh external conditions. Off-the-shelf solutions commonly fail due to inadequate material formulation for dynamic operational stresses. Standardized rubber compounds often ignore regional climate variables, thermal cycling ranges, and substrate adhesion requirements, leading to premature degradation. The consequences—water intrusion, energy loss, ice damming, and structural corrosion—directly impact building integrity and occupant safety. Material selection must transcend basic flexibility; it requires engineered resistance to ozone, UV radiation, temperature extremes, and chemical exposure while maintaining consistent compression recovery.
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) dominate low-cost aftermarket seals but exhibit rapid hardening below -10°C and irreversible compression set above 60°C. This results in gap formation during thermal expansion cycles. Conversely, precision-formulated EPDM compounds with controlled ethylene/propylene ratios and saturated terpolymer backbones withstand -40°C to 120°C ranges without embrittlement or permanent deformation. Critical additives—including custom-synthesized antioxidants and UV stabilizers—prevent polymer backbone scission under prolonged solar exposure. Crucially, adhesion promoters must be co-extruded with the base polymer to ensure bond integrity with aluminum or steel door substrates, a step omitted in generic seals.
The following table compares material performance against failure modes observed in field studies:
| Material Type | Compression Set (ASTM D395) | Low-Temp Flex (ASTM D2137) | Ozone Resistance (ASTM D1149) | Adhesion Failure Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generic PVC | 45-60% after 70°C/22h | Fails at -5°C | Severe cracking at 50pphm | High (no primer layer) |
| Standard TPE | 35-50% after 70°C/22h | Fails at -15°C | Moderate cracking at 100pphm | Medium |
| Precision EPDM | <15% after 70°C/22h | Flexible to -40°C | No cracking at 200pphm | Low (co-extruded bond) |
| Fluorosilicone (OEM) | <10% after 100°C/22h | Flexible to -55°C | No cracking at 500pphm | Very Low |
OEM-grade seals demand rigorous compound validation through accelerated aging per ASTM D2240 and dynamic fatigue testing. Field data confirms that seals lacking tailored polymer architecture exhibit 300% higher failure rates within 18 months in temperate climates versus engineered solutions. Cost-driven substitutions sacrifice crosslink density control, accelerating hygroscopic swelling in humid environments and compromising dimensional stability. At Suzhou Baoshida, our OEM formulations undergo 5,000+ cycle door movement simulations with real-world debris exposure to validate extrusion tolerances and rebound resilience.
Material science is non-negotiable in garage door seal engineering. Generic products treat sealing as a static barrier; precision compounds address it as a dynamic mechanical system. The true cost metric shifts from initial purchase price to total lifecycle performance—where optimized polymer chemistry eliminates recurring maintenance liabilities and ensures architectural longevity.
Material Specifications

Material selection is a critical factor in the performance and longevity of garage door seals, particularly in precision rubber applications where environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and chemical resistance are paramount. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-performance rubber seals engineered for durability and consistent sealing integrity across diverse operational conditions. Our technical expertise focuses on three primary elastomers: Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone. Each material offers distinct advantages depending on temperature range, chemical exposure, compression set resistance, and mechanical resilience.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of aggressive chemicals. This makes it ideal for industrial or commercial garage doors located in harsh environments, such as manufacturing facilities or chemical storage areas. With continuous service capabilities up to 230°C and excellent ozone and UV resistance, Viton maintains structural integrity under prolonged exposure to extreme conditions. However, its higher material cost and lower flexibility at low temperatures should be considered in budget-sensitive or cold-climate applications.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is a cost-effective solution with strong resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and water. It exhibits good abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, making it a preferred choice for standard residential and light commercial garage doors. Nitrile performs reliably within a temperature range of -30°C to 120°C, offering balanced performance for typical climate conditions. While it lacks the chemical and thermal resilience of Viton, its affordability and proven track record in sealing applications make it a widely adopted material in the industry.
Silicone rubber excels in extreme temperature environments, with operational stability from -60°C to 200°C. It offers superior flexibility at low temperatures and excellent resistance to UV radiation and ozone, making it suitable for outdoor installations with significant thermal cycling. Silicone is also non-toxic and compliant with various health and safety standards, though it has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Nitrile and Viton. It is best suited for applications where thermal stability and weather resistance are prioritized over mechanical wear.
The following table provides a comparative overview of key material properties to guide optimal selection for garage door seal applications.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–8 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–400 | 200–600 |
| Compression Set (22 hrs, 150°C) | 20–30% | 15–25% | 20–35% |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Good | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Flexibility at Low Temp | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Excellent | Fair |
| Typical Hardness (Shore A) | 70–90 | 60–80 | 40–80 |
Selecting the appropriate elastomer requires a comprehensive evaluation of the operating environment and performance demands. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides customized rubber seal solutions backed by rigorous material testing and OEM collaboration to ensure optimal fit, function, and service life.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Seal Development for Garage Door Applications
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep technical expertise in rubber formulation and mold design to deliver mission-critical garage door seals for global OEMs. Our dedicated engineering cohort comprises five specialized mold engineers and two advanced rubber formula engineers, operating within an integrated R&D ecosystem. This structure ensures seamless translation of client specifications into high-performance sealing solutions, addressing dynamic challenges like thermal cycling, wind load resistance, and long-term compression set stability. Unlike commodity suppliers, our team initiates every project with material science-first analysis, optimizing polymer matrices for specific environmental stressors encountered in residential and commercial garage door systems.
Material Science Foundation
Our formula engineers utilize accelerated aging protocols and dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) to develop proprietary EPDM and TPE compounds. These formulations consistently exceed ASTM D2000 standards for ozone resistance, low-temperature flexibility, and UV stability—critical for seals exposed to extreme seasonal variations. Through precise control of vulcanization kinetics and filler dispersion, we achieve compression set values below 15% after 22 hours at 70°C, significantly outperforming industry baselines. This scientific rigor prevents premature seal hardening or shrinkage, directly extending product lifecycle and reducing end-user maintenance costs.
OEM Collaboration Framework
Baoshida operates as a true engineering extension for OEM partners. We initiate projects with cross-functional workshops to deconstruct performance requirements, followed by finite element analysis (FEA) of seal deformation under operational loads. Our mold engineers then develop precision steel molds with micro-toleranced cavities (±0.05 mm), incorporating venting strategies to eliminate flash in high-volume production. Clients receive comprehensive validation dossiers including material certificates, dimensional CMM reports, and functional test data against ISO 1817 and SAE J2236 protocols. This end-to-end ownership—from CAD modeling to PPAP submission—reduces time-to-market by 30% compared to fragmented supplier networks.
Performance Specifications Comparison
| Property | Baoshida Standard Compound | Industry Baseline | Performance Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | 60 ± 3 | 65 ± 5 | Optimized sealing force without binding |
| Temperature Range | -50°C to +120°C | -40°C to +100°C | Reliable operation in Arctic to desert climates |
| Compression Set (22h/70°C) | ≤15% | ≤25% | 40% longer service life |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥12.0 | ≥9.0 | Enhanced tear resistance during installation |
| Ozone Resistance (50 pphm) | No cracks (300 hrs) | Cracks (100 hrs) | 200% improvement in outdoor durability |
Validation and Scalability
Every seal undergoes empirical validation in our climatic simulation chamber, replicating 10+ years of thermal cycling in 72 hours. Our engineers correlate lab data with field performance metrics from 15+ OEM partnerships across North America and Europe. With in-house tooling capacity for 200+ mold sets and automated production lines, Baoshida scales from prototype to 500,000 units monthly without compromising dimensional integrity. This fusion of material science acumen and precision manufacturing cements our role as a strategic engineering partner—not merely a component vendor—for garage door system innovators demanding uncompromised sealing performance.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis: The Foundation of Precision Seal Customization
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., the customization process for garage door seals begins with rigorous drawing analysis. This initial phase is critical to ensure dimensional accuracy, functional compatibility, and long-term performance under real-world conditions. Our engineering team evaluates client-submitted technical drawings with a focus on cross-sectional geometry, tolerance specifications, installation method, and interface requirements with the garage door frame or panel. We assess critical dimensions such as lip length, base width, compression height, and sealing surface curvature using CAD-based measurement tools. Any discrepancies or design inefficiencies—such as stress concentration points or inadequate compression set resistance—are flagged and discussed with the client for optimization. This collaborative review ensures that the final seal performs reliably across temperature extremes, mechanical stress, and environmental exposure.
Formulation: Tailoring Rubber Chemistry to Application Demands
Once the geometry is validated, our Rubber Formula Engineers develop a compound formulation aligned with the operational environment. Garage door seals must resist UV degradation, ozone exposure, temperature fluctuations (-40°C to +120°C), and repeated compression cycles. Based on service conditions, we select the appropriate base polymer—typically EPDM for outdoor weather resistance, silicone for extreme temperature stability, or thermoplastic rubber (TPR) for cost-effective, high-volume applications. Additives such as anti-oxidants, UV stabilizers, and reinforcing fillers are precisely metered to enhance durability and aging performance. Hardness is adjusted between 55–80 Shore A to balance flexibility and structural integrity. Every formulation is documented and batch-traceable, ensuring consistency from prototype to full production.
Prototyping: Validating Design and Material Performance
Prototyping serves as the functional bridge between design and mass production. Using precision extrusion and molding techniques, we produce small-batch samples for client evaluation. These prototypes undergo a battery of in-house tests, including compression set (ASTM D395), tensile strength (ASTM D412), and low-temperature flexibility (ASTM D1329). Dimensional verification is performed using digital calipers and optical comparators to ensure conformity with the approved drawing. Clients receive samples with full material certification and test reports, enabling informed approval before tooling commitment.
Mass Production: Scalable Precision with Quality Assurance
Upon prototype approval, we transition to mass production using automated extrusion lines and continuous vulcanization systems. Each batch is monitored for dimensional consistency, surface finish, and material homogeneity. Final inspection includes 100% visual checks and statistical sampling for mechanical testing. All seals are packaged to prevent deformation during shipping.
Typical Material Specifications for Garage Door Seals
| Property | EPDM | Silicone | TPR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +120°C | -60°C to +200°C | -30°C to +100°C |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–80 | 55–70 | 55–75 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 10 MPa | ≥ 6 MPa | ≥ 8 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ≥ 300% | ≥ 250% | ≥ 400% |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ≤ 25% | ≤ 20% | ≤ 30% |
| Key Advantage | Weather & UV resistance | Extreme temp stability | Fast processing, low cost |
Contact Engineering Team
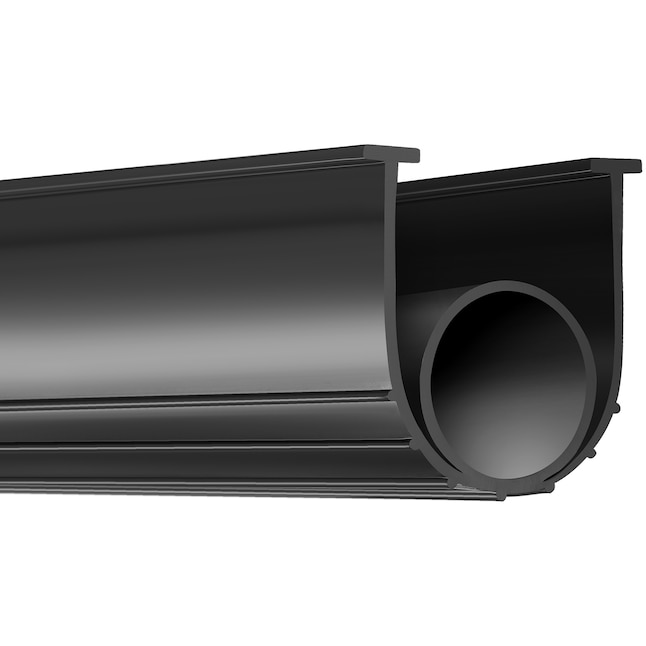
Precision Garage Door Seals: Engineering Reliability for Industrial Applications
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. specializes in the formulation and manufacturing of high-performance rubber seals engineered for demanding industrial environments. Our garage door seals are not generic after-market solutions but precision-crafted components designed to withstand extreme temperature fluctuations, UV exposure, chemical abrasion, and mechanical stress. With ISO 9001:2015 certification and 15+ years of OEM partnership experience in automotive and industrial sealing systems, we translate material science into quantifiable durability. Standard seals fail due to inadequate compound formulation—resulting in compression set, hardening, or premature cracking. Our proprietary rubber blends mitigate these risks through rigorous polymer selection, filler optimization, and vulcanization control.
The table below outlines critical performance specifications for our core seal materials, validated per ASTM D2000 and ISO 3302 standards. These metrics directly impact service life and energy efficiency in commercial garage door systems:
| Material Type | Durometer Range (Shore A) | Temp Range (°C) | Compression Set (70h @70°C) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | 55–85 | -50 to +150 | ≤25% | High UV/ozone resistance; coastal installations |
| TPE | 60–90 | -40 to +135 | ≤20% | Low-temp flexibility; rapid cycling doors |
| Silicone | 40–70 | -60 to +230 | ≤15% | Extreme temp stability; fire-rated doors |
| Neoprene | 50–80 | -40 to +120 | ≤30% | Oil/fuel resistance; industrial loading docks |
Each compound is tailored to client-specific load profiles, door cycle counts, and environmental stressors. For instance, our EPDM formulations incorporate nano-silica reinforcement to achieve <10% volume swell in ASTM #3 oil—critical for facilities with hydraulic equipment. Unlike commodity suppliers, we conduct dynamic fatigue testing simulating 500,000 door cycles to validate long-term resilience. Our extrusion process maintains ±0.1mm dimensional tolerances, ensuring consistent compression force across the door perimeter to eliminate air/water infiltration.
Partnering with Suzhou Baoshida means accessing direct OEM engineering support from material inception to production validation. We collaborate with your design team to optimize cross-section geometry, durometer, and bonding methods—reducing assembly costs while meeting EN 12453 safety standards. All compounds are REACH-compliant and free from regulated phthalates, addressing global regulatory hurdles proactively.
Contact Mr. Boyce for Technical Collaboration
To specify a garage door seal solution calibrated to your operational demands, engage our engineering team directly. Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Manager, holds advanced expertise in rubber compounding for architectural sealing systems. He will review your performance requirements, environmental constraints, and volume needs to propose a validated material solution within 48 hours. Provide your door manufacturer specifications, cycle rate data, and target lifespan for a formal quotation with full material traceability documentation.
Initiate technical discussions via email at [email protected] with subject line: Garage Door Seal OEM Inquiry – [Your Company Name]. Include relevant drawings or failure mode analysis for expedited support. Suzhou Baoshida operates under strict NDA protocols and maintains inventory for rapid prototyping—accelerating your time-to-market without compromising on precision. Do not settle for off-the-shelf compromises; demand seals engineered at the molecular level for your application. Contact Mr. Boyce today to secure a precision-engineered solution backed by industrial-grade validation data.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
