Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Concrete Expansion Joint Filler

Engineering Insight: The Critical Role of Material Selection in Concrete Expansion Joint Fillers
In industrial construction and infrastructure development, concrete expansion joints are essential for accommodating thermal movement, vibration, and structural settling. The performance and longevity of these joints are directly influenced by the material selected for the filler. While off-the-shelf expansion joint fillers are widely available and often marketed as universal solutions, they frequently fail under real-world service conditions. This failure stems from a fundamental mismatch between generic material properties and the specific environmental, mechanical, and chemical demands of the application.
Concrete expansion joint fillers must balance compressibility, recovery, durability, and resistance to degradation. Standard polyethylene or polystyrene foam fillers, commonly used due to low cost, lack sufficient resilience and long-term compression set resistance. These materials tend to crush permanently under sustained load, leading to joint failure, water infiltration, and spalling of adjacent concrete edges. Moreover, they offer minimal resistance to UV radiation, temperature extremes, and chemical exposure—factors prevalent in industrial environments such as chemical plants, cold storage facilities, and heavy traffic zones.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize engineered rubber solutions tailored to the operational profile of the joint. Closed-cell rubber foams, particularly those based on EPDM or neoprene, provide superior performance due to their inherent elasticity, weather resistance, and ability to maintain structural integrity over thousands of compression cycles. These materials exhibit low water absorption, high UV stability, and resistance to ozone and common industrial chemicals—critical attributes often overlooked in commodity-grade fillers.
Material selection must also account for joint width, movement range, and load-bearing requirements. A filler that performs adequately in a warehouse floor may fail catastrophically in a bridge deck or airport runway due to differences in dynamic loading and environmental exposure. Custom formulation allows for precise control over hardness (durometer), compression-deflection characteristics, and thermal expansion coefficients, ensuring compatibility with surrounding concrete and sealants.
The consequence of improper material selection extends beyond premature joint failure. It introduces costly maintenance cycles, safety hazards, and potential structural compromise. For example, a degraded joint filler can allow moisture ingress, accelerating rebar corrosion and reducing the service life of the entire structure.
We recommend a performance-driven approach: analyze the service environment, define movement and load parameters, and select a rubber compound engineered for those conditions. Off-the-shelf solutions may appear economical initially, but their limited service life and higher lifecycle costs make them inefficient in demanding industrial applications.
Below is a comparison of typical material properties for common expansion joint filler types:
| Property | Polyethylene Foam | Polystyrene Foam | EPDM Rubber Foam | Neoprene Rubber Foam |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (22 hrs, 70°C) | 45% | 60% | 15% | 20% |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 1.8 | 2.0 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 100 | 80 | 150 | 140 |
| Water Absorption (24 hrs, % vol) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Temperature Range (°C) | -40 to +70 | -20 to +60 | -50 to +120 | -45 to +100 |
| UV and Ozone Resistance | Low | None | Excellent | Good |
Material selection is not a commodity decision—it is an engineering imperative. At Suzhou Baoshida, we provide technical support and custom rubber solutions to ensure optimal performance in every expansion joint application.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Concrete Expansion Joint Fillers
Concrete expansion joints demand elastomeric fillers capable of enduring cyclic compression, thermal fluctuations, and environmental exposure without permanent deformation or chemical degradation. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we rigorously qualify Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ) compounds to meet stringent industrial requirements. Material selection directly impacts joint longevity, structural integrity, and maintenance cycles. Viton excels in high-temperature and aggressive chemical environments due to its fluoroelastomer backbone, maintaining resilience between -20°C and 230°C. It resists hydraulic fluids, acids, and hydrocarbon derivatives critical in industrial flooring and bridge applications. Nitrile offers cost-effective performance for general-purpose use, with robust resistance to oils, greases, and aliphatic hydrocarbons within -30°C to 120°C. Its balanced tensile strength and abrasion resistance suit warehouse and parking deck installations. Silicone provides unparalleled flexibility across extreme temperatures (-60°C to 200°C) and superior UV/ozone stability, making it ideal for exterior architectural joints. However, its lower tensile strength and susceptibility to tearing require careful design consideration in high-traffic zones.
Compression set resistance is non-negotiable for joint recovery after sustained load. Viton achieves <20% compression set per ASTM D395 after 70 hours at 150°C, ensuring decades of reliable cycling. Nitrile typically delivers 25–35% under identical conditions, suitable for moderate-service environments. Silicone ranges from 20–40% depending on filler content, with high-purity grades approaching Viton’s performance. Tensile strength must exceed 10 MPa to withstand installation stresses and concrete edge abrasion; all three materials meet this threshold when optimally compounded. Crucially, chemical compatibility must align with site-specific exposures—fuel spills demand Viton, while mild detergent exposure permits Nitrile.
The comparative analysis below details critical performance parameters per ASTM and ISO standards:
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Chemical Resistances | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Compression Set (ASTM D395) | Primary ASTM Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | -20 to 230 | Fuels, acids, oils, hydraulic fluids | 12–18 | ≤20% @ 22h/150°C | D2000, D1418 |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -30 to 120 | Oils, greases, aliphatic hydrocarbons | 10–15 | 25–35% @ 22h/70°C | D2000, D1418 |
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 to 200 | Ozone, UV, water, mild acids | 6–10 | 20–40% @ 22h/150°C | D2000, D1418 |
Optimal selection requires holistic evaluation of service temperature extremes, chemical exposure profiles, and mechanical stress intensity. Viton remains indispensable for petrochemical or high-heat infrastructure despite premium costs. Nitrile delivers economical reliability for commercial interiors with predictable exposure. Silicone dominates exterior architectural applications where thermal swing and weathering dominate failure modes. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. validates all compounds through accelerated aging per ISO 188 and fluid immersion testing per ASTM D471, ensuring compliance with global infrastructure codes. Initial savings from suboptimal material choices invariably incur higher lifecycle costs through joint extrusion, leakage, or premature replacement. Partner with our engineering team to specify the precise formulation for your project’s operational envelope.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Capability: Precision-Driven Development for Industrial Rubber Applications
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering capability forms the backbone of our industrial rubber solutions, particularly in the design and production of high-performance concrete expansion joint fillers. With a dedicated team of five experienced mould engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, we ensure that every product is developed with scientific rigor, dimensional accuracy, and long-term durability in mind. Our integrated engineering approach bridges material science with precision manufacturing, enabling us to deliver custom OEM solutions that meet exacting technical and environmental demands.
Our mould engineering team specializes in the development of complex, high-tolerance moulds tailored for extrusion and compression processes used in expansion joint filler production. Each design is optimized for uniform material flow, minimal flash, and consistent cross-sectional integrity, ensuring reliable performance under dynamic structural movement and extreme weather conditions. Utilizing advanced CAD/CAM software and iterative prototyping, our engineers validate mould performance before full-scale production, reducing time-to-market and minimizing defects.
Complementing this is our rubber formulation expertise. Our two in-house formula engineers focus exclusively on elastomer systems designed for long-term resilience in concrete infrastructure. They develop proprietary blends using SBR, EPDM, and recycled rubber compounds, adjusting cross-link density, filler loading, and plasticizer content to achieve target hardness, compression set resistance, and thermal stability. Each formulation undergoes rigorous testing for aging, UV resistance, and performance across a temperature range of -40°C to +80°C, ensuring compatibility with diverse geographic and climatic conditions.
This synergy between mould design and material science allows us to offer full OEM service capabilities. We support clients from initial concept and technical drawings through to tooling, formulation adjustment, and batch validation. Whether the requirement is for cellular sponge rubber, solid elastomeric profiles, or co-extruded multi-density fillers, our team delivers solutions engineered for seamless integration into concrete joints, with precise expansion/contraction dynamics and long service life.
Our commitment to engineering excellence is reflected not only in product performance but also in our ability to meet international standards and client-specific technical specifications. By maintaining tight control over both material and moulding processes, Suzhou Baoshida ensures repeatability, scalability, and compliance across production runs.
| Property | Typical Value | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 40–70 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 5.0 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥ 200% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ≤ 25% | ASTM D395B |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +80°C | Internal Protocol |
| Water Absorption (24h) | ≤ 3% | ASTM D570 |
Through advanced engineering and deep material knowledge, Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers industrial rubber solutions that meet the structural and environmental challenges of modern concrete infrastructure.
Customization Process
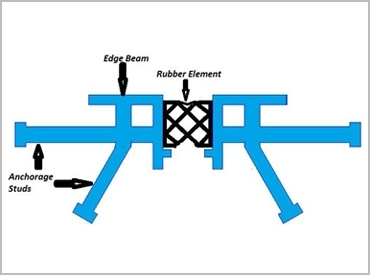
Concrete Expansion Joint Filler Customization Process
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our OEM customization for concrete expansion joint fillers follows a rigorously defined sequence to ensure dimensional accuracy, environmental resilience, and long-term performance. This process begins with comprehensive Drawing Analysis, where engineering teams dissect client-provided CAD files and technical specifications. We validate critical parameters including joint width tolerances, expected movement ranges (±25% to ±50% compression/extension), substrate adhesion requirements, and exposure conditions such as UV intensity, chemical contact, or extreme temperatures. This phase identifies potential failure points early, allowing us to align material selection with structural demands before formulation commences.
Formulation development leverages Suzhou Baoshida’s polymer science expertise to engineer compound recipes meeting exact performance criteria. Base polymers—typically EPDM for UV/ozone resistance or SBR for cost-sensitive applications—are modified with precision. Key adjustments include optimizing sulfur vulcanization systems for crosslink density, incorporating nano-silica fillers for tear strength, and integrating plasticizers to maintain flexibility below -40°C. Each formulation undergoes computational simulation to predict compression set behavior and thermal expansion coefficients, ensuring compatibility with concrete’s linear movement. Critical properties are validated against ASTM and ISO standards prior to prototyping.
Prototyping transforms validated formulations into physical samples for real-world verification. We produce 3–5 prototype batches using client-specified tooling geometries, subjecting them to accelerated aging tests (70°C for 72 hours), cyclic compression testing (10,000 cycles at 25% deflection), and adhesion peel strength measurements. Client feedback on sample performance in mock-up joints triggers iterative refinements, typically requiring 1–2 adjustment cycles to achieve zero extrusion or permanent set under operational loads.
Mass production commences only after formal client sign-off on prototypes, utilizing our ISO 9001-certified manufacturing lines. Continuous inline monitoring tracks Mooney viscosity (ML 1+4 @ 100°C), hardness deviation (±2 Shore A), and dimensional stability via laser micrometers. Every batch undergoes final inspection against the approved drawing, with traceability maintained through lot-specific certificates documenting raw material COAs, cure profiles, and test results. This end-to-end control guarantees fillers that sustain 50+ years of service life under dynamic concrete movement.
Critical Performance Specifications for Custom Expansion Joint Fillers
| Property | Test Method | Target Range | Industrial Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 40–70 | Balances compression recovery & installation ease |
| Compression Set (22h) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% @ 70°C | Prevents permanent deformation under load |
| Temp Range | ISO 188 | -50°C to +120°C | Ensures functionality in extreme climates |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥8.0 MPa | Resists tearing during joint movement |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥300% | Accommodates high joint expansion ratios |
| Water Absorption | ASTM D471 | ≤3% (7d @ 23°C) | Prevents swelling-induced joint failure |
Contact Engineering Team

For engineered performance in concrete expansion joint applications, selecting the right filler material is critical to ensuring long-term structural integrity, noise reduction, and resistance to environmental stressors. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-performance industrial rubber solutions tailored for demanding construction and infrastructure environments. Our concrete expansion joint filler products are formulated to deliver consistent compressibility, excellent recovery characteristics, and durability under repeated load cycles and extreme temperature fluctuations.
Our proprietary rubber compounds are designed to meet international quality standards, providing optimal sealing performance while accommodating dynamic joint movement in highways, bridges, airport runways, and industrial flooring systems. Whether you require closed-cell foam rubbers, EPDM-based strips, or custom-molded profiles, our materials are engineered for dimensional stability, water resistance, and long service life. We work closely with OEMs, contractors, and material suppliers to ensure compatibility with site-specific conditions and regulatory requirements.
To support your project needs, we offer technical data sheets, sample provisioning, and material testing validation upon request. Our team of rubber formulation engineers is available to assist in selecting the appropriate hardness (Shore A), density, and compression set characteristics based on your joint design parameters.
For immediate technical consultation or to request product samples, contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Manager and Rubber Formula Engineer at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. Mr. Boyce leads our industrial rubber division with over 12 years of experience in elastomer development and manufacturing optimization. He is available to discuss custom formulations, volume production timelines, and compliance documentation, including RoHS and REACH reports where applicable.
You can reach Mr. Boyce directly via email at [email protected]. In your inquiry, please include details such as required dimensions, operating temperature range, expected compression load, and annual volume estimates to enable a precise technical and commercial response. We respond to all qualified inquiries within 12 business hours and offer virtual technical meetings for large-scale procurement or co-development projects.
Below are key technical specifications for our standard concrete expansion joint filler series:
| Property | Test Method | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | – | Closed-cell EPDM Rubber |
| Density | ASTM D3574 | 45–55 kg/m³ |
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 40 ± 5 |
| Compression Set (22h at 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤ 20% |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥ 0.8 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥ 150% |
| Operating Temperature Range | – | -40°C to +100°C |
| Water Absorption (24h) | ASTM D1056 | < 2% |
| Joint Movement Accommodation | – | Up to ±25% of original width |
Partner with Suzhou Baoshida for reliable, precision-engineered rubber solutions backed by technical expertise and consistent quality control. Initiate your project with confidence—contact Mr. Boyce today at [email protected].
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
