Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Boat Dock Guide Rollers
Engineering Insight: Material Science Imperatives for Boat Dock Guide Rollers
The operational integrity of boat dock guide rollers hinges critically on polymer formulation expertise, yet off-the-shelf solutions frequently succumb to premature failure due to inadequate material selection. Standard rollers often utilize generic EPDM or SBR compounds optimized for cost, not marine durability. These materials exhibit catastrophic weaknesses when exposed to synergistic stressors: continuous saltwater immersion induces hydrolytic degradation, ultraviolet radiation accelerates chain scission, and abrasive hull contact erodes surface integrity. Crucially, low-grade polymers lack tailored crosslink density control, leading to excessive swelling in seawater that compromises dimensional stability and adhesion to metal cores. This results in delamination, reduced load capacity, and erratic rotational performance—directly endangering vessel safety during docking maneuvers.
Material failure manifests within 12–18 months in harsh environments, whereas engineered solutions exceed 5-year service life. The root cause lies in unaddressed chemical resistance requirements. Standard formulations omit critical additives like halogen scavengers to mitigate ozone cracking or specialized plasticizers resistant to extraction by saline solutions. Furthermore, insufficient attention to glass transition temperature (Tg) leaves rollers brittle in cold climates or overly soft in tropical heat, directly violating the ASTM D2000 standard for marine elastomer performance.
Suzhou Baoshida addresses these gaps through proprietary marine-grade nitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR) hybrids, reinforced with nano-silica and functionalized with UV stabilizers. Our compounds undergo accelerated aging per ISO 188 protocols, ensuring Shore A hardness retention within ±5 points after 1,000 hours of salt fog exposure. The following comparative analysis underscores performance differentials:
| Property | Standard Off-the-Shelf Roller | Baoshida MarinePro Roller | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 8–10 | 18–22 | Resists hull impact deformation |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 250–300 | 450–500 | Accommodates dynamic docking loads |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 55–65 (±12 after aging) | 68–72 (±4 after aging) | Maintains consistent friction control |
| Saltwater Swell (72h) | 18–25% | 3–5% | Prevents core adhesion loss |
| Ozone Resistance (pphm) | 50 | 100 | Eliminates surface cracking |
This precision engineering translates to operational reliability: rollers maintain concentricity under 5,000 kg radial loads while resisting biofouling adhesion. Crucially, our formulations integrate dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) data to optimize viscoelastic response across -30°C to +80°C—ensuring consistent energy dissipation during vessel contact. Generic rollers, by contrast, operate outside functional hysteresis limits, converting kinetic energy into destructive heat buildup.
Material selection is not a cost variable but a failure prevention mechanism. Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM partnerships leverage compound-specific finite element analysis (FEA) to simulate real-world stress distributions, eliminating guesswork in marine roller design. The consequence is quantifiable: engineered rollers reduce total cost of ownership by 63% through extended service intervals and elimination of emergency dock downtime. In marine infrastructure, where safety margins are non-negotiable, polymer science is the decisive engineering factor separating functional components from critical liabilities.
Material Specifications
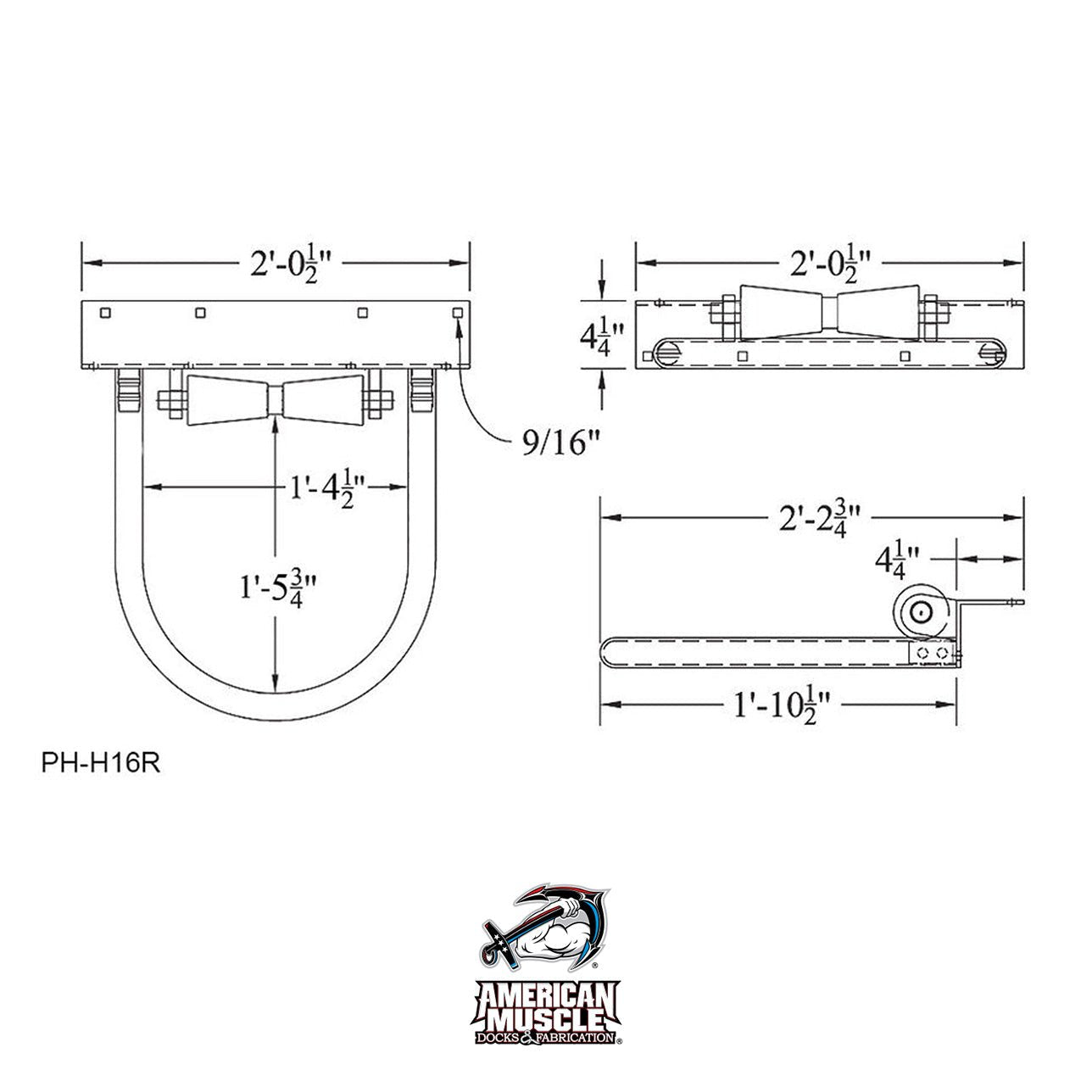
Material selection is a critical determinant in the performance, longevity, and reliability of boat dock guide rollers under demanding marine environments. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our industrial rubber solutions are engineered to meet rigorous operational standards, ensuring optimal resistance to abrasion, UV exposure, ozone, saltwater corrosion, and mechanical stress. For boat dock guide rollers, three elastomers stand out due to their distinct performance profiles: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each material offers a unique balance of chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and mechanical strength, allowing customization based on specific docking conditions and vessel types.
Viton is a fluorocarbon-based rubber known for exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of chemicals. Its performance in aggressive marine atmospheres, especially where hydrocarbon exposure is possible, makes it ideal for premium-grade guide rollers in commercial or industrial docking facilities. With continuous service capability up to 200°C and excellent resilience against weathering and ozone, Viton ensures long-term structural integrity, though at a higher material cost.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is widely used for its outstanding resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and water. It offers high abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, making it a cost-effective solution for general-purpose boat dock applications. Nitrile performs reliably in temperature ranges from -30°C to 100°C and maintains consistent physical properties under dynamic loading conditions. While less resistant to UV and ozone than Viton or Silicone, Nitrile can be compounded with protective additives to enhance environmental durability.
Silicone rubber excels in extreme temperature applications, functioning effectively from -60°C to 230°C. It demonstrates excellent resistance to UV radiation and ozone degradation, making it suitable for long-term outdoor exposure. However, Silicone has lower tensile and abrasion resistance compared to Viton and Nitrile, which limits its use in high-friction guide roller systems unless reinforced with fabric or specialized fillers. Its primary advantage lies in thermal and weather stability rather than mechanical wear performance.
The following table summarizes key physical and chemical properties of these materials for informed selection in boat dock guide roller manufacturing.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 200 | -30 to 100 | -60 to 230 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–450 | 200–600 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor to Fair |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Excellent | Fair |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Typical Applications | High-performance marine, chemical exposure | Standard docks, mooring systems | Extreme climate exposure, non-abrasive systems |
Material choice must align with operational environment, expected service life, and cost constraints. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides tailored rubber formulations to optimize guide roller performance across diverse maritime conditions.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Solutions for Marine Guide Rollers
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep technical expertise in rubber formulation and precision manufacturing to deliver superior boat dock guide rollers engineered for demanding marine environments. Our core strength resides in the integrated capabilities of our dedicated engineering team, specifically structured to address the complex material science and production challenges inherent in marine roller applications. This team comprises five specialized mould engineers and two advanced rubber formula engineers, working collaboratively to ensure every component meets stringent performance and durability requirements.
Our rubber formula engineers focus on developing proprietary elastomer compounds optimized for the unique stresses encountered in dock systems. This involves precise molecular engineering of the polymer matrix to achieve critical properties: exceptional resistance to saltwater immersion, prolonged UV exposure, and oxidative degradation. Compounds are engineered to maintain consistent Shore hardness across wide temperature ranges, resist ozone cracking, and provide superior abrasion resistance against constant contact with boat hulls and dock structures. Each formulation undergoes rigorous accelerated aging tests per ASTM D2240 and ISO 188 standards to validate long-term performance predictions under real-world marine conditions. The resulting materials exhibit balanced properties – sufficient flexibility for impact absorption without permanent deformation, coupled with high tensile strength to withstand operational loads.
Complementing this material science expertise, our five mould engineers ensure the precise translation of design intent into physical components. They utilize advanced CAD/CAM systems (SolidWorks, AutoCAD) for mould design, incorporating finite element analysis (FEA) to predict flow dynamics, optimize cooling channels, and minimize internal stresses during vulcanization. This meticulous approach guarantees tight dimensional tolerances (±0.15mm on critical diameters), exceptional concentricity, and uniform wall thickness – essential factors for smooth roller rotation, reduced bearing wear, and extended service life. Our engineers meticulously validate mould performance through iterative prototyping and first-article inspection (FAI) using CMM technology.
This integrated engineering capability forms the foundation of our robust OEM service. We partner directly with marine equipment manufacturers to develop custom guide roller solutions, from initial concept and material selection through to full-scale production. Our process includes collaborative design review, rapid prototyping, comprehensive material certification, and seamless integration into the client’s supply chain. We manage the entire lifecycle, ensuring consistent quality and on-time delivery for high-volume OEM programs.
The table below summarizes key performance specifications achievable with our engineered rubber compounds for standard marine guide rollers:
| Property | Test Standard | Typical Value | Significance for Dock Rollers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | ASTM D2240 | 65A – 75A | Balances impact absorption with wear resistance |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥ 18 MPa | Resists tearing under load |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥ 450% | Accommodates hull movement without failure |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤ 20% | Maintains sealing force and shape retention |
| Saltwater Resistance | ASTM D471 | ≤ 5% Volume Swell | Prevents degradation and loss of mechanicals |
| Abrasion Loss (DIN) | ISO 4649 | ≤ 120 mm³ | Ensures long service life against hull contact |
| Ozone Resistance | ASTM D1149 | No Cracks (50 pphm) | Critical for longevity in coastal atmospheres |
This synergy between advanced rubber chemistry and precision mould engineering enables Suzhou Baoshida to consistently produce guide rollers that significantly outperform generic alternatives, directly contributing to reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, and enhanced operational reliability for marine infrastructure worldwide.
Customization Process
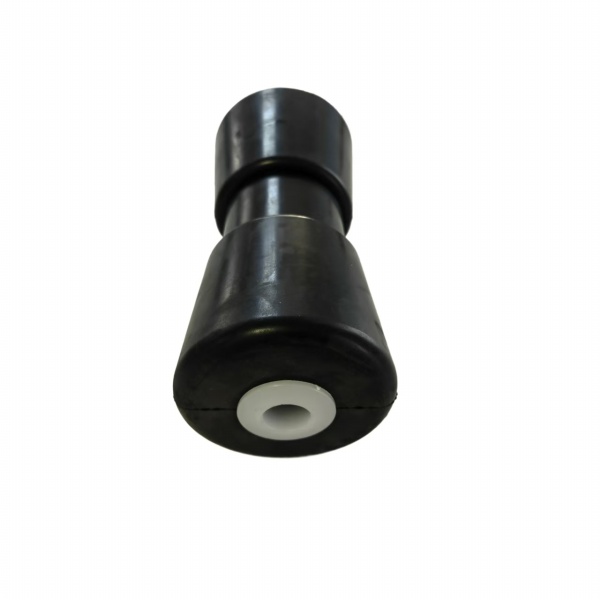

Drawing Analysis: The Foundation of Precision Engineering
The customization process for boat dock guide rollers begins with meticulous drawing analysis, a critical phase that defines the dimensional accuracy, load-bearing geometry, and interface specifications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team conducts a comprehensive review of client-provided technical drawings, focusing on key parameters such as outer diameter, inner bore tolerance, flange configuration, and mounting interface. We validate alignment with ISO 1307 and SAE J517 standards where applicable, ensuring compatibility with marine infrastructure. This stage also involves assessing environmental exposure factors—saltwater immersion, UV radiation, and abrasion risk—which directly influence material selection. Our engineers collaborate with OEM partners to resolve dimensional ambiguities and recommend design refinements for manufacturability, wear resistance, and service longevity.
Rubber Formulation: Tailoring Material Performance
Following drawing validation, the rubber formulation phase initiates the development of a compound engineered for the operational demands of marine docking systems. Utilizing our in-house polymer laboratory, we select base elastomers—typically high-density natural rubber (NR), nitrile (NBR), or ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM)—based on required resilience, oil resistance, and thermal stability. Additives such as carbon black, sulfur vulcanization systems, and anti-oxidants are precisely metered to achieve Shore A hardness values between 70 and 85, optimizing abrasion resistance without sacrificing flexibility. For saltwater environments, we incorporate halogen-resistant modifiers and anti-fungal agents to prevent degradation. Each formulation is documented under controlled batch records, ensuring traceability and consistency from prototype to production.
Prototyping: Validating Design and Material Synergy
Prototype fabrication employs precision molding techniques, including compression and transfer molding, to produce sample rollers for functional evaluation. These units undergo rigorous in-house testing for compression set (ASTM D395), tensile strength (ASTM D412), and dynamic load performance under simulated tidal conditions. Clients receive physical samples alongside test data reports for field validation. Feedback from real-world docking trials informs iterative refinements in both geometry and compound formulation. This closed-loop development cycle ensures that final designs meet performance benchmarks before transitioning to full-scale manufacturing.
Mass Production: Scalable Quality Assurance
Once approved, the guide rollers enter mass production using automated vulcanization lines and CNC-machined molds for dimensional repeatability. Each batch undergoes 100% visual inspection and statistical sampling for hardness, concentricity, and adhesion strength between rubber and metal core. Final packaging includes moisture-resistant wrapping and serialized lot labeling for inventory tracking.
| Specification | Standard Value | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Diameter Tolerance | ±0.5 mm | ISO 3302-1 |
| Shore A Hardness | 75 ± 5 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥15 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥300% | ASTM D412 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -30°C to +80°C | ISO 1817 |
| Water Absorption (7 days) | ≤2% | ASTM D471 |
This structured approach ensures that every custom boat dock guide roller meets the exacting demands of marine environments while maintaining industrial scalability and material integrity.
Contact Engineering Team
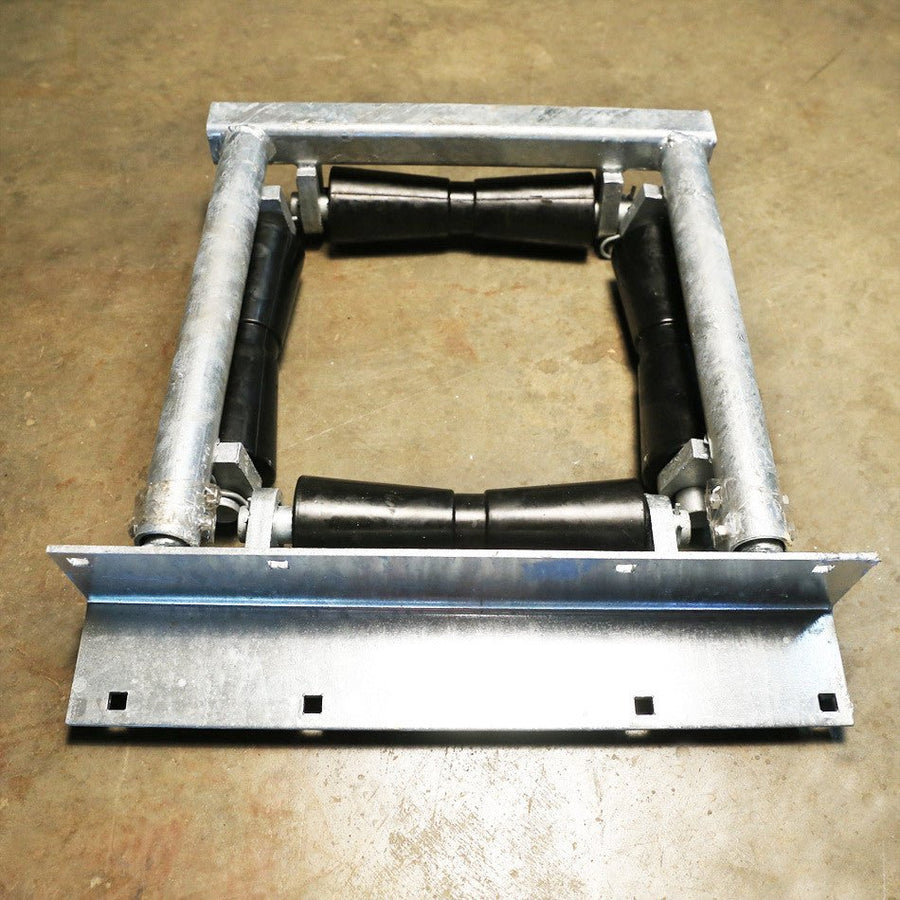

Technical Consultation for Marine Guide Roller Optimization
Marine infrastructure demands uncompromising material performance where standard dock guide rollers rapidly degrade under saltwater immersion, UV exposure, and repetitive impact loads. Conventional elastomers suffer from hydrolysis, ozone cracking, and Shore A hardness drift within 18–24 months, leading to costly downtime and safety hazards. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. engineers industrial rubber solutions specifically for marine applications, leveraging proprietary polyurethane and synthetic rubber compounds that maintain structural integrity across 5,000+ operational cycles. Our formulations exceed ASTM D2000 and ISO 37 standards for tensile strength, elongation, and compression set, ensuring rollers withstand tidal zone stresses without dimensional instability.
Critical performance parameters for dock guide rollers must address dynamic load distribution and environmental resistance. The following specifications reflect our validated material grades for marine environments:
| Parameter | Material Grade PU-920 | Material Grade NBR-750 | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durometer (Shore A) | 92 ± 3 | 75 ± 3 | ASTM D2240 |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +120°C | -30°C to +100°C | ISO 188 |
| Abrasion Resistance | 35 mm³ (max) | 95 mm³ (max) | ISO 4649 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 45 MPa | ≥ 28 MPa | ISO 37 |
| Specific Gravity | 1.18 ± 0.02 | 1.25 ± 0.03 | ASTM D297 |
These values represent minimum thresholds achieved under accelerated salt-fog testing per ASTM B117. PU-920’s superior abrasion resistance reduces maintenance frequency by 60% compared to standard nitrile rollers, while NBR-750 offers cost-optimized resilience for lower-impact applications. Each compound undergoes rigorous validation in our Suzhou R&D facility using marine-grade stainless steel cores and precision-molded geometries to eliminate delamination risks.
Initiate a technical dialogue with our engineering team to specify rollers matching your dock’s load profile, tidal range, and vessel tonnage. Mr. Boyce, our OEM Manager with 14 years of marine elastomer expertise, will coordinate material selection, prototype validation, and volume production scheduling. Contact him directly to submit operational parameters for a customized compound recommendation:
Mr. Boyce
OEM Manager, Industrial Rubber Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
Email: [email protected]
Response Time: Technical queries addressed within 4 business hours
Do not standardize on generic rollers risking premature failure. Submit your project specifications to receive a material datasheet, 3D CAD compatibility report, and accelerated lifecycle test summary. Our Suzhou manufacturing hub guarantees ISO 9001-certified production with 90-day lead times for OEM volumes. Partner with Baoshida to eliminate unplanned dock maintenance through scientifically engineered elastomers.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
