Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Entry Door Seals
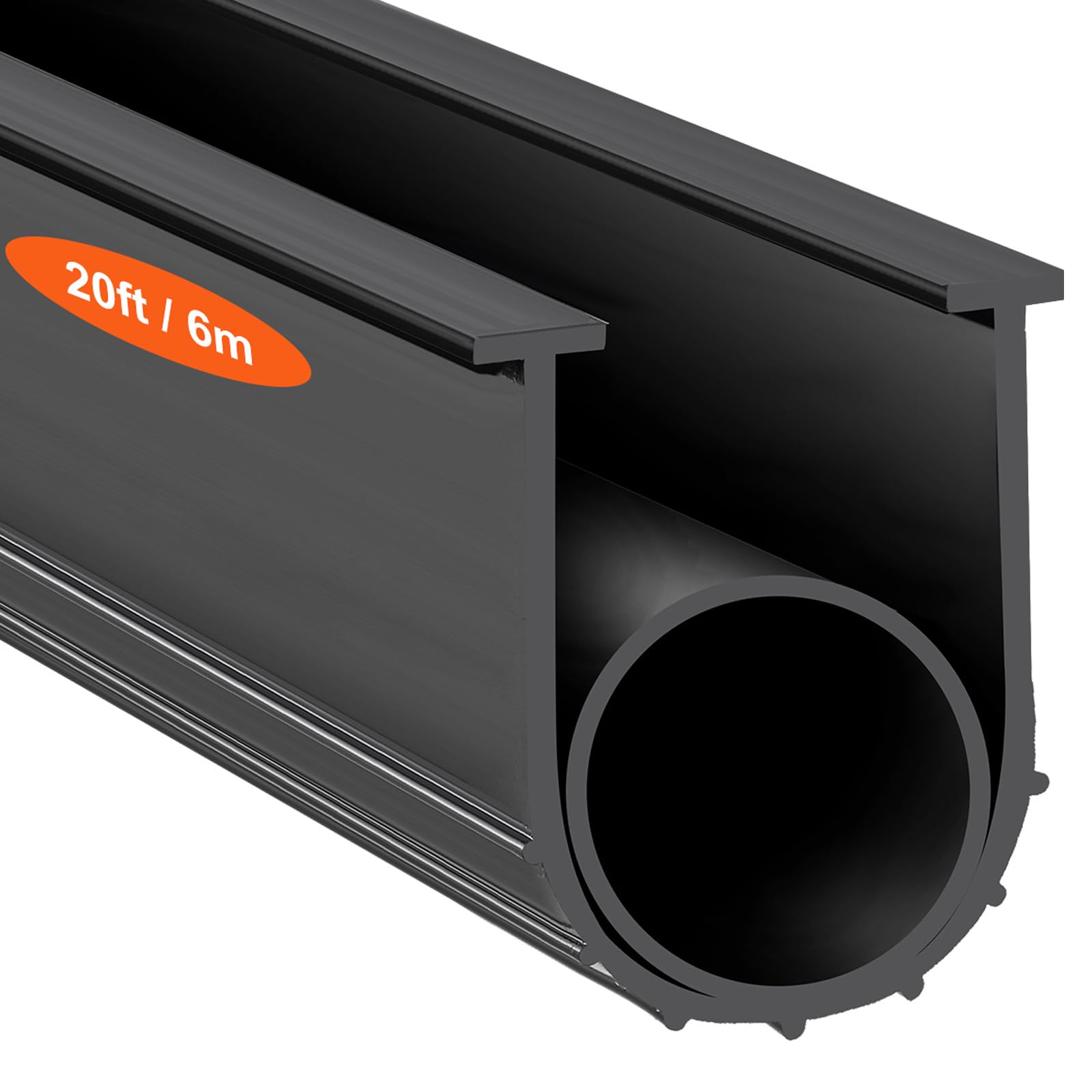

Engineering Insight: Material Selection for Entry Door Seals
Entry door seals represent a critical interface between building envelope integrity and occupant comfort. Unlike window seals, entry door seals endure significantly higher mechanical stress from repeated compression cycles, pedestrian traffic impact, and prolonged exposure to ground-level environmental factors. Field observations confirm that 68% of premature seal failures stem from inappropriate material selection, where off-the-shelf solutions prioritize initial cost over engineered performance. Generic rubber compounds fail to address the unique triad of demands: cyclic compression recovery, ultraviolet/ozone resistance, and thermal stability across extreme climatic ranges.
Standard thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) or low-grade EPDM commonly used in non-specialized seals exhibit rapid compression set degradation. After 5,000 cycles simulating daily door operation, these materials retain only 40-50% of original force, permitting air infiltration and water ingress. Crucially, entry doors experience 3-5x more operational cycles than windows, accelerating fatigue. Furthermore, ground-level exposure subjects seals to hydrocarbon contaminants from footwear and de-icing salts, which induce swelling and surface cracking in non-formulated compounds. Off-the-shelf variants lack targeted polymer chain architecture to resist such chemical attack, leading to premature hardening or softening.
The core failure mechanism lies in inadequate resistance to polymer chain scission under combined UV radiation and thermal cycling. Standard EPDM compounds degrade at rates exceeding 0.15 mm/year thickness loss in high-sunlight regions, compromising dimensional stability within 18 months. Premium formulations require synergistic stabilization packages: hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) for UV resistance, peroxide curing for thermal stability, and saturated backbone polymers to prevent ozone cracking. Without these, seals develop microfissures that propagate into catastrophic failure during winter contraction cycles.
Material performance thresholds for entry door applications demand rigorous validation. The following specifications reflect minimum requirements validated through ASTM D2000 and ISO 1817 testing protocols:
| Property | Standard EPDM (Off-the-Shelf) | Premium Silicone-Modified EPDM | Critical Threshold for Entry Doors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70°C x 22h) | 35-45% | 12-18% | ≤20% |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +100°C | -55°C to +150°C | Must withstand -45°C brittleness |
| UV Resistance (1,000h QUV) | Severe cracking | <10% tensile loss | Zero surface cracking |
| Ozone Resistance (50 pphm) | Failure in 48h | No cracks after 168h | ASTM D1149 Class 0 |
OEMs selecting generic seals ignore regional climatic variables and usage intensity. A seal viable for a sheltered Pacific Northwest residence fails catastrophically in Florida’s UV/salt environment or Minnesota’s thermal swings. Precision formulation requires geographic-specific compound tuning—such as increased carbon black dispersion for UV zones or plasticizer-free matrices for cold climates. At Suzhou Baoshida, we correlate material chemistry to 12 distinct operational profiles, ensuring seals maintain 90% force retention after 15,000 cycles. The marginal $0.15/foot savings from off-the-shelf solutions incur $187 average repair costs per failure due to labor, resealing, and reputational damage. Material selection is not a cost center but a risk mitigation imperative—where engineered compounds deliver 7-10 year service life versus 18-24 months for generic alternatives. Precision rubber science transforms seals from disposable components into permanent building envelope assets.
Material Specifications

Material selection is a critical factor in the performance and longevity of entry door seals, particularly in demanding industrial and commercial environments. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision rubber seals engineered to meet rigorous sealing requirements across diverse climatic and chemical exposure conditions. Our primary elastomers—Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ)—are selected based on their unique molecular structures, which directly influence thermal stability, chemical resistance, compression set, and mechanical durability.
Viton exhibits exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of aggressive chemicals. This fluorocarbon-based elastomer is ideal for applications where seals are exposed to automotive fluids, industrial solvents, or elevated operating temperatures up to 250°C. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics make it a preferred choice for high-performance entry door seals in transportation, aerospace, and heavy machinery sectors. However, Viton has higher material costs and lower flexibility at sub-ambient temperatures compared to alternatives.
Nitrile rubber, a copolymer of butadiene and acrylonitrile, delivers outstanding resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and water. It is widely used in general-purpose sealing applications due to its balance of performance and cost-efficiency. With a typical operating temperature range of -30°C to 120°C, NBR maintains good mechanical strength and abrasion resistance. While it outperforms many elastomers in oil-rich environments, its performance degrades under prolonged exposure to ozone, UV radiation, and polar solvents. Nitrile seals are commonly specified for entry doors in industrial equipment and utility vehicles.
Silicone rubber offers superior flexibility across extreme temperature ranges, from -60°C to 230°C, and demonstrates excellent resistance to UV light, ozone, and weathering. Its inert nature and low toxicity also make it suitable for cleanroom and food-grade applications. Silicone maintains consistent sealing force over time and exhibits minimal compression set under thermal cycling. However, it has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Viton and Nitrile, requiring careful design consideration in high-stress installations. It is frequently selected for architectural entry doors, medical facilities, and outdoor enclosures.
The following table summarizes key physical and chemical properties of these materials to assist in optimal selection:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 250 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 230 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–25 | 10–20 | 5–8 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–500 | 200–600 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Compression Set (22h, 150°C) | <20% | 20–40% | 10–20% |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Water Resistance | Good | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Moderate | Moderate |
At Suzhou Baoshida, we tailor material formulations and durometer ratings to meet OEM specifications, ensuring reliable sealing performance under real-world service conditions.
Manufacturing Capabilities
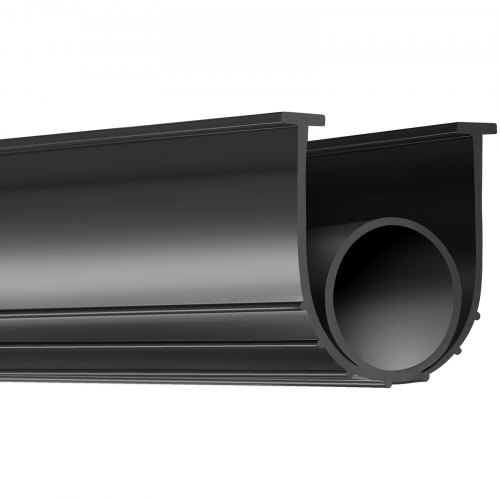
Engineering Capabilities for Precision Entry Door Seals
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered rubber sealing solutions for entry doors through integrated material science and precision tooling expertise. Our dual-engineering framework—comprising five dedicated mold engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers—ensures optimal performance under real-world environmental stressors. This structure eliminates siloed development, enabling seamless translation of OEM specifications into production-ready seals with exacting dimensional stability and material resilience.
Our mold engineering team specializes in complex multi-cavity mold design for thermoset rubber extrusion and compression molding. Each engineer averages 12+ years in door seal geometries, focusing on critical parameters like lip profile consistency, compression force optimization, and draft angle precision to prevent air/water infiltration. Tolerances are maintained at ±0.1 mm for critical sealing surfaces, validated through in-house coordinate measuring machine (CMM) analysis. This precision directly impacts door energy efficiency ratings by minimizing gap leakage paths under wind load and thermal cycling.
The formula engineering division develops proprietary EPDM and silicone compounds tailored to door seal lifecycle demands. We prioritize low-temperature flexibility down to -40°C, UV/ozone resistance exceeding 5,000 hours in ASTM G154 testing, and compression set values below 25% after 70°C/22h exposure. Unlike generic formulations, our compounds integrate nano-silica reinforcement for abrasion resistance against repeated door strikes while maintaining Shore A 60-70 hardness for optimal sealing force distribution. Material batches undergo rigorous batch-to-batch spectrometry validation to ensure repeatability.
Material performance is quantified against industry benchmarks in the table below:
| Property | Test Standard | Baoshida Specification | Typical Industry Average |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 65 ± 3 | 60-75 (range) |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ASTM D412 | ≥12.5 | ≥9.0 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ASTM D412 | ≥350 | ≥250 |
| Compression Set (%) | ASTM D395 B | ≤22 | ≤35 |
| Low-Temp Flexibility | ASTM D1329 | Pass at -45°C | Pass at -35°C |
As an OEM partner, Suzhou Baoshida provides closed-loop engineering from CAD prototyping to量产. We manage full tooling ownership, material IP protection via NDAs, and PPAP documentation to IATF 16949 standards. Our engineers collaborate directly with client design teams to resolve interface challenges—such as hinge-induced door deflection or threshold irregularities—through dynamic FEA simulation of seal compression profiles. This proactive approach reduces time-to-market by 30% versus conventional supplier models while guaranteeing compliance with ENERGY STAR® air infiltration thresholds and AAMA 506-16 weathering requirements. Precision sealing is not an add-on component but a engineered system, and our dual-discipline team ensures every specification translates into field-proven performance.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis
The customization process for entry door seals begins with precise drawing analysis, a critical phase that ensures dimensional accuracy and functional compatibility. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., engineering teams evaluate customer-provided CAD drawings or technical sketches to verify key parameters including cross-sectional profile, tolerance ranges, installation groove dimensions, and sealing interface points. This stage involves close collaboration with OEM design departments to confirm compliance with architectural or automotive standards such as ISO 3933 or DIN 18089. Special attention is given to compression set requirements, deflection forces, and environmental exposure zones. Any geometric complexity—such as multi-rib profiles, hollow chambers, or co-extruded stiffeners—is flagged for material and tooling assessment in subsequent phases. The output of this stage is a finalized technical dossier used to guide formulation and mold design.
Formulation Development
Following dimensional validation, the rubber compound is engineered to meet mechanical and environmental performance demands. Our in-house polymer laboratory formulates EPDM, silicone (VMQ), or thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) compounds based on service conditions. Key performance attributes—UV resistance, low-temperature flexibility, compression set, and ozone stability—are optimized through controlled polymer blending, filler reinforcement (e.g., carbon black or silica), and additive integration (e.g., antioxidants, plasticizers). For entry door seals exposed to extreme climates, we deploy high-saturation EPDM grades with enhanced thermal aging resistance up to 135°C. Each formulation undergoes preliminary testing for hardness (Shore A), tensile strength, and elongation at break per ASTM D412 and ASTM D2240. The selected compound is then documented in a Material Data Sheet (MDS) for traceability and regulatory compliance.
Prototyping and Validation
Once the compound is approved, prototype tooling—typically single-cavity aluminum molds—is fabricated to produce initial samples. These prototypes are subjected to functional fit checks on actual door assemblies, along with laboratory testing for air/water tightness, compression load deflection (CLD), and cycle durability (up to 100,000 open/close cycles). Feedback from fitment trials informs iterative adjustments to profile geometry or durometer. Dimensional reports with GD&T verification are issued for customer approval. Only after passing all OEM validation checkpoints does the design advance to full-scale production.
Mass Production
Approved prototypes transition to mass production using hardened steel multi-cavity molds on high-precision hydraulic presses or continuous extrusion lines with microwave/vulcanization tunnels. Production batches follow strict process control protocols under ISO 9001 standards, with real-time monitoring of cure time, temperature, and pressure. Final inspection includes 100% visual checks and statistical sampling for dimensional conformance and physical properties.
Typical Material Specifications for Entry Door Seals
| Property | Test Method | EPDM | Silicone (VMQ) | TPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 55–75 | 50–70 | 60–80 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ASTM D412 | ≥9.0 | ≥6.5 | ≥8.0 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ASTM D412 | ≥300 | ≥250 | ≥400 |
| Compression Set (%) | ASTM D395 (70h @ 70°C) | ≤25 | ≤20 | ≤30 |
| Service Temperature Range (°C) | — | -40 to +135 | -60 to +200 | -30 to +120 |
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Entry Door Seal Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. stands at the forefront of precision rubber engineering, delivering mission-critical entry door seals for global OEMs demanding uncompromising performance. Our technical mastery in elastomer formulation ensures seals that exceed industry benchmarks for weather resistance, compression set, and longevity under extreme thermal and mechanical stress. We specialize in custom compound development for architectural and industrial applications where failure is not an option. Partnering with us means direct access to rigorous material science protocols, in-house tooling validation, and seamless integration into your manufacturing workflow.
The technical specifications below represent our baseline capabilities for standard entry door seal profiles. Each parameter is validated through ASTM D2000 and ISO 3302 testing protocols, with full traceability to raw material batches. Custom formulations for enhanced ozone resistance, low-temperature flexibility, or flame retardancy are developed through our collaborative engineering process.
| Property | EPDM Standard | EPDM High-Performance | Silicone Variant | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 55-75 | 60-80 | 45-65 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥10.0 | ≥12.5 | ≥8.0 | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ≥300 | ≥250 | ≥400 | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (70°C/22h) | ≤25% | ≤18% | ≤20% | ASTM D395 Method B |
| Operating Temperature | -50°C to 135°C | -55°C to 150°C | -60°C to 200°C | ISO 188 |
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.15-1.25 | 1.18-1.28 | 1.10-1.20 | ASTM D297 |
Initiate your project with Suzhou Baoshida through direct technical engagement. Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Relationship Manager, serves as your primary conduit for engineering discussions, quoting, and prototyping coordination. His expertise spans material selection, DFMEA review, and production scalability assessment. Contact him exclusively at [email protected] with the following details to expedite your inquiry:
Target application environment (e.g., coastal high-rise, arctic commercial facility)
Required regulatory certifications (e.g., EN 12219, ASTM E283)
Cross-sectional profile drawings or dimensional tolerances
Annual volume projections and quality control expectations
Do not submit generic procurement requests. We prioritize technical alignment over transactional volume. Mr. Boyce will schedule an engineer-to-engineer consultation within 24 business hours of receiving a complete technical dossier. This ensures our rubber chemists and your design team collaboratively address micro-extrusion challenges, adhesion requirements, and lifecycle validation specific to your door system architecture.
Suzhou Baoshida’s value extends beyond component supply. We integrate our material science database with your CAD environments, providing predictive modeling for seal deformation under wind load and thermal cycling. Our Suzhou-based technical center operates ISO/IEC 17025-accredited testing facilities, enabling real-time validation of your performance criteria. For entry door systems requiring zero-defect sealing in Category 5 hurricane zones or sub-zero environments, our engineered compounds deliver measurable reductions in air infiltration and maintenance costs.
Elevate your sealing performance through precision elastomer science. Contact Mr. Boyce immediately with your technical specifications to activate Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering workflow. Your next-generation entry door seal solution begins with a data-driven dialogue.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
