Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Mean Doormats

Engineering Insight: Material Science Imperatives for High-Traffic Commercial Doormats
Commercial doormats labeled “mean” by facility managers endure extreme mechanical stress, chemical exposure, and environmental cycling far beyond residential applications. Off-the-shelf rubber matting consistently fails in these environments due to generic compound formulations prioritizing cost over performance physics. Standard mats utilize unmodified SBR or low-grade EPDM with excessive plasticizer content, leading to rapid degradation under concentrated foot traffic. Plasticizers migrate within 6–12 months, causing surface hardening, microcracking, and catastrophic loss of flexibility. Simultaneously, inadequate filler dispersion creates weak points where abrasion initiates, accelerating wear rates by 300% compared to engineered solutions. This premature failure incurs hidden costs: replacement labor, slip hazard liabilities, and facility downtime during mat replacement cycles.
Material selection must address three core failure vectors: abrasion resistance, chemical resilience, and dimensional stability. Generic mats typically employ 40–50 Shore A hardness compounds optimized for initial softness, not longevity. Under high traffic, this softness permits grit embedment, turning the mat surface into an abrasive belt that shreds shoe soles and the mat itself. Critical polymer architecture requires balanced saturation—high-purity EPDM with 50–60% ethylene content for ozone resistance, reinforced with nano-silica fillers at 35–40 phr for tear strength without sacrificing rebound resilience. Plasticizers must be non-migrating polyesters, not phthalates, to maintain elasticity across -30°C to 80°C operational ranges. Without this precision, thermal cycling induces internal stresses that manifest as edge curling or delamination from backing substrates.
Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM approach begins with site-specific wear analysis. We measure grit load composition, traffic density (steps/hour), and contaminant profiles (de-icing salts, oils, cleaning agents) to calibrate compound chemistry. Our mean-duty formulations integrate dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) data to optimize glass transition temperature (Tg) placement, ensuring consistent energy dissipation. Below are performance benchmarks demonstrating why generic solutions fail where engineered compounds succeed.
| Critical Property | Standard Off-the-Shell Mat | Baoshida Mean-Duty Specification | Failure Consequence in Service |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abrasion Loss (DIN 53516) | 180 mm³ | ≤ 75 mm³ | 2.4x faster wear; loss of scraping profile within 8 months |
| Tensile Strength (ASTM D412) | 8.5 MPa | ≥ 15.0 MPa | Edge tearing under chair/cart loads |
| Elongation at Break | 250% | 450–500% | Brittle fracture at flex points |
| Compression Set (22h/70°C) | 35% | ≤ 18% | Permanent indentation; water pooling |
| Oil Swell Resistance (IRM 903) | 45% | ≤ 15% | Surface tackiness; accelerated dirt adhesion |
The cost premium for engineered matting is eclipsed by lifecycle savings. A Baoshida mean-duty mat lasts 5–7 years in airport concourse applications where standard mats require quarterly replacement. This reliability stems from closed-loop compounding: we adjust sulfur cure systems for optimal crosslink density and incorporate proprietary anti-degradants targeting specific oxidant profiles. Material selection isn’t a cost line item—it’s the foundation of operational continuity. Suzhou Baoshida provides data-driven compound validation, ensuring your matting performs as engineered infrastructure, not disposable consumables.
Material Specifications
Material selection is a critical determinant in the performance, durability, and application suitability of industrial rubber components, including high-precision doormats used in controlled environments. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in engineered rubber solutions tailored to meet the rigorous demands of industrial, pharmaceutical, and cleanroom applications. Our expertise in material science enables us to deliver mean doormats—engineered for consistent performance under stress—with optimized resistance to abrasion, chemicals, temperature extremes, and microbial growth. The three primary elastomers utilized in our formulations are Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ), each offering distinct advantages depending on operational requirements.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad spectrum of aggressive chemicals. This makes it ideal for use in environments where exposure to solvents, acids, or hydrocarbons is frequent. Viton-based doormats maintain structural integrity between -20°C and +250°C, providing long-term stability in extreme thermal conditions. Its low gas permeability and outstanding aging characteristics further enhance reliability in sealed or sensitive environments.
Nitrile rubber, or acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), is a cost-effective solution offering excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and aliphatic hydrocarbons. With a service temperature range of -30°C to +120°C, NBR is well-suited for industrial flooring applications where oil spillage or mechanical stress is common. It also exhibits high abrasion resistance and tensile strength, contributing to extended service life in high-traffic zones. While not as chemically inert as Viton, NBR provides a balanced performance profile for general-purpose industrial use.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) delivers superior thermal stability from -60°C to +230°C and exceptional resistance to ozone and UV radiation. It is non-toxic, inherently clean, and compliant with food-grade and medical standards, making it ideal for use in pharmaceutical cleanrooms, laboratories, and food processing facilities. Silicone’s low surface energy resists microbial adhesion and facilitates easy decontamination, a key factor in hygienic environments. However, it exhibits lower mechanical strength compared to NBR and higher gas permeability than Viton, necessitating application-specific evaluation.
The following table compares the core technical specifications of these materials as applied in industrial doormat manufacturing:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +250 | -30 to +120 | -60 to +230 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 6–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–500 | 300–700 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Very Good | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Moderate | Good (limited acids) |
| Cleanroom Compatibility | High | Moderate | Very High |
Selection of the appropriate elastomer must align with environmental exposure, mechanical demands, and regulatory standards. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports OEM clients with material testing, formulation optimization, and performance validation to ensure compliance and reliability in mission-critical applications.
Manufacturing Capabilities
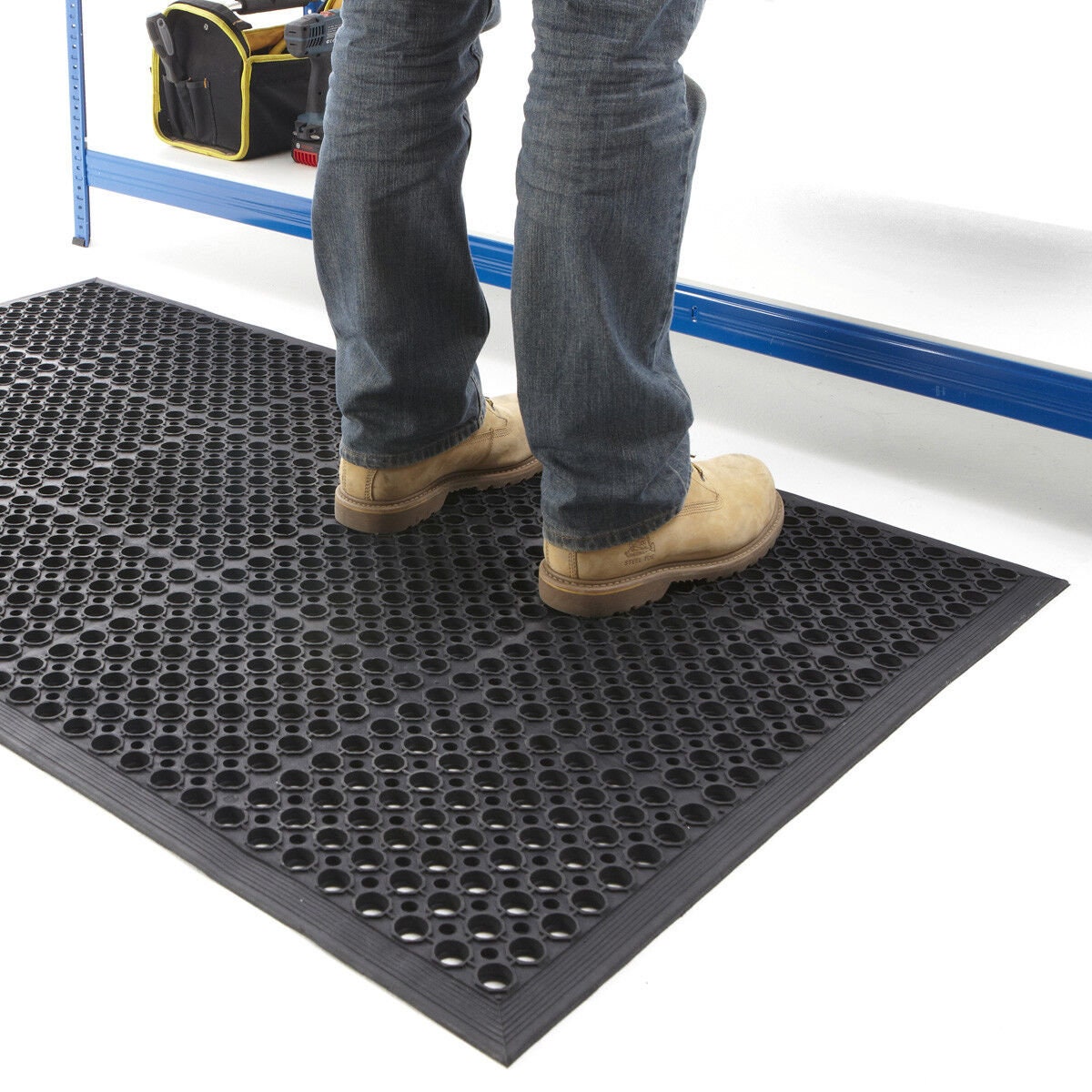

Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Solutions for Industrial Doormat Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered rubber performance for industrial-grade doormats through integrated material science and precision tooling expertise. Our dedicated team comprises five specialized Mold Design Engineers and two advanced Rubber Formula Engineers, ensuring every product meets rigorous functional and durability specifications from concept to mass production. This dual-engineering structure eliminates siloed development, enabling seamless optimization of compound formulation and mold geometry for superior wear resistance, dimensional stability, and environmental resilience in high-traffic applications.
Our Mold Engineering team utilizes 3D CAD/CAM systems and mold flow simulation software to design cavities that guarantee consistent part density, minimize flash, and extend tool life under continuous production cycles. Each mold undergoes thermal analysis to prevent warpage during vulcanization, critical for maintaining the precise tread depth and surface texture required in commercial entrance matting. Concurrently, our Rubber Formula Engineers develop proprietary elastomer blends tailored to specific client demands. We systematically adjust polymer bases (SBR, EPDM, recycled rubber), filler ratios, vulcanizing agents, and anti-degradants to achieve target properties such as Shore A hardness, oil resistance, and UV stability without compromising cost efficiency. This co-development approach ensures the rubber compound flows optimally within the engineered mold cavity, reducing scrap rates and enhancing surface definition for effective dirt-scraping functionality.
As a full-service OEM partner, we manage end-to-end production under ISO 9001 protocols. Clients provide performance requirements or physical samples; our engineers reverse-engineer or co-create specifications, validate prototypes through accelerated aging and abrasion testing, and scale to volume production with strict batch traceability. We maintain flexibility for custom color matching, branding integration, and dimensional adjustments while adhering to tight tolerances. Our facility supports low to high-volume runs with dedicated press lines for rubber compression molding, ensuring consistent cure profiles critical for long-term mat integrity.
The table below summarizes key technical capabilities for industrial rubber doormat production:
| Parameter | Capability Range | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Durometer (Shore A) | 55–85 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | 8–18 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | 200–450% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22h/70°C) | ≤ 25% | ASTM D395 |
| Temperature Resistance | -40°C to +100°C (continuous) | ISO 188 |
| Abrasion Loss | ≤ 120 mm³ (DIN abrader) | ISO 4649 |
| Customization Lead Time | 15–25 days (prototype to approval) | Internal QA Protocol |
This engineering synergy between compound science and precision tooling allows Suzhou Baoshida to solve complex material challenges inherent in commercial doormat applications. We transform functional requirements into manufacturable solutions that withstand abrasive soils, extreme weather, and constant foot traffic while meeting global safety and sustainability standards. Partner with us for technically validated rubber matting where performance specifications are non-negotiable.
Customization Process
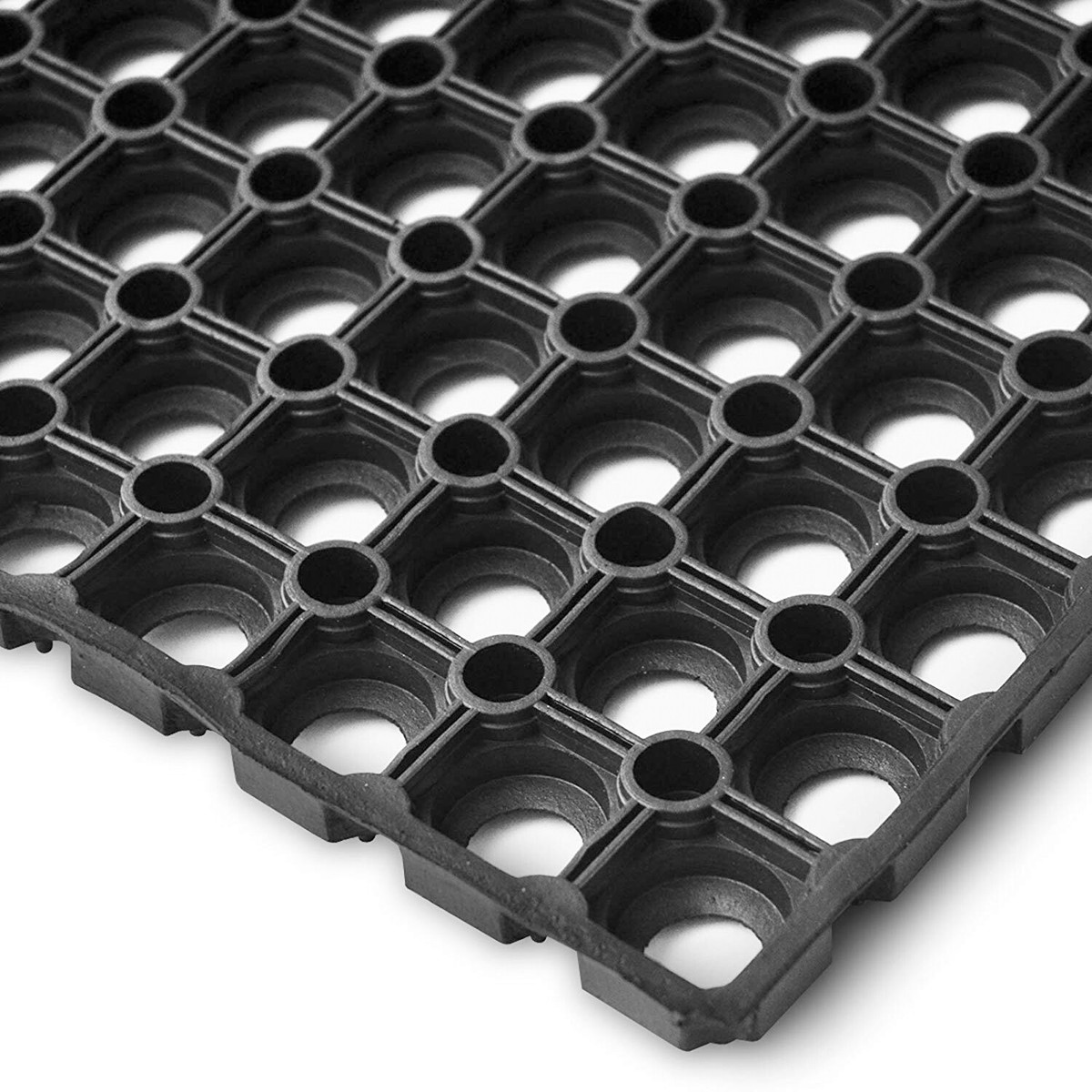

Customization Process for Industrial Rubber Doormats at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in delivering high-performance industrial rubber solutions tailored to the exact functional and dimensional requirements of our B2B clients. Our customization process for manufacturing mean doormats follows a rigorous four-stage workflow: Drawing Analysis, Formulation, Prototyping, and Mass Production. This structured approach ensures precision, durability, and compliance with industrial standards.
The process begins with Drawing Analysis, where our engineering team evaluates the client-provided technical drawings or CAD models. We assess critical parameters such as overall dimensions, surface profile depth, cleat geometry, tolerance specifications, and drainage channel design. Special attention is given to load-bearing zones and slip resistance requirements, particularly for industrial environments such as factories, warehouses, and logistics centers. Any inconsistencies or design limitations are flagged, and we collaborate with the client to refine the blueprint for optimal manufacturability and performance.
Once the design is finalized, we proceed to Formulation. Our rubber formula engineers analyze the operational environment—temperature range, exposure to oils, chemicals, UV radiation, and foot or vehicular traffic—to determine the ideal elastomer compound. We primarily utilize SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber), EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer), or NR (Natural Rubber), often compounded with reinforcing fillers, anti-aging agents, and vulcanizing systems. Shore A hardness is precisely calibrated between 55 and 75, depending on required resilience and abrasion resistance. Colorants and flame retardants are integrated if specified.
The third phase is Prototyping. Using precision molds manufactured in-house, we produce a limited batch of prototype doormats. These samples undergo a series of mechanical and environmental tests, including tensile strength, compression set, slip resistance (ASTM F2913), and accelerated aging. The prototypes are shipped to the client for field evaluation. Feedback is systematically incorporated, and design or material adjustments are made as needed before final approval.
Upon client sign-off, we transition to Mass Production. Our automated rubber compression molding lines, supported by real-time quality monitoring, ensure batch consistency and throughput efficiency. Each doormat is visually inspected and dimensionally verified before packaging. Production lead times are optimized without compromising quality, with standard delivery within 25–35 days depending on order volume.
The table below outlines typical technical specifications for our custom industrial rubber doormats:
| Parameter | Standard Range |
|---|---|
| Material | SBR, EPDM, NR, or custom blend |
| Shore A Hardness | 55–75 |
| Thickness | 8 mm – 20 mm |
| Operating Temperature | -30°C to +80°C |
| Tensile Strength | ≥10 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% |
| Slip Resistance (Dry/Wet) | ≥0.60 (ASTM F2913) |
| Custom Colors | Pantone-matched available |
| Lead Time (Mass Production) | 25–35 days after prototype approval |
Through this disciplined customization pathway, Suzhou Baoshida ensures every mean doormat meets the exacting demands of industrial applications, combining engineering rigor with manufacturing excellence.
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Rubber Doormat Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the forefront of industrial rubber compounding, delivering engineered doormat solutions that meet rigorous global manufacturing standards. Our expertise lies in formulating polymer matrices optimized for extreme environmental resilience, abrasion resistance, and dimensional stability—critical factors for high-traffic commercial and industrial applications. Unlike generic alternatives, our rubber compounds undergo stringent vulcanization control and additive integration to ensure consistent performance across temperature extremes, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress. As your dedicated OEM partner, we prioritize material science precision to extend product lifecycle while reducing total cost of ownership for facility managers and procurement specialists.
Our technical team specializes in tailoring formulations to exact client specifications, whether addressing oil resistance for automotive facilities, slip mitigation for food processing plants, or UV stability for outdoor hospitality installations. Each compound is validated through ASTM D2240 hardness testing, ISO 37 tensile analysis, and accelerated aging protocols to guarantee compliance with ISO 9001:2015 quality management systems. The table below outlines core performance metrics for our standard industrial-grade and premium extreme-duty rubber doormat materials:
| Material Grade | Shore A Hardness | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Oil Resistance (Volume Swell, ASTM D471) | Operating Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Industrial | 65 ± 3 | ≥ 12.0 | ≥ 350 | ≤ 15% | -30°C to +80°C |
| Premium Extreme Duty | 75 ± 3 | ≥ 18.5 | ≥ 280 | ≤ 8% | -50°C to +110°C |
These specifications reflect our commitment to data-driven material development. The Premium Extreme Duty formulation, for instance, incorporates proprietary antioxidant packages and high-purity silica fillers to achieve superior resistance against hydraulic fluids and ozone degradation—common failure points in industrial settings. Our Suzhou-based manufacturing facility maintains full traceability from raw material sourcing to finished goods, enabling rapid scalability for OEM volume commitments without compromising batch consistency.
For procurement teams requiring customized rubber profiles, color matching to Pantone standards, or integration of anti-microbial additives, direct collaboration with our engineering division ensures technical alignment from prototype to mass production. We eliminate supply chain vulnerabilities through dual-sourcing strategies for critical elastomers and in-house rheometer validation, providing clients with uninterrupted delivery assurance.
Initiate your project with Suzhou Baoshida’s technical leadership. Contact Mr. Boyce, our Rubber Formula Engineer and OEM Manager, directly at [email protected] to discuss material certifications, sample validation protocols, or volume pricing structures. Mr. Boyce will coordinate a comprehensive technical review within 24 business hours, including finite element analysis (FEA) simulations for load-bearing requirements and accelerated wear testing reports. Partner with an organization where compound chemistry is engineered—not negotiated—to deliver measurable operational value. Your next-generation rubber doormat solution begins with a single email.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
