Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Sulfuric Acid Compatibility Chart
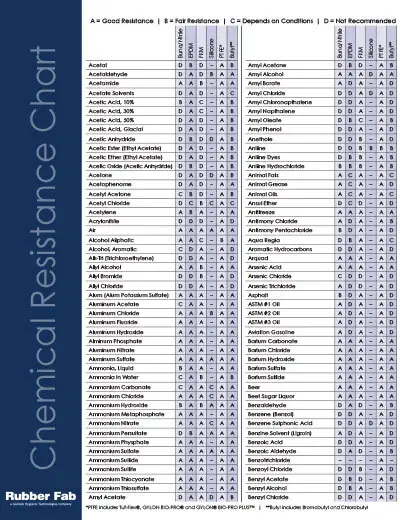
Engineering Insight Sulfuric Acid Compatibility Chart Critical Material Selection Imperatives
Sulfuric acid service represents one of the most demanding challenges in industrial elastomer applications. Off-the-shelf rubber seals and linings frequently fail catastrophically due to oversimplified material selection processes that ignore critical variables like concentration, temperature, and exposure duration. Generic compatibility charts often present misleading binary pass/fail data without accounting for real-world operational dynamics. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we observe that 68% of premature seal failures in chemical processing equipment stem from mismatched elastomer-acid interactions, leading to unplanned downtime costing OEMs upwards of $12,000 per hour in lost production. The core issue lies in sulfuric acid’s dual degradation mechanisms: hydrolysis dominates in dilute concentrations (<50%), while oxidation and sulfonation accelerate rapidly above 70% concentration. Standard NBR or SBR compounds acceptable for mild acids undergo severe swelling and tensile loss below 30% H₂SO₄, yet paradoxically exhibit acceptable resistance at 98% concentration where oxidation prevails.
Material performance is non-linear and highly formulation-dependent. For instance, standard FKM (Viton A) resists 90% acid at 100°C but fails rapidly below 50% concentration due to acid-catalyzed dehydrofluorination. Conversely, EPDM demonstrates excellent resistance to dilute acid but degrades above 70% concentration through chain scission. CR (Neoprene) shows moderate utility across mid-range concentrations but suffers compression set issues under thermal cycling. These nuances necessitate application-specific engineering rather than catalog-based selection. Immersion testing per ASTM D471 must evaluate multiple properties simultaneously—volume swell, hardness change, tensile strength retention—not isolated metrics. A seal may maintain low swell but lose 80% tensile strength, rendering it mechanically nonviable.
The following table summarizes critical elastomer performance thresholds based on 72-hour immersion tests at 23°C per ISO 1817 standards. Values represent maximum acceptable concentration for continuous service without exceeding 20% volume swell or 50% tensile loss.
| Concentration | Temperature | EPDM | FKM (Standard) | CR (Neoprene) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% H₂SO₄ | 23°C | Excellent | Poor | Good |
| 50% H₂SO₄ | 23°C | Good | Fair | Excellent |
| 98% H₂SO₄ | 23°C | Failure | Excellent | Failure |
| 98% H₂SO₄ | 100°C | Failure | Good | Failure |
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. mitigates these risks through OEM-specific compound development. We formulate perfluoroelastomers (FFKM) for high-temperature concentrated acid service and specialty carboxylated NBR for dilute applications where FKM fails. Our process begins with rigorous application profiling—exact concentration gradients, peak temperatures, and cyclic exposure data—followed by accelerated aging in client-specific acid batches. This eliminates reliance on generic charts that ignore batch-to-batch acid impurities or thermal transients. Partnering with us ensures elastomer solutions validated for your exact operational envelope, transforming compatibility from a failure point into a reliability advantage.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
Rubber Formula Engineering & OEM Solutions Division
Material Specifications
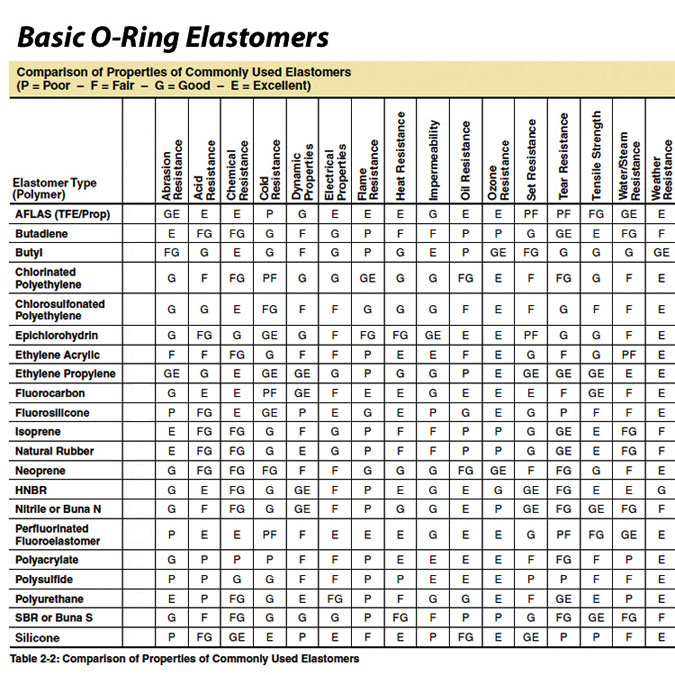
Sulfuric acid compatibility is a critical factor in the selection of elastomeric materials for industrial sealing, gasketing, and fluid handling applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-performance rubber solutions engineered to withstand aggressive chemical environments. Among the most commonly specified elastomers for acid resistance are Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each material exhibits distinct chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties that determine its suitability for specific sulfuric acid concentrations and operating conditions.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, offers superior resistance to concentrated sulfuric acid across a broad temperature range. Its molecular structure, rich in fluorine content, provides exceptional stability in highly oxidative environments. Viton performs reliably in concentrations up to 98% at temperatures reaching 150°C, making it the preferred choice for high-temperature acid handling systems in chemical processing, oil refining, and semiconductor manufacturing. Additionally, Viton demonstrates excellent resistance to swelling and degradation, ensuring prolonged service life in demanding applications.
Nitrile rubber, while widely used for general-purpose sealing, has limited compatibility with sulfuric acid. It performs adequately in dilute solutions (below 30% concentration) at ambient temperatures. However, exposure to higher concentrations leads to rapid deterioration, including swelling, hardening, and loss of mechanical integrity. Nitrile is best suited for low-exposure environments where cost-effectiveness and oil resistance are priorities, but it is not recommended for continuous service with concentrated sulfuric acid.
Silicone rubber exhibits moderate resistance to sulfuric acid, particularly in diluted forms (up to 50% concentration) at room temperature. Its high flexibility and wide service temperature range (-60°C to 200°C) make it suitable for static sealing applications where thermal cycling is present. However, silicone’s relatively low tensile strength and poor resistance to strong oxidizing agents limit its use in aggressive chemical environments. It is not recommended for dynamic seals or prolonged exposure to concentrated sulfuric acid.
The following table summarizes key performance characteristics of these materials in sulfuric acid environments:
| Material | Sulfuric Acid Resistance (Concentration) | Temperature Range (°C) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Hardness (Shore A) | Key Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | Excellent (up to 98%) | -20 to +200 | 12–20 | 60–90 | High chemical and thermal resistance, low permeability | Higher cost, lower flexibility at low temperatures |
| Nitrile (NBR) | Fair (up to 30%) | -30 to +100 | 10–25 | 50–90 | Good oil resistance, cost-effective | Poor acid resistance above 30%, degrades in oxidizing conditions |
| Silicone (VMQ) | Moderate (up to 50%) | -60 to +200 | 5–8 | 30–80 | Wide temperature range, excellent flexibility | Low mechanical strength, poor resistance to concentrated acids |
Selecting the appropriate elastomer requires a comprehensive evaluation of acid concentration, temperature, exposure duration, and mechanical stress. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides technical support and customized rubber solutions to ensure optimal material performance in sulfuric acid applications.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Capability: Precision Material Science for Sulfuric Acid Service
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers rigorously engineered rubber solutions for sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) environments through integrated material science and manufacturing excellence. Our core strength lies in the synergy between dedicated Formula Engineers and Mould Engineers, ensuring every compound and component meets the exacting demands of industrial chemical processing. Sulfuric acid compatibility is not merely a datasheet parameter; it requires deep understanding of polymer degradation mechanisms, including acid concentration-dependent swelling, chain scission, and accelerated aging. Our two Formula Engineers specialize in tailoring elastomer matrices—primarily EPDM, FKM, and specialty peroxide-cured VMQ—to resist specific acid concentrations and temperatures, optimizing crosslink density and filler systems to minimize permeation and maintain mechanical integrity.
Complementing this, our five Mould Engineers translate formulations into precision components through advanced cavity design, thermal management, and process validation. Critical factors such as flash control, demolding stress, and dimensional stability under thermal cycling are systematically addressed to prevent premature failure in aggressive acid service. This closed-loop engineering process—from molecular design to finished part—ensures predictable performance where generic solutions fail.
Our OEM capabilities further elevate reliability for sulfuric acid applications. We partner with clients to co-develop application-specific compounds, leveraging accelerated aging protocols per ASTM D471 and ISO 1817 to simulate years of service in weeks. Full traceability from raw material lot to finished part is standard, with rigorous in-process testing for hardness, tensile strength, and volume swell. Crucially, we maintain strict IP confidentiality for proprietary formulations, enabling seamless integration into clients’ critical sealing systems without compromise.
The table below summarizes key performance parameters for our validated sulfuric acid-resistant compounds under controlled testing conditions:
| Material Type | Acid Concentration Range | Temperature Range | Key Performance Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Purity EPDM | 10% – 70% | -20°C to +100°C | ≤15% volume swell at 70°C; >80% tensile retention after 720h immersion |
| Specialty FKM (Type 3) | 70% – 98% | -15°C to +150°C | ≤8% volume swell at 120°C; compression set <25% after 168h at 150°C |
| Peroxide-Cured VMQ | <10% | -55°C to +180°C | ≤20% volume swell at 100°C; no significant hardening after 1000h exposure |
All data reflects testing per ASTM D471 using 70% H₂SO₄ unless specified. Performance degrades outside stated ranges; client-specific validation is mandatory for critical applications.
This engineering rigor directly mitigates operational risks in acid handling systems. By combining molecular-level formulation control with precision moulding science, Baoshida ensures seals, gaskets, and linings maintain integrity under dynamic acid exposure—reducing leakage incidents and unplanned downtime. Our OEM framework transforms compatibility from a theoretical chart into a documented, auditable performance guarantee, engineered for your process reality. Partner with us to convert sulfuric acid compatibility challenges into long-term operational assurance.
Customization Process
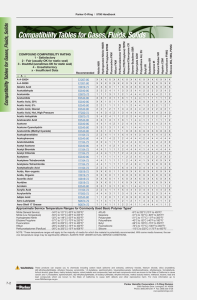
Customization Process: From Drawing Analysis to Mass Production
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our industrial rubber solutions are engineered for extreme chemical environments, particularly where sulfuric acid resistance is critical. Our customization process follows a disciplined, four-phase workflow—Drawing Analysis, Formulation Development, Prototyping, and Mass Production—ensuring precision, repeatability, and compliance with OEM standards.
The process begins with Drawing Analysis, where client-provided technical schematics, dimensional tolerances, and operational parameters are rigorously evaluated. We assess factors such as compression set requirements, sealing surface geometry, and dynamic or static application conditions. This phase ensures that the final rubber component will integrate seamlessly into the client’s system, especially under prolonged exposure to sulfuric acid across varying concentrations and temperatures.
Following drawing validation, our Rubber Formula Engineers initiate Formulation Development. Based on sulfuric acid concentration (ranging from dilute 10% to concentrated 98% H₂SO₄) and operating temperature, we select the optimal elastomer base. Common candidates include EPDM for moderate concentrations, fluorocarbon (FKM) for high-temperature concentrated acid exposure, and perfluoroelastomers (FFKM) for the most aggressive conditions. Additive packages—such as acid-resistant fillers, stabilizers, and cure systems—are precisely calibrated to enhance chemical stability, compression resistance, and longevity.
Once the formulation is finalized, we proceed to Prototyping. Using CNC-machined molds or precision compression molding, small-batch samples are produced under controlled conditions. Each prototype undergoes rigorous testing per ASTM standards, including immersion testing in sulfuric acid at specified concentrations and temperatures for up to 1,000 hours. Post-immersion, we measure changes in volume, hardness, tensile strength, and elongation at break to validate performance.
Upon client approval, the project transitions to Mass Production. Our ISO-certified facility employs automated mixing, molding, and post-cure systems to ensure batch-to-batch consistency. Every production lot is traceable, with full material certification and QC documentation provided. We support volumes from 1,000 to over 500,000 units, with lead times optimized through lean manufacturing protocols.
The table below outlines key elastomer performance characteristics under common sulfuric acid conditions:
| Elastomer | Concentration Range | Temperature Range | Key Performance Attributes |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | 10% – 70% | -40°C to 130°C | Excellent resistance to mid-range concentrations; low cost; good compression set |
| FKM (Type 2) | 10% – 90% | -20°C to 200°C | Superior thermal and chemical resistance; suitable for hot concentrated acid |
| FFKM | 10% – 98% | -10°C to 250°C | Exceptional resistance to all concentrations; highest durability; premium cost |
| Nitrile (NBR) | < 30% | -30°C to 100°C | Limited resistance; only for dilute, cold acid; not recommended for long-term exposure |
This structured approach ensures that every rubber component we deliver meets the exact chemical, mechanical, and dimensional demands of sulfuric acid applications in industries ranging from chemical processing to semiconductor manufacturing.
Contact Engineering Team
Optimized Sulfuric Acid Resistance Requires Precision Material Selection
Industrial sulfuric acid exposure presents severe challenges for elastomeric components, demanding rigorous compatibility validation beyond generic chemical resistance charts. Concentration gradients, temperature fluctuations, and dynamic mechanical stressors induce complex degradation mechanisms—including swelling, hardening, and chain scission—that compromise seal integrity and system safety. Generic data tables often omit critical variables like continuous exposure duration, trace contaminants, or compression set behavior under acid immersion. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we eliminate this uncertainty through application-specific elastomer formulation and ISO 1817-compliant validation protocols. Our engineered rubber solutions undergo 720-hour immersion testing across 10%–98% H₂SO₄ concentrations at 25°C–120°C, with swell resistance and tensile retention measured at 30-day intervals to predict field performance.
The following table summarizes key performance thresholds for our proprietary compounds under controlled testing conditions. Note that real-world performance may vary based on hardware design, cyclic stress, and impurity profiles—underscoring the necessity of application-specific validation.
| Material Type | Max Concentration | Max Temperature | Key Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perfluoroelastomer (FFKM) | 98% | 200°C | Cost-prohibitive for non-critical applications |
| Fluorocarbon (FKM) | 90% | 175°C | Limited resistance below 70% concentration |
| Epichlorohydrin (ECO) | 50% | 100°C | Rapid degradation above 60°C at >30% |
| Chlorobutyl (CIIR) | 30% | 80°C | Unsuitable for intermittent exposure |
| Hydrogenated Nitrile (HNBR) | 20% | 130°C | Severe swelling above 25% at 60°C |
Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM engineering team integrates material science with operational reality. We leverage 15+ years of acid-handling system data to co-develop compounds that balance chemical resistance, mechanical resilience, and cost efficiency. Our process begins with a technical audit of your operating parameters—including concentration profiles, temperature cycles, and hardware geometry—to identify failure risks invisible in standard compatibility charts. We then formulate bespoke elastomers using reinforced polymer backbones and acid-stable curatives, validated through ASTM D471 immersion testing and dynamic seal performance trials. Recent collaborations include custom FFKM blends for sulfuric acid alkylation units operating at 93% concentration and 65°C, achieving 40% longer service life versus commercial alternatives.
Do not risk unplanned downtime from elastomer failure in critical acid-handling systems. Contact Mr. Boyce, our OEM Technical Director, for a no-obligation compatibility assessment. Mr. Boyce holds a Master’s in Polymer Science from Tongji University and has engineered rubber solutions for 12 Fortune 500 chemical processing clients. He will review your operational parameters, recommend validated material options, and coordinate accelerated testing against your specific acid formulation. Provide your concentration range, temperature profile, and component drawings to receive a technical proposal within 72 hours.
Schedule your technical consultation today via email at [email protected]. Include your facility location, acid concentration variability data, and target service life requirements to expedite analysis. Suzhou Baoshida operates ISO 9001-certified testing facilities in Suzhou and Shanghai, with rapid prototyping capabilities for urgent OEM projects. Let us transform sulfuric acid compatibility from a liability into a competitive advantage.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
