Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Aramid Kevlar Fiber
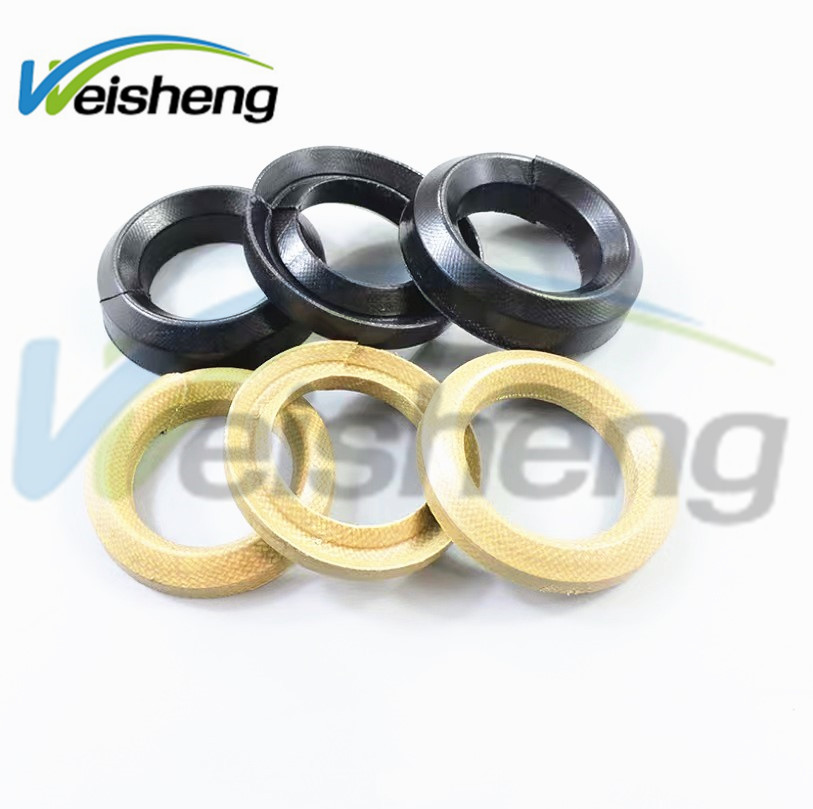

Engineering Insight: Aramid Kevlar Fiber in Industrial Rubber Applications
Material selection in industrial rubber manufacturing is not an area for compromise. Off-the-shelf rubber compounds often fail under demanding operational conditions because they lack the tailored reinforcement required for specific mechanical, thermal, and chemical environments. Among high-performance reinforcing fibers, aramid Kevlar fiber stands out for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, thermal stability, and resistance to fatigue. However, integrating this advanced material into rubber matrices requires precise engineering—not generic substitution.
Aramid Kevlar fiber, a synthetic para-aramid, exhibits tensile strength five times greater than steel on an equal weight basis. Its molecular chain alignment and hydrogen bonding contribute to outstanding resistance to elongation and impact. When embedded within rubber components such as hoses, belts, seals, or vibration dampeners, Kevlar fiber significantly enhances structural integrity under high pressure, dynamic loading, and abrasive conditions. Yet, many standard rubber products utilize lower-grade textiles like polyester or nylon, which degrade prematurely when exposed to temperatures above 120°C or aggressive media such as oils, fuels, or hydraulic fluids.
The failure of off-the-shelf solutions often originates from inadequate interfacial adhesion between fiber and rubber. Kevlar fibers are inherently chemically inert, making bonding with conventional rubber matrices—such as NBR, EPDM, or HNBR—challenging without proper surface treatment. Untreated fibers can debond under cyclic stress, leading to delamination, internal cracking, and catastrophic component failure. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we address this through proprietary adhesion-promoting coatings and optimized cure systems that ensure durable fiber-rubber integration.
Furthermore, standard formulations frequently overlook anisotropic behavior. Kevlar’s directional strength must be aligned with operational stress vectors during manufacturing. Random fiber orientation in generic composites diminishes performance gains. Precision in fiber placement, orientation, and layering sequence is essential to harness the full potential of aramid reinforcement.
Below are key mechanical and thermal properties of Kevlar fiber relevant to rubber composite design:
| Property | Value | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 3,620 MPa | ASTM D2343 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 70–112 GPa | ASTM D2343 |
| Elongation at Break | 2.8–3.5% | ASTM D2343 |
| Thermal Degradation Onset | 450°C (in inert atmosphere) | TGA, N₂ |
| Specific Gravity | 1.44 | ASTM D792 |
| Moisture Regain | 4.5% (at 50% RH) | ASTM D2344 |
These values underscore why Kevlar is ideal for high-stress, high-temperature rubber applications such as aviation hydraulic hoses, mining conveyor belts, and oilfield sealing systems. However, achieving reliable performance demands more than material substitution—it requires system-level engineering.
At Suzhou Baoshida, we specialize in custom rubber formulations reinforced with aramid Kevlar fiber, engineered for mission-critical OEM applications. Our approach ensures compatibility, durability, and performance under real-world industrial conditions—where standard solutions fall short.
Material Specifications
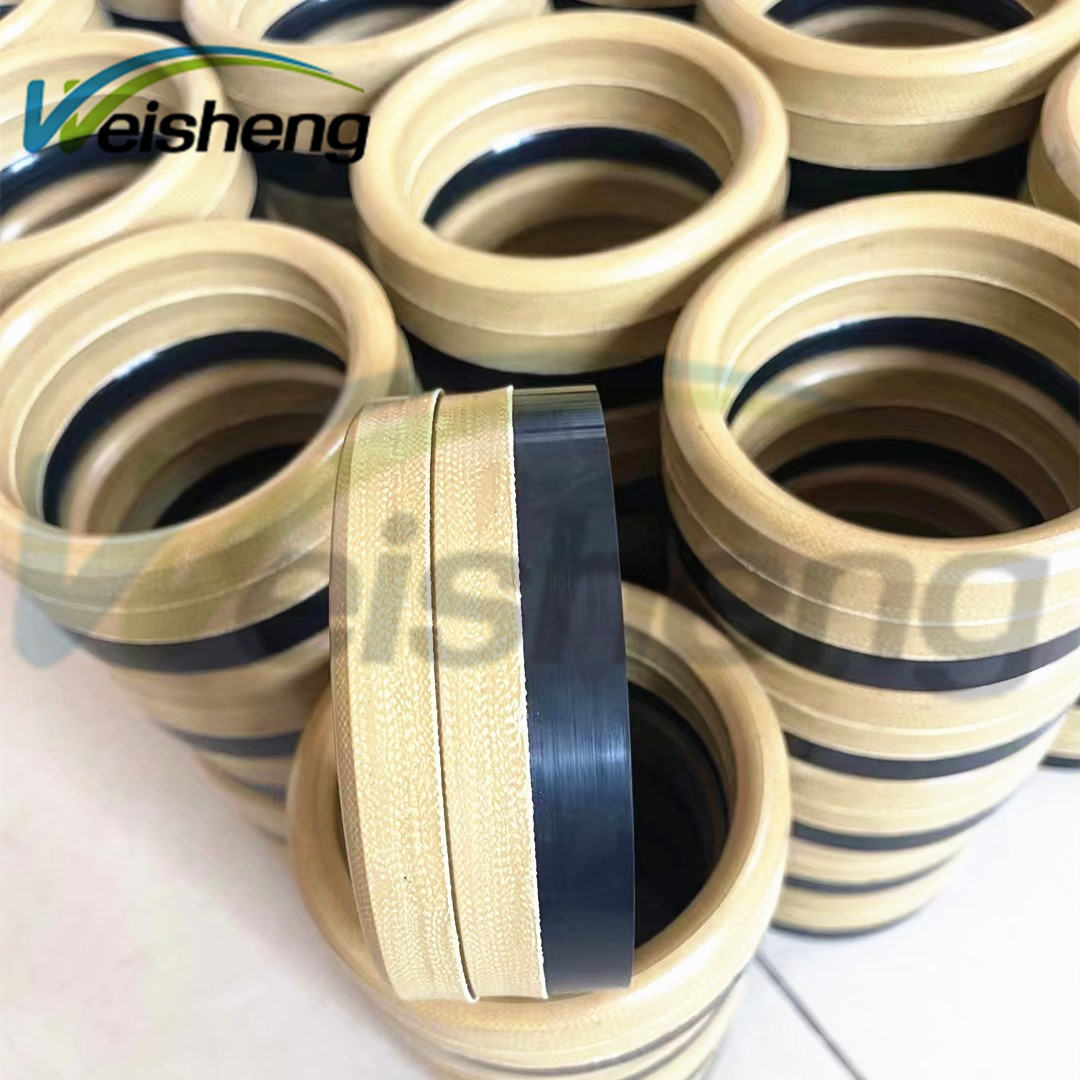

Material Specifications: Aramid-Reinforced Rubber Compounds for Critical Sealing Applications
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supplies high-performance rubber compounds engineered for extreme industrial environments. While aramid fibers like Kevlar® serve as critical reinforcement additives in specialty rubber formulations, this section details the base elastomer specifications essential for OEM sealing solutions. Viton® (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ) represent core materials where aramid reinforcement significantly enhances tensile strength, cut resistance, and dimensional stability under stress. Understanding their intrinsic properties is paramount for selecting the optimal compound for aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing applications.
Viton® fluorocarbon rubber delivers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and fuels. Standard grades maintain integrity from -20°C to +250°C, with specialty formulations extending to +300°C. Its low gas permeability and resilience against ozone, acids, and hydraulic fluids make it indispensable for jet engine seals and semiconductor manufacturing. Nitrile rubber provides cost-effective performance in oil and fuel exposure, operating effectively between -40°C and +120°C. With excellent abrasion resistance and tensile strength up to 30 MPa, it is the standard for hydraulic O-rings, fuel hoses, and industrial gaskets where petroleum-based fluid contact occurs. Silicone rubber excels in extreme temperature flexibility, functioning reliably from -60°C to +230°C. Its biocompatibility, low compression set, and electrical insulation properties suit medical devices, food processing seals, and high-voltage insulation, though it exhibits lower tensile strength and poor resistance to concentrated acids.
Aramid fiber reinforcement (typically 5-15% by weight) is strategically integrated into these base compounds to address specific mechanical challenges. Kevlar® fibers mitigate extrusion in high-pressure dynamic seals, reduce swelling in aggressive media, and enhance fatigue life in reciprocating applications. This reinforcement is particularly critical for Viton® in aerospace fuel systems and Nitrile in heavy-duty mining equipment seals, where failure consequences are severe.
The following table compares fundamental properties of unreinforced base elastomers per ASTM D2000 standards. Note that aramid-reinforced variants exhibit superior tensile strength (+25-40%) and reduced elongation at break versus standard grades.
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Hardness (Shore A) | Key Chemical Resistance | Primary Industrial Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton® (FKM) | -20 to +250 | 10-18 | 150-300 | 60-90 | Fuels, oils, acids, ozone | Aerospace seals, chemical valves, semiconductor tools |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -40 to +120 | 15-30 | 200-500 | 50-90 | Petroleum oils, aliphatic hydrocarbons | Automotive fuel systems, hydraulic equipment, printing rolls |
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 to +230 | 5-12 | 200-700 | 30-80 | Water, steam, oxygen, weak acids | Medical tubing, food processing gaskets, electrical insulation |
Suzhou Baoshida rigorously tests all aramid-reinforced compounds per OEM specifications, ensuring compliance with ISO 3601 flange standards and SAE AS568 dash numbers. Material selection must account for fluid compatibility, thermal cycling, and mechanical stress profiles. Consult our engineering team for customized formulations where standard elastomers require Kevlar® reinforcement to meet critical performance thresholds in dynamic sealing scenarios. Precision in compound specification directly correlates with service life and system reliability in demanding industrial operations.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. maintains a robust engineering infrastructure dedicated to advancing industrial rubber solutions with high-performance reinforcement materials such as aramid (Kevlar) fiber. Our in-house technical team comprises five specialized mould engineers and two senior rubber formulation engineers, enabling full-cycle product development from concept to production. This integrated engineering capability ensures precise control over material behavior, dimensional accuracy, and performance consistency in demanding applications.
Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional tensile strength, thermal stability, and low elongation, presents unique challenges in rubber bonding and processing. Our formulation engineers possess deep expertise in modifying rubber matrices—particularly NBR, EPDM, and HNBR—to achieve optimal adhesion with aramid filaments. Surface treatment of fibers, resin dipping protocols, and cure system optimization are systematically tailored to enhance interfacial bonding, minimizing delamination under dynamic stress. This molecular-level control is critical in applications such as high-pressure hydraulic hoses, timing belts, and industrial drive systems where failure is not an option.
Our mould engineering team ensures that the physical architecture of reinforced rubber components aligns with both functional requirements and manufacturing precision. Utilizing advanced CAD/CAM software and finite element analysis (FEA), we simulate stress distribution, flow dynamics, and curing behavior to refine mould design prior to tooling fabrication. This proactive approach reduces prototyping cycles and accelerates time-to-market. With extensive experience in multi-cavity moulds, insert moulding, and overmoulding techniques, we support complex geometries required in OEM fluid handling and power transmission systems.
As an OEM partner, Suzhou Baoshida delivers end-to-end engineering support, including design validation, material selection, DFM (Design for Manufacturability) feedback, and PPAP documentation. We collaborate directly with client engineering teams to co-develop solutions that meet exact performance specifications under extreme temperatures, pressures, and mechanical loads. Our facility supports low-volume prototyping and high-volume production, ensuring seamless scalability.
The following table outlines key technical parameters achievable with aramid-reinforced rubber components developed through our integrated engineering platform:
| Parameter | Typical Value | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (reinforced) | ≥ 35 MPa | ISO 37 |
| Elongation at Break | 250–400% | ISO 37 |
| Adhesion Strength (rubber-aramid) | ≥ 8 kN/m | ISO 813 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +150°C (up to +180°C intermittent) | ISO 1817 |
| Burst Pressure (hose application) | Up to 600 bar | ISO 6803 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | ISO 48-4 |
This technical foundation, supported by dedicated engineering resources and rigorous process controls, positions Suzhou Baoshida as a trusted partner for OEMs requiring mission-critical rubber components reinforced with aramid fiber. Our commitment to material science excellence and precision engineering ensures long-term reliability in the most demanding industrial environments.
Customization Process
Customization Process for Aramid Kevlar Fiber-Reinforced Rubber Components
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our aramid Kevlar fiber integration process begins with rigorous drawing analysis to align material science with functional requirements. Engineering teams dissect client CAD models and technical schematics, focusing on critical stress zones, dimensional tolerances, and operational environments. This phase identifies where Kevlar’s exceptional tensile strength (≥3,620 MPa) and thermal stability (decomposition point >500°C) must counteract dynamic loads, abrasion, or high-temperature exposure. Cross-sectional thickness deviations exceeding 0.15 mm trigger targeted Kevlar reinforcement zones to prevent delamination under cyclic stress.
Formulation follows, where Kevlar fiber dispersion and polymer matrix adhesion are optimized. We prioritize silane coupling agents to bridge hydrophobic rubber matrices (e.g., HNBR, EPDM) with hydrophilic Kevlar surfaces, ensuring covalent bonding. Fiber length (typically 0.5–3.0 mm) and loading percentages (8–15 wt%) are calibrated via Mooney viscosity testing to balance processability and mechanical gains. Excessive fiber content risks scorch during mixing; insufficient loading fails to leverage Kevlar’s 18x steel strength-to-weight ratio. All formulations adhere to ISO 23529 standards for repeatability, with accelerated aging tests validating long-term interfacial stability.
Prototyping transitions theory to validation. Components are extruded or molded using precision tooling, with in-line rheometers monitoring cure kinetics (t90 ±5 seconds). Each prototype undergoes ASTM D412 tensile testing, DIN 53504 tear resistance assays, and ISO 188 heat aging at 150°C for 72 hours. Critical metrics include:
Tensile strength retention after aging
Fiber pull-out force via SEM-verified interfacial shear strength
Dynamic fatigue cycles to 10⁷ repetitions
Only prototypes meeting 100% of client-specified performance thresholds advance.
Mass production integrates real-time quality control. Automated dosing systems maintain ±0.3% fiber weight accuracy, while inline IR thermography ensures uniform curing temperatures (±2°C). Every batch undergoes destructive testing per ASTM D2240 (Shore A hardness) and non-destructive ultrasound scanning for void detection (<0.5 mm³). Traceability is enforced via blockchain-logged material lot numbers, linking raw Kevlar batches (DuPont™ Twaron® or Teijin® Technora®) to final product certifications. This closed-loop system guarantees consistency across volumes exceeding 50,000 units monthly.
Key Performance Comparison: Standard vs. Kevlar-Enhanced Rubber
| Property | Standard EPDM Rubber | Kevlar-Enhanced EPDM (12 wt%) | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 18.5 | 32.1 | ASTM D412 |
| Tear Resistance (kN/m) | 28.3 | 54.7 | ASTM D624 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 420 | 290 | ASTM D412 |
| Heat Aging Loss (70h/150°C) | 45% | 18% | ISO 188 |
| Abrasion Volume Loss (mm³) | 185 | 62 | DIN 53516 |
This systematic approach transforms Kevlar’s theoretical advantages into field-proven reliability, reducing client downtime by up to 37% in conveyor belt and hydraulic seal applications. Suzhou Baoshida delivers not just components, but engineered resilience.
Contact Engineering Team

For industrial manufacturers seeking high-performance reinforcement materials, aramid Kevlar fiber stands as a benchmark in tensile strength, thermal stability, and cut resistance. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in integrating advanced aramid fiber solutions into industrial rubber systems, delivering enhanced durability and operational efficiency across demanding applications. From hydraulic hoses and conveyor belts to automotive sealing systems and offshore drilling components, our engineered materials meet the rigorous requirements of modern industry.
Our technical team works closely with OEMs and compounders to tailor aramid Kevlar fiber integration strategies that optimize adhesion, dispersion, and mechanical performance within rubber matrices. Whether you are upgrading existing formulations or developing next-generation products, our expertise in fiber-rubber interface chemistry ensures consistent, scalable results. We supply high-purity, surface-treated aramid fibers in various denier counts, cut lengths, and finishes, designed specifically for seamless incorporation into NR, SBR, NBR, EPDM, and specialty elastomer systems.
Below are key technical specifications for our standard aramid Kevlar fiber offerings used in industrial rubber reinforcement:
| Parameter | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Para-aramid (Poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide) |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 3.0 GPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | ≥ 70 GPa |
| Elongation at Break | 3.0–4.0% |
| Thermal Stability (Continuous) | Up to 200°C |
| Decomposition Onset | > 500°C (in inert atmosphere) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.44 g/cm³ |
| Denier Range | 150–3000 denier |
| Cut Length Options | 3 mm, 6 mm, 12 mm |
| Surface Treatment | SBR-latex, resorcinol-formaldehyde, or custom coupling agents |
| Adhesion Promotion | Compatible with dip treatments and bonding systems for rubber |
We understand that performance in dynamic environments—such as high-pressure fluid conveyance, abrasive wear zones, or extreme thermal cycling—demands more than just material substitution. It requires a systems-level approach. Suzhou Baoshida provides full technical documentation, batch traceability, and application support to ensure compliance with ISO, ASTM, and OEM-specific standards.
To discuss your aramid Kevlar fiber requirements or request sample materials for evaluation, contact Mr. Boyce directly. As Rubber Formula Engineer and OEM Manager, Mr. Boyce leads material development and client integration projects with a focus on precision engineering and supply chain reliability. Reach out via email at [email protected] to initiate technical consultation, request product data sheets, or schedule a formulation review. Our team responds to all inquiries within 24 business hours and supports global logistics with DDP terms available upon request. Partner with Suzhou Baoshida for certified, consistent, and application-optimized aramid fiber solutions engineered for industrial rubber excellence.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
