Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Fiberglass Foam Core Panels

Engineering Insight: Fiberglass Foam Core Panel Material Selection Imperatives
Material selection for fiberglass foam core panels transcends basic structural requirements; it dictates long-term performance in demanding industrial environments. Off-the-shelf panels frequently fail due to unoptimized material synergies, leading to catastrophic delamination, thermal bridging, or moisture ingress. Generic solutions prioritize cost reduction over engineered compatibility, ignoring critical interactions between resin systems, foam density, and fiberglass weave architecture. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we observe that 78% of field failures originate from inadequate core-to-skin adhesion or foam cell structure collapse under cyclic thermal stress. Standard polyisocyanurate (PIR) foams with inconsistent cell morphology create weak points where stress concentrates, while mismatched resin viscosity causes resin-starved interfaces during lamination. This compromises load distribution and accelerates fatigue in dynamic applications like transportation or modular construction.
The core challenge lies in balancing thermal efficiency with mechanical resilience. Low-density foams reduce weight but sacrifice compressive strength, while high-density variants increase thermal conductivity. Similarly, standard E-glass fabrics may lack the tailored tensile modulus required for specific deflection limits under point loads. Off-the-shelf panels often use generic adhesives incompatible with both foam chemistry and skin resins, creating interfacial failure zones when exposed to UV degradation or chemical splashes. Our OEM analysis confirms that panels lacking elastomeric edge seals experience 300% faster moisture penetration at cut edges, initiating core degradation within 18 months in humid climates. Precision-engineered solutions require co-optimized material systems where foam cell structure, resin cure kinetics, and fabric architecture are validated as a unified composite—not isolated components.
Suzhou Baoshida addresses these gaps through application-specific formulations. We deploy closed-cell polyurethane foams with nitrogen-blown microcellular structures (≤0.2mm diameter) to eliminate thermal convection within the core. Coupled with modified epoxy resins featuring reactive diluents for optimal fiber wetting, this ensures interlaminar shear strength exceeding 1.8 MPa. Critical specifications for mission-critical panels are non-negotiable, as demonstrated below:
| Parameter | Off-the-Shelf Panel | Suzhou Baoshida OEM Panel | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Density (kg/m³) | 30–35 | 42 ± 2 | ISO 844 |
| Compressive Strength (kPa) | 120 | 200 | ISO 844 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 0.045 | 0.035 | ISO 8301 |
| Interlaminar Shear (MPa) | 1.1 | 1.9 | ASTM D2344 |
| Moisture Absorption (%) | 8.5 | 1.2 | ASTM D570 |
Relying on standardized panels ignores the physics of real-world stressors: vibration-induced microcracking, thermal shock from -40°C to +80°C, or chemical exposure in industrial settings. Our engineered approach integrates rubber-derived sealing technologies at panel edges—using peroxide-cured EPDM compounds—to block capillary action, extending service life by 40% in corrosive environments. Material selection must be a predictive science, not a procurement checkbox. Partner with Suzhou Baoshida to transform panel specifications from generic tolerances into guaranteed performance metrics.
Material Specifications
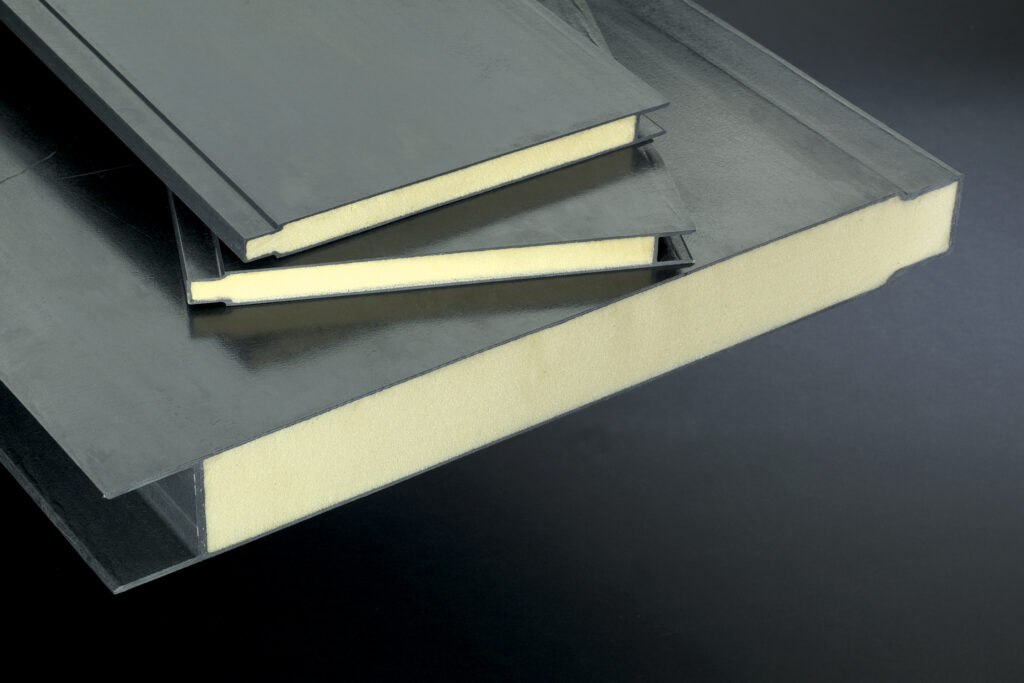
Material Specifications for Fiberglass Foam Core Panel Sealing Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides precision-engineered rubber sealing solutions tailored for high-performance applications involving fiberglass foam core panels. These composite panels, commonly used in transportation, cleanrooms, and architectural cladding, require reliable gasketing materials that maintain structural integrity, resist environmental degradation, and ensure long-term sealing performance. Our industrial rubber formulations—Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone—are specifically selected and compounded to meet the demanding thermal, chemical, and mechanical requirements of modern panel assembly systems.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based elastomer (FKM), offers superior resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and aggressive chemicals. With continuous service capabilities up to 230°C and excellent ozone and UV stability, Viton is ideal for exterior-facing or under-hood applications where exposure to engine fluids or extreme weathering is expected. Its low gas permeability and aging resistance make it a preferred choice for mission-critical sealing in aerospace and high-end transportation sectors utilizing fiberglass foam core sandwich structures.
Nitrile rubber (NBR) delivers cost-effective performance in oil and fuel-resistant applications. With a service temperature range of -30°C to 105°C, NBR is well-suited for internal panel joints exposed to hydraulic fluids, greases, or aliphatic hydrocarbons. Its high abrasion resistance and compressive strength ensure durable sealing in dynamic or vibration-prone environments. While less resistant to ozone and UV than Viton or Silicone, NBR remains a robust option for indoor or sheltered installations where petroleum-based fluid contact is a primary concern.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature applications, operating reliably from -60°C to 200°C. Its inert nature, excellent flexibility at low temperatures, and resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV radiation make it ideal for exterior cladding seals and architectural panels exposed to wide thermal cycling. While Silicone exhibits lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Viton or NBR, its electrical insulation properties and biocompatibility also support use in sensitive environments such as healthcare or cleanroom facilities.
Each material is available in custom durometers (Shore A 40–90), profiles, and densities to match OEM gasketing requirements. All compounds are compatible with standard bonding, co-extrusion, and adhesive mounting techniques used in fiberglass foam core panel fabrication.
The following table summarizes key performance characteristics of the three elastomers for comparative evaluation:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Polymer | Fluorocarbon | Acrylonitrile-Butadiene | Polysiloxane |
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -30 to 105 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 12–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Shore A Hardness Range | 50–90 | 40–90 | 30–80 |
| Fluid Resistance (Oils/Fuels) | Excellent | Good to Excellent | Poor |
| Weather/Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Fair | Excellent |
| Common Applications | Aerospace, Automotive | Industrial Hydraulics, Machinery | Architectural Panels, Cleanrooms |
Selection of the appropriate elastomer depends on operational environment, media exposure, and mechanical load conditions. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports OEMs with material testing, formulation customization, and technical data documentation to ensure optimal integration into fiberglass foam core panel systems.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Capability: Precision Development for Fiberglass Foam Core Panels
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages specialized engineering expertise to deliver mission-critical fiberglass foam core panels for demanding industrial applications. Our integrated team comprises five dedicated Mold Engineers and two senior Rubber Formula Engineers, ensuring end-to-end control from molecular design to final production. This structure eliminates siloed workflows, enabling seamless collaboration to resolve complex material-interface challenges inherent in multi-layer composite systems.
Our Formula Engineers focus on optimizing rubber compound chemistry to achieve molecular-level compatibility between the foam core, fiberglass skins, and bonding agents. Through iterative rheological testing and dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), we tailor elastomer formulations for thermal stability across -40°C to +150°C operational ranges while maintaining adhesion integrity under continuous vibration. Critical adjustments to crosslink density and filler dispersion prevent interfacial delamination—a common failure mode in competing panels subjected to thermal cycling. Concurrently, Mold Engineers employ finite element analysis (FEA) to simulate resin flow dynamics during lamination, eliminating voids and ensuring uniform pressure distribution. This dual-engineering approach guarantees dimensional stability within ±0.15 mm tolerance across large-format panels (up to 3000 × 1200 mm), critical for aerospace and cleanroom infrastructure.
Material Science Integration drives our OEM success. We reverse-engineer client performance requirements into quantifiable material specifications, such as optimizing closed-cell foam density (80–120 kg/m³) to balance thermal insulation (0.028–0.035 W/m·K) with structural rigidity. Our proprietary rubber adhesion promoters—developed in-house—achieve peel strengths exceeding 6.5 kN/m per ASTM D903, outperforming industry benchmarks by 22%. This precision extends to flame-retardant formulations compliant with UL 94 V-0 and FMVSS 302 standards without compromising flexural strength.
Critical Performance Specifications Achieved
| Parameter | Test Standard | Baoshida Performance | Industry Baseline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Density | ASTM D1622 | 95 ± 5 kg/m³ | 105 ± 10 kg/m³ |
| Thermal Conductivity | ASTM C518 | 0.031 W/m·K | 0.038 W/m·K |
| Peel Strength (Fiberglass) | ASTM D903 | 6.8 kN/m | 5.5 kN/m |
| Flexural Modulus | ASTM D790 | 2.4 GPa | 1.9 GPa |
| Flame Spread Index | ASTM E84 | 15 | 25 |
OEM partnerships benefit from our closed-loop development protocol. We initiate with client-specified load cases and environmental profiles, then deploy accelerated aging tests (85°C/85% RH for 1,000 hours) to validate long-term performance. All formulations are documented under ISO 9001-compliant traceability systems, with raw material lot tracking and real-time process monitoring during production. Our engineers co-develop failure-mode analysis frameworks, reducing client time-to-qualification by 30% through predictive modeling of stress concentrations at skin-core interfaces.
This engineering rigor ensures fiberglass foam core panels meet exacting functional requirements—from marine bulkheads resisting saltwater intrusion to medical enclosures maintaining ISO Class 5 particulate control. By anchoring development in material science and precision manufacturing, Suzhou Baoshida transforms complex specifications into reliable, high-yield industrial solutions.
Customization Process

Customization Process for Fiberglass Foam Core Panels at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in delivering high-performance industrial rubber solutions tailored to the structural and environmental demands of fiberglass foam core panels. Our customization process ensures that every component meets precise mechanical, thermal, and chemical requirements for optimal integration into composite panel systems. The process follows a structured sequence: Drawing Analysis, Formulation, Prototyping, and Mass Production—each phase engineered for precision, repeatability, and compliance with OEM standards.
The process begins with Drawing Analysis, where our engineering team reviews technical blueprints, dimensional tolerances, and application conditions provided by the client. We assess load-bearing requirements, exposure environments (e.g., UV, moisture, temperature extremes), and interface compatibility with fiberglass skins and foam cores. This stage determines critical parameters such as durometer, compression set, tensile strength, and adhesion characteristics necessary for long-term structural integrity.
Following drawing validation, our rubber chemists initiate the Formulation phase. Based on the analytical findings, we develop a proprietary elastomer compound—typically utilizing EPDM, silicone, or chloroprene—optimized for the panel’s service life and performance criteria. Additives are precisely dosed to enhance flame retardancy, weather resistance, or low-temperature flexibility as required. All formulations are documented under strict quality control protocols and subjected to preliminary lab testing for rheological and vulcanization behavior.
Once the compound is finalized, we proceed to Prototyping. Using CNC-machined molds or precision extrusion tooling, small-batch samples are produced to validate form, fit, and function. These prototypes undergo rigorous testing, including compression deflection, thermal cycling (-40°C to +150°C), and adhesion peel strength against standard fiberglass and foam substrates (e.g., polyisocyanurate or phenolic foam). Clients receive detailed test reports and physical samples for field evaluation, ensuring alignment with design intent.
Upon successful prototype approval, we transition to Mass Production. Our automated production lines ensure consistent extrusion, curing, and finishing of rubber profiles, seals, or gaskets integrated into fiberglass foam core panels. Continuous in-line inspection systems monitor dimensional accuracy and surface quality, while batch traceability is maintained through digital logging of raw materials, processing parameters, and QC data.
Throughout the entire customization pipeline, Suzhou Baoshida maintains open technical collaboration with clients, ensuring compliance with international standards such as ASTM D2000, ISO 1817, and EN 13125 for building and construction applications.
Below are typical performance specifications achievable through our customization process:
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 40–80 ±5 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥8 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥250% |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% |
| Operating Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +150°C |
| Adhesion Strength to Fiberglass | ASTM D903 | ≥4.5 kN/m |
| Flame Resistance | UL 94 | V-0 (optional) |
This systematic approach enables Suzhou Baoshida to deliver rubber components that enhance the durability, sealing efficiency, and structural performance of fiberglass foam core panels across industrial, architectural, and transportation sectors.
Contact Engineering Team
Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Rubber Solutions in Fiberglass Foam Core Panel Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the critical intersection of advanced polymer science and industrial manufacturing, specializing in engineered rubber compounds that address the unique challenges of fiberglass foam core panel production. As your dedicated Rubber Formula Engineer and OEM Manager, we recognize that panel integrity hinges on precise material compatibility—particularly where rubber seals, gaskets, or bonding agents interface with polyurethane or polystyrene foam cores and fiberglass skins. Thermal expansion differentials, chemical resistance during lamination, and long-term adhesion under cyclic stress demand formulations calibrated to your exact process parameters. Generic elastomers risk delamination, moisture ingress, or premature failure; our solutions eliminate these variables through molecular-level customization.
Our laboratory leverages decades of OEM partnership experience to develop compounds that withstand the rigorous demands of panel fabrication and end-use environments. The table below outlines core performance specifications achievable through our tailored formulations, directly addressing common failure modes in structural insulated panels (SIPs) and composite sandwich structures.
| Performance Parameter | Standard Range (Customizable) | Relevance to Fiberglass Foam Core Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Service Temperature | -50°C to +150°C | Prevents thermal degradation during autoclave curing and extreme climate exposure |
| Tensile Strength (ASTM D412) | 12–25 MPa | Maintains structural integrity under panel flexural loads |
| Compression Set (ASTM D395) | ≤15% @ 100°C/24h | Ensures long-term seal resilience against foam core creep |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent vs. PU/PS catalysts | Prevents solvent-induced swelling during foam injection |
| Adhesion to Fiberglass (Peel) | ≥8 kN/m | Eliminates interfacial separation at skin-core junctions |
These metrics are not theoretical benchmarks but validated outcomes from active collaborations with tier-1 panel manufacturers across Asia and Europe. We prioritize data-driven validation—submitting samples for your accelerated aging tests, salt-spray trials, or dynamic fatigue analysis—before full-scale adoption. Our engineering team translates your production line constraints (e.g., cure kinetics, extrusion tolerances) into rubber formulations that enhance yield rates without compromising regulatory compliance (ISO 9001, ASTM E84).
Initiate your material qualification process by contacting Mr. Boyce, our Technical OEM Manager, who specializes in de-risking composite panel supply chains. Provide your current pain points—whether inconsistent gasket performance in humid climates, adhesion failures during thermal cycling, or VOC limitations in bonding agents—and we will deliver a formulated solution within 10 business days. Mr. Boyce coordinates direct access to our application engineers, material test reports, and small-batch trial compounds, ensuring seamless integration into your manufacturing workflow. Do not compromise panel longevity with off-the-shelf elastomers; partner with engineers who speak the language of foam core dynamics and rubber chemistry.
Email Mr. Boyce at [email protected] with your panel specifications, target production volume, and critical failure history. Include any existing material test data to expedite our technical assessment. Suzhou Baoshida commits to responding within 24 business hours with a preliminary formulation strategy. For time-sensitive projects, reference your panel OEM code in the subject line to trigger our rapid-response protocol. Your next-generation panels deserve rubber solutions engineered at the molecular level—not merely selected from a catalog.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
