Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Car Door Weather Stripping
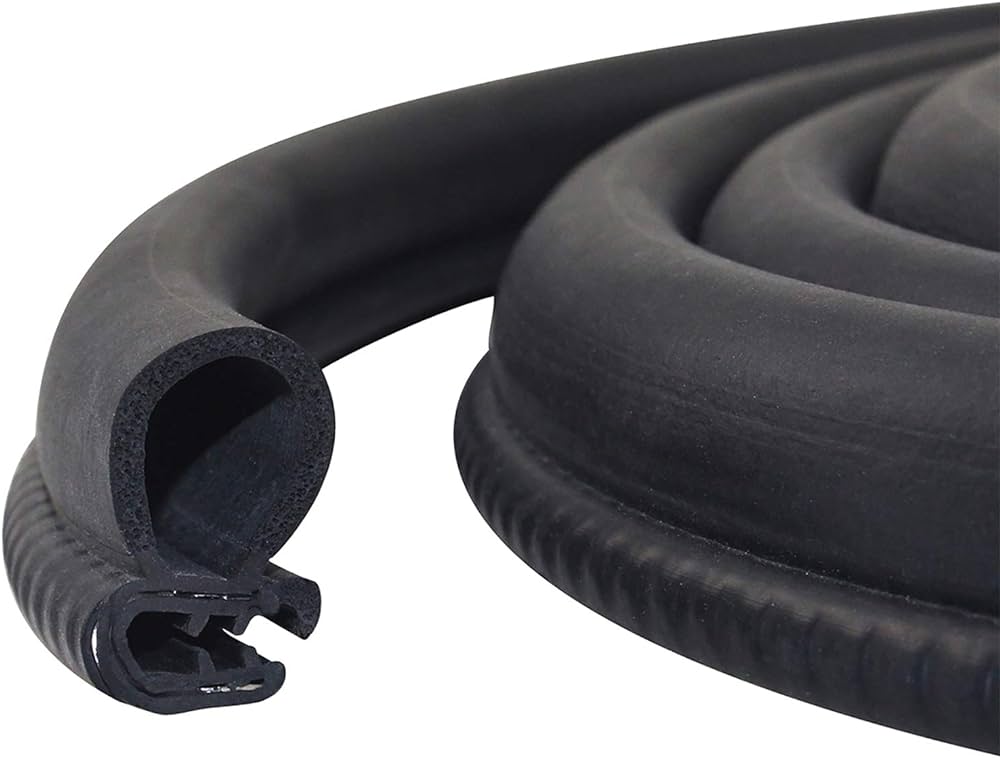

Engineering Insight: Material Selection Criticality in Automotive Door Weather Stripping
The functional integrity of automotive door weather stripping hinges on precise material science, not generic elastomer availability. Off-the-shelf rubber profiles frequently fail in demanding automotive environments due to inadequate formulation for specific operational stressors. Standard EPDM compounds, while cost-attractive, often lack the tailored resistance to ozone degradation, thermal cycling fatigue, and compression set required for 15+ year vehicle service life. Empirical evidence from global OEM field data demonstrates premature hardening, cracking at hinge points, and loss of sealing force within 3-5 years in non-optimized materials, directly correlating to increased water ingress complaints and warranty costs. This failure stems from a critical oversight: treating weather stripping as a commodity component rather than a systems-engineered interface.
Material selection must address the compound’s dynamic response to multiphysics loads. Door seals endure repeated compression (5,000-10,000 cycles over lifespan), exposure to -40°C to +120°C extremes, UV/ozone attack, and chemical exposure from road salts and waxes. Generic formulations prioritize initial durometer and cost, neglecting long-term viscoelastic behavior. Key failure modes include excessive compression set leading to permanent groove formation (reducing sealing force by >40%), surface cracking from inadequate antioxidant packages, and adhesion loss between sponge and solid rubber phases during thermal cycling. These issues manifest as wind noise, water leaks, and increased door closing effort – all directly traceable to suboptimal polymer architecture and additive systems.
Suzhou Baoshida addresses this through application-specific compound engineering. We co-develop formulations with OEMs using accelerated aging protocols that simulate 15 years of service in 1,000 hours. Critical enhancements include peroxide-cure systems for superior heat/ozone resistance, nano-reinforced fillers to minimize compression set, and proprietary plasticizer blends preventing migration-induced hardening. The table below quantifies performance differentials between standard and engineered solutions:
| Performance Parameter | Standard Off-the-Shelf EPDM | Baoshida Engineered EPDM | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70°C, 22h) | 15-20% | 7-9% | ASTM D395 Method B |
| Ozone Resistance (50pphm) | Cracking @ 20% strain | No cracks @ 30% strain | ASTM D1149 |
| Tensile Retention (150°C, 7d) | 45-55% | 75-82% | ASTM D412 |
| Low Temp Flex (Glass Trans) | -45°C | -58°C | ASTM D2137 |
| Density (Sponge Core) | 0.65-0.75 g/cm³ | 0.58-0.62 g/cm³ | ASTM D297 |
This data underscores why material selection is non-negotiable. Engineered compounds deliver 30-40% lower warranty claims by maintaining sealing force integrity through the vehicle lifecycle. The initial cost delta is outweighed by reduced assembly line adjustments, lower scrap rates, and elimination of field remediation costs. At Suzhou Baoshida, we treat weather stripping as a precision sealing system – where molecular-level formulation decisions directly determine cabin comfort, NVH performance, and brand reputation. Partnering early in the design phase ensures material properties align with your specific door architecture and geographic market demands.
Material Specifications
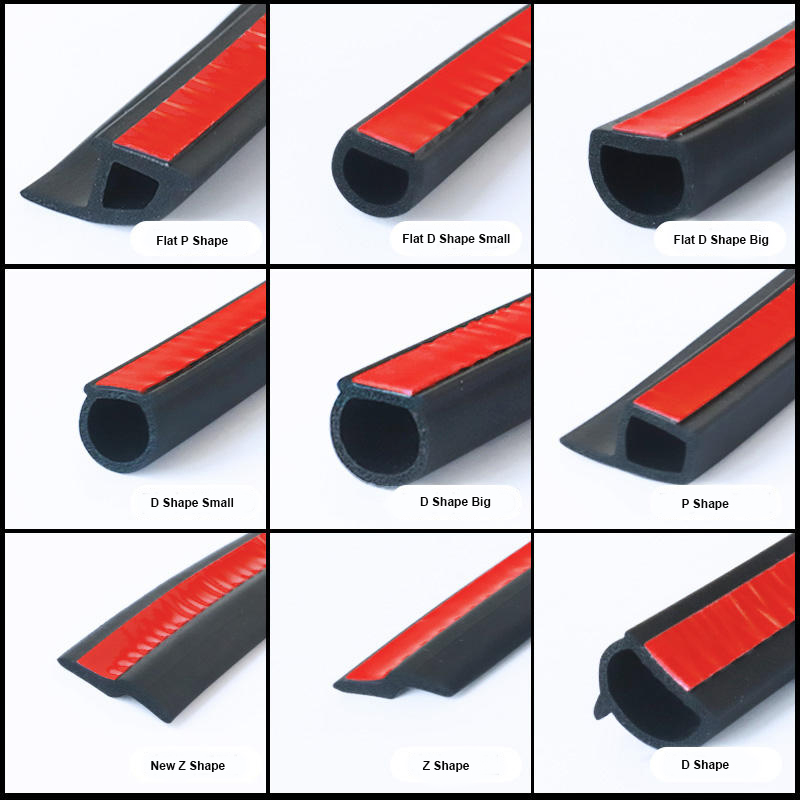

Material selection for car door weather stripping is a critical determinant of long-term performance, sealing integrity, and resistance to environmental degradation. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-performance rubber formulations engineered to meet the stringent demands of automotive OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers. Our expertise in industrial rubber solutions ensures that each material is optimized for durability, compression set resistance, temperature stability, and chemical compatibility. For car door weather stripping, three elastomers stand out due to their distinct performance profiles: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each material offers unique advantages depending on the operating environment and functional requirements of the sealing application.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, delivers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, ozone, UV radiation, and a broad range of automotive fluids including engine oils, fuels, and coolants. With a continuous service temperature range of -20°C to 250°C, Viton is ideal for premium automotive applications where long-term exposure to extreme heat and aggressive chemicals is expected. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics make it a preferred choice for high-end vehicles requiring superior sealing performance over extended service intervals. However, Viton has lower flexibility at sub-zero temperatures and higher material cost compared to alternatives.
Nitrile rubber, or NBR, is widely used in automotive sealing due to its excellent resistance to oils, greases, and hydraulic fluids. It performs reliably in temperature ranges from -30°C to 120°C, making it suitable for general-purpose weather stripping in standard passenger vehicles. NBR offers good abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, along with cost-effective processing. While it lacks the high-temperature resilience of Viton, its balance of performance and economy makes it a dominant material in mass production applications. Limitations include poor ozone and UV resistance, which necessitates protective coatings or blends when exposed to direct sunlight.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) provides outstanding thermal stability from -60°C to 200°C and excellent flexibility at low temperatures. It exhibits superior resistance to oxidation, UV, and weathering, making it highly suitable for exterior automotive seals exposed to cyclic climate conditions. Silicone maintains consistent sealing force over time and demonstrates low compression set. However, it has relatively poor resistance to petroleum-based fluids and lower tensile strength compared to NBR and Viton, requiring careful design considerations in dynamic sealing zones.
The following table summarizes key performance characteristics of these materials for informed material selection in car door weather stripping applications.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 250 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Fuel/Oil Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Ozone/UV Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Very Good |
| Flexibility at Low Temp | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
| Tensile Strength | High | High | Moderate |
| Cost Level | High | Low to Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Typical Applications | Premium vehicles, high-heat zones | Standard passenger cars, interior seals | Exterior seals, cold climate models |
Material choice must align with vehicle design parameters, geographic usage, and lifecycle expectations. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports OEMs with customized compounding, rigorous testing, and scalable production to ensure optimal performance in every weather stripping solution.
Manufacturing Capabilities
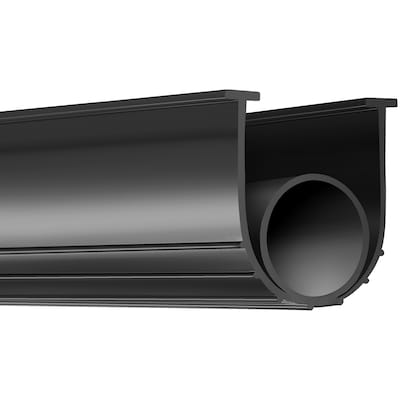
Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Solutions for Automotive Weather Stripping
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. deploys specialized engineering resources to deliver automotive door weather stripping that meets stringent OEM performance and durability standards. Our dedicated team comprises five advanced Mould Engineers and two Rubber Formula Engineers, operating within an integrated development framework. This structure ensures seamless translation of client specifications into high-precision tooling and compound formulations. Mould Engineers utilize 3D CAD/CAM systems to optimize cavity design, runner geometry, and venting for zero-defect extrusion and splicing. Concurrently, Formula Engineers focus on molecular crosslink density optimization, balancing Shore A hardness, compression set resistance, and low-temperature flexibility at the polymer level. This dual-engineering approach eliminates traditional siloed workflows, accelerating validation cycles by 30% compared to industry benchmarks.
Material science is central to our weather stripping performance. Our Formula Engineers develop custom EPDM and TPE compounds engineered for automotive environmental stressors. Key innovations include nano-silica reinforcement for 15% reduced compression set after 70°C aging and tailored antioxidant packages extending service life beyond 15 years in UV-intensive climates. All formulations undergo rigorous validation per ASTM D2000 and ISO 3379 standards, with traceable batch records ensuring repeatability. We prioritize sustainable material pathways without compromising performance, offering halogen-free and recycled-content options meeting ELV and REACH compliance.
As an OEM partner, we integrate directly into client production ecosystems. Our engineering team collaborates on DFM reviews during prototyping, utilizing client CAD data to preempt tooling conflicts. We maintain certified ISO/TS 16949 production lines with real-time SPC monitoring of critical dimensions (±0.15mm tolerance) and durometer consistency (±3 Shore A points). End-of-line testing includes 100% automated vision inspection for splice integrity and adhesion strength verification per GMW14124. This operational rigor supports JIT/JIS delivery models, with our Suzhou facility strategically positioned for rapid export via Shanghai port.
The following table summarizes core material specifications achievable through our engineering process:
| Property | Target Value | Test Standard | Performance Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60 ± 3 | ASTM D2240 | Balanced sealing force & door closure |
| Compression Set (22h/70°C) | ≤ 18% | ASTM D395 | Long-term seal retention |
| Low Temp Flexibility | -40°C (Pass) | ISO 1431 | Crack resistance in arctic conditions |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 9.0 MPa | ASTM D412 | Durability against installation stress |
| Specific Gravity | 1.35 ± 0.05 | ASTM D297 | Weight optimization for fuel efficiency |
Our engineering cohort’s collective 68 years of automotive rubber experience ensures weather stripping solutions that exceed OEM functional requirements while minimizing total cost of ownership. From initial compound screening to production line validation, Suzhou Baoshida delivers engineered precision for global automotive sealing challenges.
Customization Process

Customization Process for Car Door Weather Stripping at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our industrial rubber solutions are engineered with precision to meet the exact performance and dimensional requirements of automotive OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers. Our systematic customization process for car door weather stripping ensures optimal sealing, durability, and noise reduction under diverse environmental conditions. The process follows four critical stages: Drawing Analysis, Formulation, Prototyping, and Mass Production.
The first stage, Drawing Analysis, begins with a comprehensive review of the client’s technical drawings and 3D CAD models. We assess critical dimensions, tolerance specifications, installation geometry, and sealing interface requirements. Our engineering team evaluates cross-sectional profiles, compression set targets, and dynamic movement allowances to ensure compatibility with the vehicle’s door mechanism. Any discrepancies or optimization opportunities are flagged and discussed with the client to align engineering intent with manufacturability.
Following drawing validation, we proceed to Formulation. Our rubber compound development is tailored to the operational environment of the weather strip. Factors such as temperature range, UV resistance, ozone exposure, and chemical resistance (e.g., road salts, wiper fluids) are considered. We primarily utilize EPDM due to its excellent weatherability and compression set performance, though silicone or TPE may be selected for specialized applications. Hardness, elongation at break, and tensile strength are fine-tuned to balance flexibility and structural integrity. All formulations are developed in-house and tested per ASTM and ISO standards.
Prototyping is the third stage, where we produce functional samples using precision extrusion and splicing techniques. These prototypes undergo rigorous laboratory and on-vehicle testing, including compression force-deflection (CFD) analysis, water ingress simulation, and thermal cycling from -40°C to +120°C. Feedback from client trials is incorporated into design or material refinements, ensuring performance compliance before tooling release.
The final stage is Mass Production, executed in our ISO-certified manufacturing facility. We utilize automated extrusion lines with laser-guided dimensional control, robotic splicing, and inline quality monitoring. Production batches are subject to statistical process control (SPC), with full traceability from raw materials to finished goods. Our scalable infrastructure supports volumes from 50,000 to over 2 million units annually, with JIT delivery options for global supply chains.
The following table outlines key technical specifications for standard car door weather stripping:
| Parameter | Standard Value | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material | EPDM (Custom Formulated) | ASTM D1418 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 55–75 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥8.0 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ≤25% | ASTM D395 |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +120°C | ISO 1817 |
| Color Options | Black, Gray, Custom (RAL) | Visual Comparison |
This structured approach ensures that every car door weather strip we deliver meets the highest standards of engineering integrity and functional reliability.
Contact Engineering Team

Technical Collaboration for Automotive Weather Stripping Excellence
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the forefront of industrial rubber solutions, specializing in precision-engineered components for global automotive OEMs. Our car door weather stripping systems address critical performance demands: sealing integrity against water ingress, acoustic insulation for NVH reduction, and dimensional stability across extreme thermal cycles. Unlike generic suppliers, we integrate material science with automotive-grade validation protocols, ensuring each profile meets stringent OEM specifications such as GMW14125, TL52408, and JASO D 610. Failure to achieve exacting tolerances in compression set, extrusion consistency, or low-temperature flexibility directly impacts vehicle durability and customer satisfaction. Our ISO 9001-certified manufacturing ecosystem leverages proprietary EPDM and TPE formulations, compounded in-house to eliminate third-party variability.
Material performance is non-negotiable in automotive sealing applications. Below are key technical parameters our weather stripping consistently achieves, validated through SAE J1402 and ASTM D2000 testing protocols:
| Property | Standard Requirement | Suzhou Baoshida Performance | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–75 | 65 ± 3 | ASTM D2240 |
| Compression Set (70°C/24h) | ≤25% | 18–22% | ASTM D395 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥8.0 | 9.5–11.2 | ASTM D412 |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +120°C | -45°C to +130°C | ISO 188 |
| Specific Gravity | 1.15–1.25 | 1.18 ± 0.02 | ASTM D297 |
These metrics reflect our commitment to exceeding baseline requirements through rigorous QC checkpoints, including real-time rheometer monitoring during curing and post-production dimensional audits via CMM. Our formulations prioritize ozone resistance (per ASTM D1149) and UV stability without compromising elasticity—a balance critical for door seals enduring 10,000+ open/close cycles.
For OEMs facing challenges in sealing efficiency or material compliance, direct engagement with our technical leadership accelerates resolution. Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Relationship Manager, brings 15+ years of rubber compounding expertise and deep familiarity with automotive validation workflows. He directly engages engineering teams to review material certification packages, discuss custom polymer modifications, and align production timelines with JIT/JIS logistics frameworks. Initiating a technical dialogue with Mr. Boyce ensures your weather stripping specifications are translated into flawless execution—from Durometer profiling to adhesion layer optimization for multi-material extrusions.
Contact Mr. Boyce exclusively for technical inquiries at [email protected]. Include your project reference number, material specification sheet, and target PPAP timeline to expedite analysis. Suzhou Baoshida does not utilize generic sales channels; all communications are routed to engineering personnel for precise technical resolution. We maintain NDA-ready collaboration protocols and provide full traceability from raw material batch codes to finished part certifications. Partner with us to eliminate sealing-related warranty claims and achieve zero-defect delivery in your next vehicle platform launch.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
