Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Rubber Sleeve For Pvc Pipe
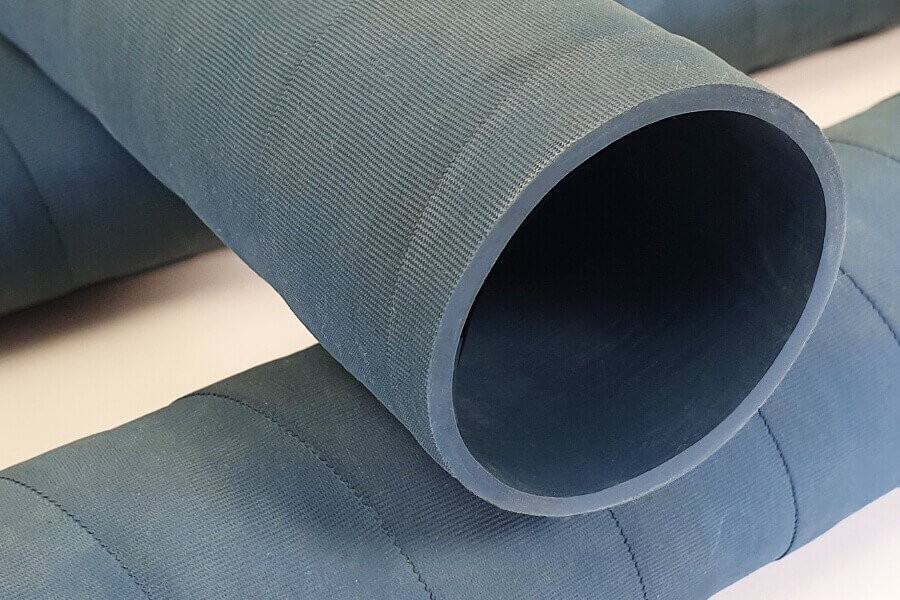

Engineering Insight: Material Selection for PVC Pipe Rubber Sleeves
The integrity of rubber sleeves in PVC piping systems hinges critically on precise material formulation. Generic off-the-shelf sleeves frequently fail in these applications due to fundamental incompatibilities with PVC pipe chemistry and operational demands. PVC formulations contain plasticizers, heat stabilizers, and processing aids that migrate into adjacent rubber components over time. Standard elastomers like conventional EPDM or SBR lack sufficient resistance to these migrating compounds, leading to accelerated degradation. This manifests as excessive swelling, loss of tensile strength, surface cracking, and ultimately, seal failure. Such failures result in costly leaks, system downtime, and potential contamination – risks unacceptable in industrial fluid handling.
Material failure mechanisms are rooted in polymer science. PVC plasticizers, particularly phthalates, readily diffuse into unsaturated rubber matrices, causing volumetric swelling that compromises dimensional stability and clamping force. Simultaneously, PVC heat stabilizers like lead or calcium-zinc compounds can catalyze oxidative degradation in susceptible rubbers at elevated service temperatures. Furthermore, the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) mismatch between standard rubber sleeves and rigid PVC pipes creates cyclic stress during temperature fluctuations. Generic sleeves often exhibit CTE values significantly higher than PVC (70-80 x 10⁻⁶/°C), leading to gap formation at the interface under thermal cycling. This gap permits fluid ingress behind the sleeve, accelerating adhesive failure and corrosion under insulation (CUI) in buried or insulated lines.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. addresses these challenges through engineered compound development. Our proprietary rubber sleeves utilize selectively hydrogenated nitrile (HNBR) or specialty EPDM formulations with saturated backbones. These polymers inherently resist plasticizer extraction and oxidative attack from PVC additives. Critical modifications include optimized filler systems for dimensional stability, tailored cure packages for high-temperature resilience, and adhesion promoters specifically designed for PVC substrates. This molecular-level engineering ensures minimal swell (<8% in ASTM #3 oil simulating PVC plasticizers), maintains tensile strength retention above 85% after 1000 hours at 125°C, and achieves CTE values closely aligned with PVC (75-85 x 10⁻⁶/°C). The result is a durable, zero-leakage seal under real-world thermal and chemical stresses.
The following table contrasts critical performance parameters between generic solutions and Baoshida-engineered sleeves:
| Property | Generic EPDM Sleeve | Baoshida Engineered HNBR Sleeve | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasticizer Resistance | Poor (Swelling >25%) | Excellent (Swelling <8%) | Prevents dimensional loss, seal failure |
| Tensile Retention (125°C) | <60% after 500 hrs | >85% after 1000 hrs | Ensures long-term mechanical integrity |
| CTE vs PVC Compatibility | High Mismatch (Δ >25) | Close Match (Δ <10) | Eliminates thermal cycling gaps |
| Adhesion to PVC | Variable, often requires primer | Direct bond, no primer needed | Reduces installation complexity, cost |
Material selection is not a cost-saving opportunity but a critical risk mitigation strategy. Off-the-shelf sleeves represent a false economy, inevitably transferring higher lifecycle costs through premature failure. Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM-focused engineering delivers sleeves where polymer chemistry is precisely aligned with PVC pipe behavior, guaranteeing system reliability and protecting our partners’ operational continuity and reputation.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Rubber Sleeves in PVC Pipe Applications
The selection of appropriate elastomeric materials for rubber sleeves used in conjunction with PVC piping systems is critical to ensuring long-term performance, chemical resistance, and mechanical integrity under operational stress. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in engineered rubber solutions tailored for industrial sealing, coupling, and protective applications. For rubber sleeves interfacing with PVC pipes, three primary elastomers are recommended based on service conditions: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each material offers distinct advantages in temperature range, chemical compatibility, and physical durability.
Viton exhibits superior resistance to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals, including hydrocarbons, acids, and ozone. This fluoroelastomer is ideal for industrial environments where exposure to oils, fuels, or chlorinated solvents is expected. With a continuous service temperature range up to 230°C, Viton provides exceptional stability in extreme conditions. However, its higher cost and limited flexibility at low temperatures make it less suitable for general-purpose or cold-environment applications.
Nitrile rubber, a copolymer of butadiene and acrylonitrile, is widely used for its excellent resistance to oils, greases, and aliphatic hydrocarbons. It offers good tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it a cost-effective solution for mechanical sealing in moderate temperature ranges. NBR performs reliably between -30°C and 100°C, with performance dependent on acrylonitrile content. While not recommended for exposure to aromatic solvents or strong oxidizing agents, Nitrile remains a preferred choice for hydraulic and pneumatic systems connected to PVC piping in manufacturing and processing plants.
Silicone rubber provides outstanding thermal stability across a broad temperature spectrum, from -60°C to 200°C, and exceptional flexibility at low temperatures. It demonstrates good resistance to ozone and UV radiation, making it suitable for outdoor installations. However, silicone has lower mechanical strength and poor resistance to hydrocarbon fluids. Its primary advantage lies in applications requiring high purity, such as food processing or pharmaceutical systems, where non-toxic, odorless materials are mandated.
Selection of the correct elastomer must consider fluid compatibility, operating temperature, mechanical stress, and regulatory requirements. Below is a comparative overview of key physical and chemical properties.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -30 to 100 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–300 | 200–500 | 200–700 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Good to Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Acids | Excellent | Fair | Fair |
| Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Fair to Good |
| Cost Level | High | Low to Medium | Medium |
Material selection directly impacts system reliability and lifecycle cost. Engineers should evaluate specific application parameters before finalizing elastomer choice. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides technical support and customized formulation services to meet exacting industrial demands.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Sleeve Development for PVC Pipe Systems
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep technical expertise in rubber formulation and mold engineering to deliver mission-critical sleeves for PVC pipe applications. Our dedicated cohort of five mold engineers and two rubber formula specialists operates at the intersection of material science and precision manufacturing. This structure ensures end-to-end control over product performance, from molecular-level compound design to final dimensional accuracy. Formula engineers optimize elastomer blends for specific operational demands, including resistance to UV degradation, ozone exposure, and chemical permeation common in municipal water and industrial fluid transfer systems. Concurrently, mold engineers utilize advanced CAD/CAM simulation tools to eliminate flow inconsistencies and minimize post-cure shrinkage, guaranteeing seamless integration with PVC pipe geometries.
Our formula development process adheres to rigorous ASTM D2000 and ISO 37 standards, with iterative validation through accelerated aging protocols and dynamic mechanical analysis. Each compound is tailored to balance Shore A hardness, tensile strength, and compression set—critical factors for maintaining seal integrity under cyclic pressure loads. For PVC pipe sleeves, we prioritize low-temperature flexibility to prevent cracking during installation in sub-zero environments and enhanced resistance to plasticizer migration from PVC substrates. This prevents premature hardening and joint failure. Mold engineering rigor extends to thermal management systems within tooling, ensuring uniform vulcanization and eliminating flash that could compromise sleeve insertion tolerances.
OEM collaboration forms a cornerstone of our operational model. We support clients through joint design reviews, providing finite element analysis (FEA) reports for stress distribution validation under operational conditions. Our facility accommodates rapid prototyping with 3D-printed mold inserts, reducing time-to-trial by 40% versus conventional methods. All production runs undergo first-article inspection per AS9102 standards, with traceability to raw material batch records. Clients benefit from scalable capacity—our presses handle volumes from 500 to 500,000 units monthly without retooling delays—while maintaining ±0.15 mm dimensional repeatability.
The following table summarizes key performance specifications for our standard EPDM-based PVC pipe sleeves, engineered for 25-year service life in potable water applications:
| Property | Test Standard | Value | Significance for PVC Pipe Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 65 ± 5 | Optimized grip without PVC deformation during insertion |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥14 MPa | Resists pull-out forces in pressurized joints |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥350% | Accommodates pipe expansion/contraction cycles |
| Compression Set (70°C/22h) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% | Ensures long-term sealing force retention |
| Water Absorption (7d) | ISO 188 | ≤1.2% | Prevents swelling-induced joint leakage |
Suzhou Baoshida’s integrated engineering framework eliminates siloed development risks. Formula adjustments are instantly validated against mold flow simulations, ensuring manufacturability without performance trade-offs. This synergy enables us to resolve complex client challenges—such as sleeves for chemically aggressive effluent lines—within 8–12 weeks from specification to validated production. Our ISO 9001-certified processes guarantee that every rubber sleeve meets the exacting demands of modern PVC piping infrastructure, where failure is not an option.
Customization Process

Customization Process for Rubber Sleeves in PVC Pipe Applications
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team follows a rigorous, science-driven customization process to deliver high-performance rubber sleeves for PVC pipe systems. These components are critical in industrial, municipal, and construction applications where sealing integrity, chemical resistance, and mechanical stability under variable pressure and temperature are essential. Our four-phase approach—Drawing Analysis, Formulation Development, Prototyping, and Mass Production—ensures dimensional accuracy, material compatibility, and long-term durability.
The process begins with Drawing Analysis, where we evaluate the client’s technical drawings and application parameters. Key factors include inner and outer diameters, wall thickness, axial length, tolerance class (typically ISO 2768-m), and installation method (e.g., slip-on, flanged, or compression fit). We also assess operating conditions such as fluid type (water, wastewater, chemicals), pressure range, ambient and media temperature, and exposure to UV or ozone. This data informs both design validation and material selection.
Next, Formulation Development is conducted by our rubber chemists. Based on the environmental and mechanical requirements, we select the optimal elastomer matrix. Common base polymers include EPDM for hot water and ozone resistance, NBR for oil resistance, and SBR for general-purpose use. The compound is then engineered with reinforcing fillers (e.g., carbon black or silica), vulcanizing agents (sulfur or peroxide systems), plasticizers, and anti-degradants to achieve target hardness (Shore A 50–80), tensile strength (≥10 MPa), elongation at break (≥250%), and compression set (<30% at 70°C for 22h). All formulations comply with ISO 3302-1 and ASTM D2000 standards.
Prototyping follows formulation finalization. Using precision molds and hydraulic curing presses, we produce small-batch samples for dimensional inspection and performance testing. Each prototype undergoes metrological verification via CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine), followed by functional tests including hydrostatic pressure resistance (up to 2.5 MPa), thermal cycling (-30°C to +120°C), and accelerated aging per ASTM D573. Client feedback is incorporated before release to production.
Finally, Mass Production is executed under ISO 9001-certified procedures. We utilize automated mixing lines, CNC mold handling, and inline inspection systems to maintain consistency. Every batch is traceable, with full material certificates (MTRs) and third-party test reports available upon request.
| Parameter | Standard Range | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 50–80 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥10 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set | <30% (70°C, 22h) | ASTM D395 |
| Operating Temperature | -30°C to +120°C | ISO 1817 |
| Fluid Resistance | Water, wastewater, mild acids | ASTM D471 |
This structured workflow ensures that every rubber sleeve meets the exact performance demands of PVC pipe integration, providing reliable, long-term sealing in dynamic industrial environments.
Contact Engineering Team
Precision Rubber Sleeve Integration for PVC Piping Systems: Engineering Partnership Pathway
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers mission-critical rubber sleeve solutions engineered specifically for PVC pipe infrastructure. Our sleeves address the unique challenges of PVC systems—including thermal expansion compensation, vibration dampening, and misalignment tolerance—where standard elastomer components often fail under cyclic stress or chemical exposure. As an ISO 9001-certified OEM partner, we prioritize material science rigor over generic manufacturing. Each formulation undergoes ASTM D2000 classification validation and ISO 3601 flange compatibility testing to ensure leak-free performance in potable water, chemical transfer, and HVAC applications. The consequences of substandard sleeves—premature extrusion, compression set, or chemical degradation—compromise system integrity and escalate lifecycle costs. Our engineered approach eliminates these risks through polymer matrix optimization and dimensional precision.
Our technical differentiators stem from proprietary compounding protocols. Unlike commodity suppliers, we tailor durometer, elongation, and fluid resistance to your PVC pipe’s operational parameters. The table below summarizes core specifications for our standard EPDM and NBR formulations, both validated for NSF/ANSI 61 compliance in water systems:
| Specification Parameter | EPDM Grade RS-PVC70 | NBR Grade RS-PVC80 | Test Standard | Application Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Durometer (Shore A) | 70 ± 5 | 80 ± 5 | ASTM D2240 | Optimized for PVC’s low rigidity; prevents over-compression |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥ 18.0 | ≥ 22.0 | ASTM D412 | Resists pull-out forces in high-vibration environments |
| Fluid Resistance (30d, IRM 903) | Volume swell ≤ 15% | Volume swell ≤ 10% | ASTM D471 | Critical for chlorinated water and mild chemical exposure |
| Temperature Range (°C) | -40 to +135 | -30 to +100 | ISO 188 | Accommodates PVC’s thermal expansion coefficient (6.5×10⁻⁵/°C) |
| Compression Set (70h, 70°C) | ≤ 20% | ≤ 25% | ASTM D395 | Ensures long-term sealing against PVC joint creep |
These metrics reflect our commitment to dimensional stability and chemical resilience—non-negotiable factors when interfacing with PVC’s lower thermal tolerance compared to metal piping. We further customize formulations for aggressive media (e.g., ozone-rich wastewater streams) through peroxide curing systems that eliminate nitrosamine risks inherent in conventional sulfur-cured compounds.
Engaging Suzhou Baoshida as your OEM partner initiates a co-engineering workflow. Our team collaborates directly with your design engineers to validate sleeve performance against your PVC pipe schedule, pressure class, and fluid dynamics. We provide finite element analysis (FEA) reports for deflection limits and accelerated aging data per ISO 11346, ensuring seamless integration without field retrofitting. This proactive technical alignment reduces validation cycles by 40% versus off-the-shelf alternatives.
Initiate your project validation with Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Manager. With 12 years of elastomer application engineering experience, he will review your PVC system schematics, fluid compatibility requirements, and performance thresholds to issue a material specification sheet within 48 hours. Contact Mr. Boyce directly at [email protected] with your project code, pipe dimensions (ASTM D1785 schedule), and operational parameters. Include any existing failure analysis from sleeve-related leaks or joint separations for prioritized technical assessment. Suzhou Baoshida does not operate as a transactional supplier—we function as your embedded rubber science division, transforming PVC piping reliability through polymer precision. All inquiries receive confidential technical review within one business day.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
