Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Automotive Door Weatherstrip
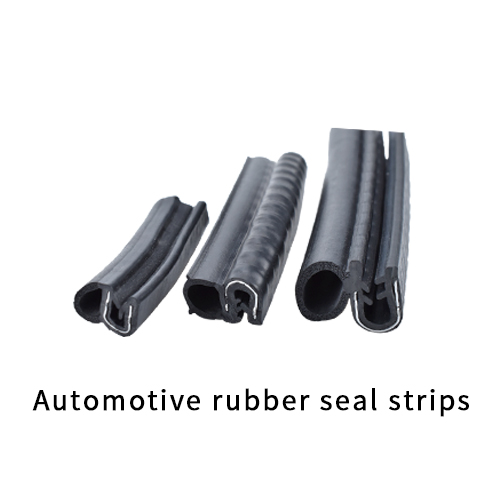

Engineering Insight: Material Selection in Automotive Door Weatherstrip Design
The performance and longevity of an automotive door weatherstrip are fundamentally governed by material selection. While off-the-shelf rubber profiles may appear cost-effective for OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers, they frequently fail to meet the rigorous demands of real-world vehicle environments. These generic solutions often overlook critical variables such as thermal cycling, UV exposure, chemical resistance, and dynamic compression loading—leading to premature degradation, air/water leakage, and customer dissatisfaction.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize engineered material systems tailored to specific vehicle platforms and operating conditions. The failure of standard weatherstrips typically stems from the use of non-optimized elastomers such as low-grade EPDM or recycled rubber compounds. These materials lack the necessary crosslink density, filler dispersion, and polymer architecture to maintain sealing force over 5,000+ door cycles or under extreme temperature swings from -40°C to +120°C.
A high-performance door weatherstrip must balance compression set resistance, tensile strength, and low-temperature flexibility. For example, advanced EPDM formulations with controlled diene content and co-agent crosslinking deliver superior resilience and ozone resistance. In aggressive environments—such as under-hood zones or coastal regions—silicone or thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) may be more suitable due to their enhanced UV and thermal stability.
Another often-overlooked factor is adhesion compatibility with adjacent substrates, including painted steel, galvanized panels, and polymer-based trim. Off-the-shelf strips may delaminate due to poor interfacial bonding, especially when exposed to humidity and thermal expansion differentials. Custom compounding allows integration of functional adhesion promoters and co-extruded bonding layers that ensure structural integrity throughout the vehicle lifecycle.
Furthermore, modern automotive design trends—lightweighting, reduced door gaps, and active noise cancellation—demand tighter tolerances and more consistent durometer control. Standard profiles often exhibit ±10 Shore A variation, whereas precision-engineered compounds maintain ±3 Shore A, ensuring uniform sealing pressure and reduced closure effort.
The following table outlines key material performance metrics for common elastomer systems used in door weatherstrip applications:
| Material | Hardness (Shore A) | Compression Set (22 hrs @ 100°C) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Operating Temp Range (°C) | UV/Ozone Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard EPDM | 60–70 | 35–45% | 8–10 | -40 to +110 | Good |
| High-Performance EPDM | 55–65 | 15–25% | 12–15 | -45 to +120 | Excellent |
| TPV | 50–60 | 20–30% | 10–13 | -40 to +135 | Excellent |
| Silicone | 45–55 | 10–20% | 6–9 | -55 to +200 | Outstanding |
Material selection is not a one-size-fits-all proposition. Each vehicle program requires a systematic evaluation of environmental exposure, assembly tolerances, and service life expectations. At Baoshida, we collaborate with engineering teams to develop application-specific compounds that outperform generic alternatives, ensuring durable, quiet, and leak-free door seals across global markets.
Material Specifications
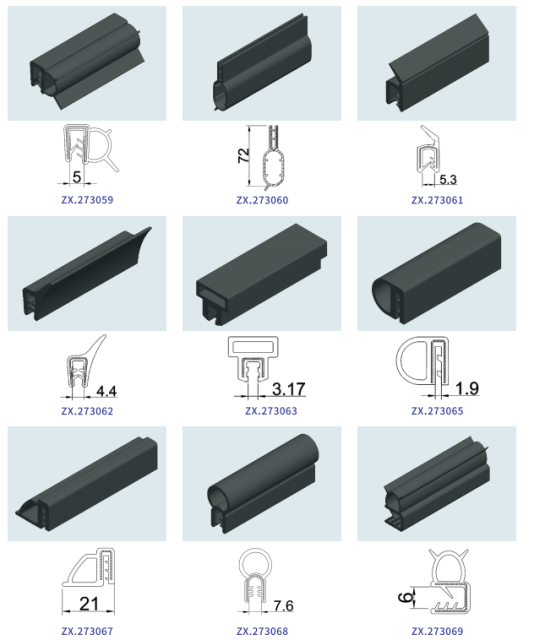

Material Specifications for Automotive Door Weatherstrip
Selecting the optimal elastomer for automotive door weatherstrip requires precise evaluation of thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical performance under dynamic sealing conditions. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we prioritize materials that ensure long-term durability against door flexure, environmental exposure, and repeated compression cycles. Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ) represent industry-standard solutions, each engineered for specific operational demands. Viton excels in extreme temperature and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance vehicles exposed to aggressive fluids like transmission oil or brake fluid. Nitrile offers a cost-effective balance for standard applications, with robust fuel and oil resistance but limited high-temperature tolerance. Silicone provides exceptional flexibility across wide temperature ranges and superior UV/ozone stability, though its lower tensile strength necessitates careful design integration for structural support.
Critical parameters include Shore A hardness (typically 55–75 for door seals to balance sealing force and recovery), tensile strength (≥10 MPa minimum for tear resistance), and compression set (≤30% after 70 hours at 100°C to prevent permanent deformation). Viton achieves superior compression set resistance but requires extended cure times, impacting production throughput. Nitrile cures rapidly, reducing cycle times, yet degrades above 120°C continuous exposure. Silicone maintains resilience from -60°C to 200°C but exhibits higher compression set in dynamic sealing scenarios without reinforced formulations. All materials must comply with ASTM D2000 classification M3BA714 for automotive weatherstripping, specifying critical tolerances for dimensional stability and extrusion consistency.
The comparative analysis below details essential physical properties per ISO 37 and ASTM D2240 standards:
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Shore A Hardness | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Compression Set (%)* | Key Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | -20 to 250 | 60–80 | 12–18 | 150–250 | ≤20 | Exceptional chemical/fuel resistance; low gas permeability | High cost; slow cure kinetics; poor low-temperature flexibility |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -40 to 120 | 55–75 | 10–15 | 200–350 | ≤30 | Fast curing; excellent oil/fuel resistance; cost-efficient | Limited high-temp stability; moderate ozone resistance |
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 to 200 | 50–70 | 6–10 | 250–400 | ≤40 | Superior low/high-temp flexibility; UV/ozone resistance | Lower tensile strength; higher compression set; prone to tear |
*Tested at 100°C for 70 hours per ASTM D395 Method B.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. validates all formulations against OEM-specific durability protocols, including 50,000+ door cycle testing and accelerated aging per SAE J2236. Material selection must align with vehicle architecture—Viton for premium/luxury segments demanding chemical resilience, NBR for economical mass production, and Silicone for electric vehicles requiring extreme thermal cycling stability. Partner with our engineering team to optimize compound specifications for your production line’s cure constraints and performance targets.
Manufacturing Capabilities
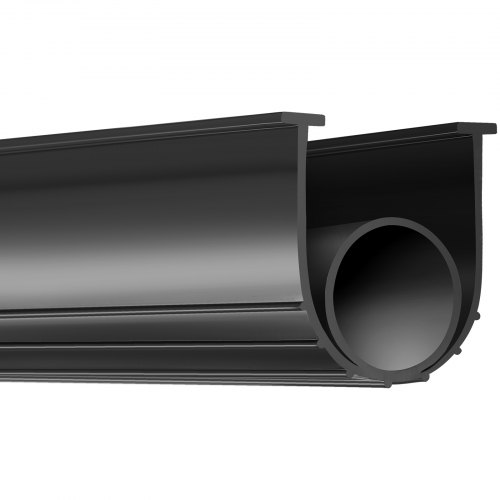
Engineering Capability
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering expertise forms the backbone of our industrial rubber solutions, particularly in the design and production of high-performance automotive door weatherstrips. Our dedicated technical team comprises five specialized mould engineers and two advanced formula engineers, enabling us to deliver precision-engineered products that meet the rigorous demands of global automotive OEMs. This integrated engineering capability ensures that both material composition and physical design are optimized for performance, durability, and seamless integration into vehicle assembly lines.
Our mould engineers bring over a decade of cumulative experience in precision tooling for rubber extrusion and injection moulding. They utilize advanced CAD/CAM software, including SolidWorks and AutoCAD, to develop highly accurate and efficient mould designs tailored to complex door sealing profiles. Finite element analysis (FEA) is routinely applied to simulate compression set, stress distribution, and sealing force under real-world conditions, allowing for design optimization prior to prototyping. This reduces time-to-market and ensures dimensional stability across high-volume production runs.
Complementing our mould design expertise, our two in-house rubber formulation engineers specialize in custom elastomer development. They focus on creating proprietary rubber compounds based on EPDM, silicone, and thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV), engineered to meet specific OEM requirements for weather resistance, compression deflection, ozone stability, and low-temperature flexibility. Each formulation is developed and tested in our on-site laboratory, where we conduct accelerated aging, UV exposure, and dynamic sealing performance tests to validate long-term reliability.
Our end-to-end OEM capability enables us to support customers from concept to mass production. We provide full technical documentation, including DFMEA, process flow diagrams, and PPAP submissions, ensuring compliance with IATF 16949 quality standards. Our collaborative engineering approach allows for rapid iteration based on OEM feedback, with prototype delivery typically within 15–20 working days.
The following table outlines key technical specifications achievable through our engineering and manufacturing platform:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Material Types | EPDM, TPV, Silicone, CR (Neoprene) |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 40–90 ±5 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +150°C |
| Tensile Strength | ≥8 MPa (ASTM D412) |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% |
| Compression Set (22h, 100°C) | ≤25% (ASTM D395) |
| Adhesion Strength (to insert) | ≥80 N/cm |
| Colour Matching | Custom (Pantone, Masterbatch) |
| Tooling Lead Time | 30–45 days |
| Sample Lead Time | 15–20 days |
With a disciplined engineering workflow and deep technical mastery in both rubber chemistry and precision tooling, Suzhou Baoshida delivers automotive door weatherstrip solutions that meet the highest standards of performance and reliability required by Tier 1 suppliers and OEMs worldwide.
Customization Process

Customization Process for Automotive Door Weatherstrip Manufacturing
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our customization process for automotive door weatherstrips integrates material science with precision engineering to meet stringent OEM performance requirements. This systematic approach ensures optimal sealing, durability, and acoustic insulation while adhering to vehicle-specific design constraints. The process begins with rigorous drawing analysis, where our engineering team deconstructs CAD models and technical specifications provided by the client. We assess critical parameters including dimensional tolerances, compression load deflection (CLD) curves, and environmental exposure conditions. This phase identifies potential manufacturing challenges early, such as complex geometries requiring multi-cavity molds or material transitions at splice points.
Following drawing validation, our rubber formulation specialists develop a compound tailored to the application’s thermal, chemical, and mechanical demands. We prioritize EPDM, TPE, or silicone elastomers based on factors like required temperature resistance, ozone exposure, and paint compatibility. Formulation adjustments target specific properties: enhancing resilience for low-temperature flexibility (-40°C) or optimizing crosslink density to minimize permanent set after 1 million door cycles. All compounds undergo preliminary lab testing for tensile strength, elongation, and compression set per ASTM D395 standards before prototyping.
Prototyping employs precision extrusion and molding techniques to produce functional samples within 15–20 days. Each prototype undergoes dynamic testing in climate chambers simulating -40°C to +120°C cycles and accelerated aging per SAE J2236. We validate sealing force uniformity, wind noise reduction, and dimensional stability under cyclic loading. Client feedback drives iterative refinements, with traceable documentation of all material and process adjustments. Only after achieving full compliance with OEM test protocols do we transition to mass production.
Mass production leverages automated extrusion lines with real-time SPC monitoring of critical dimensions (±0.15 mm tolerance) and durometer consistency (±2 Shore A). We implement PPAP Level 3 documentation, including material traceability down to batch level and 100% visual inspection via AI-powered cameras. Production runs are supported by our IATF 16949-certified quality management system, ensuring zero-defect delivery.
Key Rubber Compound Specifications for Automotive Weatherstrips
| Material | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Application Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | 50–80 | -40 to +150 | Superior ozone/weather resistance; cost-effective for primary sealing |
| TPE | 45–75 | -40 to +135 | Excellent paint adhesion; recyclable; ideal for co-extruded decorative trims |
| Silicone | 30–60 | -60 to +200 | Extreme temperature stability; low compression set for critical acoustic zones |
This end-to-end workflow, from digital blueprint to serialized production, guarantees weatherstrips that exceed automotive durability benchmarks while minimizing client time-to-market. Suzhou Baoshida’s commitment to material innovation and process control establishes us as a strategic partner for global OEMs demanding uncompromising sealing performance.
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Premium Automotive Door Weatherstrip Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. stands at the forefront of industrial rubber manufacturing, specializing in high-performance automotive sealing systems. As a trusted OEM partner, we deliver precision-engineered door weatherstrips that meet the rigorous demands of modern automotive production. Our expertise spans material formulation, extrusion tooling, and full-system validation, ensuring optimal fit, durability, and environmental sealing across diverse vehicle platforms.
Our automotive door weatherstrips are designed to provide superior resistance to compression set, UV degradation, ozone exposure, and extreme temperature fluctuations. Utilizing advanced EPDM and TPE compounds, we tailor each profile to meet specific OEM performance criteria, including acoustic insulation, water intrusion prevention, and door closing effort optimization. Whether for passenger vehicles, commercial fleets, or electric mobility platforms, our weatherstrips integrate seamlessly into automated assembly lines while maintaining long-term service integrity.
We operate under strict quality management systems compliant with IATF 16949 standards, enabling consistent batch-to-batch uniformity and traceability. Our in-house R&D laboratory conducts dynamic compression testing, aging studies, and adhesion peel strength analysis to validate every product release. This scientific approach ensures that our weatherstrips exceed industry benchmarks for longevity and functional reliability.
For engineering collaboration or sourcing inquiries, we invite you to contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Account Manager at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. Mr. Boyce brings over 12 years of experience in rubber formulation and automotive component supply chain integration. He serves as the primary technical liaison between our manufacturing team and global clients, facilitating rapid prototyping, DFMEA reviews, and on-site technical audits when required.
To initiate a technical discussion, request samples, or receive a customized quotation, please reach out directly via email at [email protected]. We respond to all inquiries within 4 business hours and offer multilingual support for English, German, and Mandarin-speaking engineering teams. Our goal is to become an extension of your product development cycle—delivering not just components, but engineered sealing solutions.
Below are key technical specifications representative of our standard automotive door weatherstrip offerings. Custom profiles and materials are available upon request.
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 55–75 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥10 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥300% |
| Compression Set (24h @ 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% |
| Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +130°C |
| Specific Gravity | ASTM D792 | 1.25–1.35 |
| Color Options | — | Black, Gray, Custom (RAL/Pantone) |
Partner with Suzhou Baoshida to ensure your vehicle sealing systems meet the highest standards of performance and manufacturability. Contact Mr. Boyce today at [email protected] to begin the conversation.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
