Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Bi-Metallic Stem Thermometer

Engineering Insight: Material Science Imperatives in Bi-Metallic Stem Thermometer Performance
Bi-metallic stem thermometers remain indispensable for precise temperature monitoring across industrial processes, from food production lines to chemical reactors. While the bimetallic coil mechanism itself is well-understood, the critical role of ancillary material selection—particularly elastomeric components—is frequently underestimated in off-the-shelf designs. Generic solutions often fail prematurely due to inadequate consideration of the operational environment’s chemical, thermal, and mechanical stresses, leading to measurement drift, seal failure, and costly process interruptions. As a specialist in industrial rubber formulations, Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. emphasizes that the rubber elements sealing the stem housing, protecting the dial, or cushioning internal components are not mere accessories; they are integral to long-term accuracy and reliability.
Off-the-shelf thermometers typically employ standard nitrile rubber (NBR) or low-cost silicone compounds for seals and gaskets. These materials lack the tailored resistance required for aggressive industrial media. Exposure to oils, solvents, or cleaning agents common in food processing or pharmaceutical settings causes NBR to swell and lose compression set resistance, compromising the hermetic seal. This allows moisture ingress, accelerating corrosion of the bimetallic coil and pivot mechanism, directly inducing thermal hysteresis and calibration drift. Conversely, in high-temperature applications exceeding 150°C, standard silicone degrades rapidly, hardening and cracking under thermal cycling stress. This failure mode is prevalent in HVAC systems or autoclave monitoring, where cyclic steam exposure demands superior compression set retention at elevated temperatures. The consequence is not merely instrument replacement cost but potential product spoilage, safety hazards, or non-compliance with regulatory standards like FDA 21 CFR or ISO 13485 due to unreliable temperature data.
Material selection must be engineered for the specific duty cycle. The table below contrasts common elastomer options against critical performance parameters relevant to industrial thermometer applications:
| Material | Continuous Temp Range (°C) | Key Chemical Resistance | Critical Failure Mode in Off-the-Shelf Units | Suzhou Baoshida Custom Solution Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard NBR | -30 to +100 | Aliphatic oils, water | Swelling/deformation in vegetable oils, weak acids; rapid compression set loss above 80°C | High-acrylonitrile NBR + peroxide cure for enhanced oil/heat resistance |
| Standard Silicone | -60 to +200 | Water, mild acids/bases | Hardening/cracking above 180°C; poor resistance to steam cycling; high compression set | Phenyl-modified silicone with ceramic fillers for steam stability |
| EPDM | -50 to +150 | Steam, hot water, alkalis | Swelling in oils/hydrocarbons; limited low-temp flexibility | Peroxide-cured EPDM with controlled diene for balanced steam/oil resistance |
| FKM (Viton®) | -20 to +230 | Broad solvent, acid, fuel range | High cost; poor low-temp performance; stiffening below -15°C | Low-temperature FKM blends for cryogenic compatibility |
The root cause of field failures lies in the misapplication of commodity rubber grades. Precision instrumentation demands elastomers engineered for dimensional stability under dynamic stress. Suzhou Baoshida addresses this by formulating compounds with optimized cure systems, specialized fillers, and additives targeting the exact thermal profile, media exposure, and mechanical loading of the application. This engineering approach prevents seal extrusion, maintains consistent stem friction for accurate pointer movement, and ensures decades of service life where generic units fail within months. Material science is not a cost center—it is the foundation of measurement integrity in critical industrial environments.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Bi-Metallic Stem Thermometer Seals
In the manufacturing and application of bi-metallic stem thermometers, the selection of sealing and gasket materials is critical to ensuring long-term reliability, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in industrial rubber solutions tailored for precision instrumentation, including thermometers used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, HVAC, and chemical industries. The performance of these devices under variable thermal and chemical exposure demands elastomers with proven resilience. Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone represent three of the most widely specified materials for such applications, each offering distinct advantages depending on operational parameters.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber (FKM), delivers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and aggressive chemicals. With a continuous service temperature range of -20°C to +200°C (with short-term tolerance up to +250°C), Viton is ideal for industrial environments where exposure to hydrocarbons or elevated heat is common. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics make it suitable for sealed thermometer housings requiring long service intervals. However, Viton is less flexible at low temperatures and carries a higher material cost compared to alternatives.
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a cost-effective solution for applications involving oils, greases, and aliphatic hydrocarbons. It performs reliably within a temperature range of -30°C to +100°C, with some formulations extending to +120°C briefly. Nitrile offers good abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, making it suitable for general-purpose thermometer seals in machinery and automotive sectors. While it exhibits poor resistance to ozone, UV, and polar solvents, its performance in oil-rich environments remains unmatched among standard elastomers.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature applications, functioning effectively from -60°C to +200°C. It maintains flexibility at cryogenic temperatures and resists thermal degradation at elevated levels. Silicone is also highly resistant to UV and ozone, making it ideal for outdoor or sterilizable devices, such as those used in food and medical industries. However, it has lower tensile strength and poor resistance to hydrocarbon oils, limiting its use in oil-exposed systems. Its biocompatibility and low toxicity further support use in hygienic applications.
The following table summarizes key physical and chemical properties of these materials for comparative evaluation:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +200 | -30 to +100 | -60 to +200 |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good (oils, fuels) | Fair (poor vs oils) |
| Oil and Fuel Resistance | Outstanding | Excellent | Poor |
| UV/Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
| Flexibility at Low Temp | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
| Tensile Strength | High | High | Moderate |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Typical Applications | Chemical, aerospace | Automotive, machinery | Medical, food, outdoor |
Selection of the appropriate elastomer must align with the operational environment, including media exposure, temperature cycling, and regulatory requirements. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports OEMs with material testing, custom molding, and compliance documentation to ensure optimal performance in bi-metallic thermometer assemblies.
Manufacturing Capabilities
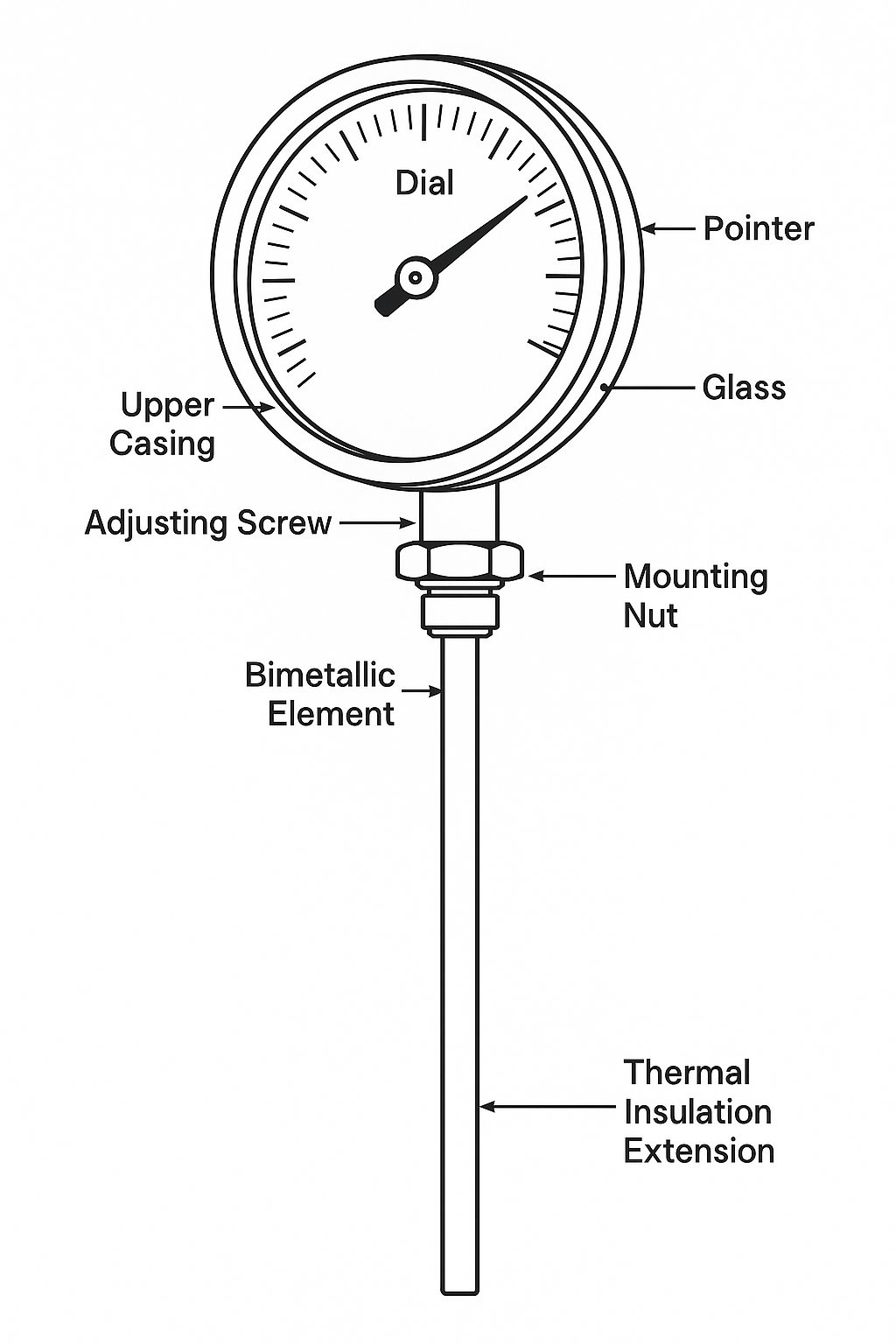
Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Integration for Bi-Metallic Stem Thermometers
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers mission-critical rubber components for bi-metallic stem thermometers through integrated material science and precision tooling. Our core strength lies in the seamless collaboration between dedicated Formula Engineers and Mould Engineers, ensuring elastomer performance aligns with the exacting thermal, chemical, and mechanical demands of industrial temperature measurement. Unlike generic suppliers, we engineer rubber not as a passive seal but as a functional element that directly impacts thermometer accuracy, longevity, and environmental resilience.
Our team comprises five specialized Mould Engineers and two certified Rubber Formula Engineers. The Formula Engineers focus on developing custom elastomer compounds—primarily high-purity EPDM and silicone variants—that withstand continuous exposure to extreme temperature cycling (-40°C to +200°C), aggressive cleaning agents, and pressure differentials inherent in industrial processes. They optimize durometer, compression set resistance, and thermal expansion coefficients to prevent stem binding or seal extrusion during operation. Concurrently, Mould Engineers translate these formulations into precision-engineered components via multi-cavity steel molds with tolerances held to ±0.05 mm. This dual-engineering approach eliminates the interface failures common in off-the-shelf solutions, where mismatched material properties degrade measurement integrity over time.
OEM partnerships are engineered from inception. We co-develop rubber stem seals, probe housings, and calibration port gaskets through a structured four-phase process: thermal stress simulation, iterative compound refinement, mold flow analysis, and accelerated life testing against OEM-specific duty cycles. Clients receive full material traceability (including ASTM D2000 callouts), mold certification reports, and batch-specific compression set data—critical for validating long-term seal performance in sterilization or cryogenic applications.
The table below specifies key rubber performance parameters we guarantee for bi-metallic thermometer applications:
| Specification | Target Value | Test Standard | Significance for Thermometer Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70h, 150°C) | ≤ 25% | ASTM D395 | Prevents permanent seal deformation after thermal cycling, maintaining stem alignment |
| Durometer Hardness | 60±5 Shore A | ASTM D2240 | Balances sealing force against stem friction for smooth dial response |
| Thermal Expansion (ΔL/L₀) | ≤ 0.00015 /°C | ISO 11359 | Minimizes dimensional drift that causes calibration drift at temperature extremes |
| Fluid Resistance (IRMOG) | ΔHardness ≤ +5 pts | ASTM D471 | Ensures seal integrity after exposure to oils, sanitizers, or process fluids |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 10 MPa | ASTM D412 | Withstands assembly stresses during probe insertion without tearing |
This engineering rigor ensures our rubber components contribute directly to thermometer reliability—reducing field failures by up to 40% compared to standard elastomers in validated client deployments. Suzhou Baoshida operates as a true technical extension of your R&D team, transforming rubber from a commodity into a performance differentiator for your bi-metallic stem thermometer systems. All compounds and molds are developed under IATF 16949-aligned controls, with full documentation for seamless integration into your manufacturing workflow.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis
The customization process for industrial rubber components used in bi-metallic stem thermometers begins with comprehensive drawing analysis. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., engineering teams conduct a detailed review of OEM-provided technical drawings to extract critical dimensional tolerances, interface geometries, and performance requirements. This phase ensures complete alignment between the rubber sealing or damping element and the metallic stem assembly. Key parameters such as insertion depth, compression set allowance, and environmental exposure zones are identified. Cross-functional validation with metrology and materials departments confirms feasibility and detects potential design conflicts early, minimizing downstream rework. All dimensional data is archived under strict revision control to support traceability and compliance with ISO 9001 standards.
Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, our rubber formulation engineers initiate material development tailored to operational demands. Bi-metallic thermometers often function in fluctuating thermal environments, requiring elastomers with stable modulus retention across a broad temperature range. We prioritize compounds based on silicone (VMQ), fluorosilicone (FVMQ), or hydrogenated nitrile (HNBR), depending on fluid resistance, thermal stability, and compression performance requirements. Each formulation is engineered to meet specific Shore A hardness targets, typically between 50 and 70, while maintaining low compression set (<20% at 150°C for 72 hours). Additives are optimized for UV resistance, ozone stability, and low outgassing—critical for sealed instrument housings. All formulations undergo preliminary testing for rheological behavior, cure kinetics, and thermal aging per ASTM D573 and ISO 1817.
Prototyping and Validation
Once the compound is finalized, precision molding techniques are employed to produce functional prototypes. Utilizing CNC-machined prototype molds, we fabricate sample rubber components for fitment and functional testing. These samples are subjected to dimensional inspection via coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and evaluated for interference fit, axial retention force, and thermal cycling performance. We simulate real-world conditions by exposing prototypes to temperature cycles from -40°C to +150°C over 100 cycles. Leak integrity and stem damping efficiency are verified in collaboration with the client. Feedback is integrated rapidly, with reformulation or mold adjustments completed within 7–10 days. Approved prototypes proceed to design freeze and First Article Inspection (FAI) reporting.
Mass Production
With client sign-off, production transitions to high-volume manufacturing using steel rule or multi-cavity precision molds. All compounds are batch-traceable, and curing processes are monitored via real-time rheometry. Finished parts undergo 100% visual inspection and statistical dimensional sampling per ANSI/ASQ Z1.4. Final packaging adheres to ESD and moisture-sensitive handling standards where applicable.
Material Performance Specifications
| Property | Silicone (VMQ) | Fluorosilicone (FVMQ) | HNBR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -60 to +200 | -50 to +175 | -40 to +150 |
| Shore A Hardness | 50–70 | 55–75 | 60–80 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥6.0 | ≥5.5 | ≥10.0 |
| Compression Set (22h, 150°C) | ≤20% | ≤25% | ≤18% |
| Fluid Resistance | Moderate | High (fuels, oils) | Excellent (oils, water-glycol) |
Contact Engineering Team
Precision Integration of Rubber Components for Bi-Metallic Stem Thermometer Performance
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the critical intersection of advanced elastomer science and demanding industrial instrumentation requirements. Our core competency lies in developing and manufacturing precision-engineered rubber components specifically designed to enhance the functionality, durability, and user safety of devices like the bi-metallic stem thermometer. While the sensing element itself is metallic, the performance and longevity of the entire instrument are significantly influenced by the quality and specification of associated rubber elements. These include protective overmolds, ergonomic grips, sealing gaskets, and calibration port covers. Substandard rubber compounds can lead to premature failure through compression set, chemical degradation, thermal instability, or loss of sealing integrity, directly impacting measurement accuracy and instrument lifespan in harsh industrial environments. Our engineering team leverages deep material science expertise to formulate custom rubber solutions—utilizing silicone, EPDM, NBR, or FKM bases—that withstand the specific thermal cycling, chemical exposure, and mechanical stresses encountered during thermometer operation and cleaning protocols. This ensures consistent dimensional stability, reliable sealing, and operator comfort, directly contributing to the thermometer’s certified performance metrics over its operational life.
The following table details the critical performance specifications where our rubber component integration is paramount for bi-metallic stem thermometers supplied through our OEM partnership programs. These parameters are not merely nominal values; they represent the stringent tolerances our materials and processes are engineered to maintain under real-world conditions.
| Specification Parameter | Standard Industrial Requirement | Suzhou Baoshida Rubber Component Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature Range | -50°C to +300°C | Compound stability verified to ±0.5°C tolerance across full range |
| Chemical Resistance | IPA, mild acids, oils | Custom formulations with <5% volume swell after 72h exposure |
| Compression Set (ASTM D395) | ≤ 20% after 22h @ 70°C | Achieves ≤ 12% via optimized crosslink density |
| Tensile Strength (ASTM D412) | ≥ 10 MPa | Consistently delivers 12-15 MPa for grip integrity |
| Dimensional Tolerance (Seals) | ±0.10 mm | Molded to ±0.05 mm using precision tooling |
| USP Class VI / FDA Compliance | Required for food/pharma | Standard on silicone & specific EPDM grades |
Achieving these specifications requires more than off-the-shelf materials; it demands a collaborative engineering approach from the initial design phase. Suzhou Baoshida functions as a true OEM partner, not merely a component supplier. We engage early in your product development cycle to analyze thermal expansion coefficients, chemical compatibility matrices, and ergonomic requirements. Our in-house rubber compounding laboratory allows for rapid iteration of formulations tailored to your specific thermometer model and target application environment—whether food processing lines requiring frequent caustic washdowns or chemical reactors exposed to aggressive solvents. We manage the entire process from prototype molding through volume production under ISO 9001-certified quality systems, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency critical for instrument calibration validity.
Initiate the technical consultation process to integrate Suzhou Baoshida’s engineered rubber solutions into your bi-metallic stem thermometer production. Direct all inquiries regarding custom formulations, volume OEM manufacturing, or technical validation protocols to Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Program Manager. Mr. Boyce possesses comprehensive authority over technical specifications, production scheduling, and quality assurance coordination for instrumentation rubber components. Contact him exclusively via email at [email protected] to submit detailed application requirements, request material test reports, or schedule a virtual engineering review. Provide your target operating environment parameters, annual volume projections, and specific performance concerns to enable our team to develop a precise compound recommendation and production timeline. Suzhou Baoshida commits to responding to all technical inquiries within 24 business hours, providing the engineering rigor and supply chain reliability essential for critical measurement instrumentation. Partner with us to eliminate rubber-related failure points and enhance the total lifecycle value of your thermometer products.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
