Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Bridge Bearing Pad
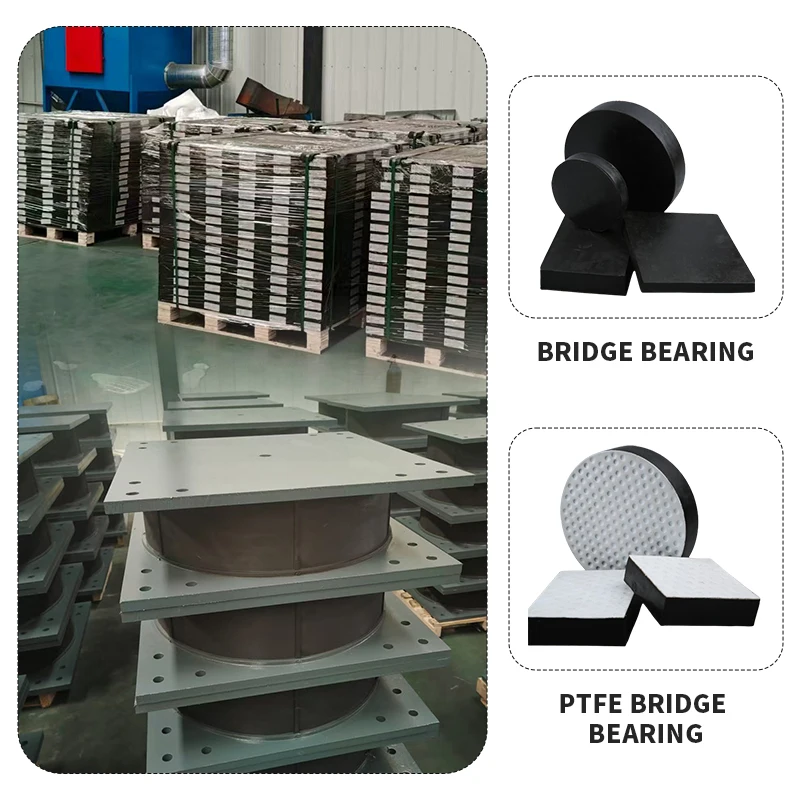

Material Selection in Bridge Bearing Pads: Engineering for Long-Term Structural Integrity
The performance and longevity of bridge bearing pads are fundamentally determined by material selection. These components serve as critical interfaces between superstructures and substructures, tasked with accommodating thermal expansion, seismic movement, and dynamic load distribution. While off-the-shelf rubber bearing pads may appear cost-effective, they frequently fail to meet the complex demands of real-world bridge environments. This failure stems from inadequate material formulation, insufficient understanding of service conditions, and lack of customization to site-specific stress profiles.
Standard elastomeric pads are often manufactured using generic natural rubber (NR) or styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) compounds with minimal reinforcement. These materials may perform adequately under static loads and mild environmental exposure, but degrade rapidly under sustained shear stress, UV radiation, ozone, and temperature extremes. In bridge applications, where service life expectations exceed 50 years, such degradation leads to cracking, creep, loss of load-bearing capacity, and ultimately structural instability.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we engineer bridge bearing pads using precision-formulated elastomers tailored to project-specific mechanical and environmental requirements. Our approach begins with a comprehensive assessment of load spectra, displacement ranges, climatic conditions, and chemical exposure. Based on this data, we select from a range of high-performance polymers—such as chloroprene (CR), ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), or specialty nitrile (NBR)—each offering distinct advantages in ozone resistance, thermal stability, or oil resistance.
Critical to our formulations is the integration of high-tensile steel reinforcement plates and advanced filler systems that enhance compressive strength while maintaining flexibility. The vulcanization process is precisely controlled to ensure optimal cross-link density, minimizing permanent set and hysteresis under cyclic loading. These engineered solutions outperform generic alternatives by maintaining dimensional stability and elastic recovery over decades of service.
The following table outlines key material properties and performance metrics for common elastomers used in bridge bearing pads:
| Material | Hardness (Shore A) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Operating Temperature Range (°C) | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber (NR) | 60–70 | 20–30 | 500–600 | -40 to +70 | High resilience, excellent fatigue resistance |
| SBR | 65–75 | 15–22 | 400–500 | -30 to +60 | Good abrasion resistance, moderate cost |
| Chloroprene (CR) | 60–75 | 18–25 | 450–550 | -40 to +100 | Superior ozone and weather resistance |
| EPDM | 65–80 | 16–24 | 400–500 | -50 to +150 | Exceptional thermal and UV stability |
| Nitrile (NBR) | 70–85 | 15–20 | 300–400 | -30 to +120 | Resistance to oils and hydrocarbons |
Selecting the appropriate elastomer is not a one-size-fits-all proposition. Off-the-shelf pads, designed for minimal compliance, often neglect the interplay between material behavior and structural dynamics. In contrast, precision-engineered bearing pads from Suzhou Baoshida ensure long-term reliability, reduced maintenance costs, and compliance with international standards such as ASTM D4014 and EN 1337. Material selection is not merely a procurement decision—it is a foundational engineering imperative.
Material Specifications

Bridge Bearing Pad Material Specifications
Bridge bearing pads demand elastomers with rigorously defined mechanical and environmental resistance properties to ensure structural integrity under dynamic loads, seismic activity, and prolonged exposure to harsh elements. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our precision-engineered rubber compounds for bridge applications are formulated to meet ASTM D2000 and ISO 22307 standards, with material selection directly impacting service life and safety margins. Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ) represent core solutions, each optimized for specific operational profiles. Viton delivers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, and ozone, making it ideal for bearings in chemically aggressive environments or near fuel-exposed infrastructure. Nitrile provides cost-effective resilience against petroleum-based fluids and moderate temperatures, serving as the industry standard for general-purpose bridge bearings where hydraulic fluid contact is anticipated. Silicone excels in extreme low-temperature flexibility and UV stability but exhibits lower tensile strength, restricting its use to non-load-intensive auxiliary components in arctic climates.
Critical performance parameters must align with project-specific stressors, including compressive modulus, creep resistance, and damping characteristics. Below is a comparative analysis of key material properties for bridge bearing pad applications:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | –20°C to +230°C | –40°C to +120°C | –60°C to +200°C |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–8 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–300 | 200–500 | 200–600 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Oil/Fuel Resistance | Excellent | Good to Excellent | Poor |
| Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Fair to Good | Excellent |
Viton’s superior chemical inertness justifies its premium cost in refineries or coastal structures where salt spray and hydrocarbons accelerate degradation. Nitrile’s balanced performance and economic viability make it suitable for 80% of standard highway and rail bridge installations, particularly where cost efficiency is prioritized without sacrificing oil resistance. Silicone’s niche application lies in regions with sustained sub-zero conditions below –40°C, though its limited load-bearing capacity necessitates engineering validation for primary bearing elements. All materials undergo rigorous compression set testing per ASTM D395 to ensure minimal permanent deformation after decades of cyclic loading.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages proprietary polymer blending and vulcanization control to enhance fatigue resistance in all compounds. Our OEM-managed production ensures lot-to-lot consistency through real-time rheometer monitoring and post-cure optimization. For critical infrastructure projects, we recommend Viton for high-risk chemical exposure zones, Nitrile for standard operational environments, and Silicone only where extreme cold is the dominant factor—always validated against site-specific load spectra and environmental modeling. Partner with our engineering team to specify the exact compound grade meeting your seismic isolation and longevity requirements.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering division forms the backbone of our precision rubber manufacturing expertise, particularly in the development and production of bridge bearing pads. We maintain a dedicated team of five certified mould engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, enabling us to deliver technically advanced, application-specific solutions for demanding civil infrastructure environments. This integrated engineering approach ensures that every bridge bearing pad we produce meets exacting standards for load distribution, seismic resistance, and long-term durability.
Our mould engineers utilize advanced CAD/CAM software and finite element analysis (FEA) tools to design precision steel moulds that guarantee dimensional accuracy and repeatability across production batches. Each mould is optimized for material flow, curing uniformity, and ease of demoulding, minimizing defects and enhancing product consistency. Concurrently, our rubber formula engineers develop custom elastomer compounds tailored to the mechanical and environmental conditions encountered in bridge applications. These include resistance to dynamic loading, UV exposure, ozone degradation, and extreme temperature fluctuations ranging from -40°C to +80°C.
By combining proprietary rubber formulations with precision tooling, we achieve superior performance characteristics such as high compressive strength, low creep, and excellent shear deformation capacity—critical for seismic isolation and thermal movement accommodation in bridge structures. Our in-house formulation capability allows us to adjust hardness, modulus, elongation, and damping properties to meet ASTM, EN, or client-specific standards.
We operate as a full-service OEM partner, supporting clients from initial concept and material selection through prototyping, validation, and high-volume production. Our engineering team collaborates directly with structural designers and construction firms to ensure compliance with project specifications, including load ratings, displacement requirements, and service life expectations. All formulations and mould designs are documented and retained for traceability, enabling seamless reorders and long-term supply continuity.
The integration of material science and precision engineering allows us to offer bridge bearing pads in a wide range of dimensions and performance grades. Below is a representative specification table for our standard product line.
| Property | Test Standard | Value Range |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 50–80 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥12 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥300% |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% |
| Operating Temperature | — | -40°C to +80°C |
| Shear Modulus (G) | EN 1337-3 | 0.8–1.2 MPa |
| Maximum Compressive Stress | EN 1337-3 | 25 MPa |
| Dynamic Load Capacity | Custom | Up to 5,000 kN |
This technical rigor, supported by our dual-engineering expertise, positions Suzhou Baoshida as a trusted OEM provider of high-performance bridge bearing pads for global infrastructure projects.
Customization Process

Bridge Bearing Pad Customization Process: Precision Engineering for Structural Integrity
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our customization process for bridge bearing pads integrates material science rigor with industrial-scale precision. Each step ensures compliance with ASTM D4014 and AASHTO M251 standards while addressing site-specific demands such as seismic activity, thermal cycling, and dynamic load profiles. We eliminate guesswork through a four-phase workflow designed to mitigate field failure risks.
Drawing Analysis initiates the process with granular scrutiny of client CAD files and technical specifications. Our engineering team validates geometric tolerances per ISO 2768-mK, load distribution requirements, and environmental exposure parameters. Critical attention is paid to compression modulus (5–15 MPa range), shear deformation limits (±25% strain), and interface geometry. Discrepancies in GD&T callouts or material callouts trigger immediate client consultation to prevent downstream rework. This phase typically concludes within 72 hours, delivering a formal feasibility report with tolerance stack-up analysis.
Formulation leverages our 15+ years of rubber compound expertise. Based on the validated drawing, our lab engineers select base polymers (EPDM, NR, or specialty blends) and optimize filler systems for target hardness (Shore A 50–75), tensile strength (≥15 MPa), and compression set (<20% per ASTM D395). Key adjustments include:
Anti-oxidant packages for UV/ozone resistance in coastal installations
Reinforcing silica for high-shear applications (>100,000 cycles)
Low-temperature flexibilizers enabling operation at -50°C
All formulations undergo Durometer stability testing across 0–80°C cycles before prototyping.
Prototyping employs CNC-machined molds to produce 3–5 test units per ISO 2230. Each pad undergoes accelerated life testing:
500-hour salt spray exposure (ASTM B117)
Dynamic load simulation at 2.5x design capacity
Creep resistance validation under 10 MPa constant stress
Clients receive full test reports with traceable material certificates. Iterations are completed within 10 business days.
Mass Production commences only after client sign-off on prototype validation. Our ISO 9001-certified facility utilizes closed-mixing systems with real-time rheometer monitoring to ensure batch consistency. Every pad is laser-etched with a unique ID for full traceability, and statistical process control (SPC) maintains dimensional tolerances within ±0.3 mm. Final inspection includes 100% visual checks and random batch testing per AASHTO T 221.
Critical Performance Specifications Comparison
| Parameter | Standard EPDM Pad | Custom-Engineered Pad |
|————————–|——————-|————————|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60 ± 5 | 55–75 (client-defined) |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15.0 min | 18.0–25.0 |
| Compression Set (%) | ≤25 | ≤15 |
| Operating Temp Range (°C)| -40 to +80 | -50 to +100 |
| Shear Modulus (MPa) | 0.8–1.2 | 0.6–2.0 (adjustable) |
This structured approach guarantees bearing pads that withstand decades of service under extreme conditions. Suzhou Baoshida’s end-to-end control—from molecular formulation to certified production—delivers OEM partners measurable reductions in lifecycle maintenance costs and structural downtime. All custom projects include lifetime technical support and rapid requalification for design revisions.
Contact Engineering Team
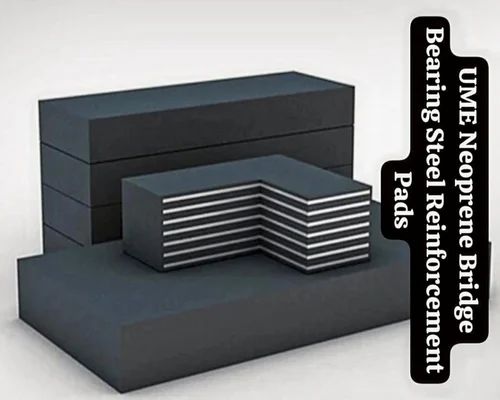
For mission-critical applications in civil infrastructure, the performance and reliability of bridge bearing pads are non-negotiable. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in the engineering and supply of high-precision rubber components, particularly tailored for structural support systems such as bridge bearing pads. Our expertise lies in formulating elastomeric compounds that meet stringent international standards while delivering exceptional load distribution, vibration damping, and long-term durability under dynamic environmental conditions.
As a trusted OEM partner in the precision rubber seals industry, we understand that every bridge project presents unique challenges—whether it’s accommodating thermal expansion, seismic movement, or sustained vertical loads. Our bridge bearing pads are manufactured using advanced vulcanization techniques and reinforced with steel plates when required, ensuring optimal shear deformation resistance and compressive strength. We work closely with engineering firms, precast manufacturers, and construction contractors to deliver custom solutions that align precisely with project specifications.
Our technical team, led by Mr. Boyce, brings decades of cumulative experience in rubber formulation and industrial application support. Whether you require pads compliant with AASHTO, EN 1337, or custom ASTM specifications, we provide full material traceability, third-party testing reports, and on-demand engineering validation. From initial concept to batch production, Suzhou Baoshida ensures consistency, repeatability, and compliance across every order.
To support global procurement needs, we maintain robust production capacity and streamlined logistics channels, enabling fast turnaround times without compromising quality. All products undergo rigorous quality control, including hardness testing, tensile strength analysis, compression set evaluation, and accelerated aging tests to simulate long-term performance.
Below are typical technical specifications for our standard bridge bearing pad series. Custom dimensions, hardness ratings, and performance parameters are available upon request.
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 60 ± 5 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥18 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥400% |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤20% |
| Shear Modulus | ASTM D4014 | 0.8 – 1.2 MPa |
| Operating Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +70°C |
| Steel Plate Thickness (if applicable) | Custom | 2 – 6 mm |
| Service Life (Design) | — | 50+ years |
Partnering with Suzhou Baoshida means gaining access to a responsive, technically driven supplier committed to engineering excellence. If you are sourcing high-performance bridge bearing pads or require support in material selection and design validation, we invite you to contact Mr. Boyce directly. He is available to discuss your project requirements, provide technical documentation, and assist in developing a supply solution that meets your timeline and performance criteria.
Reach out via email at [email protected] to initiate a technical consultation or request a detailed quotation.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
