Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Building Entrance Doormats
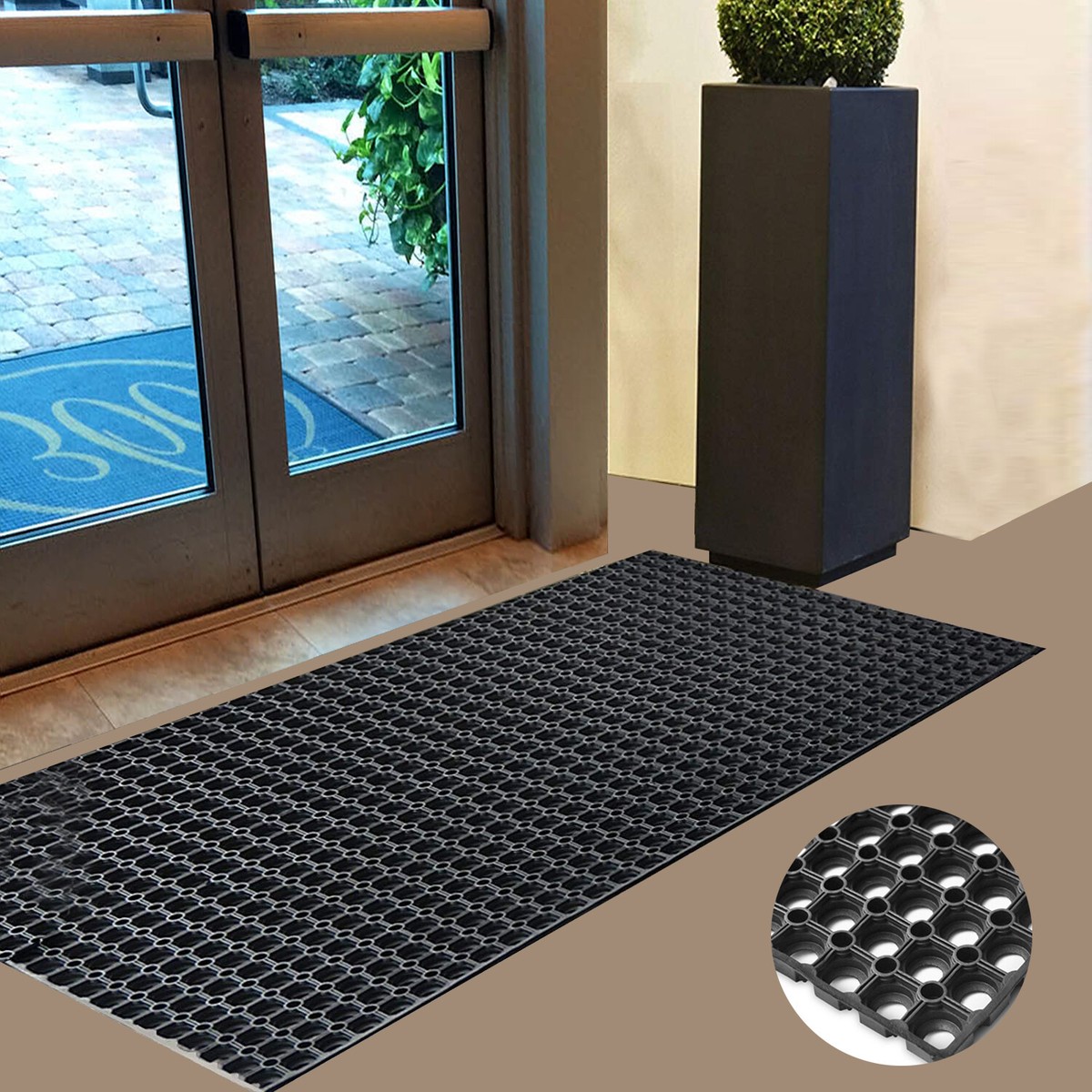

Engineering Insight: Material Science as the Foundation of Entrance Doormat Performance
The operational integrity of commercial building entrance systems hinges critically on doormat material selection—a factor frequently underestimated in procurement. Off-the-shelf solutions, typically formulated with generic PVC or recycled rubber compounds, fail under real-world conditions due to fundamental polymer limitations. These materials lack the engineered resilience required for high-traffic environments, leading to premature degradation, safety hazards, and increased lifecycle costs. Understanding the science behind material failure is essential for specifying doormats that deliver sustained performance.
Standard commercial mats exhibit rapid deterioration due to three primary failure mechanisms. First, inadequate cross-link density in low-grade rubber compounds accelerates polymer chain scission under UV exposure and thermal cycling, causing surface cracking and embrittlement within 6–12 months. Second, insufficient filler dispersion and plasticizer migration result in accelerated abrasion wear, reducing effective scraping depth by over 50% after six months in moderate traffic. Third, poor dynamic coefficient of friction (CoF) stability—particularly when wet—creates slip risks that violate ADA compliance standards. These failures stem from cost-driven formulations that prioritize initial purchase price over operational longevity, forcing facility managers into frequent replacements and incurring hidden costs from slip-and-fall liabilities.
Engineered rubber compounds address these vulnerabilities through precision-formulated polymer matrices. High-purity synthetic rubbers (EPDM or SBR) with controlled sulfur vulcanization achieve optimal cross-link density, resisting UV degradation down to -40°C. Reinforcing fillers like silica and carbon black are dispersed via multi-stage mastication to enhance abrasion resistance without compromising flexibility. Critical additives—including hydrophobic agents and ceramic grit binders—maintain wet CoF values above 0.65 across the mat’s service life. The table below quantifies performance differentials between standard and engineered solutions:
| Performance Parameter | Standard PVC/Recycled Rubber | Engineered Rubber Compound | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abrasion Loss (mm³) | 100 | 35 | ISO 4649 |
| Temperature Range (°C) | -10 to +60 | -40 to +90 | ASTM D2240 |
| Wet Dynamic CoF (min) | 0.42 | 0.68 | ASTM F2913 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 8.5 | 18.2 | ISO 37 |
| Expected Service Life (yrs) | 1.5 | 7+ | Field Validation |
Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM formulations leverage this material science rigor, integrating client-specific traffic profiles and environmental data into compound design. For airports, hospitals, or retail hubs, we calibrate durometer (65–75 Shore A), grit retention, and drainage geometry to match exact operational demands. This eliminates the compromise inherent in off-the-shelf products—where one-size-fits-all materials sacrifice safety for cost. The result is not merely a doormat, but a calibrated component of a building’s entrance ecosystem, ensuring consistent debris capture, slip resistance, and structural integrity for over 5 million footfalls. Material selection is thus not a procurement detail; it is the engineering cornerstone of facility safety and operational continuity.
Material Specifications
Material selection is a critical engineering decision in the design and manufacturing of high-performance building entrance doormats, particularly where durability, chemical resistance, and environmental stability are required. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in industrial rubber solutions tailored for demanding architectural and commercial applications. Our expertise enables us to recommend and supply premium elastomeric materials such as Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone, each offering distinct performance characteristics suited to specific operational environments. These materials are evaluated based on mechanical strength, temperature tolerance, resistance to oils and chemicals, and longevity under continuous exposure to foot traffic and outdoor elements.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, ozone, and a broad range of industrial chemicals, including hydrocarbons and solvents. This makes it ideal for doormats installed in industrial facilities, laboratories, or garages where exposure to aggressive substances is common. Viton maintains structural integrity from -20°C to +250°C, offering long-term stability in extreme conditions. However, due to its higher material cost, it is typically reserved for specialized applications where performance outweighs budget constraints.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, provides excellent resistance to oils, greases, and aliphatic hydrocarbons, making it a cost-effective solution for commercial entrances in automotive, manufacturing, and maintenance environments. With a service temperature range of -30°C to +120°C, Nitrile balances performance and affordability. It also exhibits good abrasion resistance, a key factor in high-traffic entryways. While not as thermally stable as Viton, Nitrile remains a preferred choice for standard industrial doormats requiring reliable oil and wear resistance.
Silicone rubber excels in extreme temperature applications, operating effectively from -60°C to +230°C. It offers superior UV and ozone resistance, making it highly suitable for exterior building entrances exposed to direct sunlight and weather fluctuations. Silicone is also non-toxic and exhibits excellent flexibility over time, though it has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Viton and Nitrile. Its use is often optimized in architectural settings where aesthetic consistency and weather resilience are prioritized.
The following table summarizes key performance specifications of these materials for informed selection in doormat manufacturing:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +250 | -30 to +120 | -60 to +230 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–25 | 10–20 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–300 | 200–500 | 200–600 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor to Fair |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Very Good | Moderate |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Moderate |
Selecting the appropriate rubber compound depends on the environmental exposure, expected lifespan, and functional requirements of the doormat. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports OEM partners with material testing, formulation customization, and technical data to ensure optimal product performance in real-world conditions.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Solutions for Entrance Doormats
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep technical expertise in industrial rubber formulation and precision mould engineering to deliver high-performance building entrance doormats. Our dedicated team comprises five specialized Mould Engineers and two advanced Formula Engineers, ensuring scientific validation at every development phase. This integrated approach guarantees mats that withstand extreme abrasion, weather exposure, and heavy foot traffic while maintaining dimensional stability and aesthetic integrity.
Our Mould Engineers utilize CAD/CAM-driven design protocols to optimize flow dynamics, venting, and cooling channels within steel moulds. This eliminates knit lines and sink marks, critical for textured surfaces that trap debris. Finite element analysis (FEA) validates structural resilience under cyclic compression loads exceeding 500,000 cycles, preventing premature deformation in high-traffic zones. Precision tolerances of ±0.15 mm ensure seamless integration with architectural thresholds and compatibility with automated cleaning systems.
The Formula Engineering team develops proprietary rubber compounds using SBR, EPDM, and recycled tire crumb matrices. Each formulation undergoes rigorous ASTM D2240 and ISO 48 testing to balance Shore A hardness, tear strength, and resilience. Carbon black reinforcement is calibrated to achieve optimal abrasion resistance without sacrificing flexibility in sub-zero conditions. UV stabilizers and ozone inhibitors are precisely dosed to prevent surface cracking under prolonged sunlight exposure, extending service life by 40% compared to standard compounds.
OEM capabilities are central to our value proposition. We support clients from concept to量产 with zero minimum order quantities (MOQs) for custom profiles. Our engineers collaborate on substrate adhesion systems for co-moulded metal inserts, anti-slip backing integration, and color-fast pigment dispersion. All compounds comply with REACH and RoHS standards, with full traceability via batch-specific certificates of analysis.
Critical rubber compound specifications for entrance doormats are validated per international standards:
| Property | Target Value | Testing Standard | Application Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abrasion Loss (Taber) | ≤ 85 mg/1000 cycles | ASTM D5963 | Sustains 10+ years in airport terminals |
| Shore A Hardness | 65–75 | ASTM D2240 | Optimal debris retention & comfort |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 18 MPa | ISO 37 | Resists tearing from chair legs |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +90°C | ISO 188 | No cracking in Arctic winters |
| Compression Set (22h) | ≤ 15% | ASTM D395 | Maintains sealing against drafts |
This engineering synergy ensures doormats exceed ISO 10545-14 performance benchmarks for commercial flooring. Suzhou Baoshida transforms material science into reliable entrance solutions, where every compound adjustment and mould contour is quantitatively validated for real-world durability. Clients receive not just a product, but a scientifically engineered asset with documented lifecycle performance.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis
The customization process for industrial rubber doormats begins with meticulous drawing analysis. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we receive technical drawings from clients specifying dimensions, surface patterns, groove depth, edge profiles, and installation requirements. Our engineering team conducts a comprehensive review to verify geometric feasibility, structural integrity, and compliance with intended application environments—such as high-traffic commercial lobbies, industrial facilities, or public transit entrances. Critical parameters including load-bearing zones, drainage channels, and anti-slip features are evaluated using CAD-based simulation tools. Tolerances are cross-checked against ISO 2768-mK standards to ensure manufacturability. Any discrepancies or optimization opportunities are communicated to the client for technical alignment prior to proceeding.
Formulation Development
Once the design is validated, our Rubber Formula Engineers initiate material formulation tailored to performance demands. The base polymer selection—typically SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber), EPDM, or recycled rubber crumb—is determined by environmental exposure, abrasion resistance needs, and color requirements. For exterior building entrances exposed to UV radiation and temperature extremes, EPDM is preferred due to its superior weatherability. For high-wear zones, a high-abrasion-resistant SBR compound is engineered with reinforcing fillers such as N330 carbon black and processed with sulfur-based vulcanization systems. Additives including anti-oxidants, anti-ozonants, and processing oils are dosed precisely to enhance longevity and extrusion behavior. Shore A hardness is maintained between 60–75 to balance resilience and foot comfort. All formulations are documented and archived for batch traceability and re-order consistency.
Prototyping and Validation
A functional prototype is produced using precision steel molds fabricated in-house based on approved drawings. The prototype undergoes rigorous testing, including DIN 51130 slip resistance evaluation, ISO 48-4 hardness measurement, and accelerated aging per ISO 188. Dimensional accuracy is verified using coordinate measuring machines (CMM). The client receives the physical sample along with a full test report for performance validation. Feedback is incorporated into final design or material adjustments, ensuring full compliance with operational expectations.
Mass Production Execution
Upon client approval, the project transitions to mass production. Molding is executed on hydraulic presses with temperature and pressure controls calibrated to ±2°C and ±0.5 MPa. Each mat is visually inspected and sampled hourly for conformance. Final products are palletized with protective film and shipped with material certification and QC documentation.
Typical Physical Properties of Custom Entrance Doormats
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ISO 48-4 | 65–72 |
| Tensile Strength | ISO 37 | ≥10 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ISO 37 | ≥250% |
| Abrasion Loss (DIN) | ISO 4649 | ≤120 mm³ |
| Slip Resistance (R-value) | DIN 51130 | R10–R11 |
| Operating Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +80°C |
Contact Engineering Team
Technical Collaboration Pathway: Engineering Precision for Industrial Entrance Matting
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the intersection of polymer science and industrial manufacturing, delivering engineered rubber solutions that meet rigorous performance thresholds for commercial entrance systems. Our proprietary rubber formulations undergo accelerated lifecycle testing to ensure compliance with ASTM F1637 standards for slip resistance, debris retention, and structural integrity under high-traffic conditions. As your OEM partner, we integrate material science with scalable production—transforming technical specifications into certified, field-tested products.
Material performance is non-negotiable in high-wear applications. Our vulcanized rubber compounds utilize zinc oxide-activated sulfur systems for optimal cross-link density, balancing Shore A hardness with flexural fatigue resistance. Below details core specifications validated through third-party laboratory analysis:
| Property | Test Standard | Performance Range | Industrial Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 75–85 | Optimal debris scraping without surface damage |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | 18–22 MPa | Resists tearing under foot traffic shear |
| Abrasion Loss (Taber) | ASTM D1044 | ≤ 85 mg/1000 cycles | Ensures 5+ year tread life in >5,000 daily entries |
| Compression Set (22h) | ASTM D395 | ≤ 18% | Maintains sealing integrity against door sweeps |
These metrics are not theoretical benchmarks but production-floor guarantees. Our Suzhou facility employs closed-mixing Banbury systems with ±0.5°C thermal control, ensuring batch-to-batch repeatability critical for global OEM supply chains. We support clients from prototype validation through to JIT delivery, with mold development lead times averaging 22 working days for custom extrusion profiles. Quality assurance protocols include in-line spectrometry for polymer consistency and quarterly ISO 17025-certified audits.
Initiate technical collaboration by contacting Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Engineering Liaison. With 14 years of specialized experience in polymer formulation for architectural rubber products, he will coordinate your material dossier review, tolerance analysis, and production feasibility assessment. Provide your target performance criteria—such as UV stability requirements for coastal installations or chemical resistance for industrial facilities—and we will engineer a compound meeting exact ISO 9001:2015 and REACH compliance frameworks.
Direct all technical inquiries, CAD specifications, or volume forecasts to [email protected]. Include reference code SD-MAT-2024 to expedite material compatibility analysis. Mr. Boyce schedules engineering consultations within 48 business hours, ensuring rapid transition from inquiry to production validation. For urgent project timelines, specify required delivery milestones in your initial correspondence to activate our accelerated prototyping workflow.
Suzhou Baoshida does not manufacture generic mats—we solve material failure points. Contact us to convert your performance specifications into engineered reality.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
