Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Channel Weather Stripping
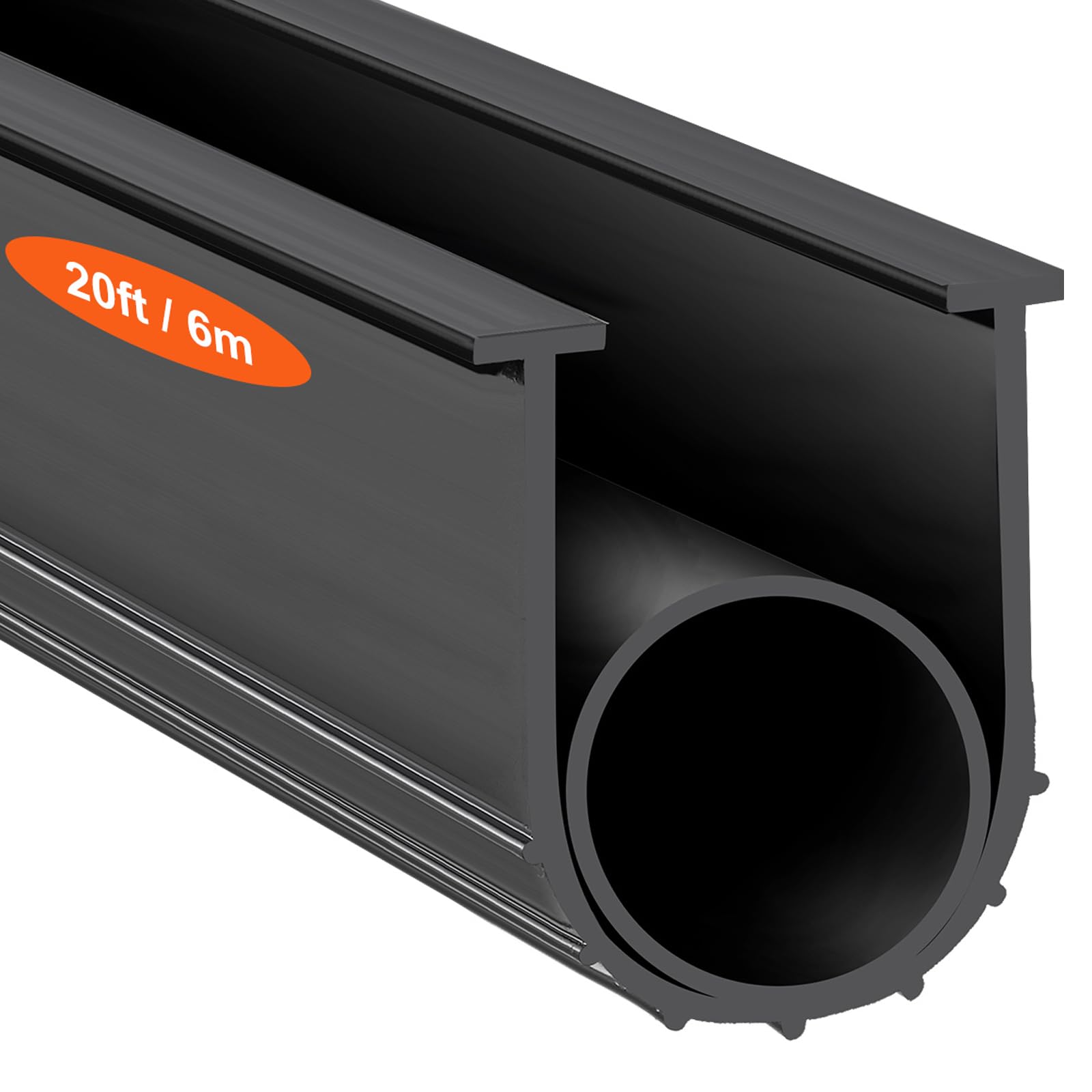

Engineering Insight: The Critical Role of Material Selection in Channel Weather Stripping
In industrial sealing applications, channel weather stripping serves as a vital interface between structural components, ensuring environmental integrity, noise reduction, and energy efficiency. Despite its seemingly simple function, the performance of a channel seal is deeply dependent on precise material selection—a factor often overlooked when off-the-shelf solutions are deployed without engineering evaluation. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize that generic rubber profiles fail not due to inherent design flaws, but because of mismatched material properties relative to operational demands.
Standard channel seals are typically manufactured using low-cost EPDM or recycled rubber compounds. While these materials offer baseline weather resistance, they lack the consistency, compression set resistance, and long-term resilience required in demanding environments. For instance, in automotive assembly lines or high-speed rail systems, fluctuating temperature ranges (-40°C to +120°C), exposure to UV radiation, ozone, and repeated mechanical stress rapidly degrade suboptimal elastomers. This leads to premature cracking, loss of sealing force, and ultimately, system failure.
Material selection must be application-driven. A seal operating in a coastal infrastructure project faces constant salt spray and humidity, demanding superior resistance to hydrolysis and marine corrosion. Conversely, seals in industrial ovens must endure prolonged thermal cycling without hardening or outgassing. Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in high-temperature applications, while chloroprene (CR) offers balanced resistance to oil, flame, and weathering. For dynamic sealing under compression, thermoplastic polyolefin (TPO) or ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) with controlled cross-link density provides optimal recovery characteristics.
Furthermore, durometer (hardness) and density must be engineered in tandem with material chemistry. A 60 Shore A EPDM may perform well in static glazing applications but fail in high-cycle door mechanisms where lower compression set and higher elasticity are required. Off-the-shelf profiles often standardize hardness without accounting for load distribution or mating surface tolerances, resulting in uneven sealing pressure and leakage paths.
At Baoshida, we apply OEM-level material science to custom-formulate compounds tailored to service conditions. Our engineered solutions integrate accelerated aging tests, finite element analysis (FEA) for compression behavior, and real-world validation under simulated operational loads.
The following table outlines key material properties for common elastomers used in channel weather stripping:
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Compression Set (%) @ 70°C, 22h | Key Advantages | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | -50 to +150 | 50–80 | ≤20 | Excellent ozone & UV resistance | Building facades, rail vehicles |
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 to +200 | 40–70 | ≤15 | High thermal stability, low compression set | Industrial ovens, cleanrooms |
| Chloroprene (CR) | -40 to +100 | 50–75 | ≤25 | Flame retardant, oil resistant | Marine, electrical enclosures |
| TPO | -40 to +110 | 60–90 | ≤10 | High resilience, recyclable | Automotive doors, windows |
Material selection is not a commodity decision—it is a precision engineering requirement. By moving beyond off-the-shelf profiles and embracing application-specific formulation, manufacturers ensure longevity, compliance, and system reliability.
Material Specifications
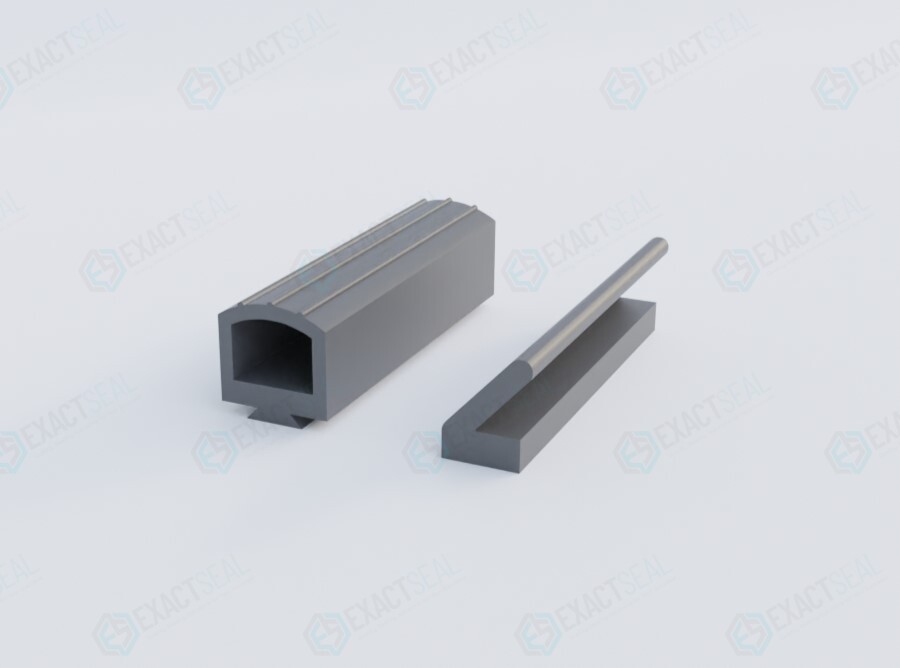

Material Specifications for Channel Weather Stripping
Selecting the optimal elastomer for channel weather stripping is critical for ensuring long-term sealing integrity across automotive, aerospace, and construction applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our formulations prioritize resistance to environmental degradation, mechanical stress, and fluid exposure while maintaining consistent compression set performance. This section details three primary materials engineered for demanding channel profiles: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each compound undergoes rigorous ASTM D2000 validation to meet OEM-specific hardness, tensile strength, and elongation requirements. Material selection directly influences service life, particularly in dynamic sealing interfaces where thermal cycling, UV exposure, and chemical contact accelerate failure.
Viton fluorocarbon compounds excel in extreme temperature and aggressive chemical environments. With a continuous service range of -20°C to 230°C, Viton maintains resilience against fuels, oils, and ozone—critical for under-hood automotive channels. Its low gas permeability prevents fluid ingress, though higher material costs necessitate strategic application in high-value systems. Nitrile rubber offers an optimal balance for cost-sensitive applications requiring oil and fuel resistance. Operating effectively from -40°C to 120°C, NBR demonstrates superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength (15–25 MPa), making it ideal for door and window channels in standard vehicles. However, its vulnerability to ozone cracking and limited high-temperature stability requires protective additives in UV-exposed installations. Silicone rubber provides unmatched flexibility across ultra-broad temperatures (-60°C to 200°C) and exceptional UV/ozone resistance. While its lower tensile strength (6–10 MPa) demands careful profile design, VMQ is indispensable for architectural glazing and EV battery enclosures where thermal expansion cycles exceed conventional limits. All compounds are engineered with controlled compression set (<25% per ASTM D395) to prevent permanent deformation after prolonged compression.
The comparative analysis below outlines key performance metrics for OEM qualification:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -40 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Shore A Hardness Range | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 10–20 | 15–25 | 6–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–300 | 200–500 | 200–700 |
| Fuel Resistance | Excellent | Good to Excellent | Poor |
| Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
| Compression Set (22h/150°C) | <20% | <30% | <25% |
Material choice must align with the channel’s operational envelope. Viton is non-negotiable for turbocharger housings or fuel system gaskets, while NBR dominates cost-driven body assembly lines. Silicone becomes essential when thermal stability spans arctic to desert climates. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides custom compound adjustments—such as peroxide-cured NBR for enhanced heat resistance or reinforced Viton for extrusion stability—to match your channel geometry and lifecycle targets. Our technical team collaborates with OEMs to validate material performance against ISO 1817 fluid immersion tests and SAE J200 aging protocols, ensuring zero field failures in serial production. Precision in material science translates directly to sealing reliability; we engineer beyond datasheets to deliver failure-proof solutions.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering capability in industrial rubber solutions is anchored in a team of highly specialized professionals dedicated to precision, durability, and performance. Our core strength lies in a dedicated technical team comprising five experienced mould engineers and two advanced formula engineers, all focused on delivering optimized channel weather stripping solutions tailored to OEM specifications. This integrated expertise allows us to maintain full control over both the material science and structural design aspects of rubber component manufacturing.
Our mould engineers possess extensive experience in precision tooling design for EPDM, silicone, and thermoplastic rubber (TPR) extrusion and molding processes. They utilize advanced CAD/CAM software and conduct rigorous tolerance analysis to ensure dimensional accuracy, sealing integrity, and long-term durability under variable environmental conditions. Each mould is engineered to support high-volume production while maintaining consistency across batches, a critical requirement for automotive, construction, and transportation OEMs.
Complementing this structural expertise are our two in-house rubber formula engineers, who specialize in polymer chemistry and compound development. They formulate custom elastomer blends that meet specific performance criteria such as UV resistance, ozone stability, low-temperature flexibility, compression set, and flame retardancy. By controlling the compounding process internally, we ensure consistent raw material quality and the ability to rapidly iterate formulations in response to client demands or regulatory changes.
This synergy between mould design and material formulation enables Suzhou Baoshida to offer true OEM manufacturing capabilities. We support clients from concept to量产 (mass production), providing prototyping, DFM (Design for Manufacturability) feedback, and full validation testing. Our engineering team collaborates directly with OEM design departments to ensure seamless integration of channel weather stripping into final assemblies, minimizing fitment issues and reducing time-to-market.
We are equipped to produce complex cross-sectional profiles with tight tolerances, multi-material co-extrusions, and inserts for enhanced structural support. All products are developed in compliance with international standards, including ISO 9001, ASTM D2000, and automotive OEM specifications such as GMW, Ford, and VW standards.
The following table outlines key technical specifications supported by our engineering team:
| Parameter | Capability |
|---|---|
| Material Types | EPDM, Silicone, TPR, Neoprene, CR |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 40–90 ±5 |
| Temperature Resistance | -50°C to +150°C (up to +200°C for silicone) |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 15 MPa (EPDM) |
| Elongation at Break | Up to 500% |
| Compression Set (24h @ 70°C) | ≤25% |
| Mould Tolerance | ±0.1 mm for critical sealing zones |
| Production Volume | Low-volume prototyping to high-volume OEM runs |
Through a combination of advanced material science, precision engineering, and deep OEM collaboration, Suzhou Baoshida delivers channel weather stripping solutions engineered for performance, reliability, and scalability.
Customization Process
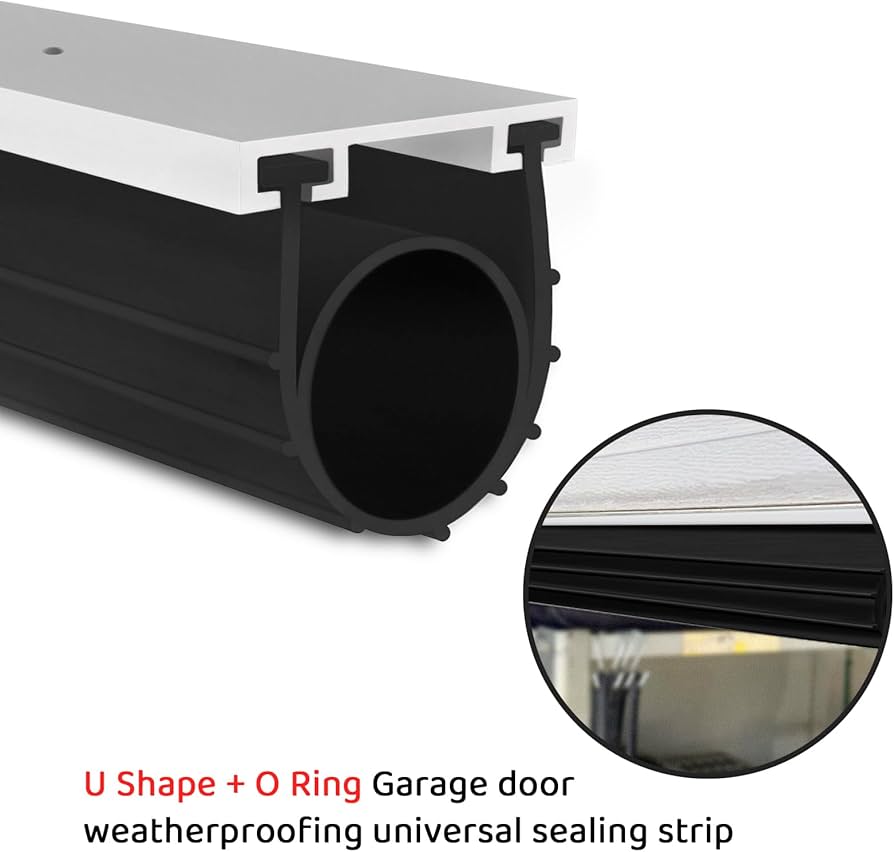

Customization Process for Channel Weather Stripping
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our channel weather stripping customization follows a rigorously defined sequence to ensure dimensional accuracy, material performance, and seamless integration into client assemblies. This process begins with Drawing Analysis, where engineering teams dissect CAD models and technical specifications provided by OEMs. Critical attention is paid to geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T), cross-sectional profiles, insertion forces, and interface requirements with mating surfaces. We validate sealing contact pressure zones and assess potential stress concentrations under dynamic compression cycles. Any ambiguities in tolerances or material callouts are resolved through direct technical consultation with the client before progression.
The Formulation phase leverages Baoshida’s 15+ years of polymer expertise to engineer compounds meeting exact environmental and mechanical demands. We prioritize base polymer selection—typically EPDM for automotive exteriors due to ozone/UV resistance or TPE for lightweight interior applications—then calibrate filler systems, plasticizers, and curatives. Key parameters include Shore A hardness (55–85 range), compression set resistance (<30% @ 100°C/22h), and low-temperature flexibility. All formulations undergo ASTM D2000 classification validation to guarantee compliance with industry-grade material specifications.
Prototyping utilizes precision extrusion dies cut to final dimensions, followed by thermoset vulcanization or thermoplastic calibration. Each prototype batch undergoes accelerated aging (SAE J2236), dynamic fatigue testing (10,000+ cycles), and adhesion validation to substrate materials. Dimensional verification via CMM ensures conformity to ±0.15mm tolerances. Clients receive test reports detailing force-deflection curves, thermal cycling results (-50°C to +150°C), and chemical resistance against fuels, wipers, and road salts. Iterations are minimized through this data-driven validation loop.
Mass Production commences only after client sign-off on prototypes. Baoshida implements statistical process control (SPC) monitoring extrusion line temperature profiles, cure state (via moving die rheometer), and dimensional stability. Every production lot undergoes 100% visual inspection and batch sampling for physical property verification. Our ISO/TS 16949-certified facility maintains traceability from raw material lot numbers to finished goods, ensuring zero-defect delivery at volumes exceeding 500,000 meters monthly.
Critical Material Specifications for Channel Weather Stripping
| Property | Test Standard | EPDM Typical Value | TPE Typical Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 65 ± 5 | 70 ± 5 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥10 MPa | ≥8 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥250% | ≥300% |
| Compression Set (22h) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% @ 100°C | ≤35% @ 100°C |
| Low-Temperature Flex | ASTM D1329 | -50°C (pass) | -40°C (pass) |
| Heat Aging (70h) | ASTM D573 | ΔTensile ≤20% | ΔTensile ≤25% |
This end-to-end workflow ensures channel weather stripping solutions that achieve leak-proof sealing, longevity exceeding 10-year service life, and full compliance with global automotive and industrial standards. Baoshida’s engineering partnership model eliminates guesswork through quantifiable material science and precision manufacturing.
Contact Engineering Team
For industrial manufacturers seeking precision-engineered rubber solutions, Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. stands as a trusted partner in the development and supply of high-performance channel weather stripping products. With years of expertise in rubber formulation, extrusion technology, and OEM collaboration, we deliver weather stripping solutions tailored to meet the rigorous demands of automotive, construction, transportation, and appliance industries. Our commitment to material science excellence and process consistency ensures that every meter of channel profile meets exact dimensional, sealing, and durability requirements.
Channel weather stripping plays a critical role in preventing air, water, dust, and noise infiltration across panel joints and access points in industrial and consumer applications. At Suzhou Baoshida, we specialize in custom EPDM, silicone, and thermoplastic rubber (TPR) formulations designed for long-term resilience under extreme temperatures, UV exposure, and mechanical stress. Our engineering team works closely with clients to optimize cross-sectional geometry, durometer hardness, compression set resistance, and adhesion properties for both functional performance and ease of installation.
Our manufacturing infrastructure integrates computer-aided design (CAD), precision die tooling, continuous vulcanization (CV) lines, and rigorous inline quality monitoring to ensure batch-to-batch consistency. Whether you require standard profiles or fully customized channel designs with integrated sealing lips, foam cores, or metal inserts, we provide scalable production with tight tolerances and full traceability.
To support global OEMs and tier suppliers, we offer comprehensive technical documentation, material certification (including RoHS and REACH compliance), and on-site engineering support where applicable. Our agile supply chain enables efficient prototyping, rapid tooling, and just-in-time delivery to manufacturing hubs across Asia, Europe, and North America.
The following table outlines typical technical specifications for our standard channel weather stripping profiles. All parameters are adjustable based on client requirements and application environments.
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Material | — | EPDM, Silicone, TPR |
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 40–80 ±5 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥8 MPa (EPDM) |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥250% |
| Compression Set (22 hrs, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% |
| Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +150°C (EPDM) |
| Color Options | — | Black, Gray, Custom (Pantone Match) |
| Standard Lengths | — | 10m, 25m, 50m spools |
| Custom Features | — | Metal Insert, Adhesive Backing, Foam Core |
For technical inquiries, custom formulation support, or sample requests, contact Mr. Boyce, Rubber Formula Engineer and OEM Manager, directly at [email protected]. Please include your project specifications, volume requirements, and target application to ensure a precise and timely response. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. is committed to accelerating your product development with scientifically grounded rubber solutions and responsive engineering partnership.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
