Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Chemical Resistant O Rings

Engineering Insight Chemical Resistant O Rings Material Selection as Critical Failure Prevention
Chemical exposure represents the primary cause of premature O ring degradation in industrial sealing applications. Off-the-shelf elastomer seals frequently fail under chemical stress due to generic material formulations that ignore specific fluid compatibility requirements. Standard Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) O rings, for example, exhibit catastrophic swelling and loss of mechanical integrity when exposed to ketones or chlorinated solvents—common in chemical processing and semiconductor manufacturing. This failure mode directly compromises system integrity, leading to leaks, environmental hazards, and costly unplanned downtime. Material selection is not a secondary consideration; it is the foundational engineering parameter determining seal longevity and safety.
The polymer backbone chemistry dictates resistance mechanisms. Fluorocarbon elastomers (FKM) leverage high fluorine content to create inert molecular structures resistant to aggressive chemicals like acids, fuels, and hydraulic fluids. However, even within FKM families, variations in vinylidene fluoride/hexafluoropropylene ratios significantly alter performance against specific compounds. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) excels in water-glycol and alkali environments but fails rapidly with petroleum-based fluids due to its saturated hydrocarbon chain. Selecting a material requires analyzing the exact chemical composition, concentration, temperature, and exposure duration—not merely matching to a broad fluid category. Generic O rings often use cost-optimized base polymers without tailored additives for chemical stability, accelerating oxidative degradation and compression set.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. mitigates these risks through application-specific elastomer engineering. Our OEM process begins with fluid compatibility analysis against ASTM D471 and ISO 1817 standards, followed by custom formulation adjustments. Below is a comparative specification guide for common chemical-resistant elastomers under typical industrial conditions:
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Chemical Resistances | Critical Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| FKM (Standard) | -20 to +200 | Fuels, oils, acids, hydraulic fluids | Poor resistance to ketones, amines, low-temperature flexibility |
| FFKM (Perfluoroelastomer) | -15 to +327 | All acids, solvents, steam, plasma | High cost, limited low-temp performance below -15°C |
| EPDM | -50 to +150 | Water, steam, alkalis, brake fluids | Swells severely in petroleum oils, hydrocarbons |
Off-the-shelf solutions fail because they prioritize inventory simplicity over chemical physics. A seal functioning adequately in one fluid system may disintegrate in another with chemically similar but structurally distinct compounds. For instance, standard FKM tolerates methanol but degrades in methylene chloride due to differing molecular polarity interactions. Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM approach integrates fluid analysis, dynamic seal motion requirements, and accelerated aging tests to formulate compounds with optimized crosslink density and filler systems. This precision engineering ensures molecular stability where generic seals succumb to chain scission or plasticization.
Ultimately, chemical resistance is non-negotiable in critical sealing applications. Investing in application-engineered O rings eliminates the false economy of off-the-shelf alternatives, preventing seal-related failures that incur exponentially higher operational costs. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers this precision through rigorous material science protocols, transforming chemical resistance from a vulnerability into a reliable engineering parameter.
Material Specifications

Chemical resistant O-rings are critical sealing components in industrial applications where exposure to aggressive media, elevated temperatures, or harsh environmental conditions is prevalent. Selecting the appropriate elastomer is essential to ensure long-term reliability, safety, and performance. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision rubber seals engineered to meet stringent OEM and industrial requirements. Our core materials—Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ)—each offer distinct performance characteristics tailored to specific chemical and thermal environments.
Viton (fluorocarbon rubber) is widely recognized for its exceptional resistance to a broad spectrum of chemicals, including hydrocarbons, acids, oils, and fuels. It performs reliably across a wide temperature range, typically from -20°C to +200°C, with short-term exposure tolerance up to 250°C. This makes Viton ideal for aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing applications where both chemical inertness and thermal stability are paramount. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics further enhance seal longevity in demanding systems.
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a cost-effective solution for applications involving petroleum-based oils, aliphatic hydrocarbons, and hydraulic fluids. With a standard operating temperature range of -30°C to +100°C (extendable to +125°C briefly), NBR offers strong abrasion resistance and mechanical durability. While it exhibits limited resistance to polar solvents, ozone, and UV exposure, NBR remains a preferred choice for general-purpose industrial seals, especially in hydraulic and pneumatic systems where cost efficiency and oil resistance are key considerations.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature environments, functioning effectively from -60°C to +200°C. It demonstrates good resistance to water, oxygen, and certain acids and alkalis, though it is not recommended for use with hydrocarbons or aromatic solvents. Silicone’s biocompatibility, low toxicity, and excellent electrical insulation properties make it suitable for pharmaceutical, food-grade, and medical applications, as well as in electronics and high-temperature insulation systems.
The selection of the appropriate material must consider not only chemical compatibility but also mechanical stress, compression set, and dynamic sealing requirements. All materials undergo rigorous quality control and testing to ensure compliance with international standards.
Below is a comparative summary of key physical and chemical properties:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +200 | -30 to +100 | -60 to +200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Compression Set (22 hrs, 150°C) | Low | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Acids | Excellent | Fair | Fair |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Common Applications | Aerospace, Chemical Processing, Automotive | Hydraulics, Pneumatics, General Industry | Medical, Food, Electronics, High-Temp Seals |
Material selection directly impacts seal performance and system integrity. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides technical support to ensure optimal material pairing for your specific operational demands.
Manufacturing Capabilities
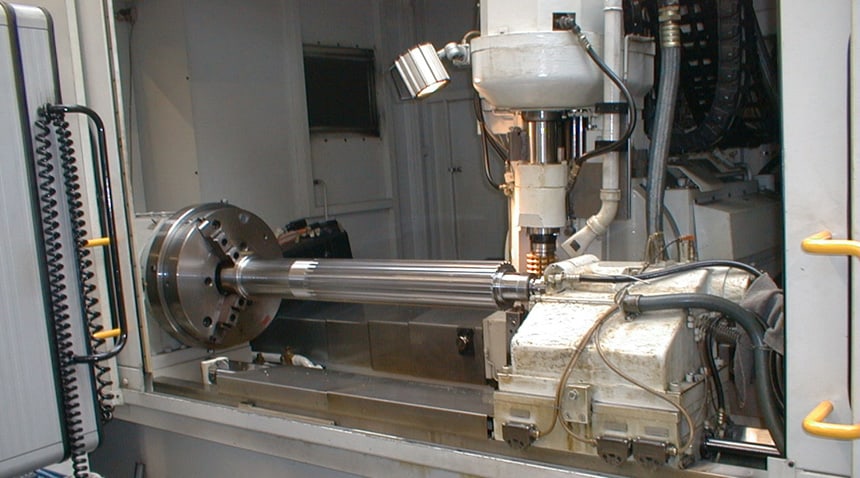
Advanced Engineering Capability for Chemical Resistant O Rings
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep technical expertise to deliver mission-critical chemical resistant O rings for demanding industrial applications. Our engineering team comprises five dedicated Mould Engineers and two specialized Rubber Formula Engineers, ensuring end-to-end precision from molecular design to finished component. This integrated structure eliminates silos between material science and manufacturing, directly translating chemical resistance requirements into optimized physical performance.
Our Formula Engineers focus on molecular crosslink density optimization and polymer backbone selection to achieve superior resistance against aggressive media. Through systematic co-agitation of fillers, curatives, and specialty additives, we develop custom elastomer compounds that maintain integrity in continuous exposure to acids, bases, solvents, and hydrocarbons. Each formulation undergoes accelerated aging tests per ASTM D471 and ISO 1817, with iterative refinement based on swelling, tensile retention, and compression set data. This rigorous protocol ensures compounds exceed standard NBR or EPDM limitations, particularly in mixed-fluid environments common in semiconductor processing and chemical transfer systems.
Complementing material innovation, our Mould Engineering team applies advanced cavity pressure analysis and thermal simulation to eliminate flash, knit lines, and cure inconsistencies. Precision ground tooling with tolerances held to ±0.025 mm guarantees dimensional stability across all durometer ranges. Critical for chemical resistance, this precision ensures uniform cross-section compression and consistent sealing force—preventing extrusion or stress relaxation during thermal cycling. Finite element analysis validates flow dynamics for complex geometries, while in-process rheometry monitors cure state in real time.
OEM collaboration is embedded in our engineering workflow. We partner with clients during R&D to co-develop application-specific compounds, sharing full material traceability from raw polymer batches to final certification. Our technical team provides DFMEA support, fluid compatibility matrices, and accelerated life testing protocols tailored to the client’s operational profile. This proactive OEM integration reduces time-to-market by 30% while mitigating field failure risks in critical sealing applications.
The following table summarizes key performance metrics for our standard chemical resistant compounds under controlled test conditions:
| Chemical Medium | Temperature Range | Max Swell (%) | Hardness Change (Shore A) | Tensile Retention (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 98% Sulfuric Acid | -20°C to +100°C | ≤ 8 | ±3 | ≥ 85 |
| 50% Sodium Hydroxide | -30°C to +120°C | ≤ 6 | ±2 | ≥ 90 |
| Toluene | -10°C to +80°C | ≤ 12 | ±4 | ≥ 75 |
| Hydraulic Fluid (MIL-PRF-5606) | -40°C to +150°C | ≤ 10 | ±3 | ≥ 80 |
| 30% Hydrogen Peroxide | -20°C to +90°C | ≤ 5 | ±2 | ≥ 95 |
All data reflects 72-hour immersion per ASTM D471 at maximum temperature. Custom formulations extend these parameters for niche applications. Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering synergy between chemistry and precision manufacturing delivers chemically inert, dimensionally stable O rings where failure is not an option. We provide full technical documentation, including material safety data sheets and OEM-specific validation reports, ensuring seamless integration into your critical systems.
Customization Process

Chemical Resistant O-Ring Customization Process
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our customization process for chemical resistant O-rings is engineered for precision, reliability, and performance under extreme industrial conditions. We follow a structured workflow that ensures every seal meets the exact chemical, thermal, and mechanical demands of the application. The process begins with Drawing Analysis, proceeds through material Formulation, advances to Prototyping, and culminates in Mass Production.
The first phase, Drawing Analysis, involves a detailed technical review of customer-provided specifications. We assess dimensional tolerances per ISO 3601 or AS568 standards, surface finish requirements, groove design, and operational parameters such as pressure, temperature, and dynamic/static movement. This step ensures compatibility between the proposed O-ring geometry and the sealing environment. Our engineering team collaborates directly with OEMs to validate critical sealing zones and identify potential risks such as extrusion gaps or compression set.
Following drawing validation, we proceed to Formulation. This is where our expertise in rubber chemistry becomes critical. Based on the chemical exposure profile—such as acids, bases, solvents, or hydrocarbons—we select the optimal polymer matrix. Common base materials include FKM (Viton®), EPDM, PTFE, FFPM (Perfluoroelastomer), and NBR, each offering distinct resistance profiles. Our in-house compounding laboratory tailors the formulation with specific additives to enhance chemical inertness, thermal stability, and compression resistance. For example, high fluorine-content FKM is used for aggressive hydrocarbon environments, while peroxide-cured EPDM is selected for steam and ozone resistance.
Once the formulation is finalized, we move to Prototyping. Using precision molding techniques—compression, transfer, or injection—we produce small-batch samples for validation testing. These prototypes undergo rigorous evaluation, including immersion testing in target media at elevated temperatures, durometer stability checks, and dynamic sealing performance under simulated service conditions. All test data is documented and shared with the client for approval.
Upon successful prototype validation, we initiate Mass Production. Our automated production lines ensure consistent quality, with 100% visual inspection and statistical dimensional sampling per AQL standards. We support high-volume OEM supply chains with JIT delivery and full traceability, including batch-specific certificates of conformance and material test reports.
The following table outlines key material options and their chemical resistance profiles:
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Chemical Resistances | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| FKM (Viton®) | -20 to +230 | Hydrocarbons, oils, acids, fuels | Automotive, aerospace, oil & gas |
| EPDM | -50 to +150 | Steam, water, alkalis, ketones | HVAC, pharmaceutical, water treatment |
| PTFE | -200 to +260 | All industrial chemicals, solvents | Semiconductor, chemical processing |
| FFPM | -15 to +327 | Extreme acids, amines, halogens | Petrochemical, semiconductor |
| NBR | -30 to +100 | Oils, greases, aliphatic hydrocarbons | Hydraulics, machinery |
This systematic approach ensures that every chemical resistant O-ring we deliver is not only dimensionally accurate but chemically optimized for long-term performance in demanding industrial environments.
Contact Engineering Team
Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Chemical Resistant O-Ring Solutions
Industrial environments demand uncompromising seal integrity when exposed to aggressive chemicals, extreme temperatures, and high pressures. Standard elastomers often fail catastrophically under such conditions, leading to costly downtime, safety hazards, and environmental compliance risks. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we engineer chemical resistant O-rings using advanced polymer science and rigorous OEM validation protocols. Our formulations target specific chemical degradation pathways, ensuring long-term performance where conventional seals deteriorate. Whether your application involves concentrated acids, hydrocarbons, ozone, or mixed chemical baths, our team leverages decades of compound development expertise to deliver seals that maintain resilience under duress.
We prioritize technical collaboration over transactional sales. Our engineering team works directly with your R&D and procurement departments to analyze fluid compatibility, stress-strain requirements, and regulatory constraints. This includes reviewing chemical exposure profiles, temperature cycling data, and mechanical load specifications to select or develop the optimal elastomer matrix. All compounds undergo accelerated aging tests per ASTM D2000 and ISO 3601 standards, with full traceability from raw material sourcing to final molding. For critical applications, we provide comprehensive validation dossiers including compression set data, volume swell reports, and chemical resistance matrices.
The table below summarizes key performance characteristics of our most deployed chemical resistant compounds. These values represent typical results under controlled laboratory conditions; actual field performance requires application-specific validation.
| Material Type | Continuous Temp Range (°C) | Key Chemical Resistances | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Compression Set (ASTM D395, 70h @ 150°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FKM (Standard) | -20 to 200 | Fuels, oils, acids, steam | 60–90 | ≤ 25% |
| FFKM (Perfluoroelastomer) | -15 to 325 | Strong acids, bases, solvents, plasma | 65–85 | ≤ 15% |
| EPDM (Peroxide Cured) | -50 to 150 | Water, steam, alkalis, ketones | 50–80 | ≤ 20% |
| Aflas® (TFE/P) | -20 to 200 | Amines, acids, hot water | 60–80 | ≤ 30% |
Suzhou Baoshida operates under strict ISO 9001-certified manufacturing controls, with cleanroom molding facilities and real-time process monitoring. Our O-rings consistently meet aerospace (AS568), automotive (SAE AS8000), and semiconductor (SEMI F57) dimensional tolerances. For custom formulations, we utilize DOE-driven compound optimization to balance chemical resistance with mechanical properties like tensile strength and elongation.
Initiate a technical dialogue with our OEM Engineering Manager, Mr. Boyce, to resolve your specific sealing challenge. Provide your chemical exposure matrix, operating parameters, and failure history for a targeted compound recommendation. Mr. Boyce will coordinate material testing, prototype validation, and scalable production scheduling within your timeline. Do not settle for generic catalog solutions when chemical resistance is non-negotiable. Contact Mr. Boyce directly at [email protected] to secure engineering support backed by Suzhou Baoshida’s 15-year track record in critical-seal manufacturing. All inquiries receive a technical assessment within 24 business hours.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
