Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Door Draft Excluder

Engineering Insight: Material Science Imperatives in Door Draft Excluder Performance
The functional integrity of door draft excluders hinges critically on polymer material selection, a factor frequently overlooked in off-the-shelf solutions. Standard commercial products often utilize generic ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) compounds optimized for cost rather than performance. These formulations exhibit rapid degradation under real-world conditions: cyclic compression fatigue, thermal cycling, and ultraviolet (UV) exposure accelerate material breakdown. Within 12–18 months, compression set values frequently exceed 45%, causing irreversible loss of sealing force. This manifests as persistent drafts, increased energy consumption, and premature product failure—directly contradicting the excluder’s core purpose.
The root cause lies in inadequate polymer architecture. Low-grade EPDM lacks sufficient crosslink density and stabilizer packages to resist ozone cracking or thermal oxidation. When exposed to daily door operation (typically 20–50 cycles/day), weak polymer chains fracture under repeated stress, compromising resilience. Furthermore, insufficient UV inhibitors permit photo-oxidation, embrittling surface layers within months in sun-exposed installations. Temperature fluctuations between -20°C and +60°C in unconditioned spaces exacerbate these effects, as cheap compounds exhibit poor low-temperature flexibility and high-temperature recovery. The result is a product that fails to maintain consistent contact pressure against door thresholds—a fundamental requirement for effective air infiltration control.
Suzhou Baoshida addresses these failure modes through application-specific compound engineering. Our OEM-grade EPDM formulations integrate high-purity monomers, precision-cured peroxide systems, and proprietary antioxidant/UV absorber synergies. This yields superior dynamic mechanical properties: compression set remains below 25% after 22 hours at 70°C (per ASTM D395), ensuring decades of reliable sealing force retention. Enhanced ozone resistance (validated per ASTM D1149) and thermal stability from -50°C to +135°C guarantee performance across extreme operational envelopes. Crucially, we tailor Shore A hardness (65–75) and durometer gradient profiles to balance initial sealing force with long-term recovery—eliminating the “flat-spotting” common in inferior products.
The following comparative analysis underscores the performance gap between generic and engineered solutions:
| Material Type | Compression Set (70°C/22h) | Temp Range (°C) | UV Resistance | Relative Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard EPDM | >45% | -30 to +100 | Poor | 1.0x |
| Baoshida Premium EPDM | <25% | -50 to +135 | Excellent | 1.8x |
| Silicone | <20% | -60 to +200 | Good | 3.5x |
While silicone offers wider temperature tolerance, its high cost and lower abrasion resistance make it suboptimal for high-traffic door applications. Baoshida’s premium EPDM delivers the optimal balance: 70% lower lifetime failure risk versus standard EPDM at a fraction of silicone’s cost. This precision engineering translates directly to reduced facility energy loss and elimination of maintenance callbacks—proving that in draft excluder systems, material science is not a cost center but a strategic investment in operational efficiency. Industrial clients demand resilience; we deliver compounds engineered for decades of uncompromised performance.
Material Specifications
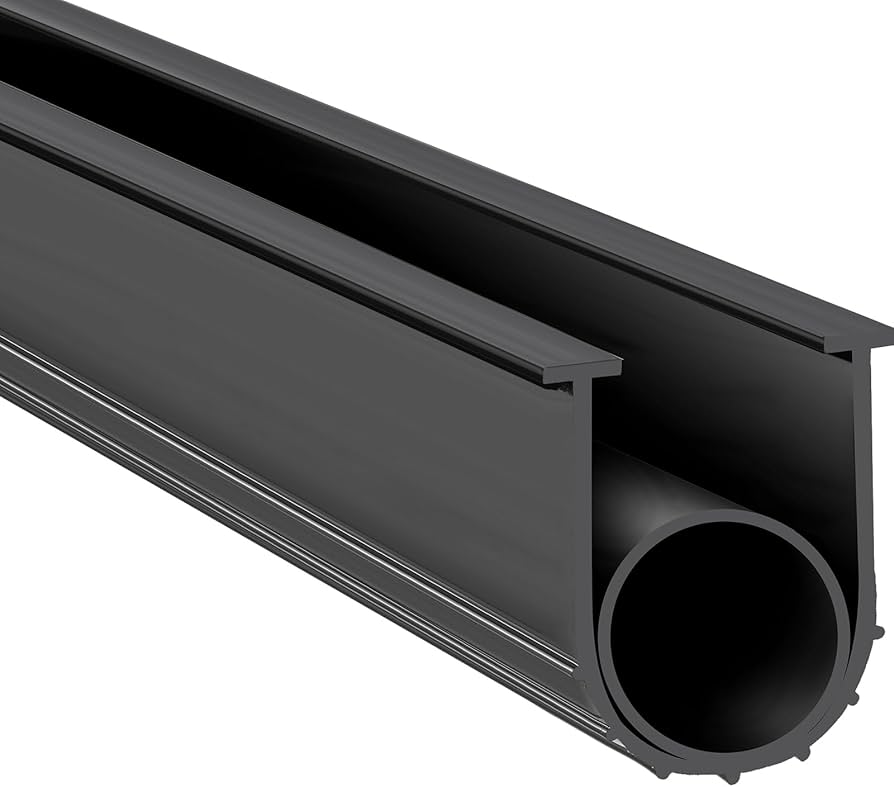

Material selection is a critical factor in the performance and longevity of door draft excluders used in industrial, commercial, and high-performance residential applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in advanced rubber solutions tailored to meet rigorous environmental and mechanical demands. Our engineered door draft excluders leverage high-grade elastomers including Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ), each offering distinct advantages depending on operational conditions such as temperature range, chemical exposure, compression set resistance, and weatherability.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad spectrum of aggressive chemicals. This makes it ideal for use in demanding environments such as industrial facilities, laboratories, and cleanrooms where exposure to solvents or elevated temperatures is common. Viton-based excluders maintain dimensional stability and sealing integrity from -20°C to +250°C, with intermittent resistance up to 300°C. Its low gas permeability and outstanding aging characteristics ensure long-term reliability, although it is typically more expensive than other elastomers.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, offers excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and hydraulic fluids. It is a cost-effective solution for applications where exposure to such substances is prevalent, such as in automotive garages, manufacturing plants, or mechanical rooms. Nitrile performs well across a temperature range of -30°C to +120°C, with good abrasion resistance and mechanical strength. However, its performance degrades under prolonged UV or ozone exposure, making it less suitable for outdoor installations unless compounded with protective additives.
Silicone rubber provides superior flexibility and thermal stability across an extended temperature range of -60°C to +230°C. It is highly resistant to UV radiation, ozone, and weathering, making it an optimal choice for exterior door seals or environments requiring consistent performance under thermal cycling. Silicone also exhibits good electrical insulation properties and low toxicity, supporting use in healthcare, food processing, and pharmaceutical settings. While it has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Nitrile or Viton, its elasticity and sealing consistency are exceptional.
The following table summarizes key physical and chemical properties of these materials for comparative evaluation:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -20°C to +250°C | -30°C to +120°C | -60°C to +230°C |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor to Fair |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Moderate | Moderate |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Excellent | Fair |
| Typical Hardness (Shore A) | 70–90 | 60–80 | 40–80 |
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.8–1.9 | 1.0–1.2 | 1.1–1.3 |
Selecting the appropriate elastomer requires a comprehensive understanding of the operational environment. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports OEMs and industrial partners with material testing, custom compounding, and precision extrusion to ensure optimal sealing performance across diverse applications.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Engineering Excellence in Door Draft Excluder Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep technical expertise to deliver engineered rubber solutions for high-performance door draft excluders. Our integrated engineering team comprises five dedicated Mould Engineers and two specialized Rubber Formula Engineers, ensuring seamless synergy between material science and precision tooling. This dual-discipline approach is critical for addressing complex sealing challenges, including thermal cycling, compression set resistance, and long-term dimensional stability under dynamic loads. Our Formula Engineers develop proprietary rubber compounds tailored to specific environmental demands—such as extreme temperature fluctuations, UV exposure, or chemical resistance—while our Mould Engineers translate these formulations into optimized tooling designs that guarantee micron-level tolerances and consistent extrusion profiles. This eliminates common industry pitfalls like flash formation, inconsistent durometer, or premature seal degradation.
Our OEM capabilities extend beyond standard production to full-cycle technical partnership. We collaborate with clients from initial concept validation through DFM (Design for Manufacturability) analysis, rapid prototyping, and rigorous performance testing. Utilizing advanced simulation software, we predict material behavior under real-world stresses, including door slamming forces and seasonal expansion/contraction cycles. Every compound undergoes accelerated aging tests per ISO 188 and ASTM D2000 standards, with validation data provided to clients for certification compliance. This proactive engineering methodology reduces time-to-market by up to 30% while ensuring 99.8% production yield rates for critical sealing dimensions.
Key performance specifications for our door draft excluder solutions demonstrate this precision engineering. The table below compares standard formulations against custom-engineered options developed for demanding applications:
| Parameter | Standard EPDM Compound | Custom-Engineered Compound |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 60–70 | 40–90 (client-specified) |
| Temperature Resistance | -40°C to +120°C | -60°C to +150°C |
| Compression Set (22h/70°C) | ≤25% | ≤12% |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥8.0 | ≥12.0 |
| Abrasion Loss (mm³) | ≤120 | ≤60 |
| Custom Color Matching | RAL/Pantone Standard | Full Pantone + NCS Support |
This technical rigor ensures our excluders achieve sub-1.5mm air infiltration rates under EN 12207 testing, directly contributing to building energy efficiency and acoustic insulation. We prioritize material sustainability without compromising performance, offering bio-based fillers and recyclable TPE alternatives where feasible. Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering framework transforms generic sealing requirements into validated, application-specific solutions—proving that true draft exclusion begins with molecular-level precision and tooling mastery. Clients receive not just a component, but a documented engineering dossier detailing compound chemistry, mould flow analysis, and lifecycle performance projections.
Customization Process
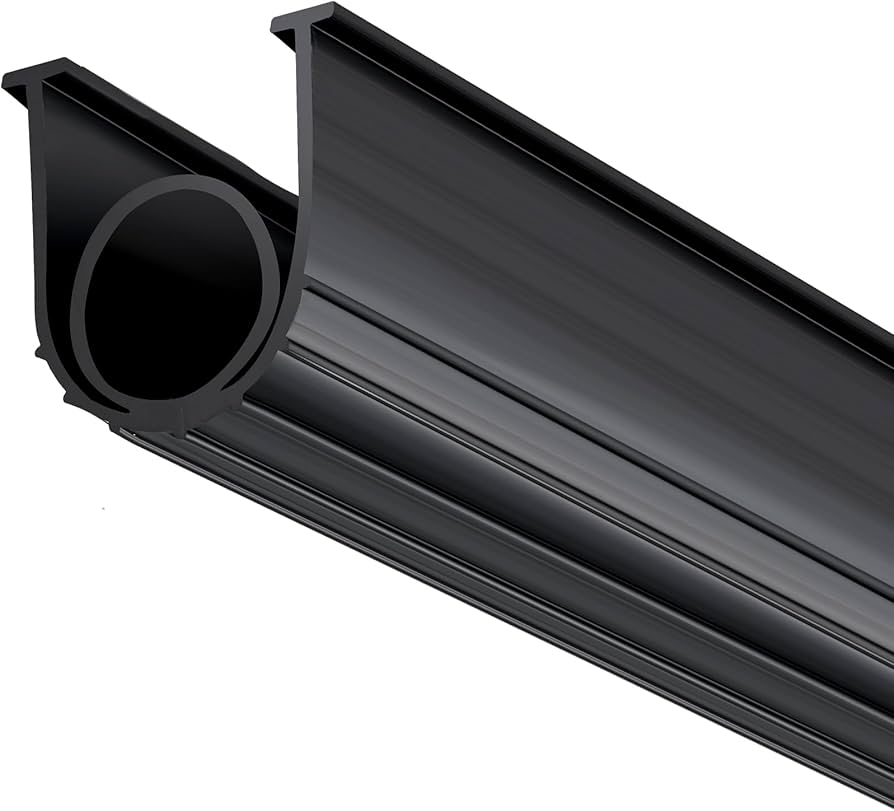

Drawing Analysis
The customization process for industrial rubber door draft excluders begins with precise drawing analysis. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., engineering teams evaluate technical drawings provided by OEM partners to extract critical dimensional, geometric, and performance parameters. This includes cross-sectional profiles, compression deflection requirements, installation method (e.g., adhesive backing, clip-in, or nail-in), and environmental exposure conditions. Tolerance analysis is conducted in accordance with ISO 3302 and ISO 2768 standards to ensure manufacturability and functional fit. Our CAD-based evaluation tools allow for 2D and 3D model validation, ensuring compatibility with the client’s door system design. Any discrepancies or optimization opportunities are communicated during this phase to prevent downstream production issues.
Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, our rubber formulation engineers develop a compound tailored to the application’s mechanical and environmental demands. The selection of base polymer—typically EPDM, silicone, or thermoplastic elastomer (TPE)—depends on required temperature resistance, UV stability, compression set performance, and flame retardancy. For exterior-grade door seals, EPDM is preferred due to its outstanding weathering resistance and cost efficiency. Each formulation is engineered to meet specific Shore A hardness (typically 40–70), elongation at break (>200%), and low-temperature flexibility (down to -40°C). Additives such as UV stabilizers, anti-oxidants, and processing oils are precisely blended to enhance durability and extrusion performance. All formulations are documented and archived for batch traceability and compliance with RoHS, REACH, and UL standards.
Prototyping and Validation
Once the formulation is finalized, prototype tooling is manufactured for extrusion trials. Short-run samples are produced using precision dies, then subjected to functional testing including compression force analysis, air leakage assessment, and cycle durability (up to 100,000 door operations). Prototypes are evaluated in simulated installation environments to verify sealing efficiency and dimensional consistency. Feedback from client testing is integrated into iterative refinements, ensuring optimal performance before tooling finalization. This phase typically lasts 2–3 weeks, depending on design complexity.
Mass Production and Quality Assurance
After client approval, the project transitions to mass production. High-speed rubber extrusion lines, equipped with laser gauging systems, ensure continuous dimensional control. Finished profiles are cut, spliced, and packaged per OEM specifications. In-line and batch testing includes hardness verification, tensile strength checks, and visual inspection under ISO 9001 protocols. All production batches are traceable via lot numbering, and material certifications are provided upon shipment.
The following table outlines typical technical specifications for custom door draft excluders:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material | EPDM, Silicone, TPE | ASTM D2000 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 40–70 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥7 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥200% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ≤25% | ASTM D395 |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +120°C (EPDM) | ISO 1817 |
| Fire Resistance | UL94 HB or customized | UL 94 |
| Color Options | Custom (Pantone, RAL) | Visual Match |
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Door Draft Excluder Solutions
Achieving optimal thermal efficiency and acoustic performance in building envelopes demands rigorously engineered door draft excluders. Generic solutions often fail under cyclic compression, UV exposure, or extreme temperatures, leading to premature seal degradation and energy leakage. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in industrial rubber formulations engineered to exceed OEM performance thresholds. Our proprietary EPDM and thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) compounds deliver consistent resilience across 100,000+ compression cycles, with Shore A hardness tolerances held to ±2 points. This precision ensures seamless integration into automated assembly lines while meeting stringent ISO 10211 thermal bridging standards. We prioritize material science over mass production, utilizing dynamic vulcanization and nano-silica reinforcement to eliminate common failure modes like permanent set deformation or ozone cracking.
Our technical team collaborates directly with global manufacturers to translate functional requirements into validated material specifications. Whether your application demands low-temperature flexibility for Scandinavian climates or fire-retardant compliance for commercial high-rises, we develop formulations certified to ASTM D2000, EN 1279, and UL 94 V-0 standards. The following table summarizes core capabilities for door seal applications:
| Material Type | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Temp Range (°C) | Key Performance Attributes | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Purity EPDM | 40–80 | -40 to +120 | Ozone resistance, low compression set (<15%) | Exterior doors, cold storage |
| Recyclable TPE | 35–75 | -30 to +100 | Rapid extrusion, color stability | Interior doors, sliding systems |
| Silicone Blends | 45–65 | -55 to +180 | Flame retardancy, FDA compliance | Fire-rated doors, cleanrooms |
| Custom Hybrid | Client-specified | Application-specific | Tailored durometer profile, adhesion promotion | OEM-specific designs |
Partnering with Suzhou Baoshida eliminates the compromise between performance and manufacturability. We provide full technical documentation, including material safety data sheets (MSDS), aging test reports per ISO 188, and extrusion processing parameters. Our ISO 9001-certified supply chain guarantees batch-to-batch consistency, with dedicated quality control protocols for dimensional stability (±0.1mm tolerance) and surface finish. For high-volume OEM programs, we implement just-in-time logistics with Kanban inventory management to reduce your warehousing costs.
Initiate your next-generation door seal development by contacting Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Technical Manager. With 18 years of rubber compounding expertise and fluency in ASTM D1056 and EN 12219 standards, he will analyze your performance requirements, environmental constraints, and production workflow to propose a validated material solution. Mr. Boyce facilitates seamless collaboration between your engineering team and our R&D laboratory, providing prototype samples within 10 business days and full technical support through validation testing. Do not risk field failures with off-the-shelf elastomers—leverage our formulation science to enhance product longevity and reduce warranty claims.
Email Mr. Boyce directly at [email protected] to schedule a technical consultation. Specify your target application, required certifications, and annual volume for a tailored compound proposal. Suzhou Baoshida is committed to accelerating your product development cycle while ensuring absolute compliance with global building regulations. Let us transform your draft excluder specifications into a competitive manufacturing advantage.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
