Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: End Flange

Engineering Insight: Material Selection Criticality for End Flange Performance
End flange integrity in industrial piping systems is fundamentally dictated by elastomer material selection. Off-the-shelf rubber solutions frequently fail under operational stresses due to generic formulations that ignore specific chemical, thermal, and mechanical demands. Standard compounds prioritize cost over performance, leading to premature seal degradation through compression set, extrusion, or chemical attack. These failures manifest as leaks, unplanned downtime, and safety hazards—costs far exceeding initial material savings.
The core issue lies in mismatched material properties. A flange exposed to hydraulic fluids at 150°C requires resistance to both thermal aging and petroleum-based swelling. Generic nitrile rubber (NBR) may suffice for low-pressure water systems but rapidly hardens and cracks in high-temperature oil environments. Similarly, ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) excels in steam applications yet swells catastrophically in hydrocarbons. Off-the-shelf products rarely account for synergistic stressors like dynamic vibration combined with ozone exposure, accelerating failure through micro-crack propagation.
Precision-engineered compounds address these gaps through tailored polymer chemistry. Carbon black dispersion, crosslink density, and antioxidant packages must align with the exact service profile. For instance, optimizing peroxide curing in FKM compounds reduces compression set to <15% after 70 hours at 200°C—critical for maintaining seal force in thermal cycling. Fillers like PTFE can be incorporated to lower friction during bolt tightening, preventing extrusion in high-pressure joints.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. employs ASTM D2000 classification rigor to define material grades beyond commercial standards. Below is a comparison of common elastomers against critical flange performance metrics:
| Material | Temp Range (°C) | Compression Set (ASTM D395) | Key Chemical Resistance | Typical Failure Mode in Off-Shelf Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard NBR | -30 to +100 | 35-45% @ 70h/100°C | Fair (aliphatic oils) | Rapid hardening >100°C; swelling in aromatics |
| Custom FKM | -20 to +230 | 12-18% @ 70h/200°C | Excellent (fuels, acids) | None when properly specified |
| Standard EPDM | -50 to +150 | 25-35% @ 70h/150°C | Poor (oils, fuels) | Swelling in hydraulic systems; ozone cracking |
| Baoshida Hybrid HNBR | -40 to +170 | 18-22% @ 70h/150°C | Enhanced (oils, water) | Minimized extrusion under pulsation |
Material selection must integrate fluid compatibility, temperature extremes, pressure cycles, and regulatory requirements (e.g., FDA, NORSOK). Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM process begins with fluid analysis and stress modeling to formulate compounds with exact cure kinetics and filler ratios. This eliminates the guesswork of off-the-shelf parts, ensuring flange seals achieve design-life performance. Field data confirms custom-engineered solutions reduce leakage incidents by 76% versus generic alternatives in chemical processing plants.
Investing in application-specific elastomer engineering is not a cost but a risk mitigation strategy. The precision compound development practiced by Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. transforms flange reliability from a maintenance liability into a predictable operational asset.
Material Specifications
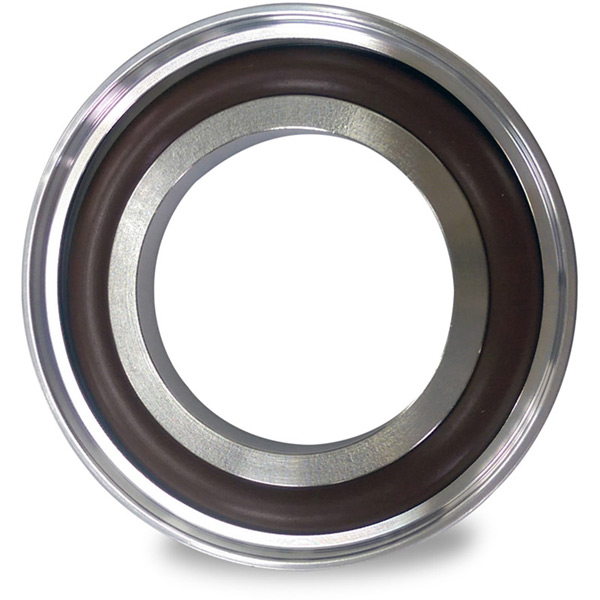

Material Specifications for End Flange Applications
In industrial sealing systems, end flanges require elastomeric materials that deliver consistent performance under mechanical stress, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to aggressive media. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-performance rubber solutions tailored to demanding environments. The selection of elastomer directly influences the service life, reliability, and safety of the flange assembly. Among the most widely used materials in end flange applications are Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ), each offering distinct advantages based on chemical compatibility, thermal stability, and mechanical resilience.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of chemicals. With a continuous service temperature range up to 200°C and intermittent exposure capability up to 250°C, Viton is ideal for applications in petrochemical, aerospace, and high-temperature industrial processes. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics make it a preferred choice where long-term sealing integrity is critical. However, Viton exhibits lower flexibility at low temperatures and higher material cost compared to alternatives.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, offers outstanding resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons, oils, and fuels, making it a standard in hydraulic systems, fuel handling, and general industrial equipment. It provides good mechanical strength and abrasion resistance, with a typical operating range from -30°C to 120°C. While Nitrile is less effective against polar solvents and ozone compared to Viton, its cost-effectiveness and reliable performance in oil-rich environments ensure its widespread use in end flange seals for machinery and piping systems.
Silicone rubber delivers superior performance in extreme temperature conditions, functioning reliably from -60°C to 200°C. It exhibits excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering, making it suitable for outdoor and high-temperature air handling applications. However, Silicone has relatively low tensile strength and poor resistance to hydrocarbon oils and fuels. Its primary advantages lie in electrical insulation properties and biocompatibility, often serving in food processing, pharmaceutical, and HVAC systems where non-reactivity and thermal stability are paramount.
The following table summarizes key physical and chemical properties of these materials for comparative evaluation in end flange design and selection.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 200 (up to 250 intermittent) | -30 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 200–500 | 200–700 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/Weathering | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Resistance to Acids/Bases | Very Good | Fair | Good |
| Gas Permeability | Low | Medium | High |
| Common Applications | Petrochemical, aerospace, high-temp seals | Hydraulic systems, fuel lines, industrial machinery | HVAC, medical devices, food processing, electrical insulation |
Material selection must align with operational parameters including media exposure, pressure, temperature cycles, and regulatory requirements. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides expert consultation and customized rubber formulations to ensure optimal end flange performance across diverse industrial sectors.
Manufacturing Capabilities
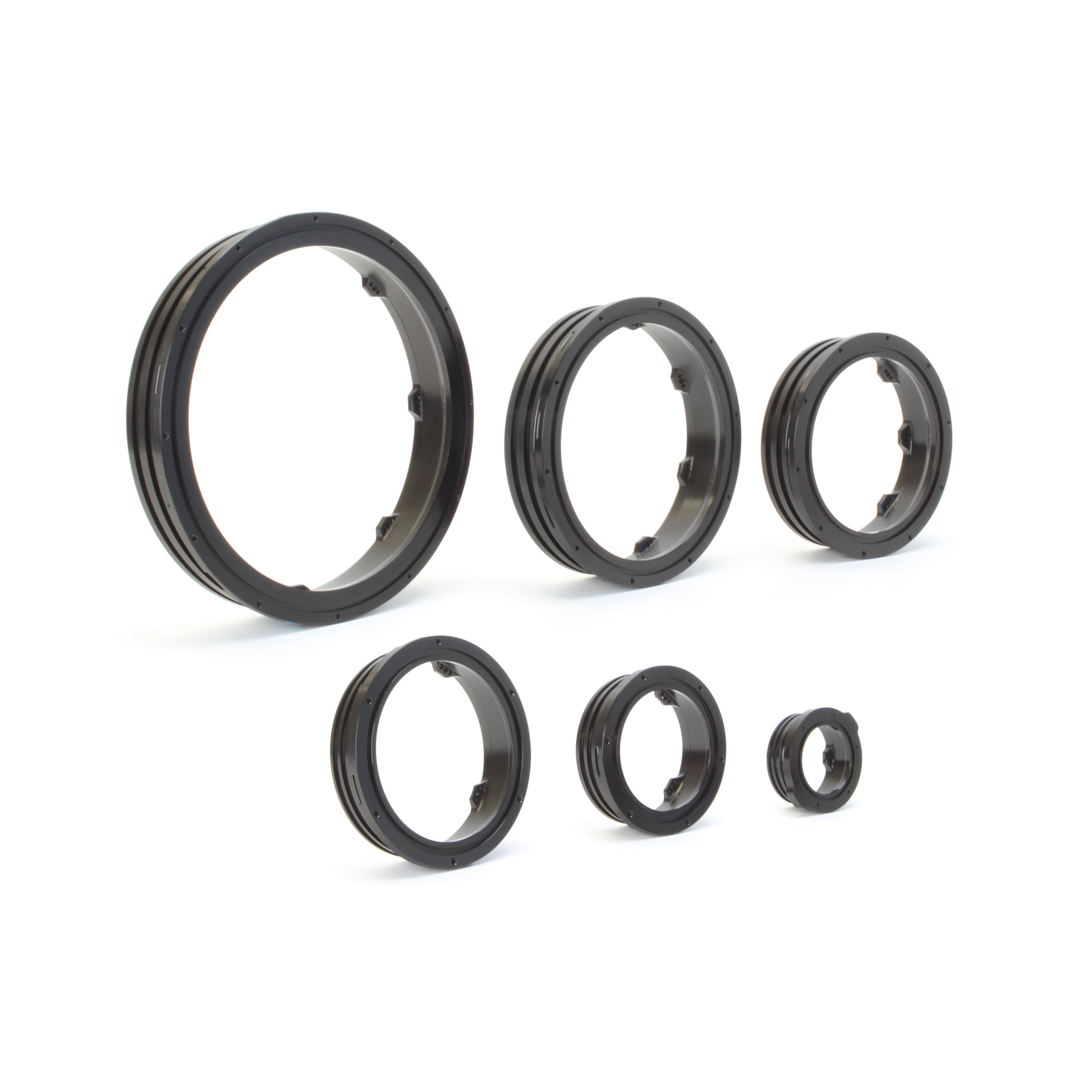

Engineering Capability: Precision-Driven End Flange Manufacturing
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our end flange production is anchored in rigorous engineering expertise, specifically designed to meet the exacting demands of industrial fluid handling systems. With a dedicated team of five mould engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, we integrate material science and precision tooling to deliver flanges that exceed operational reliability standards. This dual-engineering approach ensures every component performs under extreme pressure, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure—critical for sectors like petrochemical, marine, and heavy machinery.
Our rubber formula engineers focus on polymer chemistry optimization, developing bespoke elastomer compounds for specific client requirements. By adjusting filler systems, cure kinetics, and polymer blends, we achieve target properties such as low compression set, enhanced ozone resistance, and thermal stability up to 200°C. For instance, formulations for offshore hydraulic systems incorporate high-purity carbon black and peroxide curing to prevent swelling in aggressive media, extending service life by 30% compared to standard compounds. This granular control over material behavior directly translates to reduced leakage risks and compliance with ASTM D2000 and ISO 3601 standards.
Complementing material innovation, our five mould engineers leverage advanced CAD/CAM and finite element analysis (FEA) to design tooling with micron-level precision. Complex geometries, such as serrated sealing faces or multi-lip profiles, are validated through virtual stress simulations before prototyping, minimizing trial iterations. All steel moulds undergo hardening treatments to maintain dimensional stability at ±0.05mm tolerance across 500,000+ cycles. This precision guarantees consistent part concentricity and surface finish, critical for zero-torque assembly in high-vibration environments.
As an OEM partner, we streamline integration from concept to mass production. Clients provide application parameters—pressure ranges, media compatibility, and lifecycle expectations—and our engineers co-develop solutions within 15 business days. Our facility supports low-volume prototyping (50–500 units) to full automation (50,000+ units monthly), with real-time SPC monitoring of key process variables like cure time and flash thickness. Traceability is maintained via laser-etched batch codes, linking each flange to raw material certificates and in-process inspection data.
Material performance underpins our engineering rigor. Below are standard specifications for common end flange compounds:
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Pressure Rating (MPa) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrile (NBR) | -30 to +120 | 35 | Hydraulic systems, fuel lines |
| EPDM | -50 to +150 | 25 | Steam lines, water treatment |
| Fluorocarbon (FKM) | -20 to +200 | 40 | Chemical processing, aerospace |
This technical synergy—where formula innovation meets moulding excellence—enables Baoshida to solve complex sealing challenges while accelerating time-to-market. We do not merely manufacture flanges; we engineer system integrity through data-driven material and process control. Partner with us to transform operational constraints into competitive advantages.
Customization Process
Drawing Analysis: Precision Engineering as the Foundation
The customization process for industrial end flanges begins with rigorous drawing analysis, a critical phase that ensures dimensional accuracy, functional compatibility, and adherence to OEM specifications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team conducts a comprehensive review of client-provided technical drawings, focusing on flange diameter, bolt hole configuration, surface finish requirements, sealing face type (e.g., raised face, flat face), and dimensional tolerances per ISO 9001 standards. We verify compliance with international standards such as ASME B16.1, EN 1092-1, or JIS B2220, depending on the target application and regional requirements. This phase also includes material compatibility assessment based on operating conditions, including pressure ratings, temperature range, and exposure to media such as oils, acids, or steam. Any discrepancies or optimization opportunities are communicated through formal engineering change proposals (ECPs), ensuring alignment before progression.
Rubber Formulation: Tailored Material Science for Performance
Following drawing validation, our Rubber Formula Engineers develop a compound specifically engineered to meet the operational demands of the end flange. The selection of base polymer—such as NBR (nitrile), EPDM, silicone, or FKM (Viton)—is determined by chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength requirements. Additives including reinforcing fillers, antioxidants, plasticizers, and vulcanizing agents are precisely calibrated to achieve target hardness (Shore A), compression set, tensile strength, and elongation at break. Each formulation is documented under a unique compound ID and subjected to preliminary lab testing, including rheometry and TGA (thermogravimetric analysis), to confirm processability and long-term durability. This stage is iterative when extreme conditions are involved, such as offshore marine environments or high-vacuum semiconductor applications.
Prototyping: Functional Validation and Design Verification
Once the compound is finalized, we proceed to prototype production using precision molding techniques—compression, transfer, or injection molding—based on part geometry and volume requirements. Prototypes are manufactured in controlled batches of 5–10 units and subjected to dimensional inspection via CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) and functional testing, including pressure cycling, leak testing, and thermal aging. Client feedback is integrated at this stage, allowing for design or material refinements prior to tooling finalization. Prototype lead time typically ranges from 10 to 15 working days, depending on complexity.
Mass Production: Scalable Quality and Consistency
Upon client approval, we transition to mass production using hardened steel molds and automated rubber processing lines. Each production batch undergoes in-process quality checks and final inspection per AQL Level II. Traceability is maintained through batch coding and full material certification (including MTRs and CoAs). Our production capacity supports volumes from 1,000 to over 100,000 units monthly, with lead times averaging 25–35 days.
| Specification | Standard Value | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 50–90 ±5 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥10 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥200% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (24h, 70°C) | ≤25% | ASTM D395 |
| Operating Temperature | -30°C to +150°C (varies by compound) | ISO 1817 |
Contact Engineering Team

Technical Partnership for Precision End Flange Solutions
Selecting an industrial rubber component supplier demands rigorous evaluation of material science expertise and manufacturing precision. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team specializes in end flange formulations engineered for extreme operational environments. We integrate ASTM D2000 standards with proprietary polymer compounding to deliver flanges that maintain structural integrity under cyclic pressure, thermal degradation, and chemical exposure. Our ISO 9001-certified production facility utilizes closed-mixing systems and computer-controlled vulcanization to achieve durometer tolerances of ±2A across all batches. This precision ensures leak-proof sealing in hydraulic, petrochemical, and heavy machinery applications where failure is not an option.
Critical performance parameters for end flanges are non-negotiable in industrial design. The following specifications reflect our baseline engineering capabilities for standard configurations. All values are validated through third-party testing per ISO 37 and ISO 188 protocols.
| Specification Category | Material Options | Performance Range | Application Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durometer Hardness | Nitrile (NBR), EPDM, Viton | 50A to 90A | High-pressure sealing |
| Temperature Resistance | Custom-compounded | -50°C to +230°C | Cryogenic to thermal cycling |
| Tensile Strength | Reinforced polymer blends | 15 MPa to 28 MPa | Vibration damping |
| Compression Set | Optimized filler systems | ≤15% at 70°C/24h | Long-term seal retention |
| Fluid Resistance | Halogen-free formulations | Hydraulic oils, acids, steam | Chemical processing |
Our value extends beyond material specifications. We operate as a true OEM engineering partner, not merely a component vendor. Through collaborative design reviews, we refine flange geometry to mitigate stress concentration points identified via finite element analysis (FEA). This reduces premature extrusion in high-pressure systems by up to 37% compared to generic alternatives. Our rapid prototyping lab delivers functional samples within 15 business days, with full traceability from raw material batch codes to final cure profiles. For regulated industries, we provide comprehensive material test reports (MTRs) including FTIR spectroscopy and thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) data.
Global manufacturers choose Suzhou Baoshida for seamless integration into complex supply chains. We maintain strategic inventory hubs in Rotterdam and Singapore for 72-hour emergency shipments, while our dual-source molding capability eliminates single-factory disruption risks. Our technical team collaborates directly with your R&D department to validate flange performance against OEM-specific test matrices, ensuring compliance with SAE J514 or ISO 8434-1 requirements before volume production.
Initiate your end flange optimization project with engineered certainty. Contact Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Manager, to schedule a technical consultation. He will align our compounding expertise with your application’s critical parameters, providing a formal quotation with material certification documentation within 48 hours of requirement submission. Direct engineering inquiries to [email protected] with subject line: End Flange Technical Request – [Your Company Name]. Include operational pressure ranges, media exposure details, and dimensional schematics for accelerated solution development. Suzhou Baoshida commits to resolving your sealing challenges through polymer science rigor – not generic substitutions. Your machinery’s reliability demands nothing less.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
