Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Epdm Rubber Roofing System

Engineering Insight: Material Selection Criticality in EPDM Roofing Systems
The performance longevity of an EPDM rubber roofing system is fundamentally dictated by its material formulation. Generic off-the-shelf EPDM membranes frequently fail prematurely due to compromises in polymer chemistry and additive systems, leading to catastrophic field failures such as shrinkage-induced seam separation, surface cracking, and accelerated degradation under UV/ozone exposure. These failures stem from formulations optimized for cost reduction rather than environmental resilience, directly undermining the roofing system’s structural integrity and service life.
Precision in material selection requires rigorous control over polymer grade, filler dispersion, curative packages, and stabilizer concentrations. Standard commercial EPDM often utilizes lower molecular weight polymers with inadequate saturation levels, resulting in poor resistance to thermal cycling and ozone attack. Inadequate carbon black dispersion or substitution with cheap mineral fillers reduces tensile strength and flexibility, while substandard sulfur-based cure systems create weak polymer crosslinks prone to reversion at elevated temperatures. Crucially, insufficient antioxidant and UV stabilizer loading accelerates surface embrittlement, particularly in regions with high solar irradiance or extreme temperature fluctuations.
Field data from failed installations consistently reveals that membranes meeting only minimum ASTM D4637 requirements lack the robustness for demanding architectural applications. Premium formulations must exceed baseline standards through engineered solutions: high-purity terpolymer bases with optimal ethylene/propylene/diene ratios, nano-dispersed reinforcing fillers, and multi-stage antioxidant systems tailored to regional climate stressors. This approach preserves polymer backbone integrity across 30+ years of thermal cycling from -40°C to +150°C, preventing the micro-cracking that initiates membrane failure.
The following table contrasts critical performance parameters between standard commercial EPDM and precision-engineered roofing membranes:
| Performance Parameter | Standard Commercial EPDM | Precision-Engineered EPDM (Suzhou Baoshida OEM Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (ASTM D412) | 7.5 MPa min | 12.0 MPa min |
| Elongation at Break | 300% min | 550% min |
| Ozone Resistance (ASTM D1149) | Cracking in 72h @ 50pphm | Zero cracking after 1000h @ 100pphm |
| Low-Temperature Flexibility | -30°C | -50°C |
Off-the-shelf solutions fail because they treat EPDM as a commodity rather than a performance-critical engineered material. Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM partnerships prioritize application-specific formulation development, integrating accelerated weathering data and finite element analysis to predict real-world behavior. This methodology ensures dimensional stability under cyclic stress, eliminates shrinkage-related seam failures, and maintains watertight integrity across decades of exposure. For specifiers, the cost differential between generic and engineered EPDM is negligible against the lifecycle cost of premature replacement—making material selection not merely a technical choice, but a financial imperative. Precision in rubber chemistry is the non-negotiable foundation of a reliable roofing system.
Material Specifications

The performance and longevity of an EPDM rubber roofing system depend heavily on the compatibility and quality of associated sealing and gasket materials used in ancillary components such as flashings, seals, and joint connectors. While EPDM serves as the primary membrane due to its excellent weathering, ozone, and UV resistance, supplementary elastomers like Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone are often employed in specialized applications where enhanced chemical resistance, temperature stability, or mechanical integrity is required. Understanding the material specifications of these elastomers ensures optimal system integration and reliability under diverse environmental and operational conditions.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber (FKM), offers superior resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and aggressive chemicals. It maintains structural integrity in continuous service temperatures up to 230°C and performs reliably in harsh industrial environments where exposure to hydrocarbons or acidic compounds is common. This makes Viton an ideal choice for rooftop equipment seals, particularly near HVAC units or exhaust vents where chemical and thermal stressors are elevated. However, its higher cost and lower elasticity compared to other elastomers limit its use to critical applications.
Nitrile rubber, or acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), is widely used for its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels. With a service temperature range of -30°C to 108°C, NBR provides good mechanical strength and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for gaskets and seals in standard rooftop mechanical systems. While it lacks the UV and ozone resistance needed for exposed roofing membranes, it performs well in protected or enclosed environments. Its cost-effectiveness and availability further support its use in non-exposed components of the roofing system.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature applications, with a functional range from -60°C to 200°C. It demonstrates outstanding resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and weathering, maintaining flexibility and mechanical properties over prolonged outdoor exposure. However, silicone exhibits lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Viton or Nitrile, and it is not recommended for environments with significant oil or hydrocarbon exposure. Its primary role in EPDM roofing systems includes sealants and expansion joint materials where long-term weatherability is paramount.
The following table compares key physical and chemical properties of these elastomers relevant to EPDM roofing system integration:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -30 to 108 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–450 | 200–600 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 65–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Typical Applications | High-temp seals, chemical barriers | Gaskets, O-rings, mechanical seals | Expansion joints, weather seals |
Selection of the appropriate elastomer must consider environmental exposure, mechanical demands, and chemical contact. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we provide precision-engineered rubber solutions tailored to industrial roofing requirements, ensuring system-wide compatibility and performance longevity.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision-Engineered EPDM Roofing Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep engineering expertise to deliver mission-critical EPDM rubber roofing systems. Our dedicated team comprises five specialized mold engineers and two advanced formula engineers, ensuring every component meets stringent industrial performance benchmarks. This integrated capability translates theoretical material science into field-proven durability, directly addressing the demanding environmental stresses faced by modern roofing applications. Our engineers collaborate from initial concept through production, optimizing both polymer composition and tooling geometry to eliminate common failure points such as seam degradation, thermal cracking, and UV-induced hardening.
Material innovation forms the core of our roofing system’s longevity. Our formula engineers meticulously tailor EPDM compounds to exceed ASTM D4637 standards for roofing membranes, focusing on ozone resistance, thermal stability, and adhesion properties. Through precise control of polymerization variables and additive packages—including proprietary stabilizers and reinforcing fillers—we achieve consistent cross-link density critical for 30+ year service life. This scientific approach ensures membranes withstand extreme thermal cycling (-40°C to 150°C), prolonged UV exposure, and chemical contaminants without compromising elasticity or tensile integrity.
As a certified OEM partner, we provide end-to-end engineering support for custom roofing solutions. Our process begins with client-specific performance requirements, followed by computational mold flow analysis to predict material behavior during vulcanization. We then develop optimized tooling designs that minimize flash, ensure uniform thickness distribution, and accelerate cycle times—reducing production costs while enhancing dimensional accuracy. Clients receive comprehensive technical documentation, including finite element analysis (FEA) reports for complex geometries and full material traceability from raw compound to finished product. This OEM framework enables seamless integration with global manufacturing partners while maintaining Suzhou Baoshida’s quality governance.
Key performance metrics for our standard and custom EPDM roofing compounds are summarized below:
| Property | Standard EPDM Roofing Compound | Customizable Range | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥ 10.0 | 8.5 – 15.0 | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ≥ 450 | 400 – 600 | ASTM D412 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 55 ± 5 | 45 – 70 | ASTM D2240 |
| Ozone Resistance (200 pphm) | No cracks (100 hrs) | Enhanced formulations | ASTM D1149 |
| Temperature Range (°C) | -40 to +150 | -50 to +165 (specialty) | ASTM D573 |
This engineering rigor directly translates to client value: reduced installation callbacks, minimized lifecycle costs, and compliance with global building codes including FM 4470 and EN 13956. By embedding material science and precision tooling expertise into every project, Suzhou Baoshida ensures EPDM roofing systems perform reliably under the harshest operational conditions, delivering measurable ROI for industrial and commercial clients worldwide. Our commitment to scientific validation—through accelerated aging tests, weathering simulations, and real-world performance tracking—solidifies trust in every square meter deployed.
Customization Process
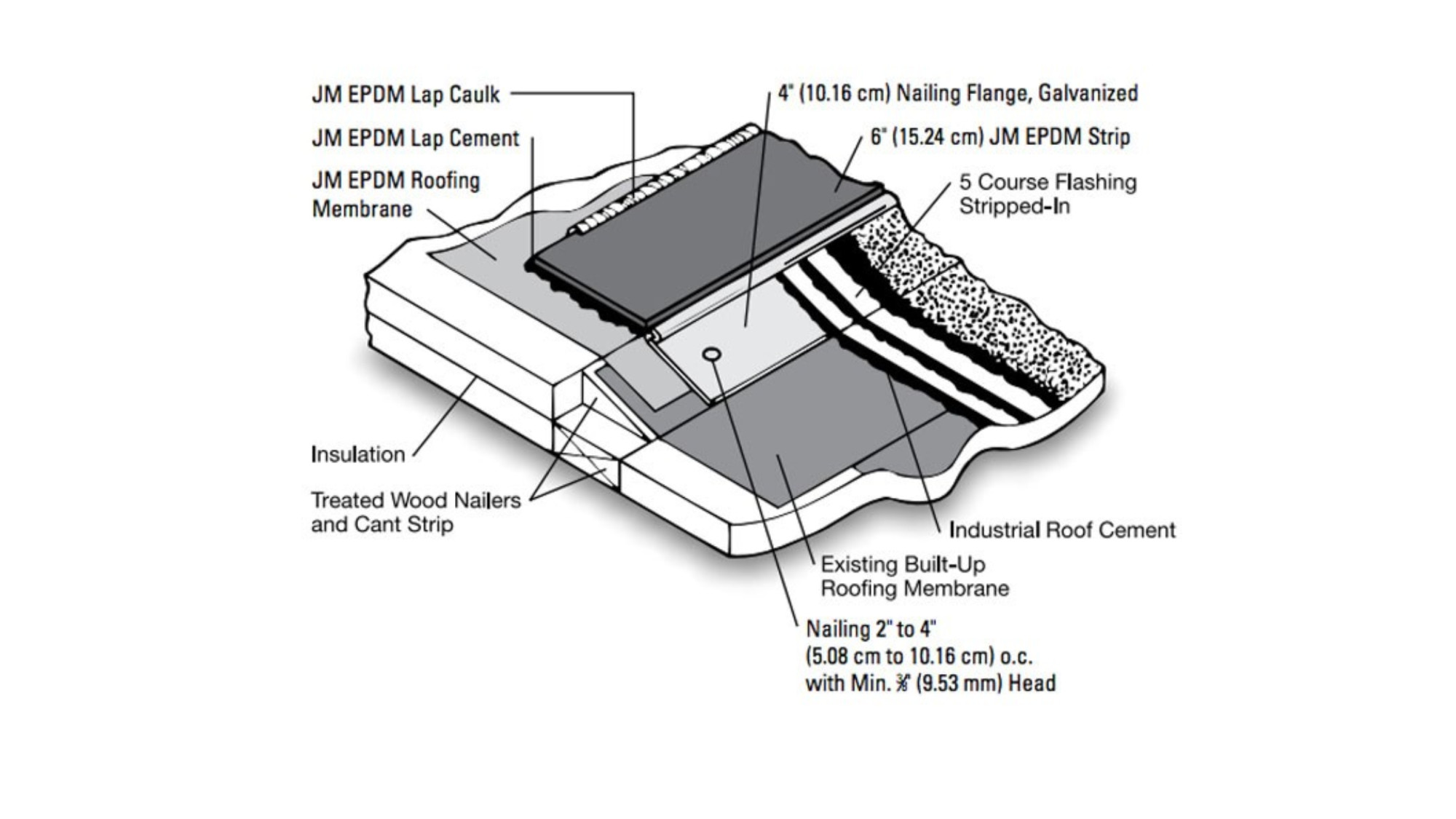
Drawing Analysis
The customization process for an EPDM rubber roofing system begins with comprehensive drawing analysis. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., technical engineers meticulously review architectural and engineering schematics provided by OEM partners or construction firms. This stage involves evaluating dimensional tolerances, joint configurations, flashing details, and integration points with adjacent building materials. Our team cross-references substrate compatibility, expected thermal expansion, and environmental exposure conditions such as UV intensity, rainfall frequency, and temperature cycling. Using CAD-based annotation tools, we identify critical stress zones and recommend reinforcement strategies where needed. This ensures the final product meets structural integrity benchmarks while adhering to international standards such as ASTM D4637 for weathering resistance and ISO 14021 for environmental claims.
Formulation Development
Based on insights from the drawing analysis, our rubber formulation engineers develop a customized EPDM compound tailored to the project’s performance requirements. The base polymer selection considers ethylene content, molecular weight distribution, and third monomer type (typically ENB) to balance cure kinetics and low-temperature flexibility. Reinforcing fillers such as N330 carbon black or precipitated silica are incorporated to enhance tensile strength and abrasion resistance. Specialty additives—including UV stabilizers, ozone scavengers, and hydrophobic agents—are dosed precisely to extend service life in harsh climates. The curing system is optimized for the intended fabrication method, whether autoclave, press, or continuous vulcanization. Each formulation is documented under a unique material specification number and subjected to preliminary lab testing for rheological behavior, scorch time, and minimum torque.
Prototyping and Validation
Once the formulation is finalized, a functional prototype is produced using pilot-scale calendering or extrusion equipment that mirrors full production conditions. Sample sheets or profiled components are fabricated to validate dimensional accuracy and surface finish. These prototypes undergo rigorous performance testing, including tensile strength, elongation at break, low-temperature brittleness (per ASTM D2136), and water absorption (ASTM D570). Adhesion tests are conducted with common roofing substrates such as plywood, steel, and insulation boards. Clients receive a detailed test report along with physical samples for field mock-up evaluation. Feedback is integrated into a final design verification loop before release to mass production.
Mass Production Readiness
Upon approval, the project transitions to automated manufacturing lines equipped with inline quality monitoring systems. Production batches are traceable through batch coding and certified with material test reports (MTRs). Our facility supports roll goods up to 15 meters in length and custom profiles with tight geometric control.
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥10 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥450% |
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 50–70 |
| Ozone Resistance | ASTM D1149 | No cracks after 100 hrs @ 50 pphm |
| Low Temperature Flexibility | ASTM D2136 | Pass at -50°C |
| Water Absorption | ASTM D570 | ≤0.5% after 7 days |
All systems are packaged with protective film and moisture barrier wrapping to ensure delivery integrity.
Contact Engineering Team

Technical Partnership for Precision EPDM Roofing Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the intersection of advanced polymer science and industrial manufacturing excellence. Our EPDM rubber roofing systems are engineered for critical infrastructure where failure is not an option. With 15 years of OEM collaboration across aerospace, renewable energy, and commercial construction sectors, we deliver formulations that exceed ASTM D4637 and ISO 1297 standards through rigorous QC protocols. Unlike commodity suppliers, our value lies in molecular-level customization—adjusting polymer architecture, filler dispersion, and vulcanization kinetics to match your project’s thermal cycling demands, chemical exposure, or wind uplift requirements.
The table below summarizes core technical parameters of our flagship EPDM roofing membrane formulation. These values represent baseline performance; all specifications are adjustable within ±5% tolerance based on client-specified environmental stressors.
| Property | Test Method | Value | Industrial Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | 24.5 MPa | Resists mechanical damage during installation |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | 580% | Accommodates structural movement without cracking |
| Heat Aging Resistance | ASTM D573 | ΔTS ≤ 15% | Maintains integrity after 720h at 150°C |
| Ozone Resistance | ASTM D1149 | No cracks | Critical for high-altitude/urban environments |
| Low-Temperature Flexibility | ASTM D2137 | -50°C | Prevents brittleness in sub-zero climates |
| Water Absorption | ASTM D570 | 0.8% | Ensures dimensional stability in monsoons |
Our engineering team addresses three universal pain points in roofing applications: seam integrity degradation under UV exposure, premature aging from plasticizer migration, and substrate adhesion failure in high-humidity zones. We resolve these through proprietary co-agent systems that create interfacial chemical bonds at seam junctions, non-migratory stabilizers that lock in flexibility, and primer formulations tuned to concrete, metal, or modified bitumen substrates. Every batch undergoes 72-hour accelerated weathering tests in our Suzhou facility before release—data sheets are provided with shipment.
For projects requiring fire-rated solutions (FM 4470, UL 790 Class A), solar reflectivity optimization (SRI ≥ 105), or ballasted system compatibility, our technical OEM division develops bespoke compound matrices. We integrate seamlessly into your production workflow, offering on-site vulcanization troubleshooting and real-time QC data sharing via encrypted cloud portals.
Initiate your technical consultation with Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Solutions Manager. With a Ph.D. in Polymer Science and 12 years of field experience resolving complex roofing failures, he will analyze your substrate conditions, climatic stressors, and lifecycle cost targets to propose a validated formulation pathway. Contact him directly at [email protected] with your project specifications, ASTM compliance requirements, and target delivery timeline. Include “EPDM Roofing Technical Query” in the subject line for priority engineering review. All inquiries receive a detailed technical response within 4 business hours, including material safety data, full test reports, and sample shipment coordination. Partner with Suzhou Baoshida to transform roofing from a cost center into a 50-year asset.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
