Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Epdm Temperature Range
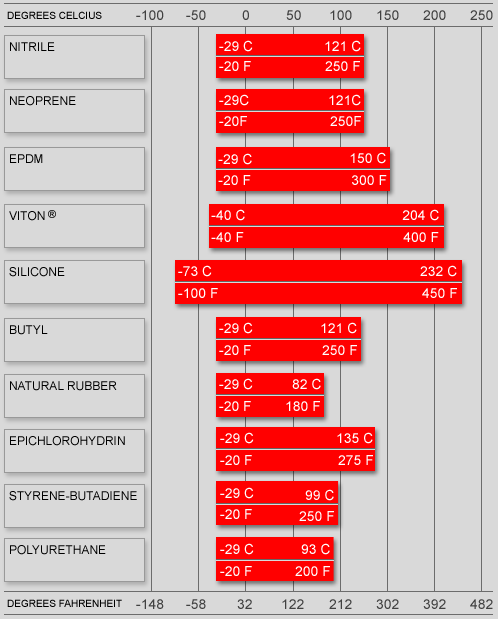
Engineering Insight: EPDM Temperature Range and the Critical Role of Material Selection
In industrial rubber applications, understanding the operational temperature range of elastomeric materials is fundamental to ensuring long-term performance and system reliability. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is widely specified across industries due to its excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering. However, its thermal performance characteristics must be carefully evaluated to avoid premature failure in demanding environments. While EPDM is often perceived as a universal solution for outdoor or moderate-temperature applications, off-the-shelf formulations frequently fail when deployed beyond their engineered limits.
The standard continuous service temperature range for conventional EPDM compounds typically spans from -50°C to +135°C. This range can vary significantly based on polymer grade, filler content, crosslink density, and the presence of specialized additives. Short-term exposure to temperatures up to +150°C may be tolerated, but prolonged operation at these extremes accelerates oxidative degradation, leading to hardening, cracking, and loss of sealing force. Conversely, at low temperatures, EPDM maintains flexibility better than many hydrocarbon-based rubbers, but formulations not optimized for cryogenic performance can suffer from embrittlement below -50°C, compromising dynamic sealing capabilities.
A primary reason off-the-shelf EPDM products fail in industrial settings is the mismatch between generic material specifications and application-specific thermal profiles. Many commercial-grade EPDM seals are formulated for cost efficiency and broad compatibility rather than targeted performance. These compounds often lack the reinforced polymer architecture or advanced cure systems needed for sustained thermal stability. For example, in HVAC systems, automotive cooling circuits, or solar thermal assemblies, temperature cycling combined with fluid exposure can induce microstructural fatigue in suboptimal compounds. The result is leakage, joint failure, or unplanned maintenance downtime—costly outcomes that could be avoided through precision material engineering.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize application-driven formulation development. Our engineered EPDM solutions are tailored to exceed standard temperature thresholds through controlled monomer ratios, peroxide curing systems, and reinforcing filler matrices. By aligning compound design with the thermal and chemical environment of the end-use application, we deliver rubber components with predictable lifecycle performance.
The following table outlines the typical temperature performance of various EPDM formulations:
| EPDM Type | Continuous Use (°C) | Short-Term Peak (°C) | Low-Temp Flexibility (°C) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Commercial | -50 to +135 | +150 | -50 | General gaskets, weatherstripping |
| High-Temp Modified | -45 to +150 | +175 | -45 | Automotive cooling systems, industrial hoses |
| Peroxide-Cured | -55 to +160 | +180 | -55 | Seals in solar thermal, power generation |
| Cryogenic-Optimized | -60 to +130 | +140 | -60 | Refrigeration, cold-climate infrastructure |
Selecting the correct EPDM grade requires more than matching a datasheet—it demands a deep understanding of operational dynamics. At Baoshida, we support OEMs with material consultation, ensuring rubber components perform reliably across their entire thermal lifecycle.
Material Specifications
EPDM Temperature Range: Critical Specifications for Industrial Sealing Applications
As a leading industrial rubber solutions provider, Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. emphasizes precise thermal performance parameters for EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) in demanding OEM environments. EPDM exhibits a standard continuous service range of -40°C to +130°C, with short-term excursions permissible up to +150°C. This range is contingent upon compound formulation, crosslink density, and application stressors such as compression set or fluid exposure. Notably, low-temperature flexibility is governed by glass transition temperature (Tg ≈ -55°C), but functional sealing below -40°C requires specialized low-temperature grades due to reduced polymer chain mobility. Conversely, prolonged exposure above 130°C accelerates oxidative degradation, leading to hardening and loss of elasticity. Engineers must account for dynamic cycling effects, as repeated thermal shocks narrow the effective operational window by 15–20°C compared to static conditions.
Material selection beyond EPDM necessitates rigorous thermal profiling against application-specific demands. Viton (FKM) excels in high-heat, chemical-rich settings with a continuous range of -20°C to +230°C and brief tolerance to 300°C. Nitrile (NBR) remains cost-effective for oil-resistant applications but is limited to -40°C to +120°C (extended to 150°C with HNBR variants). Silicone (VMQ) dominates extreme low-temperature scenarios down to -60°C while sustaining +200°C continuously, though its mechanical strength diminishes above 180°C. Crucially, all ranges assume standard ASTM D2000 classification (e.g., AA for heat resistance) and exclude synergistic stressors like ozone or hydraulic fluids, which can reduce effective limits by 25°C or more.
The following table details comparative thermal specifications per ISO 188 and ASTM D573 testing protocols:
| Material | Continuous Min Temp (°C) | Continuous Max Temp (°C) | Short-Term Peak Temp (°C) | Key Thermal Limitation Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | -40 | 130 | 150 | Oxidative chain scission above 130°C |
| Viton (FKM) | -20 | 230 | 300 | Fluorine content degradation >250°C |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -40 | 120 | 150 | Nitrile group hydrolysis in humid heat |
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 | 200 | 250 | Siloxane backbone depolymerization |
Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering team validates all thermal data through accelerated aging in controlled air-oven environments (70–168 hours per ASTM D573), correlating results with real-world field performance. For applications exceeding EPDM’s thermal envelope—such as automotive turbocharger hoses (requiring >180°C) or arctic hydraulic seals (<-50°C)—we recommend Viton or silicone alternatives with OEM-specific compound tailoring. Always consult our technical dossier BD-RUB-2024 for fluid compatibility matrices and dynamic thermal cycling test reports prior to final specification. Precision in temperature boundary definition directly governs seal longevity and system safety in critical industrial operations.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision-Driven Rubber Solutions for Demanding Environments
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our Engineering Capability division is built on deep technical expertise in industrial rubber formulation and precision mold design, ensuring optimal performance in critical applications. With a dedicated team of 5 Mould Engineers and 2 specialized Rubber Formula Engineers, we offer fully integrated OEM services that combine material science with advanced manufacturing engineering. Our focus is on delivering customized elastomeric components that meet exacting performance standards, particularly in environments where temperature extremes define operational reliability.
Our Formula Engineers possess extensive experience in polymer chemistry, with a particular emphasis on EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) compound development. EPDM is widely used in automotive, HVAC, and industrial sealing applications due to its outstanding resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering. Our team formulates custom EPDM compounds tailored to specific temperature and mechanical requirements, ensuring long-term durability under real-world conditions. Through rigorous laboratory testing and iterative formulation refinement, we optimize cross-link density, filler dispersion, and cure systems to achieve target physical properties.
Complementing our material expertise, our 5 Mould Engineers specialize in precision tooling design for complex rubber components. Utilizing advanced CAD/CAM software and collaborating closely with clients during the prototyping phase, we ensure dimensional accuracy, consistent part quality, and efficient production cycles. Our in-house mold design capability enables rapid iteration and fast time-to-market, essential for OEM partners operating in competitive industries.
One of our core strengths lies in our ability to align material formulation with mold engineering to solve application-specific challenges. For instance, in high-temperature sealing applications, our team evaluates compression set, thermal aging, and volume change data to recommend the ideal EPDM formulation, while simultaneously designing molds that accommodate material behavior during vulcanization.
The following table outlines the typical temperature and physical performance characteristics of our engineered EPDM compounds:
| Property | Standard EPDM | High-Temp Modified EPDM | Low-Temp Flexible EPDM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Use Temperature (°C) | -50 to +135 | -50 to +150 | -60 to +130 |
| Short-Term Peak Resistance (°C) | 150 | 175 | 150 |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 50–90 | 60–90 | 45–80 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥10 | ≥12 | ≥9 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ≥250 | ≥200 | ≥300 |
| Compression Set (22h at 125°C) | ≤30% | ≤25% | ≤35% |
All compounds are developed and tested in accordance with ASTM and ISO standards, ensuring global compliance and repeatability. Our OEM clients benefit from full technical documentation, including material certifications, mold flow analysis, and performance validation reports.
Through the synergy of advanced rubber chemistry and precision engineering, Suzhou Baoshida delivers reliable, high-performance EPDM solutions engineered for extreme temperature environments.
Customization Process
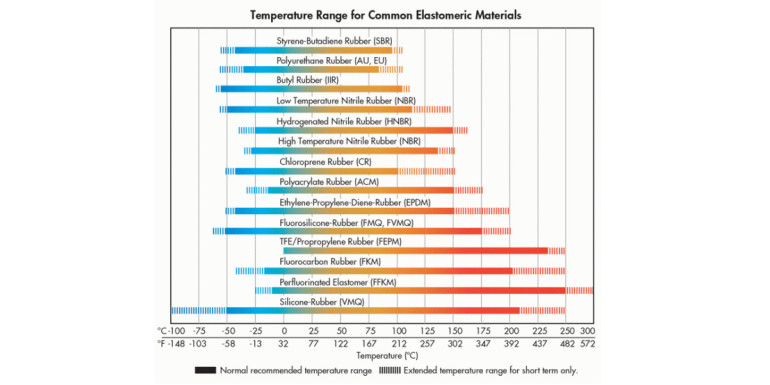
EPDM Temperature Range Customization Process
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our EPDM rubber customization process rigorously addresses temperature range requirements through four integrated phases. This ensures final products meet exact thermal performance demands in automotive, aerospace, and industrial sealing applications. We prioritize material science precision to deliver solutions operating reliably from extreme cold to sustained high-heat environments.
Drawing Analysis
Initial technical review focuses on dimensional tolerances, cross-section geometry, and critical thermal exposure zones specified in client CAD files. We cross-reference ASTM D2000 standards to identify required temperature classes (e.g., AA, BA, CA). This phase quantifies operational extremes—such as intermittent exposure to +150°C engine compartments or continuous -40°C refrigeration units—and defines compression set limits under thermal cycling. Material selection parameters are established before formulation begins.
Formulation Development
Our rubber compounders engineer bespoke EPDM blends using third-generation polymers with controlled ethylene content (45–75%) and ENB diene levels. High-temperature stability is achieved through peroxide curing systems (vs. sulfur) for superior resistance to thermal oxidation. Fillers like silica and specialty carbon blacks enhance low-temperature flexibility, while proprietary stabilizer packages prevent chain scission at elevated temperatures. Each formulation targets precise glass transition temperature (Tg) shifts and reversion resistance, validated via DSC and TGA analysis.
Prototyping and Validation
Prototype tooling produces test specimens for exhaustive thermal characterization. We conduct ASTM D2240 hardness checks after 72-hour aging at maximum service temperature and measure compression set per ASTM D395 Method B. Critical validation includes thermal cycling between -60°C and +170°C over 500 cycles to assess seal integrity. Clients receive full material test reports detailing elongation retention, tensile strength decay, and volume swell in relevant fluids at temperature extremes.
Mass Production Implementation
Approved formulations transition to ISO 9001-certified production lines with real-time rheometer monitoring. Batch consistency is enforced through automated weighing systems and closed-mixing protocols. Every production lot undergoes thermal aging verification per client-specified conditions before shipment. Traceability is maintained via laser-etched batch codes linked to raw material certificates and cure curve data.
EPDM Temperature Performance Specifications
| Property | Standard EPDM | Custom Baoshida EPDM | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Use Range | -50°C to +150°C | -60°C to +170°C | ASTM D2000 |
| Intermittent Peak | +165°C | +185°C | ISO 188 |
| Glass Transition (Tg) | -55°C | -63°C | ASTM D7426 |
| Compression Set (24h/150°C) | ≤35% | ≤22% | ASTM D395 B |
| Fluid Resistance (ATF) | Moderate | Excellent | ASTM D471 |
This structured workflow eliminates thermal performance gaps by embedding temperature range validation at every development stage. Suzhou Baoshida guarantees that final components maintain sealing force, elasticity, and chemical resistance across the client’s defined operational envelope, reducing field failure risks in critical applications.
Contact Engineering Team

For industrial manufacturers and engineering teams seeking reliable rubber solutions under extreme thermal conditions, understanding the precise temperature range of EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) is critical to ensuring system integrity, longevity, and safety. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-performance industrial rubber materials engineered to meet the rigorous demands of automotive, HVAC, electrical, and heavy machinery applications. Our expertise in EPDM formulation ensures consistent performance across a broad operational spectrum, making it a preferred choice for sealing, gasketing, and insulation components exposed to fluctuating environments.
EPDM rubber is renowned for its exceptional resistance to heat, ozone, UV radiation, and weathering. However, the actual service temperature limits depend on compound formulation, crosslink density, and application stress factors. Standard EPDM compounds typically perform reliably within a continuous operating range of -50°C to +150°C. With specialized additives and curing systems, certain high-temperature grades can withstand intermittent exposure up to +175°C. Below -50°C, the material begins to lose elasticity and may become brittle, while prolonged exposure above 150°C accelerates oxidative degradation, leading to hardening and cracking.
To support precise material selection, we provide detailed technical guidance based on real-world testing and OEM requirements. Our team at Suzhou Baoshida ensures that every EPDM solution is tailored not only to thermal specifications but also to mechanical load, compression set resistance, fluid compatibility, and regulatory standards such as RoHS and REACH.
Below is a representative temperature performance summary for common EPDM formulations we supply:
| Property | Standard EPDM | High-Temp Modified EPDM | Low-Temp Flexible EPDM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Use (Min) | -50°C | -50°C | -60°C |
| Continuous Use (Max) | +150°C | +165°C | +140°C |
| Intermittent Peak | +160°C | +175°C | +150°C |
| Glass Transition (Tg) | ~-60°C | ~-55°C | ~-70°C |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 40–90 | 50–85 | 45–80 |
| Common Applications | Seals, Roofing, Hoses | Radiator Hoses, Gaskets | Cold-Weather Seals, Outdoor |
These values are derived from ASTM D2000 standards and in-house aging protocols, including air-oven aging at 125°C for 72–168 hours and dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) for low-temperature flexibility.
For project-specific recommendations, material certifications, or custom compounding support, we invite you to contact Mr. Boyce, our lead Rubber Formula Engineer and OEM Manager. With over 15 years of experience in industrial elastomer development, Mr. Boyce leads technical collaboration with global partners to deliver optimized rubber solutions that align with production timelines, performance KPIs, and cost targets.
Reach out today via email at [email protected] to discuss your EPDM temperature requirements, request sample submissions, or initiate a technical review of your current material challenges. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we are committed to engineering reliability into every compound we deliver.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
