Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Extrusion Manufacturing Companies
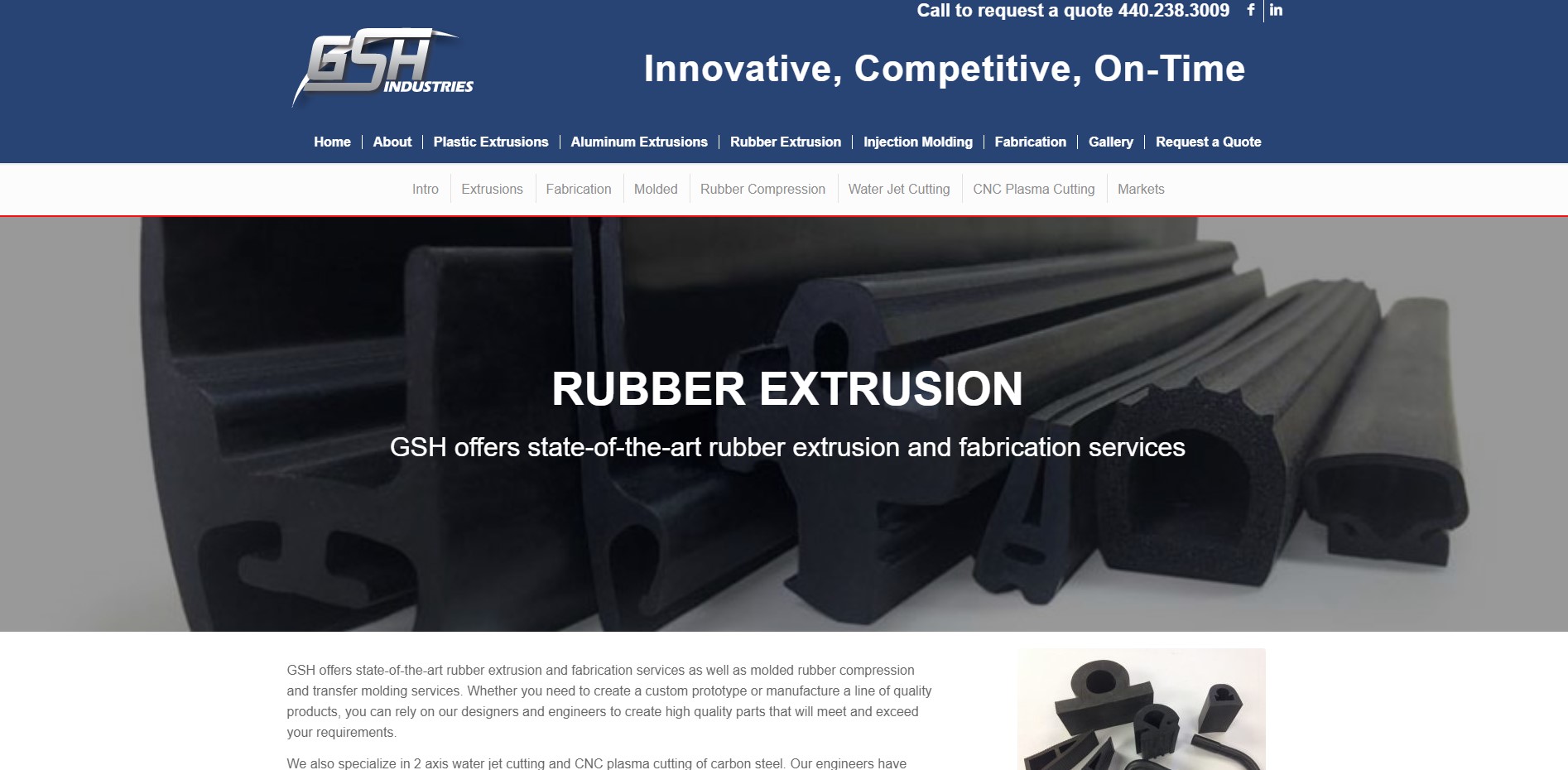
Engineering Insight: The Critical Role of Material Selection in Precision Rubber Seals for Extrusion Manufacturing
In the domain of precision rubber seals, extrusion manufacturing companies face a persistent challenge: the assumption that off-the-shelf elastomeric solutions can meet highly specialized performance requirements. This misconception often leads to premature seal failure, increased maintenance cycles, and unplanned system downtime. The root cause lies in inadequate material selection—a decision that must be driven by application-specific engineering parameters rather than availability or cost alone.
Precision rubber seals operate under dynamic conditions involving temperature extremes, chemical exposure, mechanical stress, and compression set requirements. Standard elastomers such as generic EPDM or SBR may appear functionally adequate in mild environments but fail catastrophically when exposed to aggressive media or fluctuating thermal loads. For instance, an off-the-shelf NBR seal may resist oils at room temperature but degrade rapidly above 100°C, where a custom-formulated HNBR or fluorocarbon (FKM) compound would maintain integrity.
Material selection must begin with a comprehensive analysis of the operational environment. Key factors include fluid compatibility, continuous and peak temperature ranges, exposure to UV or ozone, and mechanical loading conditions such as compression deflection and tensile strength. Extrusion processes further complicate this selection, as the rheological behavior of the compound during processing directly affects dimensional consistency, surface finish, and cure uniformity. A material optimized for molding may exhibit poor die swell control or scorch sensitivity in continuous vulcanization (CV) extrusion lines.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize engineered compound development in collaboration with extrusion partners. By tailoring polymer backbone chemistry, filler systems, and cure packages, we produce seals with enhanced resistance to specific challenges—such as low-temperature flexibility in arctic hydraulic systems or hydrolysis resistance in high-humidity pneumatic applications.
The failure of generic solutions underscores the necessity of application-driven formulation. A seal in an offshore drilling manifold, for example, must resist sour gas (H₂S), seawater, and high pressure—conditions unaccounted for in commodity-grade materials. Similarly, seals in medical fluid handling systems require USP Class VI compliance and resistance to repeated sterilization cycles, which standard compounds cannot guarantee.
Ultimately, precision rubber seals are not interchangeable components. They are engineered interfaces whose performance is intrinsically linked to material science and process compatibility. Extrusion manufacturers who prioritize custom material selection over convenience achieve superior product longevity, regulatory compliance, and system reliability.
Comparison of Common Elastomers in Extrusion Applications
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Fluid Resistance | Compression Set | Extrusion Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | -30 to +100 | Oils, fuels | Moderate | High |
| HNBR | -40 to +150 | Oils, steam | Excellent | Moderate to High |
| EPDM | -50 to +150 | Water, steam | Good | High |
| FKM | -20 to +200 | Acids, solvents | Excellent | Moderate |
| Silicone | -60 to +180 | Ozone, UV | Poor to Moderate | Moderate |
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Precision Rubber Seal Extrusion
Selecting optimal elastomers is fundamental to producing high-integrity seals via extrusion. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we rigorously evaluate material behavior under extrusion parameters to ensure dimensional stability, surface finish, and long-term performance. Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ) represent critical choices for demanding applications, each exhibiting distinct rheological and chemical properties during processing. Understanding these characteristics prevents defects like die swell inconsistency, scorching, or post-extrusion shrinkage. Extrusion temperature profiles, screw speed, and die design must align with the polymer’s cure kinetics and viscosity curve to achieve tight tolerances. ASTM D2000 and ISO 3601 standards govern critical attributes, including hardness, tensile strength, and fluid resistance, which directly impact seal functionality in automotive, aerospace, and industrial fluid systems.
Viton (FKM) excels in extreme chemical and thermal environments. Its high fluorine content provides exceptional resistance to fuels, oils, and acids, making it indispensable for aerospace and chemical processing seals. During extrusion, Viton requires precise temperature control (typically 50–70°C lower than NBR) to avoid premature crosslinking. Base compound viscosity must be optimized to prevent surface roughness, with post-extrusion vulcanization critical for achieving its full 200–300°C continuous service temperature range. Hardness grades span 60–90 ShA, balancing flexibility with extrusion stability.
Nitrile (NBR) remains the industry standard for cost-sensitive hydraulic and pneumatic applications due to its robust resistance to petroleum-based fluids. Its dual-phase acrylonitrile-butadiene structure offers tunable properties; higher ACN content improves oil resistance but reduces low-temperature flexibility. NBR extrudes efficiently at 80–100°C with minimal scorch risk, though ozone exposure necessitates protective additives. Typical hardness ranges from 50–90 ShA, with elongation at break exceeding 250%. Careful control of filler dispersion is essential to maintain consistent flow through complex dies.
Silicone (VMQ) dominates high-purity and extreme-temperature scenarios, from medical devices to automotive under-hood components. Its inorganic backbone enables operation from -60°C to 230°C, with excellent electrical insulation. Silicone’s low viscosity demands specialized extrusion tooling to manage die swell (typically 2–5%), while peroxide cure systems require strict temperature uniformity to avoid porosity. Hardness ranges from 30–80 ShA, but post-cure stabilization is mandatory to eliminate volatile byproducts in critical applications.
The comparative table below details essential specifications for extrusion manufacturing:
| Material | Base Polymer Classification | Key Extrusion Parameters | Fluid Resistance Profile | Thermal Range (Continuous) | Typical Hardness Range (ShA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton (FKM) | ASTM D1418 Type 4 | Temp: 40–60°C; Low scorch safety; High viscosity control critical | Excellent: Fuels, oils, acids, steam | -20°C to 300°C | 60–90 |
| Nitrile (NBR) | ASTM D1418 Type 1 | Temp: 80–100°C; Moderate scorch safety; Good flow stability | Excellent: Petroleum oils; Poor: Ozone, H₂O | -30°C to 120°C | 50–90 |
| Silicone (VMQ) | ASTM D1418 Type L | Temp: 50–70°C; High die swell (2–5%); Peroxide cure sensitivity | Good: Water, alcohols; Poor: Fuels, acids | -60°C to 230°C | 30–80 |
Material selection must integrate extrusion feasibility with end-use requirements. Suzhou Baoshida provides certified compound data sheets and extrusion trials to validate process parameters, ensuring seals meet ISO 3601 dimensional tolerances and ASTM D2000 quality classifications. Partner with our engineering team to optimize your formulation for yield, consistency, and performance.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering capability forms the backbone of our precision rubber seal manufacturing process, ensuring consistent performance, reliability, and customization for demanding industrial applications. We maintain a dedicated team of five experienced mould engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, enabling full in-house control over product development from concept to production. This integrated engineering approach allows us to deliver technically advanced sealing solutions tailored to the exacting requirements of extrusion manufacturing companies.
Our mould engineers possess extensive expertise in precision tooling design for rubber extrusion and compression moulding processes. They utilize advanced CAD/CAM software and GD&T principles to develop high-tolerance moulds that ensure dimensional accuracy, part consistency, and long service life. Each design undergoes rigorous simulation and fit-for-purpose validation to minimize cycle times, reduce flash, and eliminate defects—critical factors in high-volume OEM production environments. With iterative prototyping and DFM (Design for Manufacturability) analysis, we optimize every component for performance and manufacturability.
Complementing our tooling expertise, our two rubber formula engineers specialize in polymer chemistry and material performance optimization. They formulate custom elastomer compounds based on application-specific requirements such as temperature resistance, chemical exposure, compression set, and dynamic sealing performance. Utilizing ASTM and ISO-compliant testing protocols, we develop proprietary blends across silicone (VMQ), fluorocarbon (FKM), EPDM, NBR, and specialty hydrogenated nitrile (HNBR) materials. This in-house compounding capability allows us to meet stringent OEM material specifications while ensuring batch-to-batch repeatability and regulatory compliance.
Our OEM capabilities are built on a foundation of technical collaboration and scalable manufacturing. We support co-engineering initiatives, enabling seamless integration into our customers’ product development cycles. From initial concept sketches to production release, we provide full documentation including material certifications, PPAP files, and process FMEAs. Our facility supports low-volume prototyping and high-volume production, with traceability systems and SPC monitoring ensuring consistent quality across all batches.
The synergy between our mould and formula engineering teams ensures that both geometry and material properties are optimized in tandem—delivering seals that perform reliably under real-world operating conditions.
Material & Performance Specifications
| Material Type | Temperature Range (°C) | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Key Applications | Standard Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicone (VMQ) | -60 to +230 | 30–80 | Food, medical, high-temp seals | FDA, USP Class VI, ROHS |
| Fluorocarbon (FKM) | -20 to +250 | 50–90 | Automotive, chemical, aerospace | ASTM D2000, ISO 3601 |
| EPDM | -50 to +150 | 40–85 | Water, steam, HVAC systems | UL, NSF, ASTM |
| Nitrile (NBR) | -40 to +120 | 40–90 | Hydraulic, fuel systems | ISO 3302, SAE J200 |
| HNBR | -40 to +180 | 50–90 | Oil & gas, dynamic seals | NORSOK, API 6A |
Customization Process

Precision Rubber Seal Customization Process for Extrusion Manufacturing Partners
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. implements a rigorously controlled customization workflow for precision rubber seals, engineered to ensure seamless integration with extrusion manufacturing processes. Our methodology eliminates downstream production bottlenecks while guaranteeing dimensional stability and material performance under operational stress. The process initiates with comprehensive Drawing Analysis, where our engineering team deconstructs client specifications using GD&T standards. Critical parameters—including tolerance stacks, extrusion die compatibility, and secondary operation interfaces—are validated against material behavior models. We cross-reference ISO 3601 flange dimensions and SAE AS568 dash numbers to preempt interference issues, ensuring the design aligns with both functional requirements and extrusion line capabilities.
Subsequent Formulation leverages our proprietary polymer database and accelerated aging algorithms. Material selection is dictated by fluid compatibility, temperature extremes, and dynamic sealing forces. For instance, aerospace fuel system seals mandate FKM compounds with >90% volume swell resistance in Jet A-1, while automotive HVAC applications require EPDM formulations exceeding 150°C continuous service. Key material properties are quantified below:
| Material Type | Key Properties | Application Range |
|---|---|---|
| High-Purity FKM | 70-85 Shore A, Compression Set ≤15% (200°C/70h), ASTM D2000 Grade AA4 | Aerospace hydraulics, semiconductor tooling |
| Peroxide-Cured EPDM | 50-70 Shore A, Compression Set ≤20% (150°C/70h), Low-temperature flex to -55°C | Automotive coolant systems, solar thermal |
| Custom HNBR | 60-80 Shore A, Abrasion loss ≤60 mm³, Fuel C resistance >85% | Off-highway transmission seals, oilfield |
Prototyping employs CNC-machined tooling replicating production die geometries, with first-article inspection via CMM (per ISO 10360-2) and micro-hardness mapping. We subject prototypes to application-specific validation: dynamic leakage tests at 3x operational pressure, thermal cycling between -40°C to +200°C, and extrusion gap analysis under simulated assembly loads. Client feedback is integrated within 72 hours, with DOE-driven adjustments to cure kinetics or filler dispersion.
Mass Production commences only after PPAP Level 3 approval, utilizing closed-loop extrusion monitoring. Our IoT-enabled lines track barrel temperature gradients (±0.5°C stability), vulcanization state via moving die rheometry, and real-time dimensional control via laser micrometers. Every batch undergoes 100% visual inspection and statistical process control per ISO 2859-1, with traceability to raw material lot numbers. Final shipment includes full material test reports (ASTM D2240, D395) and extrusion process windows optimized for the client’s line speed and cooling configuration.
This structured approach reduces time-to-market by 30% while ensuring zero defect escalation in serial production. Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering oversight from drawing validation through量产 guarantees extrusion partners receive seals that perform predictably under the most demanding industrial conditions.
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Rubber Seals in Extrusion Manufacturing
When sourcing high-performance rubber seals for extrusion manufacturing, precision, consistency, and material expertise are non-negotiable. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in engineered rubber components designed specifically for the demanding requirements of industrial extrusion systems. Our seals ensure optimal pressure containment, thermal stability, and long service life under continuous operation—critical factors in maintaining production efficiency and minimizing downtime.
We understand that extrusion processes—whether for polymers, metals, or composites—require sealing solutions capable of withstanding high temperatures, abrasive media, and dynamic mechanical stresses. Our technical team works directly with extrusion equipment manufacturers and component integrators to develop custom rubber profiles, gaskets, and sealing elements that meet exact dimensional tolerances and performance specifications. From initial design consultation to prototyping and volume production, we provide end-to-end support grounded in material science and industrial application experience.
Our core materials include nitrile (NBR), ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), fluorocarbon (FKM/Viton®), silicone (VMQ), and specialty compounds formulated for oil resistance, ozone stability, or high-temperature resilience. Every product undergoes rigorous quality control, including hardness testing, dimensional inspection, and batch traceability, ensuring compliance with ISO 9001 standards and OEM requirements.
To facilitate seamless integration into your manufacturing workflow, we offer technical documentation, material certification packages, and on-site engineering collaboration. Whether you are upgrading existing sealing systems or developing next-generation extrusion machinery, our solutions are built to enhance reliability and reduce total cost of ownership.
For immediate technical consultation or custom quotation, contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Manager and Rubber Formula Engineer at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. Mr. Boyce leads our application engineering team and brings over 12 years of experience in rubber compounding and industrial seal design. He is available to review your project specifications, recommend optimal materials, and support rapid prototyping for validation testing.
Reach out via email at [email protected] to initiate a technical discussion. Include details such as operating temperature range, media exposure, pressure conditions, and dimensional requirements for fastest response. We respond to all inquiries within 4 business hours and offer sample delivery within 7–10 working days upon design confirmation.
Below are typical material properties of our most widely used rubber compounds for extrusion manufacturing applications:
| Material | Hardness (Shore A) | Temp Range (°C) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Key Resistance Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | 60–90 | -30 to +100 | 10–25 | 200–400 | Oil, fuel, abrasion |
| EPDM | 50–80 | -50 to +150 | 8–20 | 250–450 | Ozone, steam, weathering |
| FKM | 65–85 | -20 to +230 | 12–22 | 150–300 | High heat, chemicals |
| VMQ | 40–80 | -60 to +200 | 6–15 | 200–600 | UV, oxidation, flex |
Partner with Suzhou Baoshida to ensure your extrusion systems operate with maximum uptime and sealing integrity. Contact Mr. Boyce today at [email protected].
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
