Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Flexible Pvc Sheet
Engineering Insight: Material Selection Criticality in Flexible PVC Sheet Applications
Material selection for flexible PVC sheet is not a commodity exercise but a precision engineering decision with direct consequences for product lifecycle and operational reliability. Off-the-shelf PVC sheets frequently fail in demanding industrial environments because they prioritize cost minimization over application-specific performance parameters. Generic formulations assume benign conditions, ignoring critical variables such as dynamic stress profiles, chemical exposure spectra, temperature extremes, and required service life. This oversight leads to premature degradation modes including plasticizer migration, embrittlement, tensile strength loss, and catastrophic seal or barrier failure. The core issue lies in the homogenized nature of mass-market PVC: standardized plasticizer blends (often low-molecular-weight phthalates) lack stability under thermal cycling or solvent contact, while inadequate UV stabilizers accelerate surface cracking. Furthermore, inconsistent filler dispersion and unoptimized polymer molecular weight distribution create weak points prone to fatigue in flexing applications. These failures manifest as costly downtime, safety hazards, and reputational damage – expenses far exceeding the initial savings from generic sheet procurement.
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. addresses this through OEM-driven material science. We reject the “one-size-fits-all” approach, initiating projects with rigorous application profiling. Key parameters analyzed include continuous/peak operating temperatures, fluid compatibility matrices (oils, acids, solvents), flexural endurance requirements, and regulatory constraints (e.g., FDA, UL, RoHS). This data directly informs our compounding strategy. High-performance flexible PVC requires strategic plasticizer selection beyond standard DOP/DEHP; we utilize trimellitates or polymeric plasticizers for superior heat and extraction resistance. Polymer grade is tailored – higher K-value resins enhance tensile and tear strength for mechanical parts, while specialized impact modifiers improve low-temperature flexibility below -30°C. Critical additives include synergistic antioxidant packages, high-load UV absorbers, and processing aids ensuring uniform dispersion without compromising clarity or purity. The result is a sheet engineered at the molecular level to maintain polymer matrix integrity under the client’s exact operational stresses.
The table below contrasts critical parameters between generic and engineered flexible PVC sheet:
| Parameter | Generic PVC Sheet | Engineered PVC Sheet (Baoshida OEM) |
|---|---|---|
| Plasticizer Migration (70°C, 72h) | >25% weight loss | <5% weight loss |
| Continuous Use Temperature | -10°C to +60°C | -40°C to +105°C |
| Tensile Strength Retention (1000h, 85°C) | <50% | >85% |
| Chemical Resistance (Hydraulic Oil) | Severe swelling/cracking | Minimal swelling (<5%), no cracking |
| Flex Life (DIN 53359) | <50,000 cycles | >500,000 cycles |
| Regulatory Compliance | Basic REACH | Customizable to FDA 21 CFR, UL 94 V-0, EN 45545 |
Precision in flexible PVC sheet manufacturing demands moving beyond catalog specifications. Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering process transforms material selection from a procurement task into a risk mitigation strategy, ensuring the sheet performs as a reliable engineered component – not a failure point. Partner with us to convert application challenges into validated material solutions.
Material Specifications
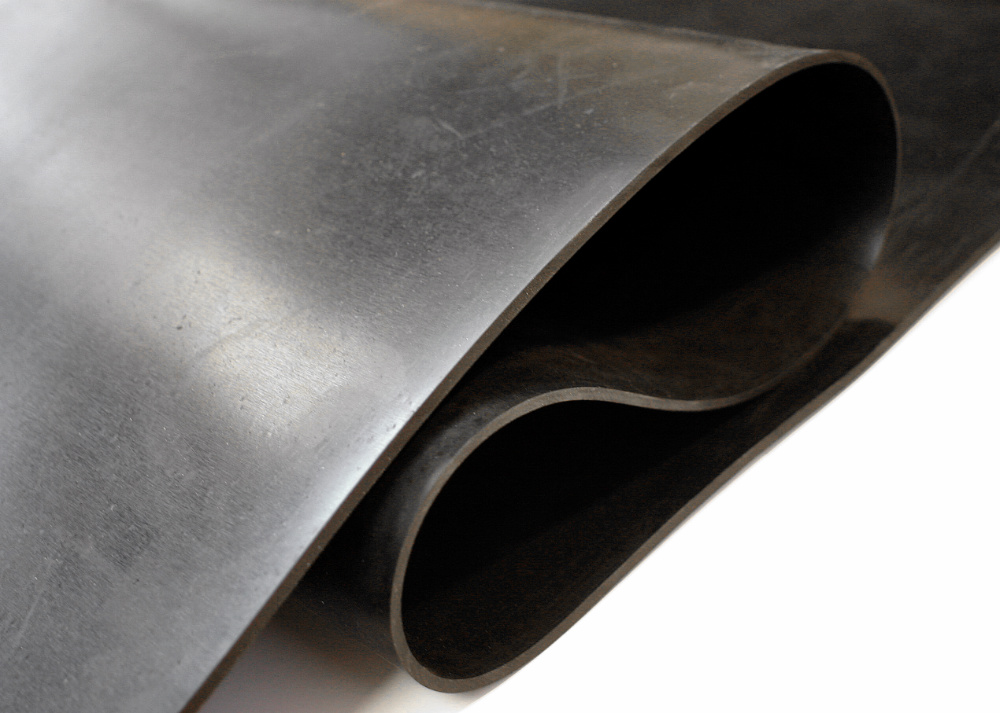

Material Specifications for Flexible PVC Sheet in Industrial Applications
Flexible PVC sheet is a critical material in industrial rubber solutions due to its balance of mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and cost efficiency. While PVC serves as the base polymer in many sealing and protective applications, its performance can be significantly enhanced when compounded with specialty elastomers such as Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone. These materials are often integrated into composite structures or used as alternative elastomeric layers where higher performance under extreme conditions is required. Understanding the technical differences between these materials enables precise material selection for demanding environments.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based elastomer developed by DuPont Performance Elastomers, offers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a wide range of aggressive chemicals. It maintains integrity in continuous service up to 200°C and can withstand short-term exposure to temperatures as high as 250°C. This makes Viton ideal for aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing industries where thermal stability and chemical inertness are paramount. However, its higher cost and lower flexibility at low temperatures may limit its use in general-purpose applications.
Nitrile rubber, or acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), is one of the most widely used elastomers in industrial sealing due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels. It performs reliably in temperatures ranging from -30°C to 120°C, with special formulations extending low-temperature performance. Nitrile offers good abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, making it suitable for hydraulic systems, gaskets, and fuel handling components. Its compatibility with flexible PVC allows for hybrid sheet constructions that combine cost efficiency with targeted fluid resistance.
Silicone rubber excels in extreme temperature applications, with continuous service capabilities from -60°C to 200°C. It exhibits outstanding resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering, making it ideal for outdoor and high-temperature environments. While its mechanical strength and abrasion resistance are lower than Nitrile or Viton, silicone provides excellent electrical insulation and biocompatibility, which is advantageous in medical, electronic, and food-grade applications. When laminated with flexible PVC, it can provide thermal protection while maintaining structural support.
The following table compares key physical and chemical properties of Viton, Nitrile, and Silicone to guide material selection for industrial flexible PVC sheet applications.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 200 (up to 250 short-term) | -30 to 120 (special grades to -50) | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–20 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–500 | 200–700 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor to Fair |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set | Excellent | Good | Good to Excellent |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Fair | Excellent |
| Common Applications | Aerospace seals, chemical gaskets | Hydraulic seals, fuel systems | Medical devices, electronics, outdoor seals |
Selecting the appropriate elastomer depends on the operational environment, including temperature extremes, chemical exposure, mechanical loading, and regulatory requirements. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we provide customized flexible PVC sheet solutions engineered with these elastomers to meet precise industrial demands.
Manufacturing Capabilities
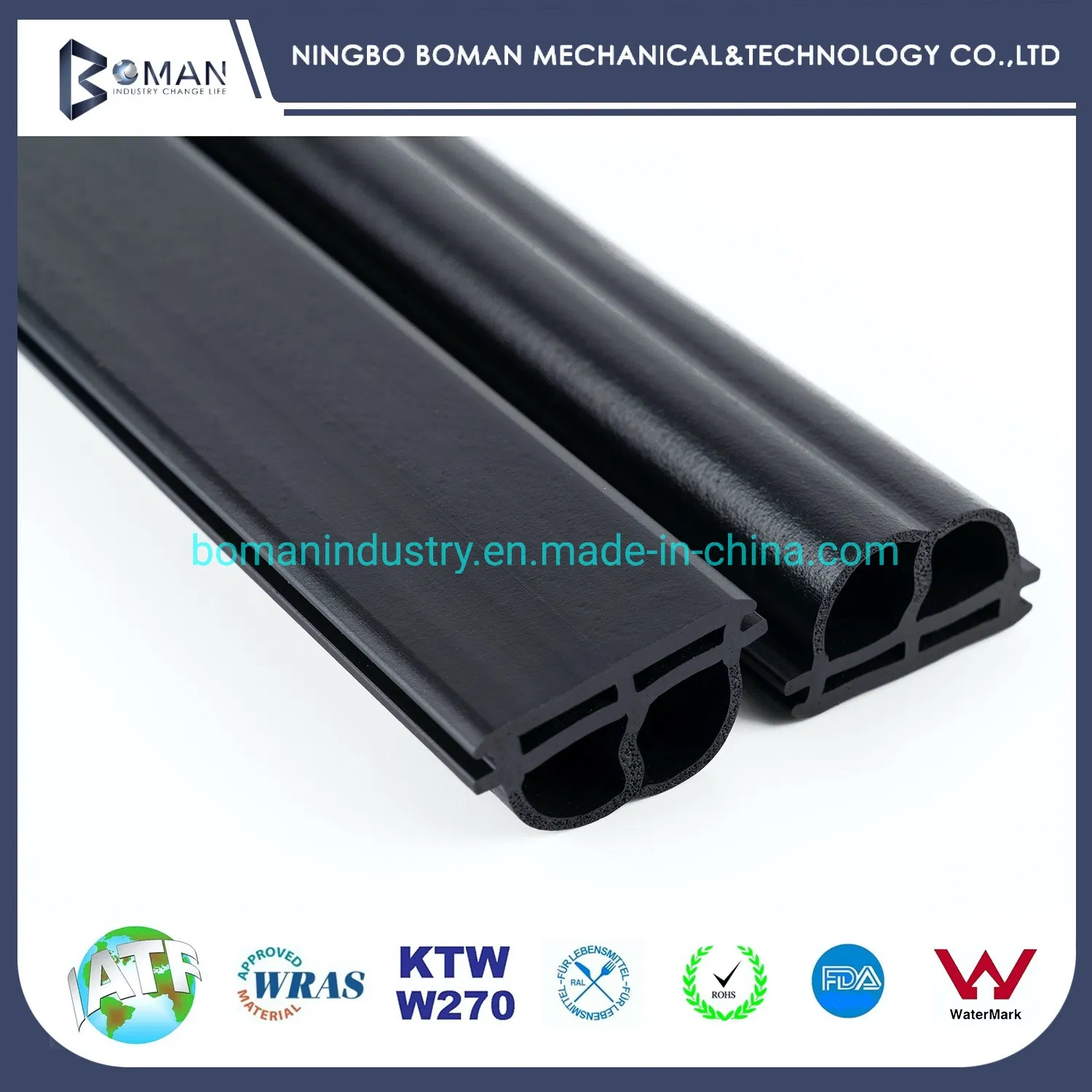
Engineering Capability: Precision Formulation and OEM Excellence for Flexible PVC Sheet Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered flexible PVC sheet solutions through integrated material science and advanced tooling expertise. Our dedicated team of 5 Mold Engineers and 2 Formula Engineers operates at the intersection of polymer chemistry and precision manufacturing, ensuring every product meets stringent industrial performance criteria. This synergy enables us to solve complex material challenges while maintaining rigorous cost-efficiency for global OEM partners.
Our Formula Engineers specialize in optimizing PVC compound formulations for targeted applications. Leveraging deep knowledge of plasticizer systems (DINP, DOTP), thermal stabilizers (Ca/Zn, organotin), and reinforcing additives, we precisely balance flexibility, durability, and processability. Each formulation undergoes iterative laboratory validation for critical properties including tensile strength, elongation at break, and low-temperature flexibility. This scientific approach eliminates trial-and-error in production, reducing time-to-market for custom solutions by up to 30%. Crucially, our engineers design compounds compatible with diverse processing methods—calendering, extrusion, and压延—ensuring seamless scalability from prototype to high-volume output.
Complementing formulation mastery, our Mold Engineering team designs and validates tooling with micron-level precision. Utilizing advanced CAE simulation (Moldflow), we optimize cavity geometry, cooling channels, and ejection systems to minimize warpage and internal stress in flexible sheets. Real-time cavity pressure monitoring during tool trials ensures uniform thickness distribution and surface finish consistency. With expertise in multi-cavity and family molds, we achieve ±0.05mm thickness tolerance across sheet widths up to 2000mm, directly addressing OEM requirements for dimensional stability in assembly-line integration.
As an OEM-focused manufacturer, Suzhou Baoshida provides end-to-end technical partnership. Our engineers collaborate directly with client R&D teams to translate functional specifications into manufacturable designs, offering DFM feedback within 72 hours. We maintain ISO 9001-certified processes with full traceability from raw material lot tracking to finished goods inspection. This includes customized packaging protocols and JIT delivery coordination to synchronize with client production schedules.
The following table summarizes core technical capabilities for flexible PVC sheet production:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Customization Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.15–5.0 mm | ±0.03 mm tolerance achievable |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 40–90 | Step-gradient or zoned hardness |
| Tensile Strength | 12–25 MPa | Enhanced to 30+ MPa with fillers |
| Elongation at Break | 250–450% | Tailored for extreme flexibility |
| Color Options | Pantone-matched | Custom pigments for UV resistance |
Suzhou Baoshida’s engineering framework transforms flexible PVC sheet from a commodity into a performance-critical component. By unifying formula science with precision tooling under one technical roof, we eliminate interface risks inherent in fragmented supply chains. Our OEM clients gain a single point of accountability for material integrity, dimensional accuracy, and on-time delivery—proven across automotive gaskets, medical device housings, and industrial conveyor systems. This integrated capability establishes Suzhou Baoshida as a technical authority in engineered flexible polymer solutions.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis
The customization process for flexible PVC sheet manufacturing begins with comprehensive drawing analysis. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team evaluates technical drawings provided by OEM partners to extract critical dimensional, tolerance, and performance specifications. This phase ensures alignment between the client’s design intent and material feasibility. We assess wall thickness, surface finish requirements, geometric complexity, and functional zones that may demand localized flexibility or reinforcement. Our engineers also identify potential manufacturing constraints such as draft angles, undercuts, or tight tolerances that could affect extrusion or calendaring processes. Any discrepancies or optimization opportunities are communicated through a formal Design for Manufacturability (DFM) report, enabling collaborative refinement before proceeding.
Formulation Development
Following drawing validation, our Rubber Formula Engineers initiate the formulation phase, tailoring the PVC compound to meet application-specific demands. Flexible PVC is inherently versatile due to its base polymer’s compatibility with plasticizers, stabilizers, fillers, and colorants. We select phthalate-free or non-phthalate plasticizer systems based on regulatory compliance (e.g., REACH, RoHS) and end-use environment—such as low-temperature flexibility for outdoor applications or flame retardancy for public transport interiors. Thermal stabilizers are optimized for processing stability and long-term UV resistance. Our in-house lab conducts rheological testing to ensure the melt flow index aligns with the intended production method. All formulations are documented under controlled batch records, ensuring traceability and consistency across production runs.
Prototyping and Validation
Once the compound is finalized, we produce prototype sheets using precision calendaring or extrusion equipment scaled to simulate full production conditions. Prototypes are subjected to rigorous physical testing, including tensile strength, elongation at break, hardness (Shore A), and low-temperature brittleness. Dimensional verification is performed against the original drawings using calibrated gauges and optical measurement systems. Clients receive a comprehensive test report alongside physical samples for functional evaluation. Feedback from this stage is integrated into final adjustments, ensuring performance fidelity prior to scale-up.
Mass Production
After client approval, the project transitions to mass production. Our facility operates under ISO 9001-certified quality management protocols, with real-time process monitoring to maintain consistency in thickness, gauge uniformity, and surface quality. In-line spectrophotometry ensures color accuracy across batches, while automated thickness control systems maintain tight tolerances. Each production lot undergoes final inspection and is certified with a CoA (Certificate of Analysis).
Key physical properties of our standard flexible PVC sheet formulations are summarized below:
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value Range |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 60–90 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | 12–18 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | 250–350% |
| Specific Gravity | ASTM D792 | 1.25–1.35 |
| Low-Temp Brittleness | ASTM D746 | -20°C to -30°C |
| Flame Resistance | UL 94 | HB Rated |
This structured approach ensures that every customized flexible PVC sheet meets exacting industrial standards, delivering performance, compliance, and reliability.
Contact Engineering Team
Technical Partnership for Precision PVC Sheet Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered flexible PVC sheet solutions for demanding industrial applications where material consistency, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability are non-negotiable. Our formulations address critical challenges in automotive sealing, conveyor systems, protective barriers, and fluid containment, leveraging proprietary plasticizer systems and reinforcement technologies to eliminate common failure modes like plasticizer migration, UV degradation, or low-temperature embrittlement. As your OEM partner, we prioritize ASTM D412 and ISO 188 compliance while optimizing cost-performance ratios through rigorous raw material vetting and in-house compounding validation.
Our technical team specializes in tailoring PVC sheet properties to exact operational parameters, including custom durometer adjustments for dynamic sealing interfaces or enhanced flame retardancy for transit infrastructure. Below are baseline specifications for our standard industrial-grade flexible PVC sheet, all subject to client-specific modification under our collaborative development framework.
| Property | Standard Range | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.5 mm – 5.0 mm | ASTM D374 |
| Shore A Hardness | 60 – 95 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥12 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% | ASTM D412 |
| Operating Temperature | -30°C to +70°C | ISO 188 |
| Flame Resistance | UL94 HB | UL 94 |
| Color Options | Custom Pantone Match | Visual Comparison |
Engage directly with Mr. Boyce, our dedicated Technical OEM Manager, to initiate a precision-driven development cycle for your PVC sheet requirements. With 14 years of formulation expertise in thermoplastic elastomers and a track record of resolving complex adhesion or extrusion defects for Tier-1 automotive suppliers, Mr. Boyce ensures your project transitions seamlessly from material specification to serial production. He will coordinate our analytical lab resources—including DSC thermal profiling and accelerated aging chambers—to validate performance against your environmental stress criteria before tooling commitment.
Do not compromise on material integrity when standard catalog sheets fail to address your application’s mechanical or regulatory constraints. Contact Mr. Boyce immediately at [email protected] with your target specifications, volume forecasts, and critical failure thresholds. Include reference to this technical guide to expedite our engineering assessment. Suzhou Baoshida operates under IATF 16949-certified quality protocols with batch traceability to raw material lot codes, ensuring zero-defect delivery for high-volume OEM programs. Our Shanghai-based R&D center provides rapid prototyping within 15 business days, allowing you to de-risk integration into existing manufacturing lines.
Partner with an organization where chemical formulation science drives commercial outcomes. Mr. Boyce will respond within 4 business hours to schedule a technical consultation focused exclusively on your material performance objectives. Forward your requirements today to secure engineering bandwidth for Q3 production ramps.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
