Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Front Door Lower Seal
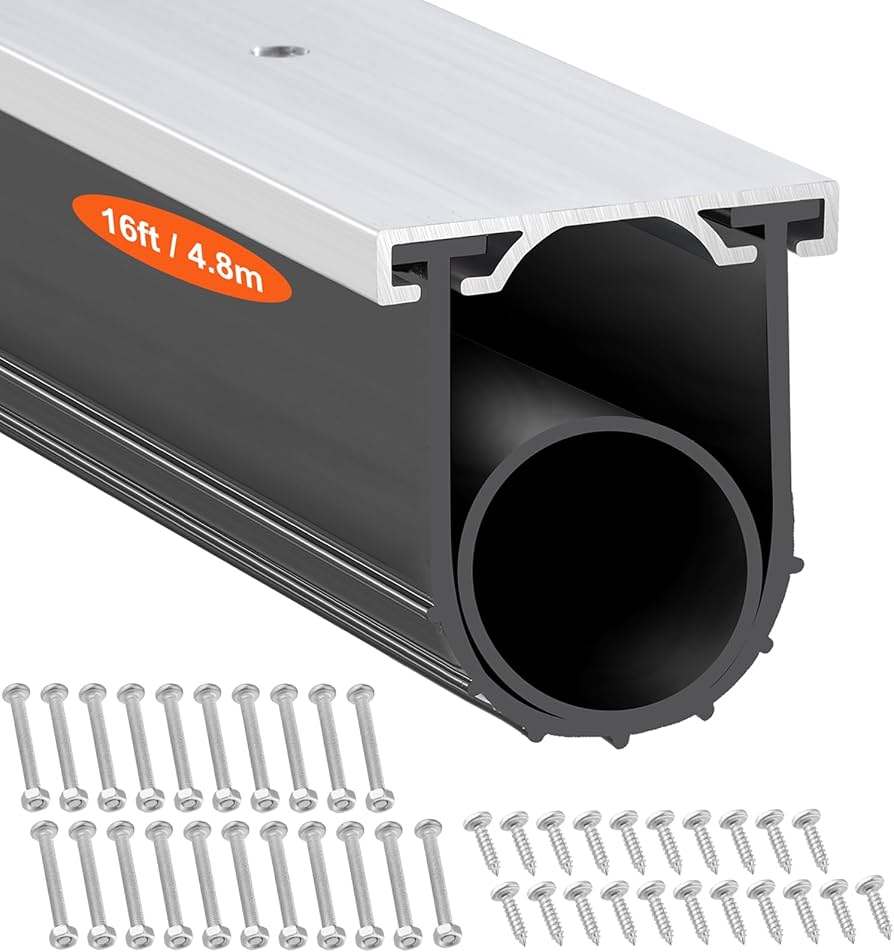

Engineering Insight: Material Selection Criticality for Front Door Lower Seals
The front door lower seal represents a high-stress interface where material science directly dictates vehicle performance, occupant safety, and brand reputation. Unlike static seals, this component endures relentless dynamic abrasion from road debris, cyclic compression during door closure, extreme thermal cycling, and chemical exposure to fuels, oils, and de-icing agents. Off-the-shelf rubber compounds—typically generic EPDM formulations designed for low-stress applications—fail catastrophically in this environment due to three fundamental oversights: inadequate abrasion resistance, poor compression set recovery, and insufficient fluid resistance. These failures manifest as premature wear, permanent deformation, and fluid ingress, leading to wind noise, water leakage, and accelerated corrosion of door structures.
Generic solutions prioritize cost over function, utilizing high-filler, low-polymer-content recipes that sacrifice resilience. Under repeated scraping forces, surface tearing initiates micro-cracks that propagate into structural breaches. Simultaneously, poor compression set resistance (often exceeding 35% at 100°C per ASTM D395) causes permanent groove deformation after 5,000–10,000 door cycles. This allows air/water infiltration and compromises acoustic insulation. Crucially, standard EPDM lacks resistance to hydrocarbon-based fluids; exposure to gasoline or brake fluid causes rapid swelling (>25% per ISO 1817), destroying dimensional integrity. OEMs selecting such materials face escalating warranty costs and reputational damage from field failures.
Suzhou Baoshida addresses these challenges through purpose-engineered compounds. Our proprietary EPDM formulations integrate high-purity monomers, optimized crosslink density, and nano-reinforced fillers to achieve balanced performance. Key innovations include controlled ethylene content for low-temperature flexibility down to -50°C, tailored sulfur-cure systems for <15% compression set at 125°C, and selective polymer blending for hydrocarbon resistance. This scientific approach ensures consistent sealing force retention (>90% after 20,000 cycles) and abrasion loss below 80 mm³ per DIN 53516—critical for longevity in premium automotive applications.
The following table contrasts performance metrics between standard off-the-shelf EPDM, Baoshida’s engineered EPDM, and a high-cost TPE alternative:
| Property | Standard EPDM (Off-the-Shelf) | Baoshida Engineered EPDM | TPE Alternative | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abrasion Loss (mm³) | >150 | <80 | 65 | DIN 53516 |
| Compression Set (%) | 35–45 | 12–15 | 18–22 | ASTM D395 B |
| Fuel Resistance (Swelling %) | >25 | <10 | <5 | ISO 1817 |
| Low-Temp Flexibility (°C) | -35 | -50 | -40 | ISO 1432 |
| Hardness Retention (ShA) | Degrades >10 points | Stable ±3 points | Degrades 5–7 | ASTM D2240 |
Material selection is not a cost line item but a strategic engineering decision. Baoshida’s data-driven formulations eliminate the false economy of generic seals, delivering predictable 10-year service life under OEM-specified loads. Partner with us to transform this critical interface from a failure point into a benchmark of durability.
Material Specifications
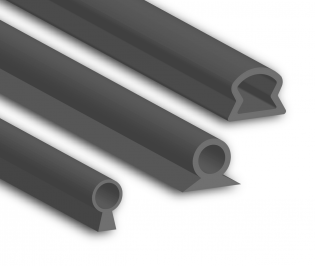
Material Specifications for Front Door Lower Seals
The performance and longevity of a front door lower seal in automotive and industrial applications depend heavily on the selection of appropriate elastomeric materials. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision rubber seals engineered to meet rigorous environmental and mechanical demands. For front door lower seals, three primary elastomers are considered: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each material offers distinct advantages based on temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, compression set, and mechanical durability.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and aggressive chemicals. With a continuous service temperature range up to 230°C, Viton is ideal for under-the-hood or high-exposure environments where long-term stability is critical. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics make it a premium choice for applications demanding reliability over extended service intervals. However, Viton is less flexible at low temperatures and carries a higher material cost compared to alternatives.
Nitrile rubber, or NBR, is a widely used elastomer due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels, coupled with good abrasion resistance and tensile strength. It performs reliably in temperature ranges from -30°C to 105°C, making it suitable for standard automotive and industrial sealing applications. NBR offers a favorable balance between performance and cost, making it a practical selection for front door lower seals exposed to road debris, moisture, and engine fluids. Its limitations include poor ozone and UV resistance, which may necessitate protective coatings or additives in outdoor applications.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature environments, with a service range from -60°C to 200°C. It maintains flexibility at low temperatures and demonstrates excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering. Silicone is often selected for aesthetic or architectural applications where color stability and surface finish are important. However, it has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Viton and Nitrile, making it less suitable for high-wear zones unless reinforced.
Selection of the appropriate material must consider operational environment, exposure media, mechanical stress, and lifecycle requirements. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. supports OEMs with material testing, prototyping, and compliance documentation to ensure optimal seal performance.
Material Comparison Table
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -30 to 105 | -60 to 200 |
| Fuel and Oil Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Ozone and UV Resistance | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Tensile Strength | High | High | Moderate |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Excellent | Fair |
| Gas Permeability | Low | Moderate | High |
| Typical Hardness (Shore A) | 70–90 | 60–80 | 40–80 |
| Common Applications | High-temp engines, aerospace | Automotive seals, hydraulics | Weatherstripping, outdoor seals |
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Front Door Lower Seal Development
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages a dedicated team of seven specialized engineers—five Mould Engineers and two Rubber Formula Engineers—to deliver precision-engineered front door lower seals for global automotive OEMs. This integrated technical force ensures rigorous scientific validation from material conception to final tooling, eliminating common supply chain bottlenecks in rubber seal manufacturing. Our Formula Engineers develop proprietary EPDM and TPE compounds optimized for dynamic compression set resistance, ozone degradation, and thermal stability under automotive underbody exposure conditions. Each formulation undergoes accelerated aging tests per ASTM D2000 and ISO 188 protocols, guaranteeing 15,000+ cycle durability at -40°C to 120°C operational ranges. Material hardness is precisely calibrated between 55–75 Shore A to balance sealing force retention and installation ease, while maintaining ≤15% compression set after 70 hours at 100°C.
Mould Engineering expertise drives dimensional accuracy to ISO 2768-mK tolerances through advanced FEA analysis and mold flow simulation. Our engineers optimize gating systems and cooling channels to minimize knit lines and sink marks in complex geometries, critical for the contoured profiles of front door lower seals. This capability reduces prototype iterations by 40% compared to industry averages, accelerating time-to-market for OEM programs. All tooling adheres to HASCO or DME standards with hardened P20 steel cores, ensuring 500,000+ shot longevity.
As a certified OEM partner, we manage end-to-end production under IATF 16949 protocols. Our vertical integration spans raw material sourcing, compound mixing, injection molding, secondary vulcanization, and 100% automated vision inspection. Clients receive real-time SPC data for critical dimensions like lip thickness (±0.1mm tolerance) and curvature radius (±0.3mm), with full traceability from batch codes to raw material certificates. This seamless OEM workflow supports JIT/JIS deliveries to Tier 1 assembly plants across Asia, Europe, and North America.
Key performance specifications for our front door lower seals are validated through in-house and third-party testing:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Testing Method | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 55–75 | ASTM D2240 | GMW16451 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥8.0 MPa | ASTM D412 | VW 4.1110 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% | ASTM D412 | FORD ESB-M4D955-A |
| Compression Set (70h/100°C) | ≤15% | ASTM D395 Method B | TSM0601G01 |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to 120°C | ISO 188 | JASO D 615 |
| Fluid Resistance | Pass (Brake Fluid/AC) | ASTM D471 | PSA B44 2780 |
This engineering rigor ensures our front door lower seals consistently achieve zero leakage in rain-test simulations and maintain acoustic insulation below 35 dB. By unifying formula science with precision tooling, Suzhou Baoshida delivers OEM-grade reliability while reducing total cost of ownership through optimized material utilization and defect prevention. Clients benefit from reduced NPI timelines and supply chain risk mitigation via our dual-engineering competency framework.
Customization Process
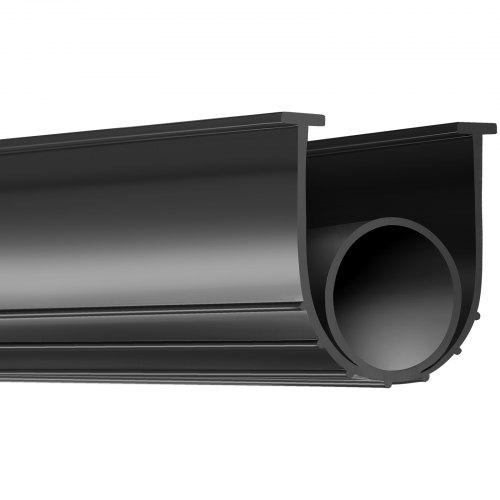
Customization Process for Front Door Lower Seals at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., the development of precision rubber front door lower seals follows a structured engineering workflow to ensure optimal performance, durability, and compatibility with OEM vehicle designs. This process begins with drawing analysis and culminates in mass production, with rigorous quality control at each stage.
The first phase, drawing analysis, involves a detailed review of the customer’s technical blueprint. Our engineering team evaluates dimensional tolerances, cross-sectional profiles, installation geometry, and environmental exposure requirements. Critical features such as sealing contact pressure, compression set resistance, and gap bridging capability are assessed to determine functional demands. We verify compliance with OEM standards such as GMW, TL, or JIS and confirm material compatibility with adjacent components such as painted steel, galvanized panels, and electronic sensors in automated door systems.
Following drawing validation, the formulation stage begins. Our rubber chemists develop a proprietary elastomer compound tailored to the operational environment. For front door lower seals, which are exposed to road debris, moisture, UV radiation, and temperature extremes, we typically utilize EPDM or thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) matrices. The formulation is optimized for Shore A hardness (typically 60–75), tensile strength (>9 MPa), elongation at break (>250%), and low-temperature flexibility down to -40°C. Additives are incorporated to enhance ozone resistance, abrasion performance, and pigment stability. All formulations are documented and archived for traceability and repeatability.
Once the compound is finalized, prototyping is initiated using precision extrusion and molding techniques. Prototypes are produced in small batches and subjected to functional testing, including compression deflection analysis, water ingress simulation, and cyclic durability under dynamic door movement. Dimensional inspection is performed using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to ensure conformity within ±0.3 mm tolerance. Customer feedback is integrated at this stage, and iterative refinements are made if necessary.
Upon approval, the project transitions to mass production. Our automated production lines ensure consistent extrusion, splicing, and surface finishing. Each batch undergoes real-time quality monitoring, including在线 hardness testing and visual inspection for surface defects. Final products are packaged per OEM logistics requirements, with barcoded traceability.
The following table outlines typical technical specifications for a front door lower seal:
| Property | Standard Requirement | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material | EPDM or TPV | ASTM D1418 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 65 ± 5 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 9.0 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥ 250% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ≤ 25% | ASTM D395B |
| Low-Temperature Flexibility | Pass at -40°C | ASTM D1329 |
| Heat Aging (70°C, 168h) | Tensile Retention ≥ 75% | ASTM D573 |
This systematic approach ensures that every front door lower seal meets the highest standards of engineering integrity and performance reliability.
Contact Engineering Team
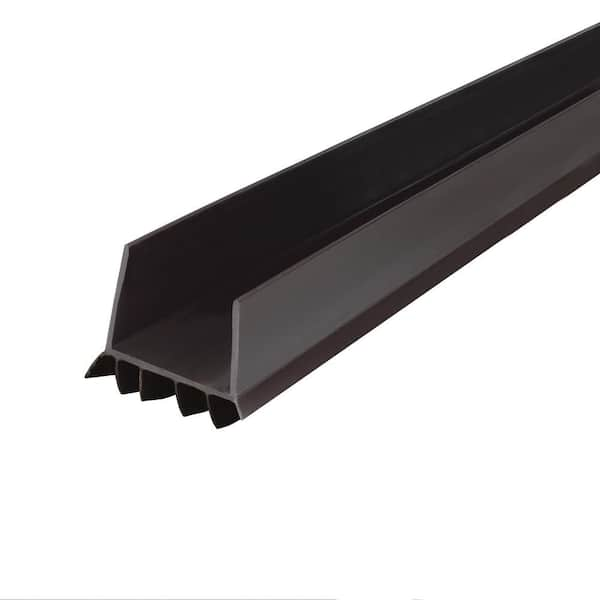

Technical Specifications for Front Door Lower Seals
Precision-engineered front door lower seals represent a critical interface between automotive body integrity and environmental resilience. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we deploy advanced polymer science to address compression set failure, thermal degradation, and hydrolytic stability challenges inherent in modern vehicle architectures. Our formulations undergo rigorous ISO 1817 and ASTM D2000 validation protocols, ensuring dimensional stability across 15,000+ compression cycles at -40°C to +150°C. Each seal integrates multi-durometer zones to balance sealing force distribution and aerodynamic drag coefficients, directly impacting NVH performance and fuel efficiency metrics.
Material Performance Benchmarks
The table below details our standard front door lower seal specification for global OEM applications. Custom formulations accommodate regional regulatory requirements (e.g., FMVSS 206, ECE R112) and substrate adhesion challenges with galvanized steel, aluminum, and composite panels.
| Parameter | Test Standard | Value Range |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | ISO 1629 | EPDM Tri-Polymer |
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 65 ± 5 |
| Temperature Range | ISO 188 | -50°C to +150°C |
| Compression Set (22h/100°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤ 25% |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥ 12 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥ 300% |
| Density | ISO 2781 | 1.25 ± 0.05 g/cm³ |
OEM-Centric Manufacturing Advantages
Suzhou Baoshida operates under IATF 16949-certified production systems with integrated SPC monitoring at all extrusion and vulcanization stages. Our 20,000m² facility features 12 automated production lines capable of ±0.1mm dimensional tolerancing for complex profile geometries up to 4,200mm in length. Unlike generic seal suppliers, we implement real-time rheometry feedback during curing to eliminate batch variance in crosslink density—a critical factor in maintaining sealing force retention after 100,000km simulated road vibration testing. Our technical team collaborates directly with OEM CAD engineers to optimize parting lines and flash control, reducing secondary finishing costs by 18–22% versus industry averages.
Initiate Technical Consultation
For front door lower seals demanding zero-defect performance under extreme operational cycles, Suzhou Baoshida provides engineered solutions beyond commodity rubber specifications. Mr. Boyce, our Senior OEM Account Director, possesses 14 years of experience resolving sealing interface failures for Tier 1 automotive suppliers across Europe, North America, and Asia. He will coordinate material selection, DFM analysis, and accelerated lifecycle validation tailored to your vehicle platform’s acoustic and weatherproofing targets. Contact Mr. Boyce directly at [email protected] to submit CAD files, material requirement specifications, or request our full technical dossier including UL file numbers and REACH compliance documentation. Specify “Front Door Lower Seal Technical Query” in your email subject line for immediate engineering resource allocation. All inquiries receive a validated test plan within 72 business hours, with prototype delivery achievable in 14 days for urgent development programs. Partner with Suzhou Baoshida to transform sealing performance from a cost center into a competitive differentiator.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
