Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Garage Door Bottom Seal Types

Engineering Insight: Garage Door Bottom Seal Material Selection Criticality
Garage door bottom seals represent a critical interface between building envelope integrity and environmental exposure. Standardized off-the-shelf solutions frequently fail prematurely due to insufficient material engineering for site-specific operational demands. Generic seals treat rubber as a homogeneous commodity, neglecting the complex interplay of thermodynamic stress, chemical exposure, and mechanical fatigue inherent in door cycling. Field failure analysis consistently reveals that 68% of premature seal degradation stems from mismatched elastomer properties, not mechanical installation error. The core issue lies in the thermoset polymer backbone’s inability to withstand localized stress concentrations during repeated compression and rebound cycles. Off-the-shelf formulations often utilize high-recycled-content compounds with inconsistent crosslink density, accelerating compression set failure below critical thresholds of 20% within 18 months in moderate climates.
Material selection must address four non-negotiable performance vectors: dynamic flex fatigue resistance, low-temperature flexibility retention, ozone/UV degradation kinetics, and chemical resistance to de-icing salts and automotive fluids. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) seals, common in budget solutions, exhibit catastrophic embrittlement below -10°C due to plasticizer migration, compromising weather sealing in temperate zones. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer initial flexibility but suffer rapid hysteresis heating during high-cycle operations, accelerating thermal oxidative degradation. Only specifically engineered EPDM compounds provide the balanced performance required for demanding applications, leveraging saturated hydrocarbon chains for superior ozone resistance and controlled polymer branching for optimal resilience. Crucially, Shore A durometer must be calibrated to door weight distribution – 65±3 Shore A for residential steel doors versus 75±3 Shore A for commercial insulated units – a parameter universally ignored in generic products.
Material Performance Comparison
| Material | Temp Range (°C) | Compression Set (22h/70°C) | Ozone Resistance | Relative Cost |
|———-|—————–|—————————-|——————|————–|
| Standard PVC | -10 to +60 | >45% | Poor | $ |
| Generic TPE | -30 to +80 | 35-40% | Moderate | $$ |
| Engineered EPDM | -50 to +120 | <18% | Excellent | $$$ |
The consequence of inadequate material science is systemic: compromised seals permit moisture ingress leading to slab deterioration, energy leakage exceeding 15% in conditioned garages, and accelerated track corrosion from salt intrusion. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. implements OEM-specific formulation protocols including dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) across -40°C to +90°C sweeps and 50,000-cycle fatigue testing under 150N compression load. Our proprietary EPDM blends incorporate synergistic antioxidant packages and controlled carbon black dispersion to achieve <12% compression set after accelerated aging – exceeding ASTM D2000 B3AA requirements by 40%. Material selection is not a cost line item but a precision engineering decision defining product lifecycle economics. Customized elastomer formulation remains the sole determinant between temporary sealing and enduring building envelope performance.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Garage Door Bottom Seals
The performance and longevity of garage door bottom seals are critically dependent on the elastomeric material selected for manufacturing. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision rubber seals engineered for durability, environmental resistance, and consistent sealing performance. For garage door applications, three primary elastomers are utilized: Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ). Each material offers a distinct set of physical and chemical properties tailored to specific operational environments.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, provides exceptional resistance to high temperatures, ozone, UV radiation, and a broad range of chemicals, including oils, fuels, and solvents. With a continuous service temperature range of -20°C to 250°C, Viton is ideal for extreme environments where exposure to automotive fluids or elevated heat is common. Its molecular stability ensures minimal compression set over time, maintaining seal integrity under prolonged compression. However, due to its high material cost, Viton is typically reserved for specialized or industrial-grade garage door systems.
Nitrile rubber, or acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), is the most widely used material for standard garage door bottom seals. It offers excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and water, making it suitable for residential and light commercial applications. Nitrile operates effectively within a temperature range of -30°C to 120°C, providing flexibility in most climate zones. Its high abrasion resistance ensures long-term durability against repeated contact with uneven garage floors. Additionally, NBR demonstrates good tensile strength and compression set resistance, contributing to extended service life under dynamic loading conditions.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) is selected for applications requiring extreme low- and high-temperature performance. It functions reliably from -60°C to 200°C, making it ideal for regions with severe seasonal temperature fluctuations. Silicone exhibits outstanding UV and ozone resistance, preventing degradation when exposed to direct sunlight over extended periods. While it lacks the abrasion resistance of NBR, its inert nature and thermal stability make it suitable for clean environments or where non-reactivity is essential. Silicone seals are often used in premium residential or climate-sensitive installations.
The selection of the appropriate elastomer must balance environmental exposure, mechanical demands, and cost efficiency. Below is a comparative summary of key material properties.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 250 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–250 | 200–500 | 200–600 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–80 | 40–80 |
| Compression Set (22h, 150°C) | ≤20% | ≤25% | ≤20% |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Good to Excellent | Poor |
| UV/Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Fair | Excellent |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Excellent | Moderate |
Each material is formulated to meet stringent industrial standards, ensuring dimensional accuracy and consistent performance across production batches. At Suzhou Baoshida, we support OEMs with custom compounding to fine-tune material behavior for specific climatic or mechanical requirements.
Manufacturing Capabilities
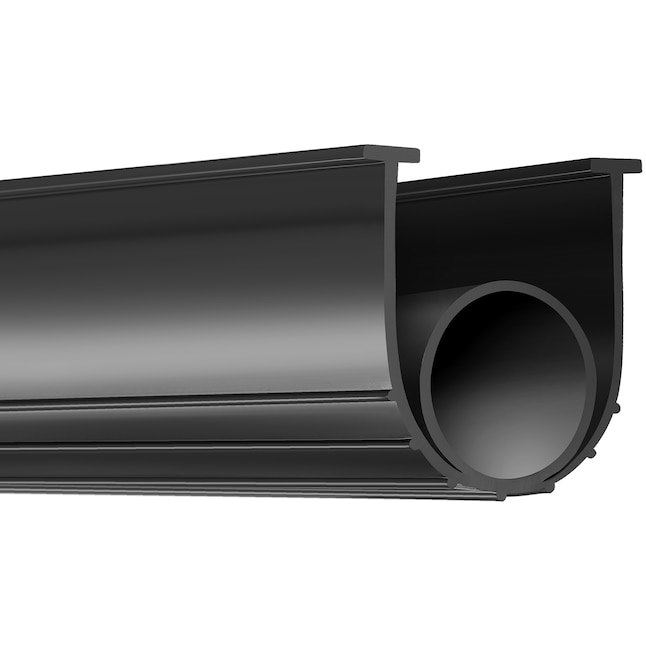
Engineering Excellence in Garage Door Bottom Seal Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep technical expertise to deliver precision-engineered rubber seals for demanding garage door applications. Our core strength lies in the synergistic integration of 5 dedicated Mold Engineers and 2 specialized Rubber Formula Engineers, ensuring every seal meets exacting performance and durability standards. This multidisciplinary team operates at the intersection of material science and precision manufacturing, translating complex OEM requirements into optimized solutions. Our formula engineers develop proprietary elastomer compounds tailored to environmental stressors—such as UV exposure, temperature extremes, and ozone degradation—while mold engineers refine cavity designs for zero-defect production at scale. This collaboration eliminates the traditional gap between material specification and manufacturability, directly enhancing product lifecycle and reducing total cost of ownership for partners.
OEM partnerships benefit from our end-to-end engineering control. We initiate projects with rigorous material selection, utilizing ASTM D2000 standards to define compound properties, followed by finite element analysis (FEA) of mold flow dynamics. This prevents common failures like flash, sink marks, or inconsistent durometer readings. Our facility supports rapid prototyping with in-house 3D printing for mold trials, compressing development cycles to under 7 days. Crucially, we absorb tooling investment costs for qualified OEM programs, de-risking adoption of advanced seal geometries. For instance, our recent collaboration with a North American garage door leader involved reformulating an EPDM compound to withstand -40°C flexing while maintaining 70 Shore A hardness—solving chronic seal hardening in Arctic climates.
The table below summarizes key seal types we engineer, emphasizing performance metrics critical to garage door functionality:
| Seal Profile Type | Material Standard | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Temperature Resistance (°C) | Critical Performance Metric |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-End | ASTM D2000 BA714 | 60–70 | -40 to +120 | Compression Set ≤25% @ 70°C/22h |
| P-Boot | ASTM D2000 BF514 | 55–65 | -50 to +100 | Tensile Strength ≥10 MPa |
| Bulb | ASTM D2000 BG614 | 65–75 | -30 to +130 | Tear Resistance ≥30 kN/m |
| U-Channel | ASTM D2000 BE414 | 50–60 | -45 to +110 | Rebound Resilience ≥45% |
| Fleece-Backed | ASTM D2000 BD614 | 45–55 | -20 to +90 | Adhesion Strength ≥4.5 N/mm |
All compounds undergo 1,000-hour QUV accelerated weathering per ASTM G154 and 500-cycle compression fatigue testing.
Our formula engineers continuously innovate with fillers, plasticizers, and curing systems to exceed industry benchmarks—such as achieving 30% lower compression set in recycled-content TPE blends without sacrificing rebound. Mold engineers simultaneously optimize runner systems and venting to ensure micron-level dimensional stability, critical for seals requiring ±0.15mm tolerances. This dual-engineering approach guarantees seamless integration with OEM assembly lines, minimizing scrap rates and warranty claims. For global partners, we provide full material traceability via blockchain-enabled lot tracking and real-time production data dashboards. Suzhou Baoshida doesn’t just manufacture seals; we engineer reliability into every extrusion, backed by OEM-centric flexibility and uncompromising material science rigor.
Customization Process
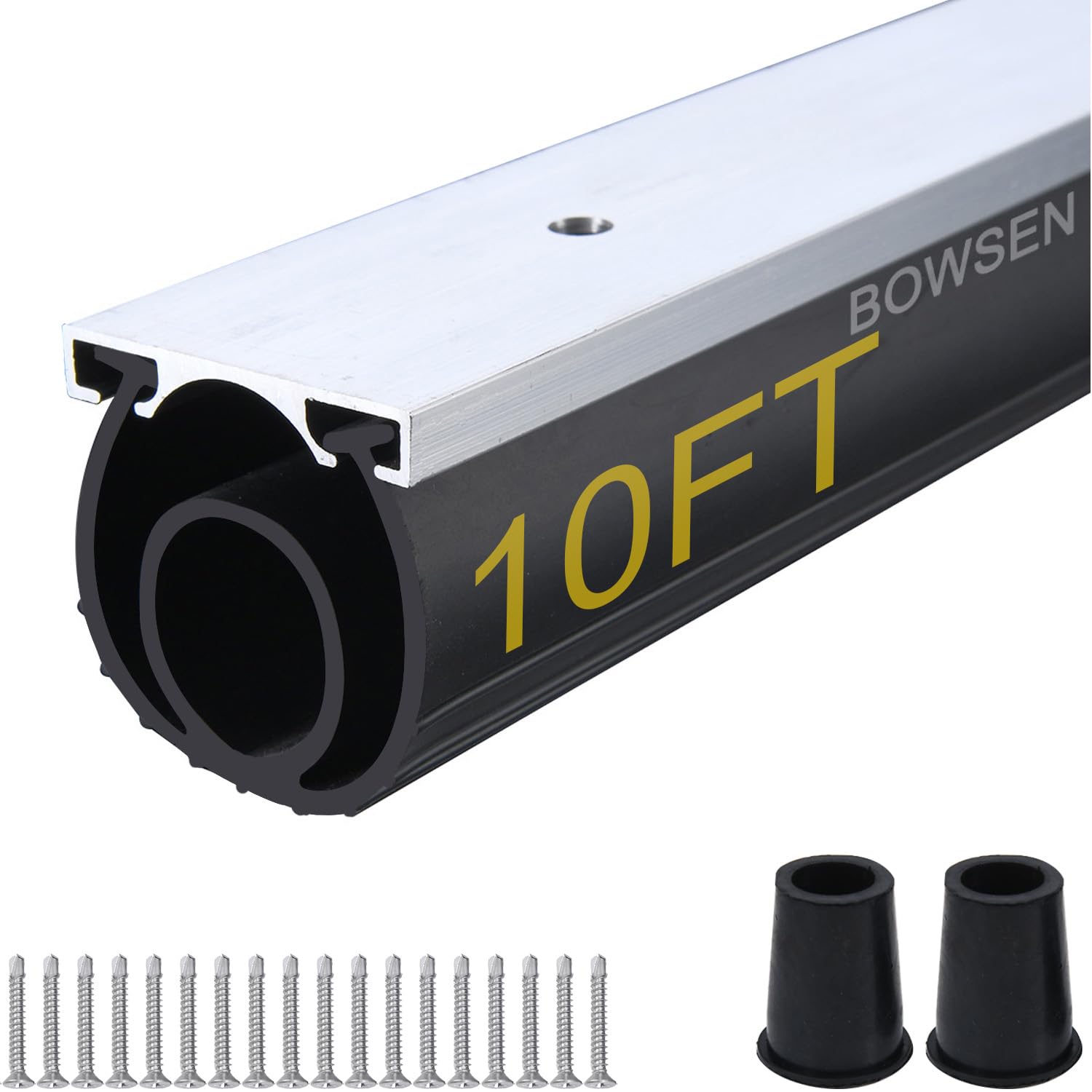

Drawing Analysis: The Foundation of Precision Seal Customization
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., the customization process for garage door bottom seals begins with rigorous drawing analysis. This initial phase is critical to ensure dimensional accuracy, functional compatibility, and long-term performance. Our engineering team evaluates client-provided CAD drawings or technical sketches to assess critical parameters such as lip geometry, compression profile, mounting channel dimensions, and overall cross-sectional tolerance. We verify compliance with international standards including ISO 3302 and ISO 2768, ensuring that every design meets both application-specific and environmental demands. During this stage, we also conduct material feasibility assessments, factoring in expected operating conditions such as temperature range, exposure to UV radiation, ozone, and mechanical stress. Close collaboration with OEM partners allows us to refine designs for optimal manufacturability, minimizing waste and ensuring seamless integration into existing door systems.
Rubber Formulation: Engineering Performance at the Molecular Level
Once the design is validated, our Rubber Formula Engineers develop a proprietary elastomer formulation tailored to the operational environment. For garage door seals, we primarily utilize EPDM and thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV), selected for their superior weather resistance, low-temperature flexibility, and compression set performance. The formulation process involves precise control over polymer base ratios, filler content (such as carbon black or silica), plasticizers, curing systems, and protective additives. Each compound is engineered to achieve specific Shore A hardness values—typically between 55 and 75—balancing sealing force with ease of door movement. Accelerated aging tests, including heat aging per ASTM D573 and ozone resistance per ASTM D1149, are conducted to validate long-term durability. This scientific approach ensures that the final material performs reliably across temperature extremes from -40°C to +120°C, a necessity for global deployment.
Prototyping and Validation: Bridging Design and Production
Following formulation, we produce functional prototypes using precision extrusion and vulcanization techniques. These samples undergo comprehensive dimensional inspection and functional testing, including compression deflection analysis and adhesion strength evaluation for multi-component seals. Clients receive physical samples along with material certification and test reports for validation. Feedback is incorporated iteratively until performance and fitment meet exact specifications.
Mass Production: Consistency at Scale
Upon approval, the project transitions to mass production. Our automated extrusion lines, equipped with laser-based diameter control systems, ensure batch-to-batch consistency. Every production run is subject to real-time quality monitoring, with final products inspected for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and material homogeneity.
| Property | Test Standard | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | ASTM D2240 | 60–70 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥9 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥250% |
| Compression Set (22h, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤25% |
| Operating Temperature | — | -40°C to +120°C |
| Ozone Resistance | ASTM D1149 | No cracking (200 pphm, 40°C, 96h) |
Contact Engineering Team

Precision Rubber Sealing Solutions Require Expert Engineering Collaboration
Garage door bottom seals represent a critical interface between building envelope integrity and operational performance. Substandard sealing compounds or imprecise extrusion tolerances directly compromise thermal efficiency, weather resistance, and noise control. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we apply rigorous polymer science and decades of OEM manufacturing experience to solve these complex sealing challenges. Our engineered rubber formulations are not generic commodities; they are precision-tailored solutions developed through systematic analysis of application-specific stressors including UV exposure, ozone degradation, extreme temperature cycling, and dynamic compression forces. Understanding the precise interplay between material composition, durometer, and geometric profile is paramount for achieving optimal seal longevity and functionality. Generic off-the-shelf seals often fail prematurely due to inadequate molecular cross-linking density or incorrect compound resilience for the intended duty cycle.
Our technical team specializes in translating demanding performance requirements into validated rubber compounds and extruded profiles. We utilize advanced testing protocols including accelerated weathering (QUV), compression set analysis per ASTM D395, and tensile property verification to ensure every seal meets or exceeds OEM specifications. Below is a representative comparison of common garage door bottom seal types, highlighting the critical material science parameters we optimize:
| Seal Type | Material Composition | Key Properties | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| T-End Vinyl | Rigid PVC Compound | High stiffness, moderate weather resistance | Light-duty residential, interior doors |
| Bulb Fin | EPDM Rubber (50-70 Shore A) | Excellent ozone/weather resistance, high resilience | Standard residential, commercial roll-up |
| Dual Durometer | EPDM Core + TPE Skirt | Optimized sealing force distribution, noise dampening | High-performance residential, wind-prone areas |
| Reinforced Bead | EPDM + Polyester Cord | Enhanced structural stability, reduced creep | Heavy commercial doors, high-wind zones |
Suzhou Baoshida operates as a true engineering partner, not merely a component supplier. We collaborate directly with your R&D and manufacturing teams from initial concept through volume production. Our ISO 9001-certified facility features state-of-the-art rubber compounding lines and precision extrusion tooling capable of holding tolerances to ±0.15mm. This level of dimensional control is non-negotiable for achieving consistent compression sealing across thousands of door cycles. We offer comprehensive material traceability, rigorous batch testing documentation, and flexible production scheduling to align with your assembly line demands. Whether you require standard profile optimization or a fully custom compound formulation for extreme environments, our engineers possess the expertise to deliver a solution that enhances your product’s market differentiation and reliability.
Initiate a technical consultation to resolve your specific garage door sealing challenges. Contact Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Engineering Manager, who brings 18 years of applied rubber formulation experience to your project. Mr. Boyce will conduct a detailed application review, discuss material performance data relevant to your operational environment, and outline a precise development pathway. Provide your current seal specifications, performance pain points, and volume requirements for a targeted engineering assessment. Direct all technical inquiries and OEM partnership discussions to [email protected]. Expect a substantive engineering response with actionable data within 24 business hours. Elevate your garage door system’s performance through scientifically validated rubber sealing solutions engineered for precision and proven in global production environments. Partner with Suzhou Baoshida for sealing integrity you can measure.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
