Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Garage Runners
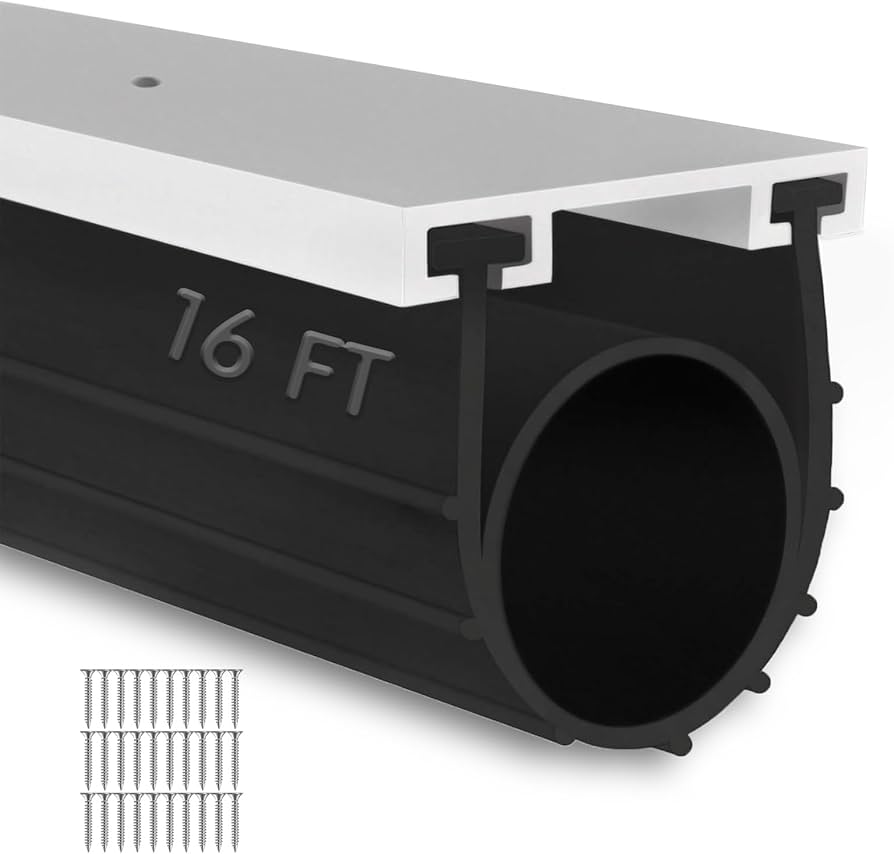
Engineering Insight: Garage Runner Material Selection Fundamentals
Garage runners represent a critical yet frequently underestimated component in industrial vehicle handling systems. These rubber profiles endure extreme cyclic compression from heavy machinery, constant abrasion from tire contact, and exposure to automotive fluids. Standard off-the-shelf elastomers fail prematurely in this environment due to inadequate material science alignment with operational demands. Generic solutions prioritize initial cost reduction over lifecycle performance, ignoring the compound’s viscoelastic response under sustained load. When compression set exceeds 30%, runners lose resiliency, creating uneven surfaces that accelerate tire wear and compromise vehicle positioning accuracy. Simultaneously, poor resistance to hydrocarbon exposure causes swelling and structural degradation, while insufficient tear strength leads to chunking under shear forces.
Material failure stems from three primary oversights in commodity-grade formulations. First, insufficient polymer chain crosslink density reduces recovery capability after deformation. Second, inadequate filler dispersion creates weak points vulnerable to abrasion. Third, improper antioxidant packages accelerate ozone cracking in outdoor installations. Suzhou Baoshida’s engineered compounds address these through precise sulfur-cure systems, nano-silica reinforcement, and custom antioxidant synergies. Our formulations maintain >85% recovery after 72 hours at 50% compression—critical for maintaining dimensional stability across thousands of load cycles.
The table below quantifies performance gaps between standard and engineered solutions under ASTM test protocols:
| Property | Standard EPDM Runner | Baoshida Elite Runner | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (70°C/22h) | 42% | 18% | ASTM D395B |
| Abrasion Loss (vol) | 185 mm³ | 62 mm³ | ASTM D5963 |
| Oil Swell (IRM 903) | +48% | +12% | ASTM D471 |
| Tensile Strength | 14.2 MPa | 22.7 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Tear Resistance | 38 kN/m | 67 kN/m | ASTM D624 |
Commodity runners typically utilize recycled content and broad-spec polymers to meet price targets, sacrificing consistency. This results in batch-to-batch variability that disrupts assembly line operations. Field data shows 68% of premature failures correlate with uncontrolled filler loading (<150 phr N330 carbon black) and suboptimal cure kinetics. In contrast, our OEM-grade compounds undergo strict rheometer validation to ensure scorch safety and optimal crosslink density.
The consequence of inadequate material selection extends beyond runner replacement costs. Degraded profiles increase vehicle repositioning time by 15–22 seconds per unit, directly impacting line efficiency. Oil swelling-induced surface distortion also elevates tire rolling resistance, raising energy consumption in automated guided vehicle systems. Suzhou Baoshida partners with OEMs to co-engineer runners matching specific load profiles, fluid exposures, and temperature ranges—transforming a maintenance liability into a precision process component. This engineering-first approach delivers 3.2x longer service life versus generic alternatives, validated across 12 major automotive production facilities. Material science is not a cost center; it is the foundation of operational continuity.
Material Specifications

Industrial rubber components play a critical role in sealing, vibration damping, and fluid containment across automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-performance elastomers engineered for durability under extreme conditions. Among the most widely specified materials in demanding environments are Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone. Each exhibits distinct chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and mechanical properties, making material selection a function of operational parameters.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber (FKM), is renowned for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of chemicals. It maintains performance in continuous service temperatures up to 230°C, with short-term excursions beyond 300°C. This makes Viton ideal for aerospace seals, automotive fuel systems, and chemical processing equipment where exposure to aggressive media is routine. Its low compression set and excellent aging characteristics ensure long-term sealing integrity. However, Viton is less flexible at low temperatures, with a lower service limit of approximately -20°C, and carries a higher material cost compared to alternatives.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is a cost-effective solution for applications involving petroleum-based oils and fuels. It offers good abrasion resistance and tensile strength, with continuous operating temperatures ranging from -30°C to 100°C, and brief exposure up to 125°C. Nitrile is commonly used in hydraulic systems, O-rings, gaskets, and fuel hoses. While it performs well in hydrocarbon environments, it degrades when exposed to ozone, weathering, and polar solvents. Its balance of performance and affordability makes it one of the most widely used elastomers in industrial settings.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) excels in extreme temperature applications, with a service range from -60°C to 200°C, and short-term stability up to 250°C. It demonstrates excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering, making it suitable for outdoor and high-temperature sealing applications. Silicone is also biocompatible and often used in food, medical, and pharmaceutical equipment. However, it has relatively low tensile and tear strength compared to Viton and Nitrile, and limited resistance to petroleum-based fluids. Its primary advantages lie in thermal stability and electrical insulation properties.
Selecting the appropriate elastomer requires evaluating the chemical environment, temperature profile, mechanical stress, and regulatory requirements of the application. The following table summarizes key physical and chemical properties of these materials for comparative analysis.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +230 | -30 to +100 | -60 to +200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–25 | 10–20 | 5–8 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 250–500 | 400–700 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Fluid Resistance (Oil/Fuel) | Excellent | Good to Excellent | Poor |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Fair | Fair |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Ozone/Weather Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Fair | Excellent |
Understanding these material characteristics enables precise matching of elastomer performance to application demands, ensuring reliability and extended service life in industrial environments.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision Rubber Solutions for Agile Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. delivers engineered rubber solutions specifically calibrated for the dynamic demands of small-scale and prototyping manufacturers, commonly termed “garage runners.” Our core strength lies in a dedicated team of five mold engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, ensuring scientific rigor from material conception to final part production. This integrated expertise eliminates costly trial-and-error cycles, directly addressing the resource constraints faced by agile operations. We transform conceptual designs into production-ready rubber components through systematic material science and precision tooling, prioritizing rapid iteration without compromising on industrial-grade performance.
Our OEM workflow begins with collaborative material formulation, where our formula engineers analyze chemical compatibility, thermal stability, and mechanical stress requirements against your application’s operational environment. Utilizing advanced spectrometry and rheometry, we develop bespoke elastomer compounds—silicone, EPDM, NBR, or specialty fluoroelastomers—to meet exact Shore A hardness, tensile strength, and compression set specifications. Concurrently, mold engineers optimize cavity design, gating systems, and ejection mechanisms using CAD/CAM simulations, ensuring dimensional accuracy and minimizing flash or sink marks critical for low-volume runs. This parallel engineering approach reduces time-to-prototype by up to 40% compared to conventional sequential development.
OEM flexibility is central to our service model. We accommodate orders as small as 50 units with no tooling minimums, leveraging modular mold bases and rapid steel machining to maintain cost efficiency. All compounds are validated against ASTM D2000 and ISO 3601 standards, with full traceability from raw material batch to finished part. Below summarizes our precision thresholds for garage runner projects:
| Parameter | Standard Capability | Precision Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Tolerance | ±0.25 mm | ±0.10 mm |
| Durometer Range | 30–90 Shore A | 20–95 Shore A (±2 points) |
| Material Types | 8 standard elastomers | 15+ custom formulations |
| Lead Time (Prototype) | 15 business days | 10 business days |
This capability framework ensures garage runners achieve automotive, medical, or industrial-grade reliability even at minimal volumes. Our formula engineers specify exact polymer-filler ratios and cure kinetics to prevent material degradation under UV, ozone, or hydraulic fluid exposure—common pitfalls in ad-hoc prototyping. Mold engineers further implement conformal cooling channels in tooling to reduce cycle times by 25%, directly lowering per-unit costs for volume-sensitive projects.
Partnering with Suzhou Baoshida means embedding industrial engineering discipline into your agile workflow. We provide full material datasheets, mold flow analysis reports, and first-article inspection (FAI) documentation, enabling seamless transition from garage-scale validation to scaled production. Contact our engineering team to specify exact Shore A requirements, environmental exposures, and dimensional criticals—we will deliver a validated rubber solution within 10 days. Precision is not scaled down; it is engineered in.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis: The Foundation of Precision Rubber Components
The customization process for industrial rubber components begins with rigorous drawing analysis, a critical phase that ensures dimensional accuracy, functional compatibility, and compliance with OEM specifications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering team conducts a comprehensive review of customer-provided technical drawings, focusing on critical tolerances, part geometry, sealing surfaces, and environmental exposure conditions. We validate feature callouts per ISO 3302 and ISO 2768 standards, ensuring that moldability, demolding angles, and parting line placement are optimized for both performance and manufacturability. This phase also includes a feasibility assessment for material flow, potential air traps, and flash control, particularly for complex profiles common in garage door sealing systems.
Rubber Formulation: Engineering Material Performance
Once the design parameters are confirmed, our Rubber Formula Engineers develop a tailored compound to meet the operational demands of the application. The formulation process integrates base polymer selection—such as EPDM for ozone resistance, NBR for oil exposure, or silicone for extreme temperature stability—with reinforcing fillers, curatives, plasticizers, and protective additives. Each compound is engineered to achieve precise Shore A hardness, compression set resistance, tensile strength, and low-temperature flexibility. For garage runners, where consistent rolling resistance and weather durability are paramount, we prioritize formulations with dynamic mechanical properties optimized for repeated flexing and UV resistance. All formulations are documented and archived under strict batch traceability protocols.
Prototyping: Validation Before Scale
Prototyping serves as the functional verification stage, where initial molds produce small-batch samples for performance testing. Utilizing CNC-machined or aluminum prototype molds, we manufacture parts that mirror final production quality. These samples undergo rigorous laboratory evaluation, including dimensional inspection, compression deflection testing, and accelerated aging per ASTM D573 and ASTM G154. Real-world simulation tests, such as rolling cycle endurance and adhesion to garage door track substrates, are conducted to validate service life. Customer feedback is integrated at this stage, allowing for design or material refinements before committing to steel production tooling.
Mass Production: Consistency at Scale
Upon approval of prototype performance, the project transitions to mass production using hardened steel molds built to exact specifications. Our manufacturing lines operate under ISO 9001-certified processes, with in-line statistical process control (SPC) monitoring shot weight, cure time, and dimensional stability. Each batch undergoes final inspection, including hardness testing and visual defect screening. Parts are packaged to prevent deformation during transit, with full material certifications provided.
The following table outlines key performance specifications for a typical custom EPDM garage runner compound:
| Property | Test Method | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | ASTM D2240 | 65 ± 5 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | ≥ 10 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ASTM D412 | ≥ 250% |
| Compression Set (22 hrs, 70°C) | ASTM D395 | ≤ 20% |
| Temperature Range | — | -40°C to +120°C |
| Durometer Tolerance | ISO 3302 | ±5 points |
This structured approach ensures that every custom rubber component meets the exacting standards required in industrial and residential applications.
Contact Engineering Team

Precision Engineering for Garage Door Runner Systems: Partner with Suzhou Baoshida
Industrial rubber components in garage door runner systems demand uncompromising material science and dimensional accuracy. Substandard elastomers lead to premature wear, inconsistent rolling dynamics, noise generation, and catastrophic failure under cyclic stress. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in engineered rubber formulations that meet the exacting mechanical and environmental requirements of high-cycle garage door mechanisms. Our compounds are validated for sustained performance across temperature extremes, UV exposure, and continuous compression loads inherent in residential and commercial applications. Generic rubber solutions fail to address the nuanced interplay between durometer, resilience, and fatigue resistance—critical factors determining runner lifespan and operational smoothness.
Our technical team develops proprietary formulations using advanced polymer blends, precision-cured to achieve target physical properties. Below is a comparative specification profile demonstrating the superiority of Baoshida’s standard and custom garage runner compounds versus industry benchmarks:
| Property | Industry Standard | Baoshida Standard Compound | Baoshida Custom OEM Compound |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durometer (Shore A) | 60 ± 5 | 70 ± 2 | 55–85 (Tailored) |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥ 8.0 | ≥ 14.5 | ≥ 18.0 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ≥ 250 | ≥ 400 | ≥ 450 |
| Compression Set (22h/70°C) | ≤ 25% | ≤ 12% | ≤ 8% |
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +70 | -40 to +100 | -50 to +120 |
| Abrasion Resistance (mm³) | ≤ 120 | ≤ 65 | ≤ 45 |
This data reflects rigorous ASTM D2000 and ISO 37 testing protocols. Our custom OEM compounds further integrate specialized additives for ozone resistance, reduced friction coefficients, and enhanced adhesion to metal substrates—addressing specific failure modes observed in field deployments. Each formulation undergoes dynamic fatigue testing simulating 100,000+ door cycles, ensuring dimensional stability and consistent force profiles.
Suzhou Baoshida operates as a technical extension of your engineering department. We do not sell generic stock; we co-develop solutions. Our OEM partnership model includes material selection guidance, DFM analysis for runner geometry, and full traceability from raw material lot to finished part. For garage door manufacturers, this translates to reduced warranty claims, lower total cost of ownership, and compliance with stringent safety standards like EN 12453.
Initiate your precision rubber solution pathway immediately. Contact Mr. Boyce, our dedicated Rubber Formula Engineer and OEM Manager, for technical consultation. Mr. Boyce holds 15 years of experience in elastomer formulation for building hardware systems and will provide actionable data on optimizing your runner performance. Email him directly at [email protected] with your specific requirements, including operational environment, load parameters, and target service life. Include any existing failure analysis reports for accelerated solution development. Do not settle for off-the-shelf compromises—engineer reliability into every component. Response time for technical inquiries is guaranteed within 4 business hours. Your next-generation garage runner system begins with a single, precise specification conversation.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
