Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: High Specification O-Rings

Engineering Insight: Material Selection Imperatives for High-Specification O-Rings
Material selection constitutes the foundational engineering decision determining the functional lifespan and reliability of high-specification o-rings. Off-the-shelf solutions, often formulated for broad compatibility and cost minimization, inherently lack the tailored polymer chemistry required for demanding industrial applications. These generic compounds prioritize initial sealing force over long-term performance under specific thermal, chemical, or mechanical stresses, leading to premature and often catastrophic field failures. The consequences extend beyond simple seal replacement; they manifest as unplanned downtime, contamination events, safety hazards, and significant financial losses exceeding the initial cost differential of a properly engineered solution. Understanding the precise interplay between application parameters and elastomer properties is non-negotiable for critical sealing.
Generic o-rings frequently fail due to insufficient resistance to specific fluid media, inadequate thermal stability for continuous service temperatures, or poor recovery characteristics after compression. Standard NBR compounds, for instance, exhibit rapid degradation when exposed to modern biofuels or phosphate ester hydraulic fluids, causing excessive swelling, loss of tensile strength, and extrusion. Similarly, off-the-shelf FKM grades may lack the necessary peroxide cure system stability required for continuous operation above 230°C, accelerating compression set and leakage in high-temperature engine or aerospace systems. The compression set performance of a material, a critical indicator of long-term sealing force retention, is often compromised in cost-driven formulations through suboptimal filler systems or inadequate cure chemistry. This results in permanent deformation, loss of contact stress, and eventual seal leakage even under static conditions.
The table below contrasts key performance parameters between typical off-the-shelf o-rings and engineered high-specification alternatives, illustrating the root causes of failure:
| Property | Off-the-Shelf Limitation | High-Spec Requirement | Consequence of Failure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Set (ASTM D395) | Often >30% after 70h @ 150°C (Standard NBR) | <15% after 1000h @ 200°C (Custom FKM) | Permanent deformation, loss of sealing force, leakage |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited to common oils/mineral hydraulics | Tailored for specific media (e.g., <5% swell in Skydrol, biodiesel) | Swelling, hardening, cracking, fluid contamination |
| Thermal Stability | Max continuous ~120°C (Standard EPDM) | Sustained performance to 250°C+ (Peroxide-cured FFKM) | Accelerated aging, hardening, loss of elasticity |
| Outgassing (ASTM E595) | High volatile content (>1.0% TML) | Ultra-low outgassing (<0.5% TML, <0.1% CVCM) | Contamination in vacuum/space systems, sensor fouling |
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. addresses these critical gaps through rigorous application analysis and proprietary compound development. We move beyond catalog numbers to engineer formulations where filler dispersion, curative systems, and polymer backbone chemistry are precisely optimized for the client’s specific pressure, temperature, fluid, and dynamic motion profile. This scientific approach to material science ensures the o-ring maintains its dimensional integrity, sealing force, and chemical resistance throughout the intended service life, transforming the seal from a potential failure point into a reliable component of system integrity. The initial investment in a correctly specified high-specification o-ring is consistently justified by eliminating the far greater costs associated with field failures and operational disruption.
Material Specifications
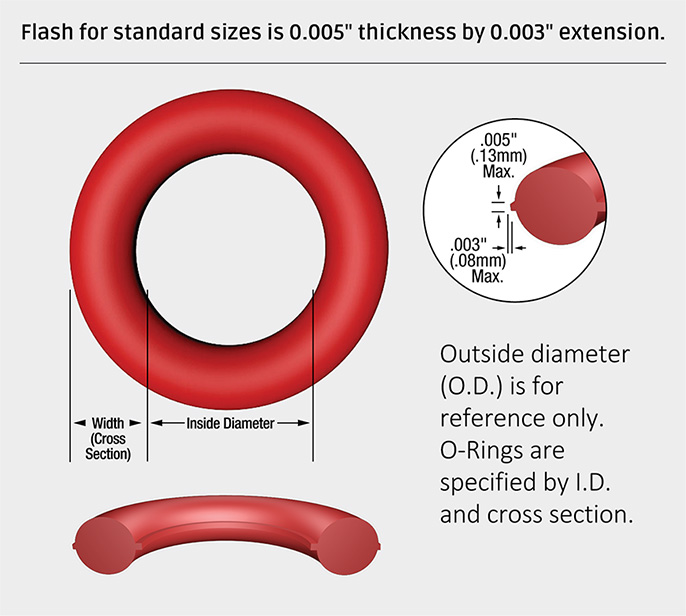
Material selection is a critical factor in the performance and longevity of high specification o-rings used in demanding industrial environments. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in precision rubber seals engineered to meet rigorous operational requirements across aerospace, automotive, chemical processing, and semiconductor industries. The choice of elastomer directly influences resistance to temperature extremes, chemical exposure, compression set, and mechanical stress. Among the most widely specified materials are Viton (FKM), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ), each offering distinct advantages depending on the application parameters.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based elastomer, exhibits exceptional resistance to high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and hydrocarbon fuels. With a continuous service temperature range of -20°C to 230°C (short-term up to 300°C), Viton o-rings are ideal for applications involving jet fuels, lubricants, and acidic environments. Its low gas permeability and outstanding aging characteristics make it a preferred choice in aerospace and oil & gas sectors where reliability under extreme conditions is non-negotiable.
Nitrile rubber, also known as Buna-N, offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and aliphatic hydrocarbons. It performs reliably in temperature ranges from -40°C to 120°C, with some formulations extending to 150°C. Nitrile is cost-effective and widely used in hydraulic systems, automotive seals, and industrial machinery. However, it exhibits limited resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and polar solvents, which must be considered in outdoor or chemical processing applications.
Silicone rubber provides superior flexibility and thermal stability across a broad temperature spectrum, typically from -60°C to 200°C. It demonstrates excellent resistance to oxidation, ozone, and weathering, making it suitable for medical devices, food processing equipment, and outdoor electrical applications. While silicone has poor resistance to petroleum-based fluids and lower tensile strength compared to Viton or Nitrile, its biocompatibility and low toxicity support compliance with FDA and USP Class VI standards.
The following table summarizes key physical and chemical properties of these materials to assist in material selection for high specification o-ring applications.
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 (300 short-term) | -40 to 120 (150 short-term) | -60 to 200 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–20 | 5–8 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 200–300 | 200–500 | 200–700 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils & Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Resistance to Acids/Chemicals | Very Good | Fair | Fair |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| FDA Compliance | Yes (specific grades) | Limited | Yes (specific grades) |
Selecting the appropriate material requires a comprehensive understanding of the operational environment, including media exposure, thermal cycling, and mechanical loading. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. provides custom formulation support and rigorous quality testing to ensure every o-ring meets exacting OEM and industry standards.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision Foundation for Critical Sealing Applications
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering infrastructure forms the backbone of high-specification o-ring production, directly addressing the stringent demands of aerospace, semiconductor, and energy sectors. We deploy a dedicated team of five certified Mold Engineers and two advanced Rubber Formula Engineers, operating as an integrated unit to eliminate design-to-manufacturing disconnects. This structure ensures material science expertise directly informs tooling precision, a critical factor in achieving micron-level dimensional stability and zero-defect performance under extreme pressure, temperature, and chemical exposure.
Mold Engineering Excellence centers on computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation for cavity filling and vulcanization kinetics. Our engineers optimize runner systems, gate geometry, and thermal management to prevent knit lines, flash, or incomplete cure—common failure points in high-compression-set environments. All molds undergo rigorous validation via cavity pressure monitoring and 3D metrology against AS568C and ISO 3601-1 standards, with tolerances held to ±0.05mm for critical diameters. This precision guarantees consistent part geometry across production runs exceeding 500,000 units, essential for zero-leakage systems in ultra-high-vacuum applications.
Advanced Compound Development leverages our Formula Engineers’ expertise in polymer chemistry and additive synergism. We formulate proprietary elastomer blends—spanning FKM, FFKM, EPDM, and specialty silicones—to meet exact fluid compatibility, thermal stability, and outgassing requirements. Each compound undergoes accelerated aging per ASTM D2000 and NASA outgassing testing (ASTM E595), with molecular architecture tailored to suppress compression set at 200°C+ or maintain flexibility down to -60°C. This capability enables custom solutions where off-the-shelf materials fail, such as hydrogen sulfide resistance in downhole tools or plasma etch stability in 300mm wafer chucks.
Our OEM framework transforms engineering rigor into client-specific value. We initiate projects with joint Design for Manufacturability (DFM) reviews, integrating client CAD data with material selection matrices to preempt tooling conflicts. Full process validation includes Minitab-driven capability studies (CpK ≥1.67) and PPAP Level 3 documentation, ensuring traceability from raw material lot to final inspection. This end-to-end control allows rapid iteration—prototype to production in 15 days—while maintaining compliance with NADCAP and IATF 16949 protocols.
Material performance is quantified through standardized testing protocols, as exemplified below for critical aerospace-grade compounds:
| Material Type | Hardness (Shore A) | Temp Range (°C) | Fluid Resistance (ASTM D471) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Custom FFKM | 75 ± 3 | -25 to +325 | Jet Fuel A, Hydraulic Fluid 46, H₂SO₄ (70%) | Jet Engine Seals, Rocket Propulsion |
| Perfluoroelastomer | 80 ± 3 | -15 to +315 | Ultrapure HCl, NH₃, O₂ Plasma | Semiconductor CVD Chambers |
| High-Purity EPDM | 70 ± 3 | -50 to +150 | Deionized Water, Glycol Coolants | Fuel Cell Bipolar Plates |
Quality assurance extends beyond conformance; our engineers deploy real-time SPC during molding and post-cure plasma surface treatment to enhance seal integrity. By fusing formula science with mold physics, Suzhou Baoshida delivers o-rings where failure is not an option—proven in 120+ OEM programs with Tier-1 industrial and defense suppliers. This engineering-led approach ensures every seal meets the uncompromising reliability demanded by next-generation machinery.
Customization Process

Drawing Analysis: The Foundation of Precision
The customization process for high specification o-rings begins with rigorous drawing analysis, a critical phase that ensures dimensional accuracy and functional compatibility. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., every customer-provided technical drawing undergoes comprehensive review by our engineering team. We assess key parameters including inner diameter (ID), cross-sectional diameter (CS), tolerance grades per ISO 3601 or AS568 standards, and any special surface or geometrical requirements. This stage also involves verifying application-specific details such as groove design, mating components, and installation constraints. Where necessary, we conduct Design for Manufacturability (DFM) evaluations to recommend adjustments that enhance performance without compromising sealing integrity. This collaborative review minimizes downstream risks and establishes a clear technical baseline for material and process selection.
Formulation: Engineering Material Performance
Once dimensional specifications are confirmed, the formulation phase tailors the rubber compound to meet exact operational demands. Our in-house rubber chemistry team develops proprietary formulations based on the required resistance to temperature extremes, chemical exposure, compression set, and dynamic stress. Common base polymers include FKM (Viton®), EPDM, NBR, and silicone, selected according to media compatibility and environmental conditions. Additives such as reinforcing fillers, antioxidants, and processing aids are precisely metered to achieve target hardness (Shore A), tensile strength, and elongation at break. Each formulation is documented under controlled batch records and subjected to preliminary testing for consistency. This step ensures that the final o-ring not only fits but performs reliably under real-world service conditions.
Prototyping: Validation Before Scale
Following formulation approval, we produce functional prototypes using precision molding techniques—typically compression or transfer molding—to simulate production conditions. These prototypes are subjected to dimensional inspection via optical comparators and CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines), ensuring compliance with drawing tolerances. Simultaneously, samples undergo accelerated aging, fluid immersion, and compression set testing per ASTM or ISO standards. Performance data is compiled into a test report for customer review. This iterative stage allows for refinement of both geometry and material before committing to full-scale tooling, reducing time-to-market and minimizing rework.
Mass Production: Consistency at Scale
Upon prototype validation, the project transitions to mass production. High cavitation molds are deployed in automated rubber molding lines, with real-time process monitoring to maintain consistency. Each production batch is traceable, with full QC documentation including material certificates, mold logs, and inspection reports. Final o-rings are packaged per customer requirements, with options for cleanroom packaging and barcoded inventory control.
Typical Material Properties for High Specification O-Rings
| Property | FKM (Viton®) | EPDM | NBR | Silicone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to +230 | -50 to +150 | -30 to +120 | -60 to +200 |
| Fluid Resistance | Excellent (oils, fuels) | Good (water, steam) | Good (oils, fuels) | Fair (water, oils) |
| Compression Set (ASTM D395) | ≤20% @ 200°C/70h | ≤25% @ 150°C/70h | ≤30% @ 100°C/70h | ≤20% @ 175°C/70h |
| Shore A Hardness Range | 60–90 | 50–80 | 50–90 | 30–80 |
| Typical Applications | Aerospace, Automotive, Chemical | HVAC, Water Systems | Hydraulics, Fuel Systems | Medical, Food Grade, High Temp |
Contact Engineering Team

Initiate Precision Sealing Solutions Through Direct Engineering Partnership
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. operates at the intersection of advanced polymer science and industrial sealing performance. As your dedicated Rubber Formula Engineer and OEM Manager, I emphasize that high-specification O-rings demand more than standard manufacturing—they require material science rigor, process control, and application-specific validation. Our engineering team specializes in resolving complex sealing challenges where conventional elastomers fail under extreme thermal cycling, aggressive chemical exposure, or ultra-high-pressure differentials. We do not merely supply components; we co-engineer solutions with traceable documentation from compound formulation through final inspection, ensuring compliance with AS568C, ISO 3601, and customer-specific dimensional tolerances down to ±0.05mm.
The following table summarizes critical performance parameters achievable through our engineered compounds and precision molding processes. These specifications reflect our baseline capabilities for aerospace, semiconductor, and pharmaceutical applications—sectors where failure is non-negotiable.
| Parameter | Standard Range | High-Specification Capability | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Compounds | NBR, EPDM, FKM | Perfluoroelastomer (FFKM), HNBR, Custom Blends | ASTM D2000, ISO 3623 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 50–90 | 30–98 (with ±2 tolerance) | ASTM D2240 |
| Temperature Range | -30°C to +150°C | -55°C to +275°C (continuous) | ISO 188, ASTM D573 |
| Compression Set (70h/150°C) | ≤35% | ≤12% | ASTM D395 Method B |
| FDA/USP Class VI Compliance | Optional | Standard for Pharma/Food Grade | 21 CFR 177.2600 |
When standard O-rings exhibit premature extrusion in hydraulic systems above 5,000 psi, or when semiconductor tooling requires outgassing rates below 0.1% mass loss (per ASTM E595), our technical collaboration begins. We analyze your fluid dynamics, surface finish requirements, and failure mode history to reformulate compounds with targeted filler systems and crosslink densities. For instance, our proprietary FFKM blends maintain seal integrity in 98% sulfuric acid at 200°C—conditions that degrade standard FKM within hours. Every batch undergoes rigorous lot traceability, including FTIR spectroscopy for raw material verification and 100% vision inspection for critical dimensions.
Do not compromise on sealing integrity when system reliability hinges on micron-level precision. Contact Mr. Boyce directly to initiate a technical dialogue grounded in engineering evidence. He will coordinate material compatibility testing using your specific media, provide 3D tolerance analysis reports, and facilitate rapid prototyping within 15 business days. Mr. Boyce operates as your single point of accountability from initial specification review through PPAP submission, ensuring seamless integration into your supply chain.
Reach Mr. Boyce at [email protected] to submit your application data sheet. Include operational parameters, failure analysis reports, and target service life expectations. Our engineering team will respond within 24 business hours with a compound recommendation and validation protocol tailored to your operational envelope. For time-sensitive projects requiring expedited tooling or accelerated aging data, reference project code SB-ORING-2024 in your correspondence. Suzhou Baoshida commits to transforming sealing vulnerabilities into engineered advantages—where molecular stability meets industrial certainty.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
