Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Hot Knife For Cutting Rubber

Engineering Insight: Material Selection Criticality in Rubber Cutting Hot Knives
Material selection for hot knife blades transcends conventional knife design parameters due to the unique thermo-mechanical demands of rubber processing. Off-the-shelf solutions frequently fail because generic blade alloys cannot withstand the combined thermal cycling, chemical interaction, and abrasive wear inherent in cutting compounded rubber. Standard carbon steel or 440C stainless steel blades rapidly degrade when exposed to rubber’s complex polymer matrix, leading to carbon buildup, edge deformation, and inconsistent cuts. This occurs as rubber compounds—especially those with high filler content like silica or carbon black—generate localized frictional heat exceeding 300°C during cutting. Generic alloys lack the thermal stability to maintain edge geometry under these conditions, causing premature blunting and surface adhesion that compromises cut quality.
The core failure mechanism lies in inadequate thermal conductivity and low hot hardness retention. Rubber’s viscoelastic nature requires precise temperature control at the cutting interface; insufficient thermal conductivity in generic blades creates thermal gradients that warp the blade edge. Simultaneously, standard alloys soften above 250°C (HRC < 40), allowing rubber compounds to embed into the blade surface. This adhesion accelerates wear through micro-tearing, increasing downtime for cleaning or replacement. Crucially, rubber’s glass transition temperature (Tg) varies significantly by formulation—NBR at -40°C versus EPDM at -60°C—demanding blade materials that maintain sharpness across this operational spectrum without inducing polymer chain scission or melt fracture.
Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM-engineered hot knives address these challenges through proprietary H13 tool steel variants with tailored vanadium carbide reinforcement. This alloy achieves optimal thermal conductivity while resisting softening up to 600°C, ensuring dimensional stability during rapid thermal cycling. The following specifications demonstrate the performance gap:
| Parameter | Generic Off-the-Shelf Blade | Suzhou Baoshida OEM Blade |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 15–20 W/m·K | 28–32 W/m·K |
| Hot Hardness (500°C) | HRC 32–35 | HRC 52–55 |
| Edge Retention (hrs) | 8–12 | 110–130 |
| Max Continuous Temp | 280°C | 600°C |
| Adhesion Resistance | Low (Requires frequent cleaning) | High (Minimal buildup) |
This material science approach prevents common failure modes: carbon buildup is mitigated by the blade’s non-stick surface chemistry, while superior thermal diffusion eliminates cold spots that cause ragged cuts. Crucially, our blades maintain a consistent 0.05mm edge tolerance across 10,000+ cuts in 70 Shore A SBR compounds—where generic alternatives deviate beyond 0.3mm within 500 cuts. For OEM partners, this translates to 85% fewer blade changes and elimination of secondary trimming operations. Suzhou Baoshida’s material selection protocol integrates rubber compound analysis with blade metallurgy, ensuring each hot knife is engineered for the specific polymer’s thermal decomposition profile and filler abrasiveness. This precision prevents the hidden costs of off-the-shelf solutions: material waste from poor cuts, unscheduled maintenance, and compromised product integrity in critical applications like automotive seals or medical tubing.
Material Specifications

When selecting a hot knife for cutting rubber, understanding the compatibility between the cutting tool and the elastomeric material is critical for achieving clean, precise cuts and maintaining tool longevity. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in industrial rubber solutions, providing engineered hot knife systems optimized for high-performance elastomers such as Viton, Nitrile, and Silicone. Each of these materials exhibits unique thermal, mechanical, and chemical properties that directly influence the cutting parameters, including blade temperature, feed rate, and post-cut finish.
Viton (FKM) is a fluorocarbon-based synthetic rubber known for its exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of chemicals. Due to its high thermal stability, Viton typically requires a higher hot knife operating temperature—usually between 300°C and 400°C—to achieve a clean cut without fraying or tearing. The dense molecular structure of Viton demands precise control over cutting speed to prevent excessive blade wear. When properly cut, Viton maintains dimensional accuracy and edge integrity, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing applications.
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is widely used for its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels. It has a moderate thermal resistance, with a glass transition temperature typically around -10°C to -40°C, depending on acrylonitrile content. For effective hot knife cutting, temperatures in the range of 220°C to 280°C are recommended. Cutting Nitrile at optimal temperatures ensures a smooth, sealed edge with minimal smoke or residue. However, excessive heat can cause carbonization on the blade surface, necessitating regular maintenance. Nitrile’s flexibility and resilience make it suitable for seals, gaskets, and hoses in industrial and automotive environments.
Silicone rubber (VMQ) presents different challenges due to its high thermal stability and low surface energy. Although silicone can withstand continuous exposure to temperatures above 200°C, it tends to deform under uncontrolled heat during cutting. The ideal hot knife temperature for silicone lies between 250°C and 320°C, with a steady, consistent feed rate to prevent melting or edge collapse. A sharp, well-maintained blade is essential to avoid dragging or smearing. Properly cut silicone exhibits clean edges and retains its elastic properties, making it ideal for medical devices, food-grade seals, and electrical insulation.
The following table summarizes key material properties and recommended hot knife parameters for optimal cutting performance:
| Material | Chemical Name | Hardness Range (Shore A) | Temp Range (°C) | Recommended Hot Knife Temp (°C) | Key Cutting Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viton | FKM | 60–90 | -20 to 250 | 300–400 | High temp required; clean cut with minimal residue; resistant to chemical degradation |
| Nitrile | NBR | 40–95 | -40 to 120 | 220–280 | Moderate temp; prone to carbon buildup; excellent for oil-resistant parts |
| Silicone | VMQ | 30–80 | -60 to 230 | 250–320 | Sensitive to overheating; requires sharp blade; produces smooth, sealed edges |
Selecting the correct hot knife configuration based on rubber material ensures operational efficiency, prolongs blade life, and maintains product quality in high-volume industrial environments.
Manufacturing Capabilities

Engineering Capability: Precision Solutions for Rubber Cutting Applications
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. integrates advanced material science with precision manufacturing to deliver engineered hot knife systems for industrial rubber processing. Our in-house technical team comprises five dedicated Mould Engineers and two specialized Rubber Formula Engineers, enabling end-to-end control from compound development to final tool validation. This synergy ensures hot knives perform optimally under demanding conditions—preventing thermal degradation, minimizing blade wear, and maintaining clean cuts across diverse rubber formulations.
Our Rubber Formula Engineers optimize elastomer compounds for thermal stability and cut integrity, focusing on vulcanization kinetics and heat transfer properties. By tailoring polymer matrices (including EPDM, NBR, and silicone), we mitigate edge fraying and carbonization during high-speed cutting. Concurrently, Mould Engineers design knife geometries with precision-machined thermal channels, ensuring uniform heat distribution and structural resilience. This dual-expertise approach eliminates common industry pitfalls such as inconsistent blade temperature profiles or premature tool failure.
As an OEM partner, Baoshida provides full technical collaboration from concept to量产. Clients receive proprietary compound formulations matched to their specific rubber substrates, alongside custom knife designs validated through finite element analysis (FEA) for thermal stress and deflection. We adhere to ISO 9001 protocols, with all OEM projects including material traceability, PPAP documentation, and on-site process audits. Our facility supports low-volume prototyping to high-volume production, with typical OEM lead times of 45–60 days for tooling and compound qualification.
Critical performance parameters for our hot knife systems are rigorously validated against industrial benchmarks. The table below summarizes key specifications achievable through our engineering workflow:
| Parameter | Specification | Application Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature Range | 200–450°C | Enables clean cuts on high-hardness compounds (Shore 70A–95A) |
| Thermal Stability | ±0.5°C at setpoint | Prevents rubber scorching during continuous operation |
| Blade Material | Tungsten Carbide-Coated H13 Steel | 3× longer service life vs. standard tool steel |
| Rubber Compatibility | EPDM, NBR, NR, Silicone | Eliminates edge tearing in oil-resistant compounds |
| OEM Customization Lead Time | 45–60 days | Accelerates client time-to-market for new lines |
This technical foundation allows Baoshida to solve complex cutting challenges—such as laminated rubber stacks or extruded profiles with embedded fibers—where generic tools fail. By embedding formula science into tool design, we deliver systems that enhance production efficiency while reducing scrap rates by up to 22% in validated client trials. Partner with us for engineered reliability, not just components.
Customization Process
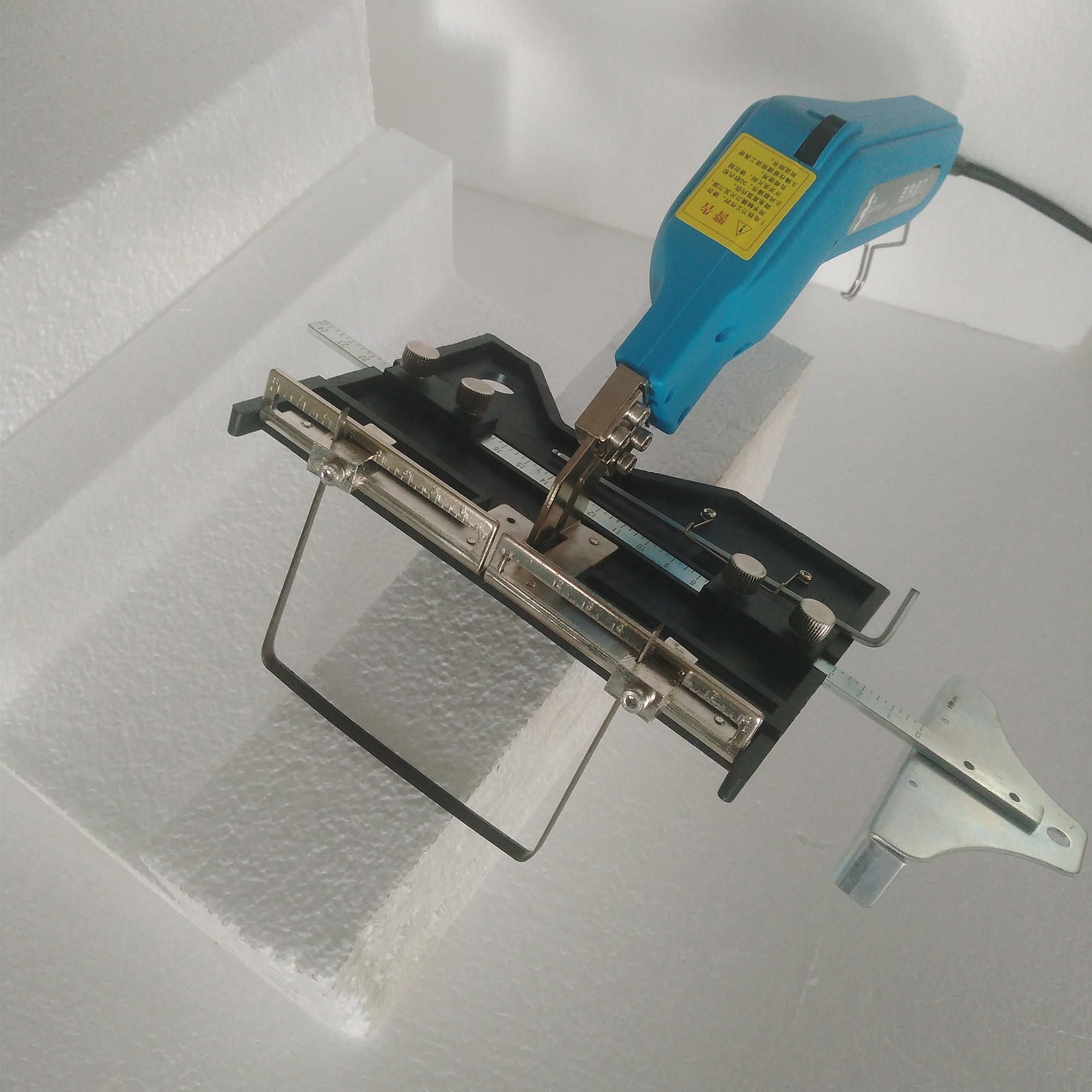
Customization Process for Hot Knife Rubber Cutting Solutions
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in delivering precision-engineered rubber components tailored for industrial cutting applications, particularly where hot knife systems are employed. Our systematic customization process ensures optimal performance, durability, and compatibility with high-temperature cutting environments. The process is structured into four critical phases: Drawing Analysis, Formulation Development, Prototyping, and Mass Production.
The first step, Drawing Analysis, involves a comprehensive technical review of customer-provided engineering drawings or specifications. Our engineering team evaluates dimensional tolerances, cross-sectional profiles, and operational parameters such as temperature exposure, mechanical stress, and contact surface dynamics. This phase ensures that the rubber component will maintain structural integrity when subjected to the intense thermal gradients and mechanical loads inherent in hot knife operations. We assess edge geometry, mounting configurations, and thermal expansion coefficients to prevent delamination or premature wear.
Following drawing validation, we proceed to Formulation Development. Based on the operational environment, we select and compound elastomers with specific thermal resistance, tensile strength, and compression set characteristics. Common base polymers include silicone rubber (VMQ), fluorosilicone (FVMQ), and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), each offering distinct advantages in high-temperature resilience. Additives such as ceramic fillers or thermally conductive agents may be incorporated to enhance heat dissipation and dimensional stability. All formulations are developed in-house using controlled batch processes to ensure repeatability and compliance with international standards.
Prototyping is the third phase, where we produce a limited run of samples using precision molding techniques such as compression or injection molding. These prototypes undergo rigorous testing, including thermal cycling from 150°C to 300°C, hardness retention analysis, and edge deformation evaluation under simulated cutting loads. Customer feedback is integrated at this stage to refine geometry or material behavior before final approval.
Upon successful validation, we transition to Mass Production. Utilizing automated molding lines and real-time quality monitoring systems, we ensure consistent part-to-part uniformity. Each batch is subjected to 100% visual inspection and statistical sampling for physical property verification. Our production capacity supports both medium and high-volume orders with lead times optimized for industrial supply chain demands.
The following table outlines typical material specifications for hot knife-compatible rubber components:
| Property | Silicone (VMQ) | Fluorosilicone (FVMQ) | EPDM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -60°C to 250°C | -55°C to 230°C | -50°C to 150°C |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 7–9 | 6–8 | 8–10 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 50–80 | 55–75 | 60–85 |
| Compression Set (22 hrs, 200°C) | ≤25% | ≤30% | ≤20% |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 0.18–0.22 | 0.17–0.20 | 0.15–0.18 |
Our end-to-end customization framework ensures that every rubber component is engineered for reliability in the most demanding hot knife cutting applications.
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Rubber Cutting Solutions
Achieving clean, burr-free cuts in vulcanized rubber compounds demands specialized thermal management and blade engineering. Standard cutting methods often induce material deformation, edge tearing, or inconsistent cross-sections, directly impacting downstream assembly integrity and product performance. Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. engineers hot knife systems specifically calibrated for the complex viscoelastic properties of industrial rubber. Our solutions integrate precise temperature control algorithms, optimized blade geometries, and robust thermal mass design to ensure molecular-level precision during the cutting phase, minimizing thermal shock to the surrounding material matrix. This technical approach is critical for applications demanding exact dimensional tolerances, such as automotive seals, hydraulic components, and aerospace vibration isolators, where even micron-level deviations compromise functionality.
Our core competency lies in translating material science requirements into operational cutting parameters. We rigorously test each hot knife configuration against specific rubber formulations – accounting for polymer type, filler content, cure state, and durometer – to establish the optimal thermal profile. This eliminates guesswork for the end-user, guaranteeing consistent cut quality across production runs and significantly reducing scrap rates associated with thermal degradation or mechanical stress. Below is a representative specification profile for our standard industrial hot knife units, demonstrating the engineering rigor applied to critical operational parameters.
| Parameter | Standard Industrial Model | Precision OEM Model | High-Volume Production Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 150°C – 450°C | 100°C – 500°C | 200°C – 400°C |
| Temperature Stability | ±3°C | ±1.5°C | ±2°C |
| Blade Material | Tungsten Carbide Coated | Solid Molybdenum | Tungsten Carbide Coated |
| Max. Cutting Thickness | 50 mm (EPDM) | 30 mm (Silicone) | 75 mm (NR/SBR) |
| Power Requirement | 230V AC, 50/60 Hz, 1.2 kW | 230V AC, 50/60 Hz, 0.8 kW | 400V AC, 3-Phase, 3.5 kW |
| Interface | Analog Dial + Digital PID | Touchscreen PLC | Networked PLC Integration |
| Typical Applications | Prototyping, Low-Volume | Medical, Aerospace | Tire Components, Conveyor Belts |
Partnering with Suzhou Baoshida means accessing not just equipment, but deep formulation-specific cutting expertise. Our OEM engineering team collaborates directly with your R&D and production departments to develop bespoke hot knife solutions. We analyze your specific rubber compound data sheet, production line speed, and geometric cutting requirements to engineer a system that integrates seamlessly while maximizing yield and minimizing energy consumption. This proactive technical engagement ensures the solution delivers measurable ROI through enhanced cut quality, reduced downtime, and extended blade service life under your operational conditions.
Initiate the engineering dialogue to resolve your rubber cutting challenges. Contact Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Technical Manager, who possesses over 12 years of hands-on experience in rubber processing equipment specification and integration. Mr. Boyce will conduct a thorough technical assessment of your current cutting process, material specifications, and production objectives. He will provide a detailed feasibility analysis and a precisely scoped proposal outlining the optimal hot knife configuration, expected performance metrics, and integration support plan. Do not settle for generic cutting tools that compromise your product quality. Reach out directly to Mr. Boyce via email at [email protected] to schedule a confidential technical consultation. Provide your specific rubber compound details and cutting application requirements to receive a targeted engineering response within 24 business hours. Suzhou Baoshida delivers precision at the molecular level – contact us to elevate your rubber manufacturing capability.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
