Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Intumescent Strips
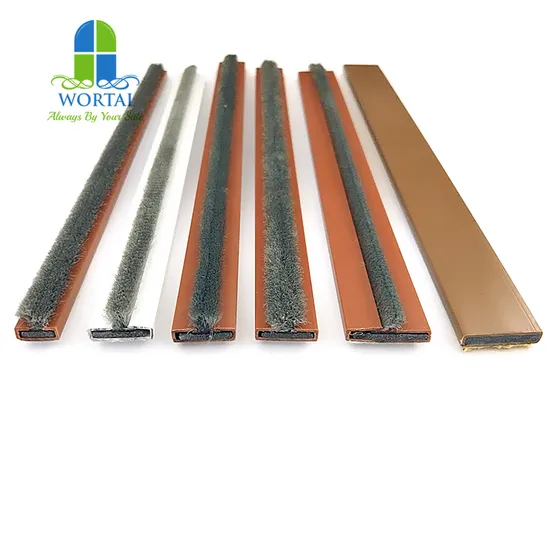

Engineering Insight: The Critical Role of Material Selection in Intumescent Strips
In the field of passive fire protection, intumescent strips serve as a vital component in fire-rated door and glazing systems. Their primary function—expanding under elevated temperatures to seal gaps and prevent the spread of smoke and flames—demands precision in both design and material composition. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we emphasize that material selection is not a secondary consideration but the cornerstone of performance, reliability, and compliance.
Off-the-shelf intumescent solutions often fail to meet the rigorous demands of real-world applications due to generic formulations that prioritize cost over function. These standard products typically utilize base-grade expandable graphite and polymer matrices with limited thermal stability, leading to premature activation, inconsistent expansion, or structural collapse under prolonged heat exposure. In fire-critical environments, such failures compromise safety and invalidate fire ratings.
True performance begins with engineered material systems. High-performance intumescent strips require a balanced composite of acid-source, carbon-source, and blowing agents, precisely calibrated to respond at defined temperature thresholds. The polymer binder must exhibit excellent adhesion across substrates—steel, aluminum, timber, or composite door cores—while maintaining mechanical integrity during storage and service life. Poor binder selection results in delamination, cracking, or moisture absorption, all of which degrade fire performance.
Moreover, environmental exposure—including humidity, UV radiation, and mechanical stress—demands robust material resilience. Standard strips often lack the necessary weathering resistance, leading to embrittlement or swelling. This is particularly critical in exterior or high-traffic installations where long-term durability cannot be compromised.
At Suzhou Baoshida, we specialize in custom-formulated intumescent compounds tailored to OEM specifications. Our formulations integrate high-purity expandable graphite with reinforced elastomeric binders, ensuring predictable expansion ratios, sustained char integrity, and compliance with international standards such as EN 1634-1, BS 476, and UL 10C.
The following table outlines key performance parameters differentiating standard versus engineered intumescent strips:
| Property | Standard Off-the-Shelf Strip | Engineered Strip (Baoshida) |
|---|---|---|
| Expansion Ratio (at 600°C) | 3:1 to 5:1 | 8:1 to 12:1 |
| Activation Temperature Range | 180–220°C | 190–210°C (tight tolerance) |
| Char Cohesion After Expansion | Moderate (cracks common) | High (intact, stable seal) |
| Adhesion Strength (to steel) | 0.3 MPa | ≥0.8 MPa |
| Humidity Resistance (96h @ 85% RH) | Poor (swelling >10%) | Excellent (swelling <3%) |
| Service Life (indoor) | 5–7 years | 15+ years |
Material selection directly dictates fire performance, longevity, and compliance. Generic solutions may appear cost-effective initially, but their failure risk in critical applications leads to costly recalls, liability exposure, and reputational damage. For OEMs and system integrators, investing in purpose-engineered intumescent technology is not an expense—it is a commitment to safety, precision, and industrial excellence.
Material Specifications

Material Specifications for Intumescent Strip Performance
Material selection critically determines the functional efficacy and service life of intumescent strips in fire-sealing applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our OEM-engineered strips leverage advanced polymer formulations to ensure reliable expansion, adhesion, and environmental resistance under extreme thermal conditions. We rigorously qualify three primary elastomer systems—Viton fluorocarbon, Nitrile rubber (NBR), and Silicone—each optimized for distinct operational profiles. Viton excels in high-temperature stability and chemical inertness, withstanding continuous exposure up to 230°C and intermittent peaks near 260°C. Its fluorinated polymer backbone provides exceptional resistance to oils, acids, and hydrocarbon derivatives, making it ideal for aerospace and chemical processing environments where aggressive media contact occurs. Compression set values remain below 25% after 70 hours at 150°C, ensuring long-term seal integrity during non-activation periods.
Nitrile rubber offers a cost-effective solution for moderate-temperature applications, maintaining functionality between -30°C and 120°C. Its acrylonitrile content (typically 34–45%) delivers superior resistance to petroleum-based fluids, hydraulic oils, and greases, positioning it as the standard for automotive and industrial machinery seals. Tensile strength ranges from 15 to 25 MPa, with elongation at break exceeding 300%, facilitating robust mechanical resilience during installation and service. However, NBR exhibits limited ozone and weathering resistance, necessitating protective coatings in outdoor deployments.
Silicone formulations provide unmatched low-temperature flexibility down to -60°C and thermal stability up to 200°C continuous exposure. Its inorganic siloxane backbone ensures minimal compression set (≤20% at 150°C) and exceptional resistance to UV, ozone, and steam—critical for exterior building facades and electrical enclosures. While tensile strength is moderate (6–10 MPa), high-purity medical-grade variants meet stringent biocompatibility standards for cleanroom applications. Silicone’s inherent hydrophobicity prevents moisture absorption, preserving intumescent kinetics in humid climates.
The following table summarizes key performance parameters for OEM specification:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 230 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 200 |
| Compression Set (ASTM D395) | ≤25% @ 150°C/70h | ≤30% @ 100°C/22h | ≤20% @ 150°C/70h |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 12–18 | 15–25 | 6–10 |
| Key Chemical Resistance | Acids, fuels, oils | Petroleum oils, fuels | Ozone, UV, steam |
| Primary Applications | Aerospace, chemical plants | Automotive, hydraulics | Construction, medical |
Suzhou Baoshida’s OEM division tailors compound recipes to balance intumescent filler loading (typically 40–65% by weight) with elastomer performance. Fillers such as ammonium polyphosphate and expandable graphite must integrate homogeneously without compromising the base polymer’s mechanical properties. For critical infrastructure projects, Viton-based strips are recommended where sustained high-heat exposure occurs, while NBR dominates cost-sensitive industrial sealing. Silicone remains the benchmark for architectural glazing systems requiring decades of weathering resistance. All materials undergo accelerated aging per ISO 188 and fire testing per EN 1366-1 to validate expansion ratios exceeding 300% at 650°C. Partner with our engineering team to align material specifications with your fire-rating certification requirements.
Manufacturing Capabilities
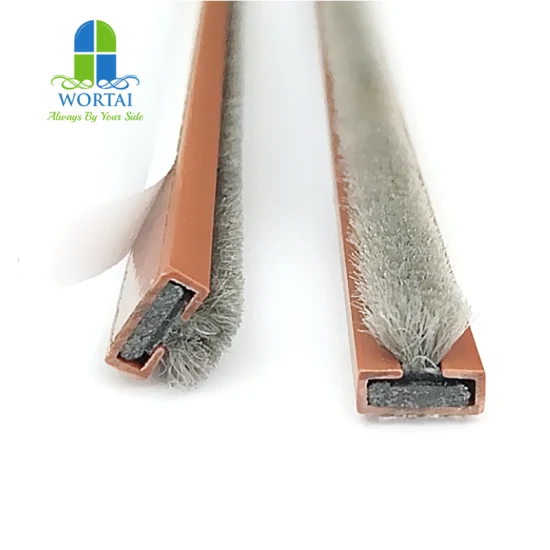

Engineering Capabilities in Intumescent Strip Manufacturing
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our engineering expertise forms the backbone of our industrial rubber solutions, particularly in the development and production of high-performance intumescent strips. With a dedicated team of five mold engineers and two specialized rubber formula engineers, we deliver precision-engineered products tailored to the exact thermal, mechanical, and environmental demands of modern fire safety systems. Our integrated approach ensures that both material composition and physical design are optimized in tandem, resulting in reliable, compliant, and efficient intumescent solutions for global OEMs.
Our mold engineering team possesses extensive experience in designing and refining tooling systems for complex rubber profiles. Utilizing advanced CAD/CAM software and precision CNC machining, we develop molds that ensure dimensional accuracy, consistent extrusion profiles, and rapid cycle times. Each mold is subjected to rigorous simulation and testing protocols to validate flow dynamics, thermal stability, and wear resistance—critical factors in maintaining long-term production integrity. This capability allows us to support both low-volume prototyping and high-volume manufacturing with equal proficiency.
Complementing our mold expertise, our two in-house rubber formulation engineers bring deep knowledge of polymer chemistry and fire-retardant additive systems. They specialize in developing proprietary EPDM and silicone-based compounds engineered to expand predictably under heat, forming a char barrier that seals gaps during fire events. These formulations are fine-tuned to meet specific flame, smoke, and toxicity (FST) standards, including UL 94, BS 476, and EN 13501-1. By controlling the formulation process internally, we ensure batch-to-batch consistency, accelerated development cycles, and full traceability—key requirements for industrial and construction applications.
Our OEM capabilities are built on a foundation of co-engineering partnerships. We work closely with clients from concept through to mass production, offering material selection guidance, DFM (Design for Manufacturability) analysis, and full validation testing. This collaborative model enables rapid customization of intumescent strips for door seals, glazing systems, cable penetrations, and structural joints, with options for adhesive backing, multi-durometer designs, and co-extruded functional layers.
The following table outlines key technical specifications achievable through our engineering platform:
| Parameter | Typical Range / Value | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Expansion Ratio | 10:1 to 30:1 (volume) | ISO 1716, UL 1709 |
| Activation Temperature | 150°C to 220°C | ISO 834, BS 476-20 |
| Fire Resistance Rating | Up to 120 minutes | EN 1634-1, UL 10C |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 40 to 80 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 5.0 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥ 150% | ASTM D412 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +150°C (EPDM) | ISO 1817 |
| -60°C to +250°C (Silicone) |
Through the synergy of advanced mold design and proprietary material science, Suzhou Baoshida delivers intumescent strip solutions that meet the highest standards of performance and reliability. Our engineering team is committed to innovation, precision, and long-term partnership in serving the evolving needs of industrial OEMs.
Customization Process
Customization Process for Intumescent Strip Manufacturing
Precision-engineered intumescent strips demand a rigorously controlled customization pathway to ensure flawless fire-sealing performance under extreme conditions. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our OEM process systematically transforms client specifications into certified, high-integrity products through four critical phases, each governed by stringent industrial protocols and material science expertise.
The initial phase involves meticulous Drawing Analysis. Our engineering team dissects client-provided technical drawings and performance requirements, focusing on dimensional tolerances, substrate compatibility (steel, aluminum, timber), required fire rating duration (e.g., 60, 90, 120 minutes per UL 10C or EN 1634-1), and environmental exposure factors. This analysis identifies critical parameters such as expansion ratio targets, activation temperature thresholds, and adhesion strength requirements. Non-conformance risks are flagged early, and collaborative refinement with the client ensures all functional and regulatory criteria are explicitly defined before formulation begins. Ambiguity in drawings is eliminated to prevent costly downstream deviations.
Subsequent Formulation leverages our proprietary rubber compounding database and advanced polymer chemistry. Based on the drawing analysis, our rubber formula engineers select the optimal elastomeric base (typically EPDM or specialized silicone for high-temperature stability), intumescent agent system (acid source, carbonific, spumific), and functional additives (reinforcing fillers, adhesion promoters, stabilizers). Each component ratio is calculated to achieve the precise expansion kinetics, char integrity, and low-temperature flexibility demanded by the application. Computational modeling predicts compound behavior, but final validation occurs through iterative laboratory mixing and small-batch curing, measuring key properties against the defined targets. This phase is non-negotiable for meeting fire safety standards.
Prototyping validates the formulated compound in the actual strip geometry. Using precision extrusion or molding tooling mirroring production conditions, we produce functional prototypes. These undergo exhaustive in-house testing: thermal profiling in calibrated furnaces to verify expansion onset temperature and volume, adhesion peel tests on specified substrates, compression deflection analysis, and long-term aging studies. Prototypes are subjected to client-specific abuse tests if required. Data from this phase is compared directly against the initial drawing specifications and international fire test standards. Only upon achieving 100% conformance to all critical parameters does the prototype receive approval for tooling sign-off.
The transition to Mass Production utilizes Suzhou Baoshida’s ISO 9001-certified manufacturing facility. Full-scale extrusion or molding lines operate under strict Statistical Process Control (SPC), with real-time monitoring of temperature profiles, line speeds, and vulcanization parameters. Batch traceability is maintained from raw material lot to finished roll. Every production batch undergoes rigorous first-article inspection and ongoing quality checks against the approved prototype specifications. Final shipment includes comprehensive material test reports (MTRs) documenting conformance to the agreed performance criteria, ensuring seamless integration into the client’s fire door or glazing assembly without requalification risk.
Key Intumescent Strip Performance Specifications
| Parameter | Typical Value Range | Test Standard | Performance Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expansion Ratio | 15:1 to 50:1 | ASTM E136 / EN 1363 | Achieve seal integrity at rating |
| Onset Temperature | 150°C to 220°C | ISO 834 | Match substrate fire response |
| Char Cohesion | > 95% Retention | Internal Protocol | Maintain barrier integrity |
| Density (Pre-Expansion) | 1.1 – 1.4 g/cm³ | ASTM D297 | Optimize material usage |
| Adhesion Strength | > 0.8 MPa (to steel) | ASTM D429 Method B | Prevent debonding during fire |
| Compression Deflection | 25% – 40% @ 25% strain | ASTM D575 | Ensure effective door sealing |
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Premium Intumescent Strip Solutions
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we specialize in delivering high-performance industrial rubber solutions tailored to the rigorous demands of fire safety and passive fire protection systems. As a trusted OEM partner in the manufacturing and supply of intumescent strips, we combine material science expertise with precision engineering to ensure compliance, reliability, and long-term performance in critical applications. Whether you are integrating fire-sealing components into door assemblies, window frames, or structural joints, our intumescent strips are engineered to expand predictably under heat, forming a resilient char that seals gaps and inhibits the spread of fire and smoke.
Our manufacturing process adheres to international fire safety standards, including EN 1634-1, BS 476, and ASTM E814, ensuring that every product batch meets the required certification benchmarks for commercial and industrial construction. We offer customizable formulations based on graphite, silicone, or elastomeric composites, allowing for optimal performance in diverse environmental conditions—whether exposed to high humidity, extreme temperatures, or mechanical stress. With in-house R&D capabilities and strict QC protocols, Suzhou Baoshida guarantees consistency, dimensional accuracy, and long shelf life across all intumescent strip variants.
We understand that B2B clients require more than just product supply—they demand technical collaboration, responsive logistics, and scalable production capacity. Our team supports clients from prototype development through to mass production, offering material data sheets, fire test reports, and application-specific engineering guidance. As a strategic partner, we ensure seamless integration of our intumescent strips into your manufacturing workflow, minimizing downtime and maximizing compliance.
For immediate technical consultation or sample requests, contact Mr. Boyce, OEM Account Manager at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. Mr. Boyce brings over a decade of experience in industrial rubber solutions and serves as the primary liaison for global clients seeking customized fire protection components. He is available to discuss material specifications, volume pricing, lead times, and certification documentation to support your next project.
Below are key technical specifications of our standard intumescent strip offerings:
| Property | Standard Graphite-Based Strip | Silicone-Intumescent Hybrid | Elastomeric Composite Strip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expansion Ratio | 15:1 to 20:1 | 12:1 | 10:1 to 15:1 |
| Activation Temperature | 180–220°C | 200–250°C | 170–210°C |
| Fire Resistance Rating | Up to 120 minutes | Up to 90 minutes | Up to 120 minutes |
| Substrate Compatibility | Steel, wood, aluminum | Glass, aluminum, composites | PVC, timber, metal |
| Compression Set (24h @ 70°C) | ≤25% | ≤20% | ≤30% |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +90°C | -50°C to +100°C | -30°C to +85°C |
| Certifications | CE, UL, BS 476 Part 22 | FM, UL, EN 13501-2 | CE, ISO 9001 |
To initiate a technical discussion or request product samples, please contact Mr. Boyce directly at [email protected]. We respond to all inquiries within 12 business hours and offer virtual or on-site engineering support for high-volume partnerships. Suzhou Baoshida is committed to advancing fire safety through innovation—partner with us to build smarter, safer industrial solutions.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
