Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for is rubber conductor
Rubber-insulated conductors are at the heart of countless electrical systems, providing the backbone for safe, efficient, and flexible energy transmission. As global infrastructure projects accelerate and industries modernize across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for high-performance conductors built with reliable, robust materials has never been higher. Yet the diversity of applications, environmental conditions, and regulatory landscapes across these regions means that choosing the right “is rubber conductor” product is both critical and complex.
For international B2B buyers—from energy companies in Kenya expanding grid access, to industrial installers in Colombia or construction firms in the Middle East—sourcing the right rubber conductor is a decision with direct implications on safety, operational efficiency, and long-term costs. With rapid advancements in insulation materials, evolving global standards, and frequent raw material price fluctuations, a well-informed procurement process is essential.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower decision-makers at every stage of the sourcing journey. It covers:
- Types & Applications: A detailed review of is rubber conductor categories and their ideal use-cases.
- Material Science: Insights into copper, aluminum, and advanced rubber compounds—what they mean for performance and durability.
- Manufacturing & Quality Control: Best practices, certifications, and what distinguishes top-tier suppliers from the rest.
- Sourcing Strategies: Evaluating global suppliers, negotiating costs, and mitigating risks in volatile markets.
- Regional Considerations: Navigating compliance, climatic, and logistical factors relevant to Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
- FAQs & Market Outlook: Addressing common challenges and future trends shaping procurement decisions.
Whether you are upgrading national infrastructure, building out renewable energy projects, or seeking reliable partners for long-term supply, this guide provides actionable insights and proven frameworks to help you secure the most fit-for-purpose is rubber conductor solutions—balancing quality, safety, and total cost of ownership in your local context.
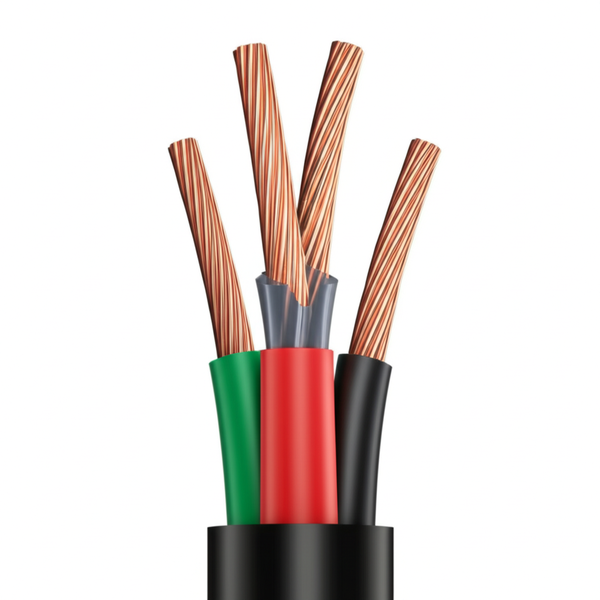
Understanding is rubber conductor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber Conductor | Uses natural rubber insulation; high elasticity | Mining, automotive, flexible connections | Excellent flexibility; less suitable in extreme temperatures |
| EPDM Rubber Conductor | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer insulation; weather-resistant | Outdoor installations, renewables | Superior weather/UV resistance; lower oil/chemical resistance |
| Silicone Rubber Conductor | High-temperature silicone rubber insulation | Industrial ovens, petrochemical plants | Exceptional heat resistance; higher cost |
| EPR Rubber Conductor | Ethylene Propylene Rubber insulation; electrical grade | Power cables, marine, industrial motors | Good electrical properties and moisture resistance; more expensive |
| NBR/PVC Blended Rubber Conductor | Nitrile/PVC blend for oil and abrasion resistance | Oil & gas, heavy-duty machinery | Excellent oil resistance; may have reduced weather resistance |
Natural Rubber Conductor
Natural rubber conductors are characterized by their use of natural rubber as the primary insulation material. This type delivers high elasticity and flexibility, making it ideal for applications that require repeated movement, such as mining machinery, automotive cables, and mobile installations. B2B buyers should note that while natural rubber offers excellent handling and ease of installation, it is less robust under extreme heat, ozone, and UV exposure. Suitability is high for indoor, protected environments or temporary setups in moderate climates.
EPDM Rubber Conductor
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber conductors excel in outdoor and renewable energy applications thanks to their superior resistance to weather, ozone, and UV radiation. These properties suit them for solar installations, outdoor lighting, and field-based industrial equipment. For B2B procurement, the key consideration is balancing the improved longevity in outdoor conditions against marginally reduced resistance to oils and certain chemicals. EPDM is also preferred where cables function under fluctuating environmental conditions.
Silicone Rubber Conductor
Silicone rubber conductors stand out for their high-temperature tolerance, performing reliably up to 200°C and sometimes higher. This makes them indispensable in settings like industrial ovens, refineries, petrochemical plants, and high-temperature manufacturing. The initial investment can be higher compared to other rubber-insulated cables, but their extended service life in harsh thermal environments often justifies the cost. B2B buyers should focus on total cost of ownership and lifecycle durability when considering silicone-insulated options.
EPR Rubber Conductor
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) is specially formulated for robust electrical insulation and moisture resistance. EPR rubber conductors are widely implemented in industrial power cables, marine environments, and large machinery in humid or variable conditions. The electrical properties of EPR are superior to many basic rubber blends, and its longevity enhances operational efficiency. B2B buyers should assess the value in higher upfront costs against reduced maintenance and downtime risks for mission-critical operations.
NBR/PVC Blended Rubber Conductor
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) blended with PVC produces conductors with enhanced oil, fuel, and abrasion resistance, making them an excellent fit for the oil & gas sector, construction machinery, and manufacturing plants exposed to lubricants and solvents. The blend offers a pragmatic solution for demanding industrial sites where exposure to harsh chemicals is routine. Buyers should weigh reduced weather and UV resistance against operational needs—NBR/PVC blends are optimal for controlled indoor or covered environments rather than long-term direct sunlight exposure.
Related Video: What are Transformer Models and how do they work?
Key Industrial Applications of is rubber conductor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of is rubber conductor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power & Energy | Flexible power transmission in renewable installations | Resilient performance under harsh climates | UV/ozone resistance, high dielectric strength, local grid compatibility |
| Construction & Building | Wiring for temporary and permanent electrical systems | Safety, fire resistance, easy deployment | Compliance with fire/safety codes, durability in variable weather, certification |
| Mining & Heavy Industry | Power supply for mobile mining equipment & conveyors | Abrasion and oil resistance, high mobility | Mechanical toughness, heat/oil resistance, supply of specialized cross-sections |
| Automotive & Transport | Cable harnesses for electric vehicles and public transit | Vibration dampening, chemical resistance | Flexibility at temperature extremes, lightweight, conformity to automotive specs |
| Industrial Automation | Connection of mobile robots and automated machinery | Flexibility, long cycle life, easy maintenance | Fatigue resistance, minimum bend radius, compatibility with moving applications |
Power & Energy
In the power and energy sector, particularly for renewable energy installations such as solar and wind farms, rubber conductors are indispensable. They are used for interconnecting photovoltaic panels, connecting transformers, and transmitting power across varied terrain subject to extreme sunlight, rain, or temperature fluctuations—conditions common in regions like Kenya or Brazil. Their robust insulation protects against UV and ozone degradation, ensuring minimal downtime and maintenance. B2B buyers must focus on procuring conductors rated for high dielectric strength and proven durability in challenging climates.
Construction & Building
Rubber conductors serve construction and building industries as both temporary power solutions for work sites and as permanent wiring in areas requiring supplementary safety, such as public venues and emergency systems. Their flame-retardant properties and flexibility make installation quick and secure, even in tight or hazardous spaces, a crucial factor for infrastructure projects across fast-growing cities in Africa and the Middle East. Buyers should prioritize cable types that comply with stringent fire and safety codes, possess robust outer jackets, and are tested for durability in diverse weather conditions.
Mining & Heavy Industry
In mining and heavy industry, rubber conductors are vital for supplying power to mobile equipment, conveyors, pumps, and drilling machinery operating in rugged environments. These cables withstand abrasion, oil exposure, and repeated flexing, which are routine in South American or African mining operations. The reliability of equipment—and thus, operational safety and productivity—depends on high-quality rubber conductors with excellent mechanical strength. Sourcing should emphasize enhanced protection against oils, chemicals, and heat, and the availability of specialized sizes or armoured variants.
Automotive & Transport
For automotive manufacturing and public transport electrification, rubber conductors are the preferred choice in cable harnesses for electric vehicles, trains, and buses. Their superb flexibility, vibration absorption, and resistance to road chemicals ensure sustained electrical performance and longevity even under continuous mechanical stress and temperature changes—critical for European automotive suppliers and Latin American transit authorities. Buyers are advised to seek rubber conductors with outstanding low-temperature flexibility, lightweight construction, and adherence to international automotive standards.
Industrial Automation
Within industrial automation environments, rubber conductors connect mobile robots, conveyor systems, and other automated machinery that operate around the clock in factories. Their flexible design supports continuous movement and resists fatigue, reducing maintenance intervals and machine downtime for manufacturers in regions like the Middle East or Europe. Key specifications for buyers include superior cycle life, minimal bend radius, and compatibility with motion-intensive applications—a focus on materials and construction that withstand repetitive flexing is essential for reliable, long-term operation.
Related Video: Rubber manufacturing process|Natural Rubber Production|#INSTANTMADE
Strategic Material Selection Guide for is rubber conductor
Key Materials for ‘is rubber conductor’: Comparative Analysis
Selecting the optimal material for ‘is rubber conductor’ applications is essential for ensuring performance, safety, and compliance with international market requirements. Each potential conductor and insulation material comes with unique properties that influence overall product reliability, cost, and suitability for specific environments, including those found in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below is a comparative overview of three core material options used in ‘is rubber conductor’ manufacturing.
1. Copper Core with Natural Rubber Insulation
Key Properties:
Copper provides superior electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and excellent flexibility. When paired with natural rubber insulation, the conductor boasts good abrasion resistance and remains functional at moderate temperatures (typically -25°C to +70°C).
Pros & Cons:
* Pros include high conductivity, ease of installation (due to flexibility), and reliable performance in general-purpose industrial applications. Cons center on natural rubber’s limited resistance to oil, chemicals, and UV exposure, along with a relatively short lifespan in hot or humid environments.
Impact on Application:
Best for indoor use or protected outdoor settings in power tools, lighting, and small machinery, where chemical exposure is minimal. Less suited for heavy industry or harsh weather installations.
International Considerations:*
Widely accepted in markets like Kenya, Colombia, and other emerging regions due to its affordability and ease of use. Meets common standards (e.g., ASTM B3 for copper, IEC 60245 for rubber cables); however, local buyers should verify compliance with regional regulations, especially regarding fire safety standards.
2. Tinned Copper Core with Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) Insulation
Key Properties:
Tinned copper resists corrosion, particularly in high-humidity or salt-laden environments, while EPR insulation offers outstanding thermal performance (up to +90°C), flexibility, and resistance to ozone, UV, and many chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
* Pros include long operational life, strong resistance to weathering and chemicals, and stable performance in marine/offshore or renewable energy contexts. Cons are higher material and manufacturing costs, and the insulation can be more challenging to process compared to natural rubber.
Impact on Application:
Highly suitable for demanding environments, such as solar or wind installations, ports, chemical plants, and exposed industrial sites. Provides reliable service under sustained exposure to sunlight and fluctuating temperatures.
International Considerations:*
Preference is growing in regions with harsh climates, common in parts of Africa and the Middle East. EPR-insulated cables often comply with advanced international standards (e.g., IEC 60502, BS 7655), aligning with the requirements of European and Middle Eastern buyers. Check supplier certifications to ensure local regulation compliance and avoid potential import rejections.
3. Aluminum Core with Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) Insulation and Rubber Sheath
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective, though less conductive than copper. XLPE insulation paired with a tough rubber outer sheath results in high dielectric strength, exceptional temperature resistance (+90°C continuous, short-term up to +250°C), and good mechanical protection.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantages are lower weight (reducing shipping and installation costs), competitive material price, and suitability for high-voltage applications. Limitations include aluminum’s increased susceptibility to oxidation and more meticulous termination/connection requirements.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for large infrastructure and utility projects, especially where budget constraints and long cable runs are considerations—common for energy transmission or distribution in emerging and cost-sensitive markets.
International Considerations:
Frequently specified in Africa and South America due to favorable price-to-performance ratio. Buyers must ensure compliance with local standards (such as DIN VDE, IEC 60228, or national grid codes) and work closely with experienced installers to mitigate failure risks associated with improper terminations.
Summary Table: Comparative Overview
| Material | Typical Use Case for is rubber conductor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper Core + Natural Rubber | General industrial wiring, indoor or protected outdoor settings | Excellent conductivity, flexible, established standards | Limited chemical/UV resistance; moderate lifespan in humid/hot climates | Med |
| Tinned Copper Core + EPR | Harsh/Outdoor/Marine use, solar/wind, chemical plants | Superior corrosion/weather/chemical resistance, long life | Higher cost, complex manufacturing/processing | High |
| Aluminum Core + XLPE Insulation + Rubber Sheath | Utility/infrastructure, large-scale distribution, cost-sensitive installations | Lightweight, cost-effective for long runs, good high-temp resistance | Lower conductivity, connectors must be properly installed to avoid oxidation issues | Low |
Action Points for International B2B Buyers:
– Always align material selection with both performance needs and regional regulatory requirements.
– Request declarations or certifications of compliance (e.g., IEC, DIN, ASTM) from prospective suppliers.
– Prioritize materials based on application environment and total lifecycle cost, rather than initial price alone.
– When sourcing from global regions, factor in climate and local installation practices to avoid premature failures or costly retrofits.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for is rubber conductor
Rubber conductor manufacturing is a sophisticated process that integrates precise material engineering with stringent quality assurance protocols to ensure reliable electrical performance and safety across diverse environments. For B2B buyers in markets such as Kenya, Colombia, and similar regions, understanding the end-to-end production and quality control journey is essential to securing supply chain reliability and compliance with local and international standards.
Overview of the Manufacturing Workflow
Rubber conductor manufacturing consists of several tightly controlled stages designed to achieve optimal conductivity, flexibility, and durability.
1. Raw Material Preparation
– Conductor Materials: The core conductor is typically made from high-grade copper or aluminum, chosen for optimal electrical performance and cost efficiency. Copper remains the industry standard for premium conductivity, while aluminum offers lighter weight and cost advantages.
– Rubber Compounding: The insulating and sheathing layers are derived from specialized rubber compounds. These can include natural or synthetic rubbers such as EPR (ethylene propylene rubber) or silicon rubber, depending on application requirements like environmental resistance, flexibility, and voltage rating.
2. Wire Drawing and Stranding
– Wire Drawing: Metal rods are drawn through dies to achieve the precise diameter and surface smoothness needed for uniform conductivity.
– Stranding: Multiple fine wires are twisted together to form the conductor core. Stranding enhances flexibility—a key attribute for rubber-insulated cables intended for dynamic industrial or outdoor use.
3. Insulation and Sheathing
– Extrusion: The prepared rubber compound is extruded onto the conductor using specialized machinery. Precise control of thickness and adhesion ensures performance and longevity.
– Vulcanization: The extruded product undergoes vulcanization, a heat and pressure process that cross-links the rubber materials for enhanced thermal and mechanical properties.
4. Assembly and Cabling
– For multi-core cables, individual insulated wires are twisted and combined according to the cable’s design specification. Fillers, tapes, or screens may be added for reinforcement or electromagnetic shielding.
5. Finishing and Cutting
– The finished cable is cooled, marked, and cut to length. Laser or ink-jet printing applies critical product information, including manufacturing date, standards compliance, and batch codes for traceability.
Key Manufacturing Techniques
- Cross-Linking Technology: Advanced cross-linking, particularly for EPR or silicon rubbers, improves thermal endurance, resistance to chemicals, and electrical integrity.
- Automated Extrusion Lines: High-precision, automated extrusion and curing lines increase product consistency and reduce defect rates.
- Environmental Conditioning: Some cable lines undergo specialized conditioning to enhance weather, UV, or moisture resistance, a vital consideration for installations in humid or tropical climates found throughout Africa and South America.
Quality Control Protocols
Consistent and rigorous quality control is crucial to ensure reliability, lifespan, and regulatory compliance.
International Standards and Certifications
– ISO 9001: Most reputable manufacturers operate under ISO 9001 quality management systems, ensuring traceable procedures, corrective actions, and continuous improvement.
– Regional/International Standards: Products exported to Europe, Africa, or the Middle East often require additional certifications (e.g., CE marking for European Union, SASO for Saudi Arabia, SONCAP for Nigeria, or Smark for South America).
– Industry Certifications: Depending on the end-use, specific certifications such as IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) or API (American Petroleum Institute) might apply—especially for cables destined for critical infrastructure or oil & gas projects.
Primary QC Checkpoints
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Rigorous scrutiny of raw materials (metals, rubber compounds) for purity, mechanical strength, and compliance with batch specifications. Buyers should request raw material COAs (Certificates of Analysis) and ensure supplier traceability systems are robust.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, process parameters are continuously monitored—such as conductor dimensions, insulation thickness, concentricity, and surface defects. Inline electrical testing is often performed to detect insulation faults or abnormal resistance.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished cables are subjected to multiple end-of-line checks, including:
– Electrical Testing: High-voltage withstand, insulation resistance, and conductor continuity.
– Mechanical Testing: Tensile strength, elongation, and flexibility.
– Environmental Testing: Where applicable, samples are tested for resistance to flame, UV, oil, and water ingress.
– Dimensional Verification: Ensures compliance with design and tolerance standards.
Common Testing Methods
– Spark and Hi-Pot Testing: Detects micro-defects or insulation weaknesses.
– Hot Set and Ageing Tests: Assesses material stability under high temperatures and mechanical load.
– Flame Retardance and Smoke Density: Ensures compliance with fire safety requirements relevant for construction and industrial settings.
– Cold Bend and Cold Impact: Critical for products used in colder climates (e.g., parts of Europe or Andean South America).
Supplier Quality Assurance: Best Practices for B2B Buyers
Ensuring product quality and compliance is not only about supplier trust but requires proactive verification, especially in international transactions.
1. Auditing and Facility Evaluation
– Factory Audits: On-site or virtual audits provide insight into the supplier’s manufacturing capability, process control, and adherence to QC protocols. Look for ISO 9001 certification and evidence of regular internal audits.
– Process Capability Studies: Request data on process capability indices (Cp, Cpk) for critical manufacturing steps. High values indicate low risk of out-of-spec products.
2. Third-Party Inspection and Testing
– Pre-shipment Inspections: Engage recognized inspection agencies (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, Intertek) to verify product conformity before dispatch. This protects against sub-standard or counterfeit products.
– Random Batch Testing: Consider independent lab testing on arrival, especially when first partnering with a supplier or entering a new regulatory environment.
3. Documentation and Traceability
– Quality Certificates: Always require batch test reports, certificates of conformity (CoC), and, where applicable, international certification copies (CE, SASO, IEC).
– Lot Traceability: Ensure the supplier can trace every finished product to its component materials and production batch, facilitating recall or root-cause analysis if quality issues arise.
Regional and Regulatory Considerations
International buyers face varying regulatory landscapes and logistical challenges:
- Africa and South America: Markets like Kenya or Colombia may have unique standards or customs documentation requirements. Delays can arise from incomplete paperwork or non-conforming certification. Partner with suppliers familiar with export processes to your target region.
- Middle East: Regulatory environments such as Saudi Arabia’s SASO enforce strict import conformity. Ensure suppliers are registered with local conformity assessment bodies.
- Europe: The CE mark is mandatory for products sold in the EU; verify that your supplier’s CE declaration is genuine and up-to-date.
- Local Language Documentation: For smooth customs clearance, request product documentation in the relevant official language, particularly critical in Africa and South America.
Actionable Guidance for B2B Buyers
- Supplier Due Diligence: Regularly review your supplier’s certifications, audit reports, and market reputation—especially for long-term projects or government contracts.
- Customized Quality Agreements: Set clear, contractually binding quality and documentation standards tailored to your project and regional requirements.
- Ongoing Communication: Establish open lines of communication for resolving QC issues quickly—a crucial aspect for time-sensitive infrastructure or industrial developments.
By maintaining rigorous oversight across every stage of production and validation, B2B buyers can mitigate risk, enhance supply chain resilience, and ensure end products perform reliably under local operating conditions. Demand strong traceability, robust quality documentation, and proactive supplier engagement to position your organization for success in the global rubber conductor market.
Related Video: Water Quality Testing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for is rubber conductor Sourcing
Key Cost Components in ‘is Rubber Conductor’ Sourcing
Careful breakdown of total landed cost is fundamental when sourcing rubber conductor cables internationally. Below are the most significant cost contributors:
- Raw Materials: The conductor itself is typically copper or aluminum, with costs closely tied to global commodity prices, which can be volatile. The rubber insulation—often natural or synthetic (e.g., EPDM, silicone, or EPR)—adds cost based on type, thickness, and quality standards.
- Labor: Wages vary by manufacturing region. Emerging markets can offer more competitive labor rates, but buyers should weigh this against possible impacts on quality control or lead times.
- Manufacturing Overhead: Energy consumption, plant maintenance, process automation, and compliance with regulatory standards all influence fixed overhead allocation.
- Tooling & Customization: Orders requiring specialized diameters, multi-core configurations, or unique jacket colors incur setup or tooling fees, particularly for bespoke runs or at lower volumes.
- Quality Control & Certification: Stringent inspection protocols, batch testing, and compliance with standards (such as IEC, UL, or regional equivalents) add to unit cost but are crucial for risk mitigation.
- Logistics & Shipping: International buyers must account for inland transportation, port handling, ocean/air freight, duties, and insurance. Costs are highly variable based on shipment mode, volume, and region.
- Supplier Margin: Manufacturer or exporter margins reflect their market positioning, supply stability, and required after-sales support. Higher-value suppliers may cost more but can reduce downstream risk and deliver more predictable service.
Influencers of Rubber Conductor Cable Pricing
Several market and transaction-specific factors can cause significant swings in pricing:
- Order Volume & Minimum Orders (MOQ): Large-volume or long-term contracts generally allow for lower per-unit pricing due to economies of scale. Smaller orders may attract premiums or surcharges.
- Product Specifications: Requirements such as cross-section area, voltage rating, flame retardancy, flexibility, or UV/oil resistance directly affect both material and process costs. High-performance or custom-jacketed conductors command higher prices.
- Material Selection: Copper, the premium conductor, is much costlier than aluminum, with prices fluctuating according to global commodities markets. Similarly, the choice of rubber compound (e.g., silicone for high temp, EPR for general use) is a key pricing driver.
- Quality Assurance & Certification: Products meeting demanding certifications (CE, ROHS, local regulatory marks) require more rigorous processes and documentation, pushing costs up.
- Supplier Geography & Capabilities: Proximity to raw materials, efficiency of supplier operations, and presence of modern manufacturing infrastructure can all impact baseline prices.
- Incoterms: The terms of trade (FOB, CIF, DDP, etc.) determine the division of logistics costs and can meaningfully alter the total landed price for buyers.
Actionable Cost-Saving Tips for International B2B Buyers
Buyers in Kenya, Colombia, the Middle East, Europe, and beyond benefit from a strategic approach to sourcing:
- Negotiate with Full Transparency: Request a detailed cost breakdown from suppliers to clarify where savings can be made, especially for higher volumes or longer-term commitments.
- Optimize Order Quantities: Consolidate demand where possible to achieve better scale pricing. Flexibility in delivery timelines can also help suppliers batch production, reducing setup costs.
- Standardize Specifications: Where feasible, align product specs with commonly available standards—avoiding unnecessary customization keeps both material and tooling costs down.
- Verify Certification Needs: Only select certifications and quality levels essential for your application and regulatory requirements to avoid excess premium charges.
- Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Factor in expected cable lifespan, local testing costs, failure risk, and potential import duties or taxes in your region. Sometimes, slightly higher upfront prices justify themselves via lower lifecycle costs.
- Compare Incoterm Scenarios: Carefully review quotes under different Incoterms; in markets with complex logistics (such as landlocked African countries), DDP offers visibility but also potential supplier markups that may be negotiated.
- Leverage Alternative Materials: Where your application allows, consider aluminum conductors or blends to reduce costs, especially in large projects or installations not requiring maximum conductivity.
Regional Considerations for International Buyers
- Africa (e.g., Kenya): Import duties, customs procedures, and local standards can meaningfully affect total costs. Bulk orders may offset high maritime shipping costs.
- South America (e.g., Colombia): Review local market incentives, such as tariff reductions under trade agreements, and prioritize suppliers with established regional distribution channels.
- Middle East: Emphasize certification alignment with GCC or Gulf standards; hot-climate rubber compounds may be required and affect pricing.
- Europe: Expect higher compliance requirements (CE, RoHS), but also broader supplier choice and potential for intra-European Union logistical efficiencies.
Disclaimer: The above pricing analysis is intended as a guideline only; due to ongoing volatility in raw material and logistics costs, as well as shifting market demand, actual prices should be confirmed directly with vetted suppliers. Always secure updated, binding quotations before making procurement decisions.
Spotlight on Potential is rubber conductor Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘is rubber conductor’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Google (www.google.com)
Google is recognized in industry directories and global sourcing platforms as a referenced name among ‘is rubber conductor’ suppliers, although detailed public information on its specific manufacturing capabilities in this sector is limited. B2B buyers searching for top ‘is rubber conductor’ manufacturers frequently encounter Google as a major search and information aggregation platform, aggregating global vendor and sourcing options. While there is no indication that Google itself directly produces or certifies ‘is rubber conductor’ products, its global reach enables international buyers—especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—to access a broad database of manufacturers, potentially filtering by certifications, supply capacity, and specialization. However, for rigorous B2B procurement, it is advisable for buyers to carefully verify the legitimacy and credentials of any listings accessed through Google search results to ensure direct manufacturer engagement and compliance with relevant quality standards.
Quick Comparison of Profiled Manufacturers
| Manufacturer | Brief Focus Summary | Website Domain |
|---|---|---|
| Information aggregator; not a known manufacturer | www.google.com |
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for is rubber conductor
Key Technical Properties of Is Rubber Conductor
When sourcing is rubber conductor for industrial or infrastructure projects, understanding specific technical properties is essential. These specifications directly impact performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness in diverse operating environments, from African manufacturing plants to renewable energy projects in South America. The following are the most critical technical properties to evaluate:
-
Conductor Material and Purity
The core of an is rubber conductor is typically made from copper or, less commonly, aluminum. High-purity copper enhances electrical conductivity, ensuring efficient power transmission and minimal energy loss. For buyers, specifying the conductor material and its purity (e.g., 99.9% copper) is important for both performance and compliance with regional electrical standards. -
Insulation Material and Grade
The rubber insulation acts as the primary protective barrier, providing electrical isolation and guarding against mechanical damage, moisture, and chemicals. Common grades include natural rubber and synthetic rubbers like EPDM or EPR. The insulation’s heat resistance, flexibility, and flame retardancy should align with the targeted application (e.g., construction, mining, or outdoor renewable installations). -
Voltage Rating
This specification defines the maximum electric potential the conductor can safely carry. Standard ratings range from low-voltage (LV, e.g., 450/750V) up to medium-voltage (MV, e.g., 3.6/6 kV). Buyers should always match voltage ratings to intended system requirements to ensure operational safety and regulatory compliance, avoiding under-specification or unnecessary cost. -
Temperature Range
Is rubber conductors are engineered to operate within specific ambient and conductor temperatures (commonly -30°C to +90°C). This resilience is crucial for projects in regions with extreme climates, such as North Africa’s heat or Eastern Europe’s winters. Always confirm the specified range to guarantee safe, continuous operation in your target geography. -
Flame Retardant and Environmental Resistance
High-quality rubber insulation should exhibit strong flame retardancy, oil, ozone, and UV resistance. These features not only improve lifespan and safety but can also be mandated by building codes in sectors such as energy, transport, and construction. -
Conductor Size and Tolerance
The cross-sectional area of the conductor (measured in mm² or AWG) determines its current-carrying capacity. Industry standards set tolerance levels for diameter and resistance; tight tolerances indicate higher manufacturing precision and quality. Clear specifications here ensure compatibility and prevent issues during installation.
Common Industry and Trade Terms
Global B2B trade in is rubber conductor relies on shared terminology to define commercial expectations and contractual obligations. Understanding these terms streamlines procurement and reduces risk.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to producers who supply cables under their own or clients’ brands—critical for custom solutions, private label requirements, or ensuring industry certifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest order a supplier will accept, often expressed in meters or reels. Buyers must negotiate MOQ based on project scale or storage constraints, especially in markets where logistics and stockholding costs are high. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal process to request pricing and terms for a specified cable type, quantity, and delivery timeline. Clearly detailed RFQs help streamline supplier responses and enable accurate cost comparisons. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized terms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DAP) that define the division of shipping, insurance, and customs responsibilities between buyer and seller. Selecting the correct Incoterms is essential—especially for buyers in Africa or South America where customs processes can vary widely. -
Lead Time
The duration from order placement to delivery—impacts project scheduling and inventory planning. Buyers should confirm lead times, considering factors like manufacturing load, shipping routes, and potential customs delays in regions such as the Middle East. -
Compliance Certificates
Documentation (such as CE, RoHS, or local fire safety marks) proving that products meet regulatory and industry standards. Always request certificates to ensure products are accepted by authorities and insurers in your market.
Actionable Takeaways for International B2B Buyers
- Specify conductor material purity, insulation grade, voltage, and temperature ratings tailored to your project environment.
- Confirm flame retardancy and environmental resistance meet local codes, especially for exposed or hazardous settings.
- Use trade terms like RFQ and Incoterms strategically to clarify expectations, reduce hidden costs, and protect against delays.
- Always request and verify compliance certificates before shipment to avoid customs clearance or insurance issues.
By mastering both the technical and commercial vocabulary, international buyers can assess supplier offers with confidence—leading to better pricing, compliance, and long-term reliability.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the is rubber conductor Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global demand for rubber conductor cables continues to surge, driven by increased investment in infrastructure, energy, and industrial automation across both emerging and mature economies. For international B2B buyers—particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—the robust growth in construction, electrification, renewables, and mobility projects shapes sourcing priorities. Countries such as Kenya and Colombia, aiming to expand power access and upgrade grids, are seeking conductors with enhanced durability, weather resistance, and flexibility provided by advanced rubber insulation.
Key market drivers include ongoing urbanization, the expansion of renewable energy (notably solar and wind), and the digitalization of industrial operations. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing cables that maintain performance under harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, humidity, and exposure to chemicals. This is especially relevant in regions with challenging climates or where cables are deployed for mining, oil & gas, or heavy industry. In Europe and parts of the Middle East, regulatory compliance and adherence to international standards (such as IEC, EN, or BS) are major factors influencing supplier selection.
Technological advancements in rubber compositions—such as enhanced cross-linked rubber and hybrid materials—are enabling cables to deliver improved electrical safety, longer service life, and fire resistance. These innovations also open new opportunities for cost-effective, lighter-weight solutions, which are critical for large-scale infrastructure projects and renewable energy deployments. Sourcing trends reveal growing interest in long-term supplier relationships, joint R&D for specification alignment, and local value-addition to ensure rapid supply and post-sales support. Raw material price volatility, especially in copper, aluminum, and petrochemicals, remains a persistent challenge, prompting buyers to look for suppliers with stable procurement channels or substitute material strategies.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is swiftly moving from a niche concern to a core procurement criterion for rubber conductor buyers worldwide. The environmental footprint of cable production—spanning energy consumption, emissions, and waste management—is under increased scrutiny. B2B buyers, particularly those engaged in public sector, infrastructure, or energy projects, now frequently require suppliers to demonstrate green manufacturing credentials, including ISO 14001 certification and compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH guidelines.
Rubber conductors derived from eco-friendly or recycled materials are gaining traction, especially as green building regulations become more strict in markets like the EU and Gulf states. Using low-smoke, halogen-free rubber compounds is another important trend, reducing toxic emissions in case of fire and ensuring safer environments for end-users. Buyers are also prioritizing traceability and transparency in the supply chain—seeking assurance that natural rubber or synthetic sources are not linked to deforestation, social exploitation, or illegal practices.
Effective supplier evaluation now extends to carbon footprint assessments, water use, and ethical labor practices. Some leading cable manufacturers are adopting circular economy principles, designing rubber conductors for recyclability and easy material recovery at end of life. To strengthen ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) credentials, buyers in Africa, South America, and beyond are leveraging third-party sustainability audits and favoring suppliers with internationally recognized ecolabels such as EcoVadis, UL Environment, or IECQ Green Process. These measures are not only central to fulfilling tender requirements but also enhance corporate reputation and long-term project resilience.
Brief Evolution/History (Sector Context)
Rubber-insulated conductors have a long-standing legacy, tracing back to the early 20th century as a response to the need for safer electrical cabling. Natural rubber was initially used as a primary insulating material due to its inherent flexibility, water resistance, and insulating properties. Over decades, the sector has shifted toward synthetic and cross-linked rubbers, resulting in cables that can withstand harsh industrial and outdoor conditions while delivering superior electrical performance.
As applications diversified—from early power distribution in urbanizing regions to today’s sophisticated deployments in renewable energy and automation—the technology behind rubber conductors evolved in parallel. The sector now emphasizes not only improved safety and reliability but also sustainability and adaptability for a wide range of regional and industry-specific requirements. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution aids in specifying products that balance legacy robustness with the latest advances in material science and regulatory compliance.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of is rubber conductor
-
How can I effectively vet international suppliers of rubber conductors?
Assess prospective suppliers by reviewing their compliance with recognized industry standards (such as ISO, IEC, or UL), track record in exporting to your region, and client references. Request documentation on product testing, previous export consignments, and quality certifications. Where possible, conduct virtual or on-site audits, and explore third-party inspection options. Confirm supplier registration, business licenses, and trade association memberships to minimize risk and ensure legitimacy. -
Can rubber conductors be customized to meet specific regional or industry requirements?
Yes, most reputable manufacturers offer customization options to accommodate local regulations, voltage mandates, environmental factors, and installation conditions. Clearly communicate your required technical specifications, such as conductor size, insulation thickness, temperature resistance, color-coding, and flame-retardant properties. Request written confirmation of compliance with your market’s safety and electrical standards, and arrange for pre-shipment product samples or prototypes to validate suitability before placing bulk orders. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs), lead times, and payment terms for bulk orders?
MOQs for rubber conductors typically range from 1 to 10 kilometers per specification, depending on supplier capacity and customization level. Standard lead times are 4–8 weeks, though extra time may be needed for non-standard designs or busy production seasons. Payment terms usually include a deposit (30–50%), with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Consider negotiating for flexible terms, especially if establishing a long-term relationship, and verify payment security through escrow or trade finance options. -
Which quality assurance measures and certifications should I require?
Insist on third-party inspection certificates and test reports that verify conductor dimensions, insulation integrity, electrical performance, and compliance with key standards (such as IEC 60245 or BS 6004 for rubber cables). Ask to review the supplier’s ISO 9001 (Quality Management) and, if necessary, ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) certificates. For high-risk applications, require additional documentation, such as RoHS or CE compliance, to ensure environmental and safety requirements are met. -
What are the main logistical considerations when importing rubber conductors internationally?
Rubber conductors are heavy and often shipped on reels or in coils, requiring careful packing to prevent damage. Work with suppliers who provide robust packaging and clear product labeling, and ensure they offer export documentation (bill of lading, certificate of origin, packing list). Confirm available shipping methods (sea, air, road) and incoterms (FOB, CIF, DAP), and coordinate with a reliable freight forwarder familiar with import procedures and clearance in your country. Factor in potential transit delays linked to customs and port handling. -
How should I address language barriers, technical communication, and documentation during procurement?
To ensure clarity, use bilingual contracts where possible and confirm all technical requirements in writing, including drawings and datasheets. Request documentation and product labeling in English and, if relevant, your local language. Opt for suppliers with experienced export sales staff who are responsive to inquiries, and consider employing a local procurement partner or third-party inspection agency to facilitate communication, onsite inspections, and smooth order execution. -
What steps can I take if I encounter product defects or disputes with my supplier?
Clearly define dispute resolution procedures in your contract, including inspection periods, acceptable tolerance limits, and return or replacement terms. Specify an agreed arbitration body (such as ICC) and jurisdiction for dispute resolution. When issues arise, document defects thoroughly with photos and testing reports, and communicate promptly in writing. Most established suppliers will offer a remedy such as credit, replacement, or refund, but having third-party documentation and a clear contractual framework is vital for successful claims. -
Are there strategies to mitigate risks from raw material price fluctuations when ordering rubber conductors?
Given the volatility in costs for copper, aluminum, and rubber-based insulation, request valid quotations with locked-in prices for a specific timeframe, and consider forward contracts for anticipated reorders. Monitor market trends and negotiate volume-based discounts or price adjustment clauses to account for large swings in raw materials. Building strong relationships with suppliers or utilizing inventory hedging strategies can also help cushion against short-term market shocks and improve cost predictability.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for is rubber conductor
As global demand for electrically robust and cost-effective solutions increases, rubber conductors have emerged as a versatile choice across sectors including construction, power distribution, and renewable energy. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the evolving landscape is vital for achieving competitive advantage. Key takeaways include the necessity to evaluate not only the conductor materials—such as copper or copper-clad aluminum—but also the quality of rubber insulation, which directly impacts safety, flexibility, and long-term durability.
Strategic sourcing remains essential in minimizing supply chain risks related to raw material volatility, especially given fluctuations in copper, aluminum, and petrochemical prices. Partnering with trusted suppliers, leveraging multi-source procurement approaches, and prioritizing certifications for environmental and fire resistance standards can strengthen resilience and ensure regulatory compliance. Embracing advances in insulation and sheathing technology—from cross-linked polymers to low-halogen materials—can further differentiate your projects in terms of reliability and sustainability.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of infrastructure modernization, accelerating adoption of renewables, and tightening environmental regulations will continue to shape the rubber conductor market. Forward-thinking organizations should monitor global material trends, invest in supplier relationships, and remain agile to rapidly capitalize on new innovations. Now is the time to position your business at the forefront of safe, efficient, and sustainable power systems—through informed, strategic sourcing of advanced rubber conductors.