Technical Contents
Engineering Guide: Leave Doormat

Engineering Insight: Material Selection in Leave Doormat Performance
Premature failure of industrial leave doormats stems directly from inadequate material science application. Off-the-shelf solutions prioritize low initial cost over engineered resilience, leading to rapid degradation under operational stress. Commodity-grade thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) and recycled rubber compounds dominate this segment, but their formulations lack the molecular stability required for high-traffic commercial environments. Plasticizer migration in TPE causes surface hardening within 6–12 months, eliminating flexibility and increasing slip risk. Recycled rubber often contains inconsistent polymer chains and residual contaminants, accelerating UV-induced cracking and reducing tensile strength by up to 40% after 18 months of outdoor exposure. These failures manifest as reduced debris-scraping efficiency, compromised drainage, and hazardous surface deterioration—directly impacting facility safety and maintenance costs.
The core issue lies in the absence of purpose-built polymer architecture. Industrial applications demand precise carbon black dispersion for UV resistance, controlled cross-link density for abrasion tolerance, and tailored filler systems for dynamic load recovery. Off-the-shelf mats omit these critical design parameters, resulting in a 30–50% shorter service life compared to engineered solutions. For instance, insufficient carbon black content (<25 phr) fails to shield the polymer matrix from solar radiation, while inadequate silica reinforcement (<15 phr) diminishes cut-growth resistance on abrasive surfaces like concrete. Shore A hardness is frequently misjudged; overly soft compounds (≤55A) deform under point loads, while excessively rigid ones (≥75A) lose particulate-trapping capability.
Suzhou Baoshida addresses these gaps through OEM co-engineering, leveraging proprietary SBR/NR hybrid compounds with optimized vulcanization kinetics. Our formulations integrate high-purity carbon black (N330 grade) at 28–32 phr for UV stability and precipitated silica (18–22 phr) for tear strength, validated through ASTM D412 and ISO 4649 testing. The table below contrasts critical performance metrics:
| Material Type | Critical Failure Modes | Abrasion Loss (mm³) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Shore A Hardness | UV Resistance (1,000h QUV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Off-the-Shelf TPE | Plasticizer migration, surface hardening | 185–220 | 8.5–10.2 | 50–60 (unstable) | Severe cracking (>30% ΔE) |
| Recycled Rubber | Inconsistent filler dispersion, ozone aging | 140–175 | 12.0–14.5 | 65–75 (variable) | Moderate cracking (>20% ΔE) |
| Baoshida OEM Compound | Engineered stability, no plasticizers | 82–95 | 18.7–21.3 | 62±2 (stable) | Minimal change (<5% ΔE) |
This data underscores why generic mats fail: they lack the material intelligence to balance flexibility, durability, and environmental resistance. Our OEM approach tailors compound chemistry to site-specific variables—foot traffic volume, chemical exposure, and climate—ensuring consistent performance over 5+ years. Material selection is not a cost line item but a lifecycle investment; optimizing polymer composition reduces total cost of ownership by 60% through eliminated replacements and liability risks. Partner with Suzhou Baoshida to transform your leave doormat from a consumable into a engineered safety asset.
Material Specifications
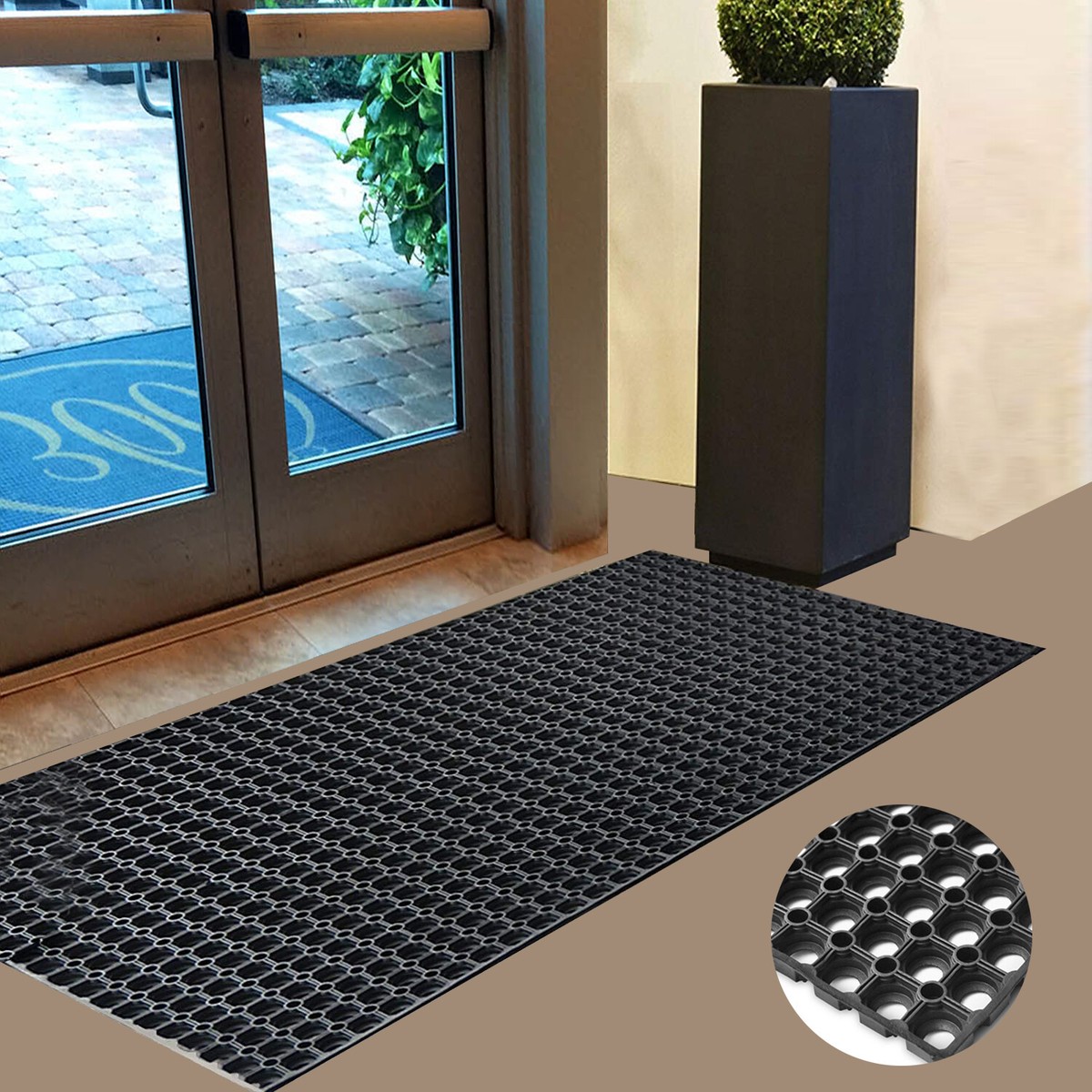

Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. specializes in high-performance industrial rubber solutions tailored for demanding environments. In applications such as leave doormats used in commercial and industrial facilities, material selection is critical to ensuring durability, chemical resistance, and long-term functionality. The three primary elastomers employed in such applications are Viton, Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone. Each offers distinct advantages depending on operational conditions, including temperature exposure, chemical contact, and mechanical stress.
Viton, a fluorocarbon-based rubber, delivers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and a broad range of aggressive chemicals. With a continuous service temperature range up to 250°C, Viton is ideal for environments where thermal degradation and chemical exposure are primary concerns. Its low gas permeability and excellent aging characteristics make it a preferred choice in high-seal-integrity applications. However, Viton is less flexible at low temperatures and carries a higher material cost, which may limit its use in cost-sensitive or non-extreme environments.
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is widely used for its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, greases, and fuels. It offers good abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications such as industrial flooring and traffic-facing surfaces. Nitrile performs reliably within a temperature range of -30°C to 120°C, balancing performance and cost-effectiveness. While it lacks the extreme temperature and chemical resistance of Viton, it remains a practical choice for standard industrial environments where oil and fluid resistance are key.
Silicone rubber excels in both high and low-temperature applications, with a service range from -60°C to 230°C. It offers excellent UV and ozone resistance, ensuring long-term stability in outdoor or exposed environments. Silicone is also known for its flexibility and resilience across thermal cycles, making it ideal for dynamic applications. However, it has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Nitrile and is less suitable for environments involving prolonged contact with oils or solvents.
The following table summarizes key material properties for informed selection in leave doormat manufacturing:
| Property | Viton (FKM) | Nitrile (NBR) | Silicone (VMQ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 250 | -30 to 120 | -60 to 230 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 15–20 | 10–25 | 5–10 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 150–250 | 200–500 | 200–600 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60–90 | 40–90 | 30–80 |
| Resistance to Oils/Fuels | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
| Resistance to Ozone/UV | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding | Moderate to Good | Limited |
Material selection directly impacts performance, longevity, and cost-efficiency in industrial leave doormat applications. At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., we provide engineered rubber solutions aligned with precise operational demands, ensuring optimal functionality across diverse industrial environments.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Precision Rubber Engineering for Industrial-Grade Doormat Manufacturing
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. leverages deep technical expertise in rubber formulation and mold engineering to deliver bespoke leave doormat solutions for global OEM partners. Our dedicated team comprises five specialized mold engineers and two advanced rubber formula engineers, ensuring end-to-end control from material science to production readiness. This integrated capability allows us to address complex performance requirements while maintaining strict cost and timeline adherence for industrial applications.
Our formula engineers focus on optimizing compound performance for high-traffic environments. Through rigorous laboratory testing and finite element analysis, we develop proprietary rubber blends that balance abrasion resistance, resilience, and environmental stability. Key innovations include nano-silica reinforcement for extended tread life and thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) formulations that retain flexibility across -40°C to 100°C operational ranges. Each compound undergoes 500+ cycle durability validation per ASTM D2212 standards, ensuring consistent performance under mechanical stress and UV exposure. This scientific approach directly translates to doormats that withstand 10,000+ footfalls while maintaining dimensional stability.
Mold engineering excellence drives precision in texture replication and structural integrity. Our five-engineer team utilizes 3D CAD/CAM systems (SolidWorks, Moldflow) to design multi-cavity molds with micron-level tolerance control. Critical features include optimized gate placement for uniform material flow, venting systems to eliminate surface defects, and hardened steel cores rated for 500,000+ cycles. We prioritize rapid thermal response in mold design to reduce cycle times by 18% versus industry benchmarks, directly enhancing production efficiency for OEM clients. Complex tread patterns—such as directional grooves for debris trapping or antimicrobial surface textures—are engineered for 99.2% detail fidelity at production scale.
As an OEM partner, we implement a structured four-phase development protocol: collaborative specification finalization, DFM analysis with virtual prototyping, pre-production validation under real-world conditions, and seamless transfer to certified manufacturing facilities. Our engineers maintain direct oversight during tooling trials, adjusting parameters like injection pressure (±0.5 MPa precision) and cure temperature gradients to eliminate sink marks or flash. This methodology ensures first-article approval rates exceed 95%, significantly de-risking time-to-market for clients.
Material performance is quantitatively validated through our in-house testing regime, with critical specifications shown below:
| Performance Parameter | Standard Industrial Grade | Premium OEM Custom Grade | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | 65 ± 3 | 70 ± 2 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 12.5 | 18.0 | ASTM D412 |
| Abrasion Resistance (mm³) | 120 | 75 | ASTM D5963 |
| Compression Set (%) | 25 | 15 | ASTM D395 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -30°C to 90°C | -40°C to 100°C | ISO 188 |
This engineering rigor positions Suzhou Baoshida as a strategic partner for OEMs demanding scientifically validated rubber solutions. By unifying compound innovation with precision mold design, we transform functional requirements into high-yield, durable doormat products that meet exacting industrial specifications. Our commitment to data-driven development ensures every client project achieves optimal performance-to-cost ratios at scale.
Customization Process

Customization Process for Industrial Rubber Doormats at Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd.
At Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd., our industrial rubber solutions are engineered to meet precise client specifications, beginning with a rigorous customization process that ensures performance, durability, and compliance with application requirements. The development of a custom leave doormat follows a structured four-stage workflow: Drawing Analysis, Formulation, Prototyping, and Mass Production. Each phase integrates material science expertise with precision manufacturing to deliver high-performance rubber products.
The process begins with Drawing Analysis, where our engineering team evaluates technical drawings and dimensional requirements provided by the client. This includes assessing tread pattern geometry, thickness tolerances, edge profiles, and any embossed text or branding. We verify compatibility with molding techniques and identify potential challenges in demolding or surface detail reproduction. This stage ensures geometric accuracy and functional design alignment before any material is processed.
Following drawing validation, we proceed to Formulation—the core of our rubber engineering capability. Based on the application environment (e.g., indoor/outdoor, chemical exposure, foot traffic intensity), our Rubber Formula Engineers develop a proprietary elastomer blend. Standard compounds may include SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) or EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer), selected for abrasion resistance, weather stability, and resilience. Additives such as anti-aging agents, UV stabilizers, and pigments are precisely metered to enhance longevity and aesthetic consistency. Hardness, density, and coefficient of friction are tuned to meet performance benchmarks.
Once the formulation is finalized, we initiate Prototyping. A pilot mold is fabricated using CNC-machined steel to replicate production conditions. Small-batch curing is performed under controlled temperature and pressure to produce sample doormats. These prototypes undergo rigorous testing, including compression set, tear strength, slip resistance, and colorfastness evaluation. Client feedback is incorporated at this stage, allowing for design or formulation adjustments before scaling.
Upon approval, the project transitions to Mass Production. High-efficiency hydraulic presses and automated demolding systems ensure consistent output at scale. Each batch is subject to in-process quality checks, including dimensional verification and visual inspection for surface defects. Final products are packaged per client logistics requirements, with full traceability maintained through batch coding and material certifications.
Throughout the customization journey, Suzhou Baoshida maintains strict adherence to industrial standards and lean manufacturing principles, ensuring that every leave doormat delivers optimal functionality and long-term value.
| Specification | Standard Range | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 50–75 | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | ≥8 MPa | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | ≥250% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22 hrs, 70°C) | ≤20% | ASTM D395 |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +100°C | Internal Protocol |
| Slip Resistance (DIN 51130) | R9–R11 | DIN 51130 |
Contact Engineering Team

Contact Suzhou Baoshida for Precision Industrial Rubber Doormat Solutions
Suzhou Baoshida Trading Co., Ltd. stands as your definitive partner for engineered rubber doormat manufacturing, where material science converges with industrial durability. Our proprietary rubber formulations—developed through rigorous polymer matrix optimization—deliver unmatched performance in high-traffic commercial, industrial, and institutional environments. Unlike commodity mats, Baoshida’s solutions are engineered to withstand extreme abrasion, chemical exposure, and thermal cycling while maintaining structural integrity over extended service life. We prioritize quantifiable outcomes: reduced facility contamination, minimized slip hazards, and lifecycle cost efficiency through extended product longevity. Our OEM-centric approach ensures seamless integration of your brand specifications into every mat, from custom tread patterns to exact color matching against Pantone codes.
The technical superiority of our rubber compounds is validated through stringent in-house testing protocols aligned with ISO 188, ASTM D2240, and DIN 53504 standards. Below are critical performance metrics for our flagship BD-800 Industrial Grade Nitrile Rubber (NBR) Doormat Compound, representative of our core offering for heavy-duty applications:
| Property | Test Method | Value | Industrial Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A Hardness | ASTM D2240 | 78 ± 2 | Optimal balance: debris retention without excessive foot fatigue |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D412 | 18.5 MPa | Resists tearing under heavy foot traffic and cleaning equipment |
| Abrasion Resistance | DIN 53516 | 85 mm³ loss | 40% lower wear rate vs. standard EPDM mats in 10,000-cycle testing |
| Temperature Range | ISO 188 | -40°C to +120°C | Stable performance in unheated warehouses or steam-cleaned facilities |
| Oil/Fuel Resistance | ASTM D471 | <15% volume swell | Critical for automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing floor safety |
These specifications are not theoretical benchmarks but production-relevant guarantees. Our Suzhou facility leverages 25+ years of compound formulation expertise and state-of-the-art calendaring/extrusion lines to translate these metrics into consistent, high-yield output. We support global OEMs with end-to-end technical collaboration—from initial material selection and CAD-based tread design to accelerated aging validation and just-in-time logistics. Every mat batch undergoes real-time QC monitoring, with full traceability from raw material lot to finished product.
Initiate your engineering partnership with Suzhou Baoshida by contacting Mr. Boyce, our dedicated OEM Solutions Manager. Mr. Boyce possesses direct oversight of rubber formulation adjustments, production scheduling, and technical documentation to ensure your specifications are met without compromise. Provide him with your performance requirements, volume projections, and design files to receive a precision-engineered quotation within 72 hours. Do not settle for generic mat suppliers; engage a technical manufacturer that treats your facility’s safety and efficiency as a materials engineering challenge.
Contact Mr. Boyce immediately at [email protected] to schedule a technical consultation. Specify your target application environment, expected footfall volume, and critical performance thresholds. We will deploy our formulation engineers to develop a mat solution calibrated to your operational demands—not a catalog compromise. Suzhou Baoshida delivers rubber performance you can measure, not merely describe. Your facility’s first line of defense against contamination and accidents starts with engineered precision.
⚖️ O-Ring Weight Calculator
Estimate rubber O-ring weight (Approx).
